Outcomes after early treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: An analysis of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients
et al., New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188, Apr 2023 (preprint)
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 423 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
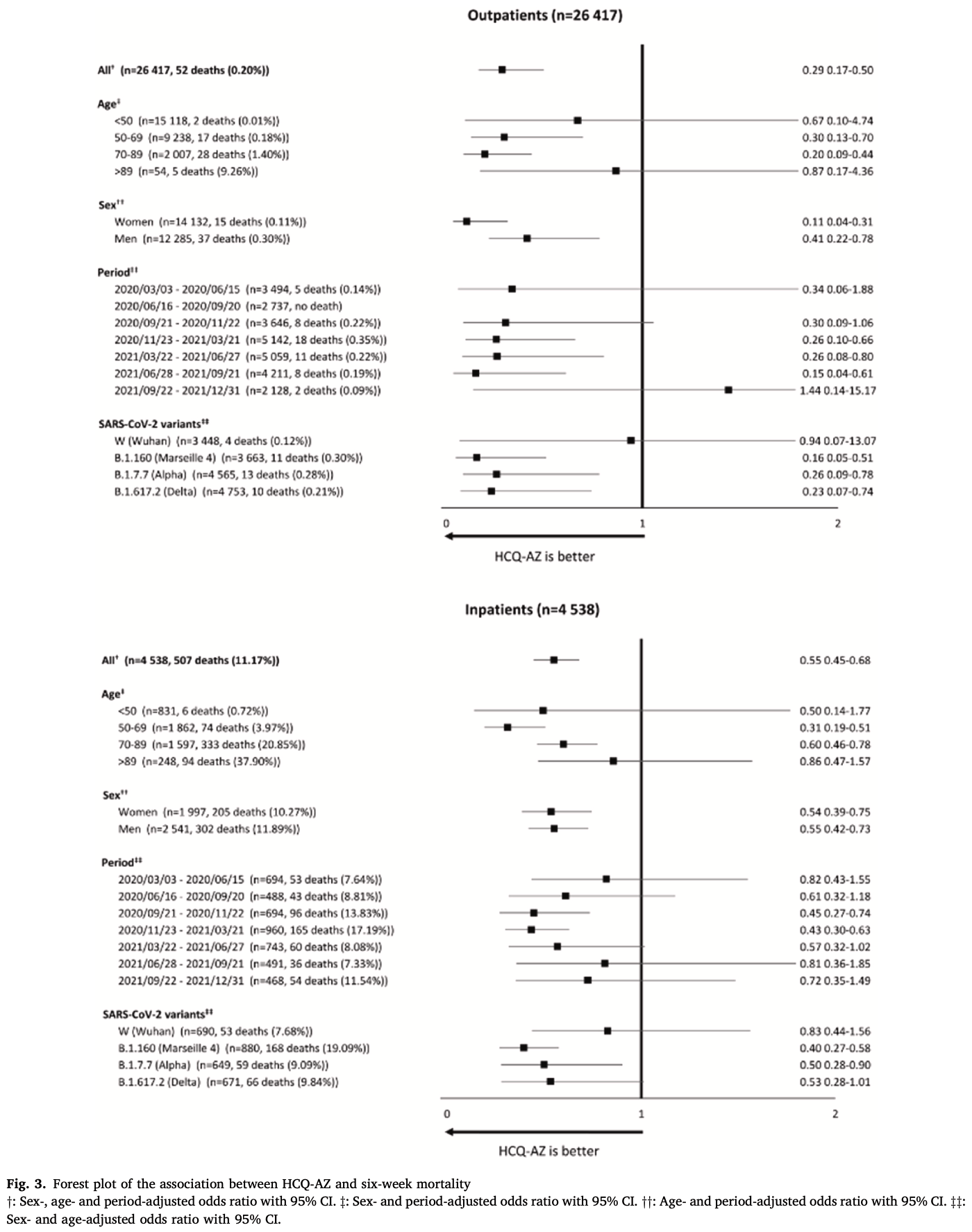
Retrospective 30,423 patients in France, showing significantly loewer mortality with HCQ+AZ treatment. Efficacy was greater for outpatients vs. inpatients. Data is publicly available at Science Data Bank1 and DRYAD2.
An independent analysis3 confirms efficacy.
|
risk of death, 71.0% lower, OR 0.29, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, HCQ+AZ, outpatients, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of death, 45.0% lower, OR 0.55, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, HCQ+AZ, inpatients, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Brouqui et al., 4 Apr 2023, retrospective, France, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period 2 March, 2020 - 31 December, 2021.
Contact: didier.raoult@gmail.com.
Outcomes after early treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: An analysis of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients
New Microbes and New Infections, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188
Background: Many studies have evaluated the use of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19. Most retrospective observational studies demonstrate a benefit of using HCQ on mortality, but not most randomized clinical trials. Methods: We analyzed raw data collected from a cohort of 30,423 patients with COVID-19 cared for at IHU Méditerranée Infection in Marseille France and extracted from the DRYAD open data platform. We performed univariate and multivariable logistic regressions with all-cause mortality within six weeks. Multivariable logistic regressions were adjusted for sex, age group (<50, 50-69, 70-89 and > 89 years), periods (or variants), and type of patient management. Results: Among 30,202 patients for whom information on treatment was available, 191/23,172 (0.82%) patients treated with HCQ-AZ died, compared to 344/7030 (4.89%) who did not receive treatment with HCQ-AZ. HCQ-AZ therapy was associated with a lower mortality than treatment without HCQ-AZ (odds ratio (OR) 0.16; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.14-0.19). After adjustment for sex, age, period, and patient management, HCQ-AZ was associated with a significantly lower mortality rate (adjusted OR (aOR) 0.55, 95% CI 0.45-0.68). On a subsample of 21,664 patients with available variant information, results remained robust after adjustment on sex, age, patient management and variant (aOR 0.55; 95% CI 0.44-0.69). On a subsample of 16,063 patients, HCQ-AZ was still associated with a significantly lower mortality rate (aOR 0.47, 95%CI 0.29-0.75) after adjustment for sex, age, period, patient management, vaccination status and comorbidities. Conclusion: Analysis of this large online database showed that HCQ-AZ was consistently associated with the lowest mortality.
Transparency declaration DR (the guarantor) affirms that the manuscript is an honest, accurate, and transparent account of the study being reported, that no important aspects of the study have been omitted, and that any discrepancies in the study as planned (and, if relevant, registered) have been explained.
Declaration of competing interest The authors have completed the Unified Competing Interest form (available on request from the corresponding author). DR declares grants, contracts, royalties and/or licenses from Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. DR is a scientific board member of Eurofins. DR is founder and shareholder of four startups, none which have yet generated an income: a microbial culture company (Culture Top), two biotechnology companies (Techno-Jouvence and Gene and Green TK), and a rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases company (Pocramé). PB, MM and PMC declare no support from any organization for the submitted work, no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years, and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi. org/10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188.
References
Ader, Discovery, Group, An open-label randomized, controlled trial of the effect of lopinavir and ritonavir, lopinavir and ritonavir plus interferon-β-1a, and hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: final results, Clin Microbiol Infect
Ader, Peiffer-Smadja, Poissy, Bouscambert-Duchamp, Belhadi et al., An open-label randomized controlled trial of the effect of lopinavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir plus IFN-β-1a and hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Clin Microbiol Infect
Andrade, Internal, external, and ecological validity in research design, conduct, and evaluation, Indian J Psychol Med
Anglemyer, Horvath, Bero, Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Bosdriesz, Stel, Van Diepen, Meuleman, Dekker et al., Evidence-based medicine-When observational studies are better than randomized controlled trials, Nephrology
Brouqui, Drancourt, Raoult, There is no such thing as a Ministry of Truth and why it is important to challenge conventional "wisdom" -a personal view, New Microbes New Infect
Brouqui, Raoult, Construction, quality control and regulatory aspect of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients cared for at the IHU Méditerranée infection France, Biomed J Sci & Tech Res
Dubée, Roy, Vielle, Parot-Schinkel, Blanchet et al., Hydroxychloroquine in mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019: a placebocontrolled double blind trial, Clin Microbiol Infect
Lagier, Million, Cortaredona, Delorme, Colson et al., Outcomes of 2111 COVID-19 hospitalized patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France, 2020: a monocentric retrospective analysis, Therapeut Clin Risk Manag
Lagier, Million, Gautret, Colson, Cortaredona et al., Outcomes of 3,737 COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/ azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France: a retrospective analysis, Trav Med Infect Dis
Million, Lagier, Tissot-Dupont, Ravaux, Dhiver et al., Early combination therapy with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin reduces mortality in 10,429 COVID-19 outpatients, Rev Cardiovasc Med
Mokhtari, Mohraz, Gouya, Tabar, Tabrizi et al., Clinical outcomes of patients with mild COVID-19 following treatment with hydroxychloroquine in an outpatient setting, Int Immunopharm
Nguyen, Engleton, Davison, Ravaud, Porcher et al., Risk of bias in observational studies using routinely collected data of comparative effectiveness research: a meta-research study, BMC Med
Nunez-Gil, Ayerbe, Fernandez-Perez, Estrada, Eid et al., Hydroxychloroquine and mortality in SARS-cov-2 Infection;the HOPE-covid-19 Registry, Anti-Infective Agents
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Preziosi, Sathiyamoorthy, Repurposed antiviral drugs for covid-19 -interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med
Recovery Collaborative Group, Horby, Mafham, Linsell, Bell et al., Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Rojanaworarit, Misleading epidemiological and statistical evidence in the presence of simpson's paradox: an illustrative study using simulated scenarios of observational study designs, J Med Life
Simpson, The interpretation of interaction in contingency Tables, J Roy Stat Soc B
Tsang, Colley, Lynd, Inadequate statistical power to detect clinically significant differences in adverse event rates in randomized controlled trials, J Clin Epidemiol
Ulrich, Troxel, Carmody, Eapen, Bäcker et al., Treating COVID-19 with hydroxychloroquine (TEACH): a multicenter, double-blind randomized controlled trial in hospitalized patients, Open Forum Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188",
"ISSN": [
"2052-2975"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188",
"alternative-id": [
"S2052297523001075"
],
"article-number": "101188",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Outcomes after early treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: An analysis of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "New Microbes and New Infections"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6125-2805",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Brouqui",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Million",
"given": "Matthieu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parola",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mccullough",
"given": "Peter A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raoult",
"given": "Didier",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "New Microbes and New Infections",
"container-title-short": "New Microbes and New Infections",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-30T18:54:46Z",
"timestamp": 1698692086000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-02T00:38:33Z",
"timestamp": 1698885513000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-02T04:13:32Z",
"timestamp": 1698898412349
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1696118400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 17,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1697587200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2052297523001075?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2052297523001075?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101188",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101155",
"article-title": "There is no such thing as a Ministry of Truth and why it is important to challenge conventional “wisdom” - a personal view",
"author": "Brouqui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "New Microbes New Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib1",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2022926",
"article-title": "Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with covid-19",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2030",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib2",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed antiviral drugs for covid-19 - interim WHO solidarity trial results",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib3",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31083/j.rcm2203116",
"article-title": "Early combination therapy with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin reduces mortality in 10,429 COVID-19 outpatients",
"author": "Million",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1063",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Rev Cardiovasc Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib4",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and mortality in SARS-cov-2 Infection;the HOPE-covid-19 Registry",
"author": "Nunez-Gil",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Anti-Infective Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.020",
"article-title": "An open-label randomized controlled trial of the effect of lopinavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir plus IFN-β-1a and hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Ader",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1826",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib6",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.03.005",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine in mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019: a placebo-controlled double blind trial",
"author": "Dubée",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1124",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib7",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa446",
"article-title": "Treating COVID-19 with hydroxychloroquine (TEACH): a multicenter, double-blind randomized controlled trial in hospitalized patients",
"author": "Ulrich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofaa446",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib8",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The interpretation of interaction in contingency Tables",
"author": "Simpson",
"first-page": "238",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Roy Stat Soc B",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib9",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1951"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nep.13742",
"article-title": "Evidence-based medicine-When observational studies are better than randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Bosdriesz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "737",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nephrology",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib10",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-021-02151-w",
"article-title": "Risk of bias in observational studies using routinely collected data of comparative effectiveness research: a meta-research study",
"author": "Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib11",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials",
"author": "Anglemyer",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib12",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib13",
"unstructured": "Dryad | Data -- Monocentric retrospective cohort of 30,423 COVID-19 patients [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 6]. Available from: https://datadryad.org/stash/dataset/doi:10.5061/dryad.ksn02v78v."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib14",
"unstructured": "Science data Bank. Science Data Bank Monocentric Retrospective Cohort of 30,423 COVID-19 Patients [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 4]. Available from: https://www.scidb.cn/en/detail?dataSetId=68f37f29decd4d7b91722657f3e437de.."
},
{
"DOI": "10.26717/BJSTR.2023.52.008265",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib15",
"unstructured": "Brouqui P, Raoult D. Construction, quality control and regulatory aspect of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients cared for at the IHU Méditerranée infection France. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res. 52(3):43999–43804.."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/TCRM.S364022",
"article-title": "Outcomes of 2111 COVID-19 hospitalized patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France, 2020: a monocentric retrospective analysis",
"author": "Lagier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "Therapeut Clin Risk Manag",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib16",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib17",
"unstructured": "Fichiers des personnes décédées depuis 1970 | Insee [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 6]. Available from: https://www.insee.fr/fr/information/4190491."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107636",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes of patients with mild COVID-19 following treatment with hydroxychloroquine in an outpatient setting",
"author": "Mokhtari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharm",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib18",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/IJPSYM.IJPSYM_334_18",
"article-title": "Internal, external, and ecological validity in research design, conduct, and evaluation",
"author": "Andrade",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "498",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Indian J Psychol Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib19",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101791",
"article-title": "Outcomes of 3,737 COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France: a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Lagier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Trav Med Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib20",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Misleading epidemiological and statistical evidence in the presence of simpson's paradox: an illustrative study using simulated scenarios of observational study designs",
"author": "Rojanaworarit",
"first-page": "37",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Med Life",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib21",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.04.016",
"article-title": "An open-label randomized, controlled trial of the effect of lopinavir and ritonavir, lopinavir and ritonavir plus interferon-β-1a, and hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: final results",
"author": "Ader",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1293",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib22",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.08.005",
"article-title": "Inadequate statistical power to detect clinically significant differences in adverse event rates in randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Tsang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "609",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101188_bib23",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2009"
}
],
"reference-count": 23,
"references-count": 23,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2052297523001075"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Outcomes after early treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: An analysis of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "55"
}
