Clinical characteristics and pharmacokinetics of PAXLOVID in COVID-19 patients with hematological tumor
et al., Medical Review, doi:10.1515/mr-2023-0068, Mar 2024
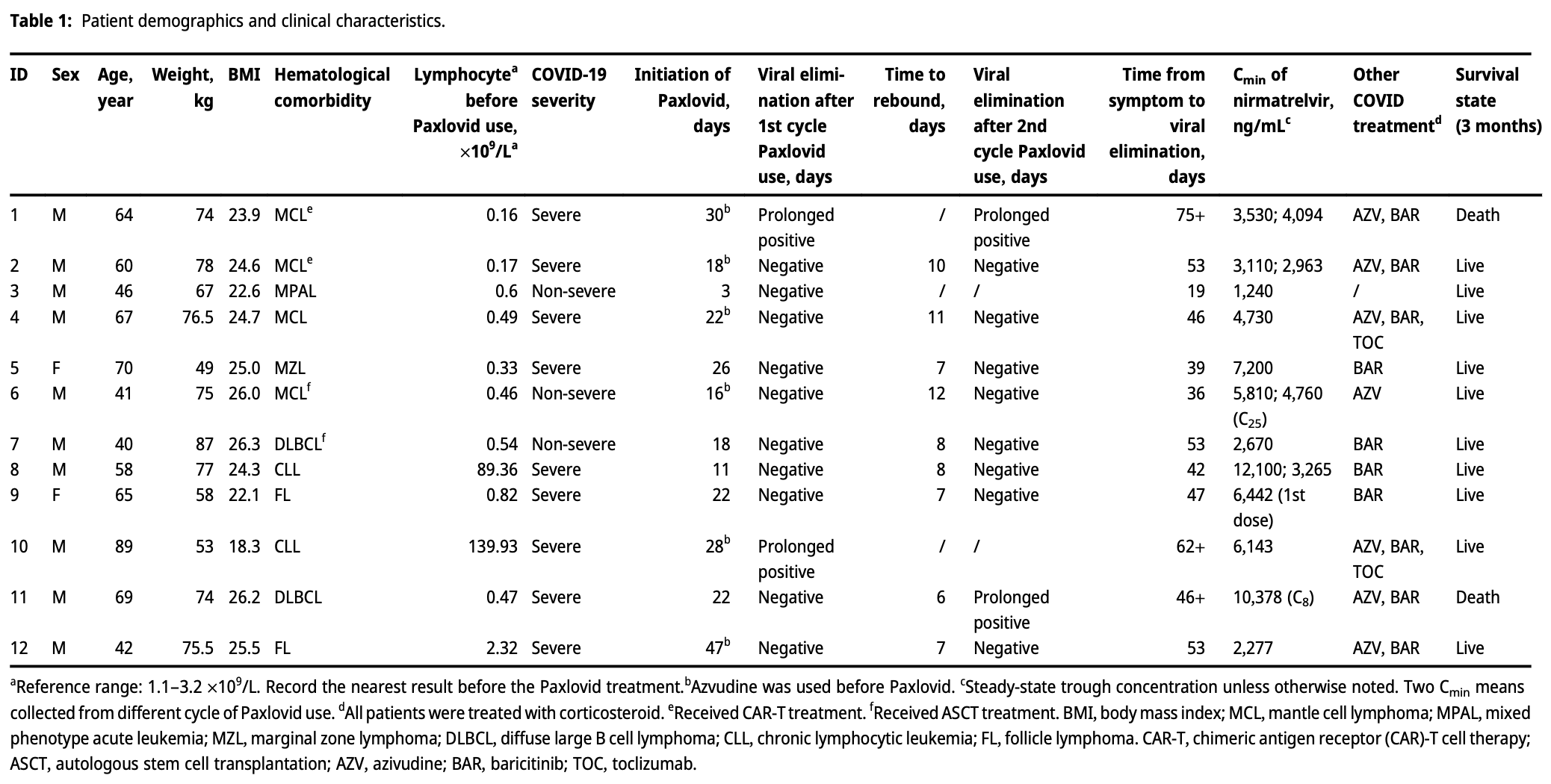
Retrospective 12 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hematological malignancies showing one death and two cases of liver injury with paxlovid treatment. The study focused on pharmacokinetics, finding nirmatrelvir concentrations approximately 3-fold higher than those observed in clinical trials, with substantial individual variability. Two patients experienced liver injury with ALT levels increased 2.2 and 7.5 times baseline, with one patient having extremely high nirmatrelvir concentrations. Eight patients experienced viral rebound with a median of 7 days. No correlation was found between nirmatrelvir concentration and duration of viral shedding.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Liu et al., 4 Mar 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: libozhao2011@163.com, zhaorongsheng@bjmu.edu.cn.
Clinical characteristics and pharmacokinetics of PAXLOVID in COVID-19 patients with hematological tumor
Medical Review, doi:10.1515/mr-2023-0068
min means collected from different cycle of Paxlovid use. d All patients were treated with corticosteroid.
References
Lamers, Beumer, Van Der Vaart, Knoops, Puschhof et al., SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human gut enterocytes, Science
Liu, Clinical characteristics and pharmacokinetics of PAXLOVID
Liu, Zhu, Cao, Boucetta, Song et al., Simultaneous determination of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in human plasma using LC-MS/MS and its pharmacokinetic application in healthy Chinese volunteers, Biomed Chromatogr
Mikulska, Sepulcri, Dentone, Magne, Balletto et al., Triple combination therapy with 2 antivirals and monoclonal antibodies for persistent or relapsed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in immunocompromised patients, Clin Infect Dis
Singh, Toussi, Hackman, Chan, Rao et al., Innovative randomized Phase I study and dosing regimen selection to accelerate and inform pivotal COVID-19 trial of nirmatrelvir, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Sun, Lin, Wang, Gao, Ye, Paxlovid in patients who are immunocompromised and hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Lancet Infect Dis
Xiong, Ying, Zhang, Liu, Lu et al., Simultaneous determination of nirmatrelvir, ritonavir and baricitinib concentrations in human plasma by LC-MS/MS (in Chinese), Chinese Pharm J
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1515/mr-2023-0068",
"ISSN": [
"2749-9642"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/mr-2023-0068",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1515/mr-2023-0068"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1773-5156",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy , 66482 Peking University Third Hospital , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology Center of Peking University , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 NMPA Key Laboratory for Research and Evaluation of Generic Drugs , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "Institute for Drug Evaluation , Peking University Health Science Center , Beijing , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy , 66482 Peking University Third Hospital , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology Center of Peking University , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "Institute for Drug Evaluation , Peking University Health Science Center , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 NMPA Key Laboratory for Research and Evaluation of Generic Drugs , Beijing , China"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8398-5391",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Hematology , 66482 Peking University Third Hospital , Beijing , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy , 66482 Peking University Third Hospital , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology Center of Peking University , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "Institute for Drug Evaluation , Peking University Health Science Center , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 NMPA Key Laboratory for Research and Evaluation of Generic Drugs , Beijing , China"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Hematology , 66482 Peking University Third Hospital , Beijing , China"
}
],
"family": "Jing",
"given": "Hongmei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4968-6045",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy , 66482 Peking University Third Hospital , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology Center of Peking University , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "Institute for Drug Evaluation , Peking University Health Science Center , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 NMPA Key Laboratory for Research and Evaluation of Generic Drugs , Beijing , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Libo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3266-3496",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy , 66482 Peking University Third Hospital , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology Center of Peking University , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "Institute for Drug Evaluation , Peking University Health Science Center , Beijing , China"
},
{
"name": "66482 NMPA Key Laboratory for Research and Evaluation of Generic Drugs , Beijing , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Rongsheng",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medical Review",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-01T11:40:28Z",
"timestamp": 1709293228000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-26T10:53:56Z",
"timestamp": 1714128836000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100009399",
"award": [
"BMU2023XY019",
"BYSYDL2023001-05",
"BYSYDL2023001-08"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100009399",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Peking University Third Hospital"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-22T00:39:35Z",
"timestamp": 1740184775176,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
26
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
25
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1709510400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/mr-2023-0068/xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/mr-2023-0068/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "374",
"original-title": [],
"page": "169-171",
"prefix": "10.1515",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
25
]
]
},
"publisher": "Walter de Gruyter GmbH",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00430-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2024042610492623753_j_mr-2023-0068_ref_001",
"unstructured": "Sun, F, Lin, Y, Wang, X, Gao, Y, Ye, S. Paxlovid in patients who are immunocompromised and hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Infect Dis 2022;22:1279. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00430-3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad181",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2024042610492623753_j_mr-2023-0068_ref_002",
"unstructured": "Mikulska, M, Sepulcri, C, Dentone, C, Magne, F, Balletto, E, Baldi, F, et al.. Triple combination therapy with 2 antivirals and monoclonal antibodies for persistent or relapsed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis 2023;77:280–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciad181."
},
{
"key": "2024042610492623753_j_mr-2023-0068_ref_003",
"unstructured": "Xiong, X, Ying, Y, Zhang, X, Liu, W, Lu, M, Chen, J, et al.. Simultaneous determination of nirmatrelvir, ritonavir and baricitinib concentrations in human plasma by LC-MS/MS (in Chinese). Chinese Pharm J 2023;11:1015–9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2603",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2024042610492623753_j_mr-2023-0068_ref_004",
"unstructured": "Singh, RSP, Toussi, SS, Hackman, F, Chan, PL, Rao, R, Allen, R, et al.. Innovative randomized Phase I study and dosing regimen selection to accelerate and inform pivotal COVID-19 trial of nirmatrelvir. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2022;112:101–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2603."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bmc.5456",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2024042610492623753_j_mr-2023-0068_ref_005",
"unstructured": "Liu, C, Zhu, M, Cao, L, Boucetta, H, Song, M, Hang, T, et al.. Simultaneous determination of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in human plasma using LC-MS/MS and its pharmacokinetic application in healthy Chinese volunteers. Biomed Chromatogr 2022;36:e5456. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.5456."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc1669",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2024042610492623753_j_mr-2023-0068_ref_006",
"unstructured": "Lamers, MM, Beumer, J, van der Vaart, J, Knoops, K, Puschhof, J, Breugem, TI, et al.. SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human gut enterocytes. Science 2020;369:50–4. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc1669."
}
],
"reference-count": 6,
"references-count": 6,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/mr-2023-0068/html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical characteristics and pharmacokinetics of PAXLOVID in COVID-19 patients with hematological tumor",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "4"
}