Clinical characteristics, outcomes, and risk factors of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among 572 fully vaccinated (BBIBP-CorV) hospitalized patients
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387, Oct 2023
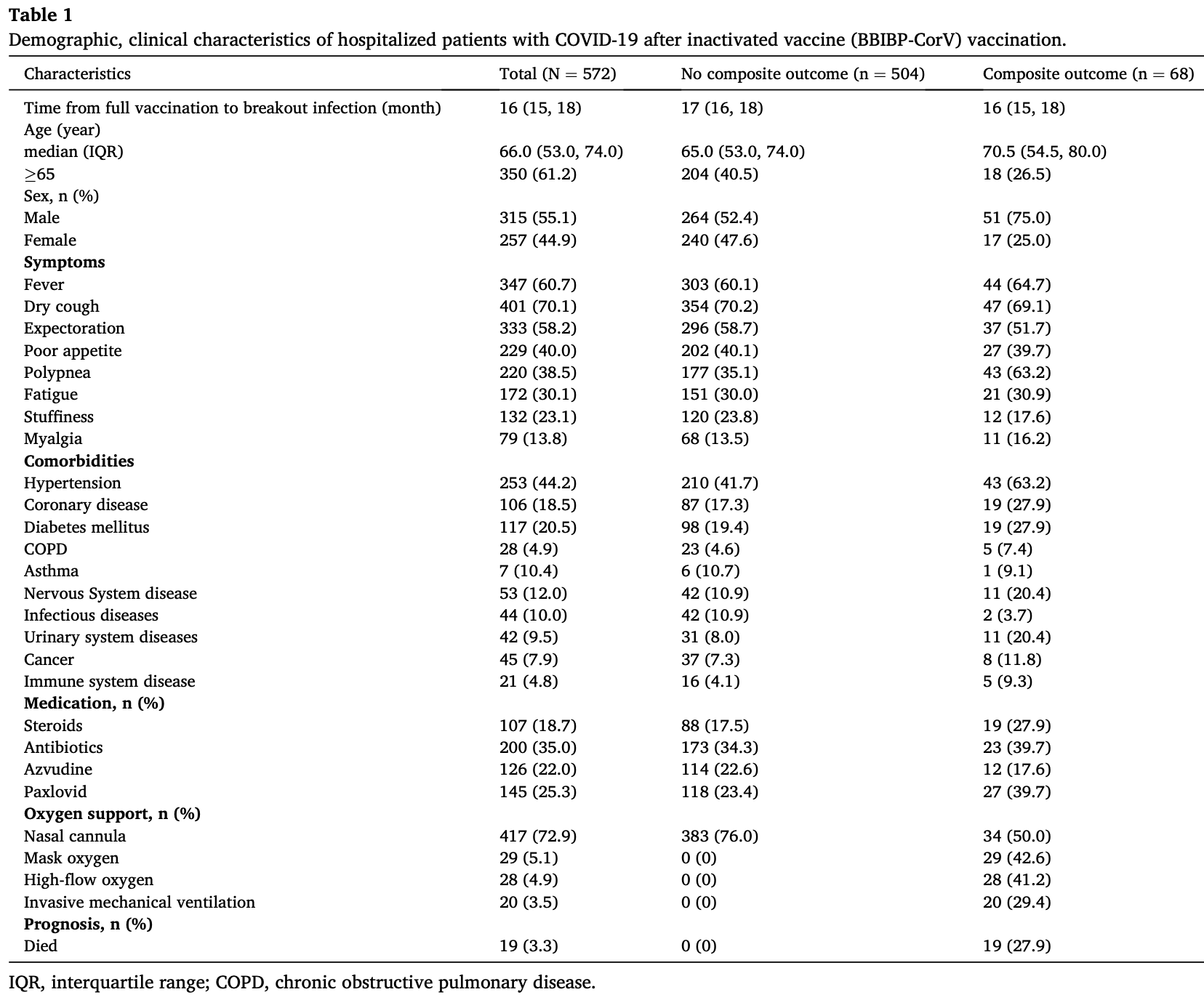
Retrospective 572 fully vaccinated hospitalized patients in China, showing higher risk with paxlovid use. The composite outcome included intubation, non-invasive respiratory support, ICU admission, and all-cause death. Details for analysis of confounding are not provided. The results for paxlovid can be compared with the alternative antiviral azvudine, which shows lower risk (without statistical significance). Paxlovid was not included in the multivariable analysis (only combined antiviral therapy was used without explanation).
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
Study covers azvudine and paxlovid.
|
risk of progression, 93.9% higher, RR 1.94, p = 0.007, treatment 27 of 145 (18.6%), control 41 of 427 (9.6%), intubation, non-invasive respiratory support, ICU admission, and all-cause death.
|
|
risk of progression, 24.1% lower, RR 0.76, p = 0.44, treatment 12 of 126 (9.5%), control 56 of 446 (12.6%), NNT 33, intubation, non-invasive respiratory support, ICU admission, and all-cause death.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Liu et al., 21 Oct 2023, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period 5 December, 2022 - 31 January, 2023.
Contact: 962881298@qq.com, dengguangtong@outlook.com.
Clinical characteristics, outcomes, and risk factors of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among 572 fully vaccinated (BBIBP-CorV) hospitalized patients
Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387
Background: Breakthrough infections have been widely reported in vaccinated individuals. However, the clinical characteristics, outcomes, and risk factors of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among fully vaccinated (BBIBP-CorV) hospitalized patients have not yet been fully elucidated. Methods: In the single-center cohort study conducted at Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, we enrolled the hospitalized COVID-19 patients who had received full (2 doses) vaccination with the BBIBP-CorV vaccine between December 5, 2022, and January 31, 2023. We collected and analyzed information related to clinical characteristics, laboratory results, treatments, outcomes and prognostic data. Univariate and multivariable Cox regression were performed to assess the impact of clinical characteristics and laboratory results on the composite outcome (including the initiation of endotracheal intubation, non-invasive respiratory support, intensive care unit admission, and all-cause death). Results: A total of 572 COVID-19 hospitalized patients with fully vaccinated (BBIBP-CorV) were included. The median age of the patients was 66 years (IQR 53, 74). The most common symptoms included fever (347 [60.7 %]), dry cough (401 [70.1 %]), and expectoration (333 [58.2 %]). Among those with pre-existing chronic comorbidities, 44.2 % had hypertension and 20.5 % had diabetes. Laboratory tests revealed that the majority of patients (425/549 [77.4 %]) had normal white blood cell counts. Composite outcome occurred in 11.9 % of patients, with 96.7 % of patients discharged and 3.3 % of patients died. Multivariate Cox regression analyses suggested that the NLR >4 (adjusted HR,]; P = 0.008), D-dimer >0.5 mg/ml (adjusted
Ethics statement Our research has been approved by the institutional review committee of Xiangya Hospital of Central South University (202002024). All patients in the retrospective cohort study were anonymous, and the individual informed consent was not required.
Y. Liu et al.
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Albreiki, Mousa, Azman, Vurivi, Alhalwachi et al., Risk of hospitalization and vaccine effectiveness among COVID-19 patients in the UAE during the Delta and Omicron outbreaks, Front. Immunol
Andrews, Stowe, Kirsebom, Toffa, Rickeard et al., Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the omicron (B.1.1.529) variant, N. Engl. J. Med
Belayachi, Obtel, Mhayi, Razine, Long term effectiveness of inactivated vaccine BBIBP-CorV (Vero Cells) against COVID-19 associated severe and critical hospitalization in Morocco, PLoS One
Creech, Walker, Samuels, Al Kaabi, Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 vaccines effect of 2 inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines on symptomatic COVID-19 infection in adults: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Dawood, Increasing the frequency of omicron variant mutations boosts the immune response and may reduce the virus virulence, Microb. Pathog
Deng, Yin, Chen, Zeng, Clinical determinants for fatality of 44,672 patients with COVID-19, Crit. Care
Fiolet, Kherabi, Macdonald, Ghosn, Peiffer-Smadja, Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: a narrative review, Clin. Microbiol. Infect
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Antonelli, Cabrini et al., Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the lombardy region, Italy, JAMA
Hacisuleyman, Hale, Saito, Blachere, Bergh et al., Vaccine breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 variants, N. Engl. J. Med
Heidarzadeh, Amini Moridani, Khoshmanesh, Kazemi, Hajiaghabozorgi et al., Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines on hospitalization and death in Guilan, Iran: a test-negative case-control study, Int. J. Infect. Dis
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Kuhlmann, Mayer, Claassen, Maponga, Burgers et al., Breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 omicron despite mRNA vaccine booster dose, Lancet
Laine, Cotton, Moyer, COVID-19 vaccine: what physicians need to know, Ann. Intern. Med
Li, Deng, Ye, Sun, Du et al., Clinical significance of plasma D-dimer in COVID-19 mortality, Front. Med
Li, Lin, Wu, Factors predicting re-hospitalization for inpatients with bipolar mania-A naturalistic cohort, Psychiatr. Res
Li, Wang, Tian, Pang, Yang et al., COVID-19 vaccine development: milestones, lessons and prospects, Signal Transduct. Targeted Ther
Li, Xu, Yu, Wang, Tao et al., Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol
Lipsitch, Krammer, Regev-Yochay, Lustig, Balicer, SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in vaccinated individuals: measurement, causes and impact, Nat. Rev. Immunol
Liu, None
Metzler, Dvorsky, Wyss, Nordt, Walitza et al., Neurocognition in help-seeking individuals at risk for psychosis: prediction of outcome after 24 months, Psychiatr. Res
Peeling, Heymann, Teo, Garcia, Diagnostics for COVID-19: moving from pandemic response to control, Lancet
Ramasamy, Minassian, Ewer, Flaxman, Folegatti et al., Safety and immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine administered in a prime-boost regimen in young and old adults (COV002): a single-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial, Lancet
Sun, Jin, Dian, Shen, Zeng et al., Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine
Tan, Kwan, Rodriguez-Barraquer, Singer, Park et al., Infectiousness of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections and reinfections during the Omicron wave, Nat. Med
Tian, Song, Zhang, Pan, Ge et al., Genomic, immunological, and clinical analysis of COVID-19 vaccine breakthrough infections in Beijing, China, J. Med. Virol
Wang, Guo, Iketani, Nair, Li et al., Antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.2.12, BA.4 and BA
Wang, Guo, Zeng, Sun, Lu et al., Transmission characteristics and inactivated vaccine effectiveness against transmission of SARS-CoV-2 omicron BA.5 variants in urumqi, China, JAMA Netw. Open
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan, China, JAMA Intern. Med
Wu, Li, Liu, Wang, Zhou et al., Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the mRNA vaccine CS-2034 as a heterologous booster versus homologous booster with BBIBP-CorV in adults aged ≥18 years: a randomised, double-blind, phase 2b trial, Lancet Infect. Dis
Xia, Zhang, Wang, Wang, Yang et al., Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV, in people younger than 18 years: a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial, Lancet Infect. Dis
Xie, Ding, Li, Wang, Guo et al., Characteristics of patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) confirmed using an IgM-IgG antibody test, J. Med. Virol
Zeng, Li, Zeng, Deng, Huang et al., Can we predict the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 with a routine blood test?, Pol. Arch. Intern. Med
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387",
"ISSN": [
"2405-8440"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387",
"alternative-id": [
"S240584402308595X"
],
"article-number": "e21387",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Clinical characteristics, outcomes, and risk factors of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among 572 fully vaccinated (BBIBP-CorV) hospitalized patients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Heliyon"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yihuang",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Peilin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Yuming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4424-9727",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Guangtong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Heliyon",
"container-title-short": "Heliyon",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"cell.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-21T15:35:19Z",
"timestamp": 1697902519000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-06T13:40:24Z",
"timestamp": 1699278024000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-07T00:27:38Z",
"timestamp": 1699316858336
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698796800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1697760000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S240584402308595X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S240584402308595X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e21387",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib1",
"series-title": "Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19 - 22 March",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.10.005",
"article-title": "Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: a narrative review",
"author": "Fiolet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "202",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib3",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2105000",
"article-title": "Vaccine breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Hacisuleyman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2212",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib4",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00090-3",
"article-title": "Breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 omicron despite mRNA vaccine booster dose",
"author": "Kuhlmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "625",
"issue": "10325",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib5",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00662-4",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in vaccinated individuals: measurement, causes and impact",
"author": "Lipsitch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib6",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-02138-x",
"article-title": "Infectiousness of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections and reinfections during the Omicron wave",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "358",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib7",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27636",
"article-title": "Genomic, immunological, and clinical analysis of COVID-19 vaccine breakthrough infections in Beijing, China",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2237",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib8",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00996-y",
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccine development: milestones, lessons and prospects",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Targeted Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib9",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1049393",
"article-title": "Risk of hospitalization and vaccine effectiveness among COVID-19 patients in the UAE during the Delta and Omicron outbreaks",
"author": "Albreiki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib10",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0278546",
"article-title": "Long term effectiveness of inactivated vaccine BBIBP-CorV (Vero Cells) against COVID-19 associated severe and critical hospitalization in Morocco",
"author": "Belayachi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib11",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.12.024",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines on hospitalization and death in Guilan, Iran: a test-negative case-control study",
"author": "Heidarzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "212",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib12",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib13",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.006",
"article-title": "Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib14",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.psychres.2018.10.073",
"article-title": "Factors predicting re-hospitalization for inpatients with bipolar mania--A naturalistic cohort",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "749",
"journal-title": "Psychiatr. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib15",
"volume": "270",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.psychres.2016.08.065",
"article-title": "Neurocognition in help-seeking individuals at risk for psychosis: prediction of outcome after 24 months",
"author": "Metzler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "188",
"journal-title": "Psychiatr. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib16",
"volume": "246",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02346-1",
"article-title": "Diagnostics for COVID-19: moving from pandemic response to control",
"author": "Peeling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "757",
"issue": "10326",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib17",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3199",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 vaccines effect of 2 inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines on symptomatic COVID-19 infection in adults: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Creech",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1318",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib18",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00462-X",
"article-title": "Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV, in people younger than 18 years: a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial",
"author": "Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "196",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib19",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32466-1",
"article-title": "Safety and immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine administered in a prime-boost regimen in young and old adults (COV002): a single-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial",
"author": "Ramasamy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1979",
"issue": "10267",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib20",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-6841",
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccine: what physicians need to know",
"author": "Laine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "830",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib21",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05053-w",
"article-title": "Antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"issue": "7923",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib22",
"volume": "608",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119451",
"article-title": "Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the omicron (B.1.1.529) variant",
"author": "Andrews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1532",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib23",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.5755",
"article-title": "Transmission characteristics and inactivated vaccine effectiveness against transmission of SARS-CoV-2 omicron BA.5 variants in urumqi, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib24",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00199-8",
"article-title": "Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the mRNA vaccine CS-2034 as a heterologous booster versus homologous booster with BBIBP-CorV in adults aged ≥18 years: a randomised, double-blind, phase 2b trial",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1020",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib25",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25930",
"article-title": "Characteristics of patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) confirmed using an IgM-IgG antibody test",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2004",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib26",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"article-title": "Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib27",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib28",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib29",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"article-title": "Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the lombardy region",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1574",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Italy, JAMA.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib30",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105400",
"article-title": "Increasing the frequency of omicron variant mutations boosts the immune response and may reduce the virus virulence",
"author": "Dawood",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Microb. Pathog.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib31",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02902-w",
"article-title": "Clinical determinants for fatality of 44,672 patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "179",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib32",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Can we predict the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 with a routine blood test?",
"author": "Zeng",
"first-page": "400",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Pol. Arch. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib33",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical significance of plasma D-dimer in COVID-19 mortality",
"author": "Li",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21387_bib34",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S240584402308595X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical characteristics, outcomes, and risk factors of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among 572 fully vaccinated (BBIBP-CorV) hospitalized patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "9"
}