Effect of the povidone iodine, hypertonic alkaline solution and saline nasal lavage on nasopharyngeal viral load in COVID-19
et al., Authorea, doi:10.22541/au.166675335.56566797/v1, Oct 2022
PVP-I for COVID-19
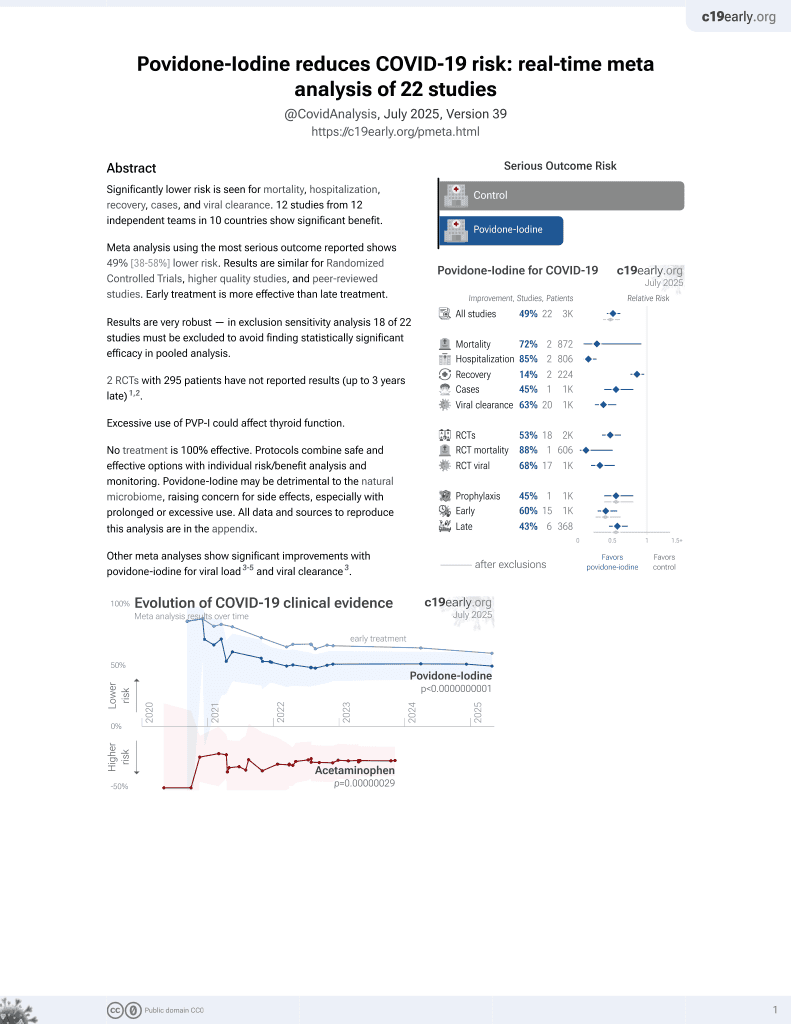
15th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.000000000016 from 22 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 120 outpatients in Turkey, showing improved reduction in viral load with PVP-I nasal irrigation.
PVP-I prepared with hypertonic alkaline solution had better results.1 show that SARS-CoV-2 requires acidic pH to infect cells, therefore alkalinization may add additional benefits.
All patients received favipiravir. PVP-I 1% 4 times per day.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects.
|
viral load, 83.1% lower, relative load 0.17, p = 0.007, treatment 30, control 30, relative change in viral load, PVP-I vs. control, day 5.
|
|
viral load, 85.5% lower, relative load 0.14, p = 0.001, treatment 30, control 30, relative change in viral load, PVP-I + HANI vs. control, day 5.
|
|
viral load, 82.1% lower, relative load 0.18, p = 0.14, treatment 30, control 30, relative change in viral load, PVP-I vs. control, day 3.
|
|
viral load, 90.8% lower, relative load 0.09, p < 0.001, treatment 30, control 30, relative change in viral load, PVP-I + HANI vs. control, day 3.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Karaaltin et al., 26 Oct 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Turkey, preprint, 16 authors, study period September 2021 - October 2021, average treatment delay 1.0 days.
EFFECT OF THE POVIDONE IODINE, HYPERTONIC ALKALINE SOLUTION AND SALINE NASAL LAVAGE ON NASOPHARYNGEAL VIRAL LOAD IN COVID-19
doi:10.22541/au.166675335.56566797/v1
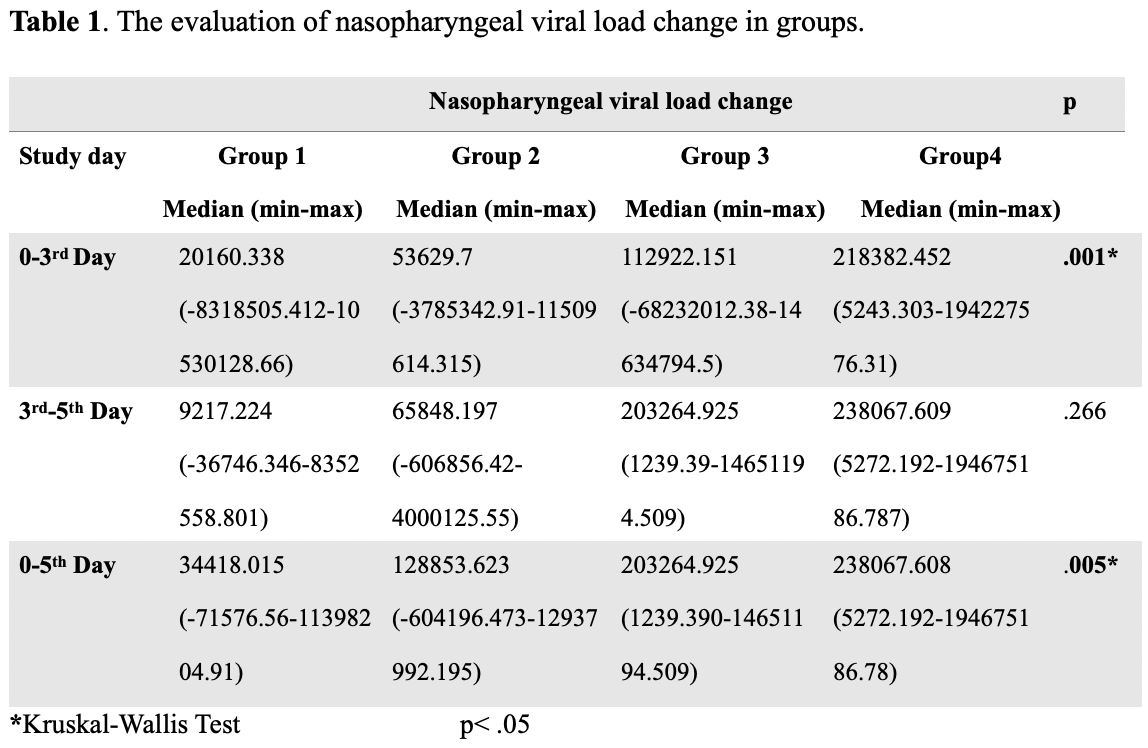
Objective: The causative virus of COVID-19 is SARS-CoV-2. The aim of the present study was to invastigate the in vivo virucidal activity of nasal irrigation with saline, nasal irrigation with Povidone-iodine (PVP-I) 1%, nasal irrigation with hypertonic alkaline and nasal irrigation with PVP-I 1% against SARS CoV-2. Design: The present study was a prospective randomized clinical trial. Setting: A multicenter study involving tertiary care centers. Participants: The study included adult outpatients whose qualitative SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR tests in nasopharyngeal swabs were positive. One hundred twenty patients divided into four equal groups. Standard COVID-19 treatment was given to group 1 (n=30), nasal irrigation containing isotonic solution was added to patients' treatment in group 2 (n=30), nasal irrigation containing 1% PVP solution was added to patients' treatment in group 3(n=30), and nasal irrigation containing 1% PVP solution and nasal irrigation containing hypertonic alkaline solution was added to patients' treatment in group 4 (n=30). Main outcome measures: On the first day of diagnosis (day 0), nasopharyngeal swab samples were taken, on the 3rd and 5th days the nasopharyngeal viral load reduction in quantitative RT-PCR tests were calculated. Results: Between the 0-3rd Day and 0-5th days, the nasopharyngeal viral load reduction was significant in all groups (p< .05). In paired comparisons of groups, the nasopharyngeal viral load decrease in group 4 in first 3 days was significantly lower than all groups (p < .05). The nasopharyngeal viral load degrease in groups 3 and 4 in the first 5 days were significantly lower than group 1 (p < .05). Conclussion: This study was reveal that the use of hypertonic alkaline nasal irrigation together with 1% povidone-iodine was more effective in reducing viral load in the early period. The decreased nasopharyngeal viral load may reduce the carriage of infectious SARS-CoV-2 in patients. Our results suggest that 1% povidone-iodine and hypertonic alkaline nasal irrigation may be promising modality to prevent the COVID-19 epidemic.
alkaline-solution-and-saline-nasal-lavage-on-nasopharyngeal-viral-load-in-covid-19 Hosted file table 1.docx available at https://authorea.com/users/337860/articles/592062-effect-of-thepovidone-iodine-hypertonic-alkaline-solution-and-saline-nasal-lavage-on-nasopharyngealviral-load-in-covid-19 Hosted file
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22541/au.166675335.56566797/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.22541/au.166675335.56566797/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:p id=\"p1\">Objective: The causative virus of COVID-19 is SARS-CoV-2. The aim of the\npresent study was to invastigate the in vivo virucidal activity of nasal\nirrigation with saline, nasal irrigation with Povidone-iodine (PVP-I)\n1%, nasal irrigation with hypertonic alkaline and nasal irrigation with\nPVP-I 1% against SARS CoV- 2. Design: The present study was a\nprospective randomized clinical trial. Setting: A multicenter study\ninvolving tertiary care centers. Participants: The study included adult\noutpatients whose qualitative SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR tests in nasopharyngeal\nswabs were positive. One hundred twenty patients divided into four equal\ngroups. Standard COVID-19 treatment was given to group 1 (n=30), nasal\nirrigation containing isotonic solution was added to patients’ treatment\nin group 2 (n=30), nasal irrigation containing 1% PVP solution was\nadded to patients’ treatment in group 3(n=30), and nasal irrigation\ncontaining 1% PVP solution and nasal irrigation containing hypertonic\nalkaline solution was added to patients’ treatment in group 4 (n=30).\nMain outcome measures: On the first day of diagnosis (day 0),\nnasopharyngeal swab samples were taken, on the 3rd and 5th days the\nnasopharyngeal viral load reduction in quantitative RT-PCR tests were\ncalculated. Results: Between the 0-3rd Day and 0-5th days, the\nnasopharyngeal viral load reduction was significant in all groups\n(p< .05). In paired comparisons of groups, the nasopharyngeal\nviral load decrease in group 4 in first 3 days was significantly lower\nthan all groups (p < .05). The nasopharyngeal viral load\ndegrease in groups 3 and 4 in the first 5 days were significantly lower\nthan group 1 (p < .05). Conclussion: This study was reveal\nthat the use of hypertonic alkaline nasal irrigation together with 1%\npovidone-iodine was more effective in reducing viral load in the early\nperiod. The decreased nasopharyngeal viral load may reduce the carriage\nof infectious SARS-CoV-2 in patients. Our results suggest that 1%\npovidone-iodine and hypertonic alkaline nasal irrigation may be\npromising modality to prevent the COVID-19 epidemic.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8620-4375",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul University"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Karaaltin",
"given": "Aysegul",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "istanbul education and research hospital"
}
],
"family": "yigit",
"given": "ozgur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa"
}
],
"family": "cakan",
"given": "dogan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Aydin Universitesi"
}
],
"family": "akgül",
"given": "özer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Teaching and Research Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Yiğit",
"given": "Enes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "İstanbul Üniversitesi-Cerrahpaşa"
}
],
"family": "yılmaz",
"given": "yetkin zeki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Universitesi-Cerrahpasa"
}
],
"family": "Çakır",
"given": "Kays Burak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "İstanbul Üniversitesi-Cerrahpaşa"
}
],
"family": "çiftçi",
"given": "gamze",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Teaching and Research Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Seden",
"given": "Nihal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Teaching and Research Hospital"
}
],
"family": "çağlıyan",
"given": "abdurrahman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Teaching and Research Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Can",
"given": "Efe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Education Research Hospital"
}
],
"family": "dikme",
"given": "özgür",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Teaching and Research Hospital"
}
],
"family": "hacıoğlu",
"given": "yalçın",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "İstanbul Üniversitesi-Cerrahpaşa"
}
],
"family": "balkan",
"given": "ilker inanç",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul Aydin Universitesi"
}
],
"family": "enver",
"given": "özgün",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Istanbul University Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty"
}
],
"family": "Ozdogan",
"given": "Ahmet",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-26T03:02:41Z",
"timestamp": 1666753361000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-26T03:02:42Z",
"timestamp": 1666753362000
},
"group-title": "Preprints",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-27T05:09:14Z",
"timestamp": 1666847354285
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Authorea, Inc."
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
]
},
"member": "9829",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.22541",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Authorea, Inc.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.authorea.com/users/337860/articles/592062-effect-of-the-povidone-iodine-hypertonic-alkaline-solution-and-saline-nasal-lavage-on-nasopharyngeal-viral-load-in-covid-19?commit=bcb03d2ad8d86742ebd473271b70f5ab7211094d"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "EFFECT OF THE POVIDONE IODINE, HYPERTONIC ALKALINE SOLUTION AND SALINE NASAL LAVAGE ON NASOPHARYNGEAL VIRAL LOAD IN COVID-19",
"type": "posted-content"
}