One Week of Oral Camostat Versus Placebo in Nonhospitalized Adults With Mild-to-Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Randomized Controlled Phase 2 Trial
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad342, ACTIV-2, NCT04518410, Jun 2023
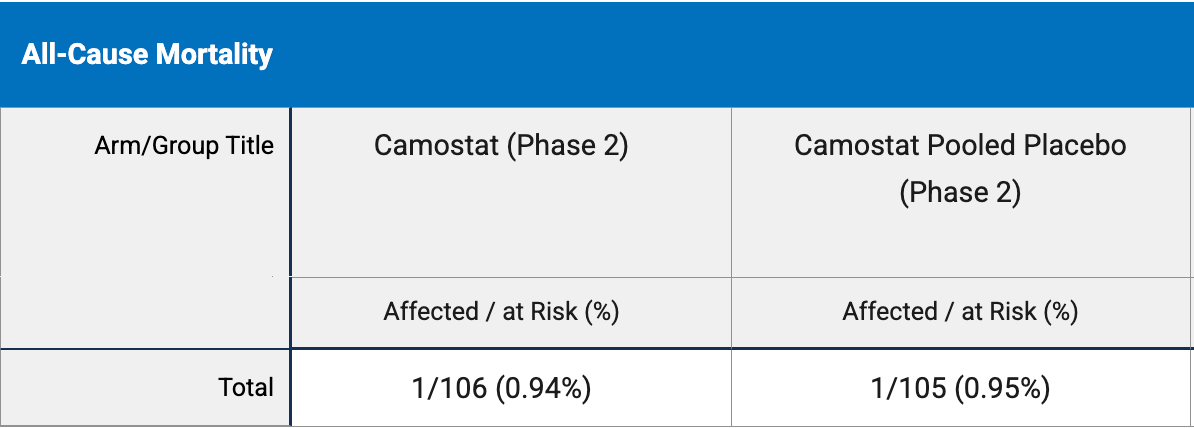
RCT 216 patients, 55% >5 days from symptom onset, showing no significant difference with camostat treatment. Longer-term mortality results are from the registry and are not shown in the paper.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers TMPRSS2 inhibitors and camostat.
|
risk of death, 0.9% lower, RR 0.99, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 106 (0.9%), control 1 of 105 (1.0%), NNT 11130, clinical trials registry.
|
|
risk of death, 198.2% higher, RR 2.98, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 109 (0.9%), control 0 of 107 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 17.8% higher, RR 1.18, p = 1.00, treatment 6 of 109 (5.5%), control 5 of 107 (4.7%), day 28.
|
|
risk of progression, 10.3% lower, RR 0.90, p = 0.11, treatment 85 of 109 (78.0%), control 93 of 107 (86.9%), NNT 11, Table S6.
|
|
no improvement, 13.4% lower, RR 0.87, p = 0.70, treatment 15 of 109 (13.8%), control 17 of 107 (15.9%), NNT 47, no improvement, day 28.
|
|
recovery time, no change, relative time 1.00, p = 0.99, treatment 109, control 107.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 14.3% lower, RR 0.86, p = 0.48, treatment 109, control 107, time to all targeted symptoms absent for 4 days, Table S6.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 14.3% lower, RR 0.86, p = 0.84, treatment 109, control 107, time to return to usual health for 2 days, Table S6.
|
|
risk of no recovery, no change, RR 1.00, p = 0.47, treatment 109, control 107, time to return to usual health for 4 days, Table S6.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 8.3% lower, RR 0.92, p = 0.76, treatment 109, control 107, time-averaged total daily symptom score, Table S6.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Jilg et al., 5 Jun 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 37.0, 39 authors, trial NCT04518410 (history) (ACTIV-2).
One Week of Oral Camostat Versus Placebo in Nonhospitalized Adults With Mild-to-Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Controlled Phase 2 Trial
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad342
Background. Camostat inhibits severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in vitro. We studied the safety and efficacy of camostat in ACTIV-2/A5401, a phase 2/3 platform trial of therapeutics for COVID-19 in nonhospitalized adults. Methods. We conducted a phase 2 study in adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 randomized to oral camostat for 7 days or a pooled placebo arm. Primary outcomes were time to improvement in COVID-19 symptoms through day 28, proportion of participants with SARS-CoV-2 RNA below the lower limit of quantification (LLoQ) from nasopharyngeal swabs through day 14, and grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) through day 28. Results. Of 216 participants (109 randomized to camostat, 107 to placebo) who initiated study intervention, 45% reported ≤5 days of symptoms at study entry and 26% met the protocol definition of higher risk of progression to severe COVID-19. Median age was 37 years. Median time to symptom improvement was 9 days in both arms (P = .99). There were no significant differences in the proportion of participants with SARS-CoV-2 RNA <LLoQ on days 3, 7, and 14. Through day 28, 6 (5.6%) participants in the camostat arm and 5 (4.7%) in the placebo arm were hospitalized; 1 participant in the camostat arm subsequently died. Grade ≥3 TEAEs occurred in 10.1% of camostat versus 6.5% of placebo participants (P = .35). Conclusions. In a phase 2 study of nonhospitalized adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, oral camostat did not accelerate viral clearance or time to symptom improvement, or reduce hospitalizations or deaths. Clinical Trials Registration. ClinicalTrials.
Age Median age (Q1, Q3), y 37 (29, 49) 39 (29, 48) 37 (29, 48) ≥ 60 y, n (%) 3 (3) 8 (7) 11 (5) Female sex, n (%) 63 ( 58 Gamma, n (%) 11 Delta, n (%) 1 (1) 0 (0) Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author.
References
Abuelazm, Ghanem, Awad, The effect of nitazoxanide on the clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clin Drug Investig
Activ-3, Tico, Group, Barkauskas, Mylonakis, Efficacy and safety of ensovibep for adults hospitalized with COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial, Ann Intern Med
Avezum, Oliveira, Oliveira, Hydroxychloroquine versus placebo in the treatment of non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19 (COPE-Coalition V): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial, Lancet Reg Health Am
Berg, Zhen, Lucic, Development of the RealTime SARS-CoV-2 quantitative laboratory developed test and correlation with viral culture as a measure of infectivity, J Clin Virol
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med
Chupp, Spichler-Moffarah, Sogaard, A phase 2 randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial of oral camostat mesylate for early treatment of COVID-19 outpatients showed shorter illness course and attenuation of loss of smell and taste
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients, N Engl J Med
Group, Lundgren, Grund, A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Gunst, Staerke, Pahus, Efficacy of the TMPRSS2 inhibitor camostat mesilate in patients hospitalized with Covid-19-a double-blind randomized controlled trial, EClinicalMedicine
Guo, Porter, Crozier, Topical TMPRSS2 inhibition prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection in differentiated human airway cultures, Life Sci Alliance
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hoffmann, Hofmann-Winkler, Smith, Camostat mesylate inhibits SARS-CoV-2 activation by TMPRSS2-related proteases and its metabolite GBPA exerts antiviral activity, EBioMedicine
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Horiguchi, Nakajima, Ito, Clinical experience with FOY-305 for pancreatitis, New Horiz Med
Iketani, Liu, Guo, Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Nature
Jilg, Nuttal, A randomized controlled trial of camostat in outpatients with COVID-19 [CROI Abstract 459, Top Antiv Med
Kim, Jeon, Kim, A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II clinical study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of camostat mesylate (DWJ1248) in adult patients with mild to moderate COVID-19, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Kinoshita, Shinoda, Nishizaki, A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of camostat mesilate in patients with COVID-19 (CANDLE study), BMC Med
Koch, Uckeley, Doldan, Stanifer, Boulant et al., TMPRSS2 expression dictates the entry route used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect host cells, EMBO J
Mahoney, Damalanka, Tartell, A novel class of TMPRSS2 inhibitors potently block SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV viral entry and protect human epithelial lung cells, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature
Mitja, Reis, Boulware, Hydroxychloroquine for treatment of nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19: a meta-analysis of individual participant data of randomized trials, Clin Transl Sci
Salleh, Deris, In silico molecular characterization of human TMPRSS2 protease polymorphic variants and associated SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility, Life
Sciences, received research funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and consulting fees paid to the institution from Sagent Pharmaceuticals. A. L. G.: reports contract testing from Abbott, Cepheid, Novavax, Pfizer, Janssen, and Hologic and research support from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Gilead
Sun, Sui, Zhou, Structural basis of covalent inhibitory mechanism of TMPRSS2-related serine proteases by camostat, J Virol
Takashita, Yamayoshi, Simon, Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against Omicron BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5 subvariants, N Engl J Med
Tobback, Degroote, Buysse, Efficacy and safety of camostat mesylate in early COVID-19 disease in an ambulatory setting: a randomized placebocontrolled phase II trial, Int J Infect Dis
Yao, Ye, Zhang, In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin Infect Dis
Zhou, Tsybovsky, Gorman, Cryo-EM structures of SARS-CoV-2 spike without and with ACE2 reveal a pH-dependent switch to mediate endosomal positioning of receptor-binding domains, Cell Host Microbe
Zhou, Vedantham, Lu, Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry, Antiviral Res
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad342",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciad342",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Camostat inhibits severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in vitro. We studied the safety and efficacy of camostat in ACTIV-2/A5401, a phase 2/3 platform trial of therapeutics for COVID-19 in nonhospitalized adults.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We conducted a phase 2 study in adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 randomized to oral camostat for 7 days or a pooled placebo arm. Primary outcomes were time to improvement in COVID-19 symptoms through day 28, proportion of participants with SARS-CoV-2 RNA below the lower limit of quantification (LLoQ) from nasopharyngeal swabs through day 14, and grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) through day 28.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Of 216 participants (109 randomized to camostat, 107 to placebo) who initiated study intervention, 45% reported ≤5 days of symptoms at study entry and 26% met the protocol definition of higher risk of progression to severe COVID-19. Median age was 37 years. Median time to symptom improvement was 9 days in both arms (P = .99). There were no significant differences in the proportion of participants with SARS-CoV-2 RNA &lt;LLoQ on days 3, 7, and 14. Through day 28, 6 (5.6%) participants in the camostat arm and 5 (4.7%) in the placebo arm were hospitalized; 1 participant in the camostat arm subsequently died. Grade ≥3 TEAEs occurred in 10.1% of camostat versus 6.5% of placebo participants (P = .35).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In a phase 2 study of nonhospitalized adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, oral camostat did not accelerate viral clearance or time to symptom improvement, or reduce hospitalizations or deaths.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Clinical Trials Registration. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT 04518410.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9154-2769",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital and Department of Medicine, Brigham Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School , Boston, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jilg",
"given": "Nikolaus",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of California , Los Angeles, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Chew",
"given": "Kara W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health , Boston, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Giganti",
"given": "Mark J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles Center , Torrance, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Daar",
"given": "Eric S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina , Chapel Hill, North Carolina , USA"
}
],
"family": "Wohl",
"given": "David A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of AIDS, National Institutes of Health , Rockville, Maryland , USA"
}
],
"family": "Javan",
"given": "Arzhang Cyrus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health , Boston, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kantor",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health , Boston, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Moser",
"given": "Carlee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Washington , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Coombs",
"given": "Robert W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quantum Clinical Trials , Miami Beach, Florida , USA"
}
],
"family": "Neytman",
"given": "Gene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Miami Clinical Research , Miami, Florida , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hoover",
"given": "Keila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sagent Pharmaceuticals , Schaumburg, Illinois , USA"
}
],
"family": "Jana",
"given": "Atasi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center , Columbus, Ohio , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hart",
"given": "Phil A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Washington , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Greninger",
"given": "Alexander L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sagent Pharmaceuticals , Schaumburg, Illinois , USA"
}
],
"family": "Szurgot",
"given": "Bob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina , Chapel Hill, North Carolina , USA"
}
],
"family": "Eron",
"given": "Joseph J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Los Angeles , Los Angeles, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Currier",
"given": "Judith S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health , Boston, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "Michael D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of California, San Diego , San Diego, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Davey M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School , Boston, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jonathan Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hosey",
"given": "Lara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roa",
"given": "Jhoanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Nilam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Degli-Angeli",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goecker",
"given": "Erin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daza",
"given": "Glenda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harb",
"given": "Socorro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dragavon",
"given": "Joan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldrovandi",
"given": "Grace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murtaugh",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Marlene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gutzman",
"given": "Howard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knowles",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Erhardt",
"given": "Bill",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waring",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hessinger",
"given": "Diane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "Stacey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "for the ACTIV-2/A5401 Study Team",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-09T13:34:09Z",
"timestamp": 1686317649000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-24T17:53:48Z",
"timestamp": 1687629228000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"award": [
"UM1AI068636"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-21T09:51:22Z",
"timestamp": 1695289882746
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685923200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciad342/50682365/ciad342.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciad342/50682365/ciad342.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"author": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B1"
},
{
"author": "Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"article-title": "Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients",
"author": "Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B3",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B4",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B5",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4",
"article-title": "Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages",
"author": "Iketani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "553",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B6",
"volume": "604",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2207519",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against Omicron BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5 subvariants",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "468",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B7",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B8",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "In silico molecular characterization of human TMPRSS2 protease polymorphic variants and associated SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility",
"author": "Salleh",
"journal-title": "Life (Basel)",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00861-21",
"article-title": "Structural basis of covalent inhibitory mechanism of TMPRSS2-related serine proteases by camostat",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B10",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2108728118",
"article-title": "A novel class of TMPRSS2 inhibitors potently block SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV viral entry and protect human epithelial lung cells",
"author": "Mahoney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B11",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103255",
"article-title": "Camostat mesylate inhibits SARS-CoV-2 activation by TMPRSS2-related proteases and its metabolite GBPA exerts antiviral activity",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B12",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.01.011",
"article-title": "Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B13",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical experience with FOY-305 for pancreatitis",
"author": "Horiguchi",
"journal-title": "New Horiz Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B14",
"year": "1980"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00751-9",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of two neutralising monoclonal antibody therapies, sotrovimab and BRII-196 plus BRII-198, for adults hospitalised with COVID-19 (TICO): a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "ACTIV-3/Therapeutics for Inpatients with COVID-19 (TICO) Study Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "622",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B15",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033130",
"article-title": "A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "ACTIV-3/TICO LY-CoV555 Study Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B16",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-1503",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of ensovibep for adults hospitalized with COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "ACTIV-3/TICO Study Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1266",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B17",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-022-02518-7",
"article-title": "A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of camostat mesilate in patients with COVID-19 (CANDLE study)",
"author": "Kinoshita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "342",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B18",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100849",
"article-title": "Efficacy of the TMPRSS2 inhibitor camostat mesilate in patients hospitalized with Covid-19—a double-blind randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Gunst",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B19",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of camostat mesylate in early COVID-19 disease in an ambulatory setting: a randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial",
"author": "Tobback",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "628",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B20",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "A phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oral camostat mesylate for early treatment of COVID-19 outpatients showed shorter illness course and attenuation of loss of smell and taste",
"author": "Chupp",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.00452-22",
"article-title": "A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II clinical study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of camostat mesylate (DWJ1248) in adult patients with mild to moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0045222",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B22",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104945",
"article-title": "Development of the RealTime SARS-CoV-2 quantitative laboratory developed test and correlation with viral culture as a measure of infectivity",
"author": "Berg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B23",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "A randomized controlled trial of camostat in outpatients with COVID-19 [CROI Abstract 459]",
"author": "Jilg",
"first-page": "175",
"journal-title": "Top Antiv Med",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B24",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine versus placebo in the treatment of non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19 (COPE—Coalition V): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial",
"author": "Avezum",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health Am",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B25",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.13468",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine for treatment of non-hospitalized adults with COVID-19: a meta-analysis of individual participant data of randomized trials",
"author": "Mitja",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "524",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B26",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa237",
"article-title": "In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "732",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B27",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40261-022-01213-y",
"article-title": "The effect of nitazoxanide on the clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Abuelazm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1031",
"journal-title": "Clin Drug Investig",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B28",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.11.004",
"article-title": "Cryo-EM structures of SARS-CoV-2 spike without and with ACE2 reveal a pH-dependent switch to mediate endosomal positioning of receptor-binding domains",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "867",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B29",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2021107821",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 expression dictates the entry route used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect host cells",
"author": "Koch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EMBO J",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B30",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"article-title": "Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity",
"author": "Meng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B31",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26508/lsa.202101116",
"article-title": "Topical TMPRSS2 inhibition prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection in differentiated human airway cultures",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Life Sci Alliance",
"key": "2023062300024026300_ciad342-B32",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciad342/7190261"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "One Week of Oral Camostat Versus Placebo in Nonhospitalized Adults With Mild-to-Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Randomized Controlled Phase 2 Trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}
jilg