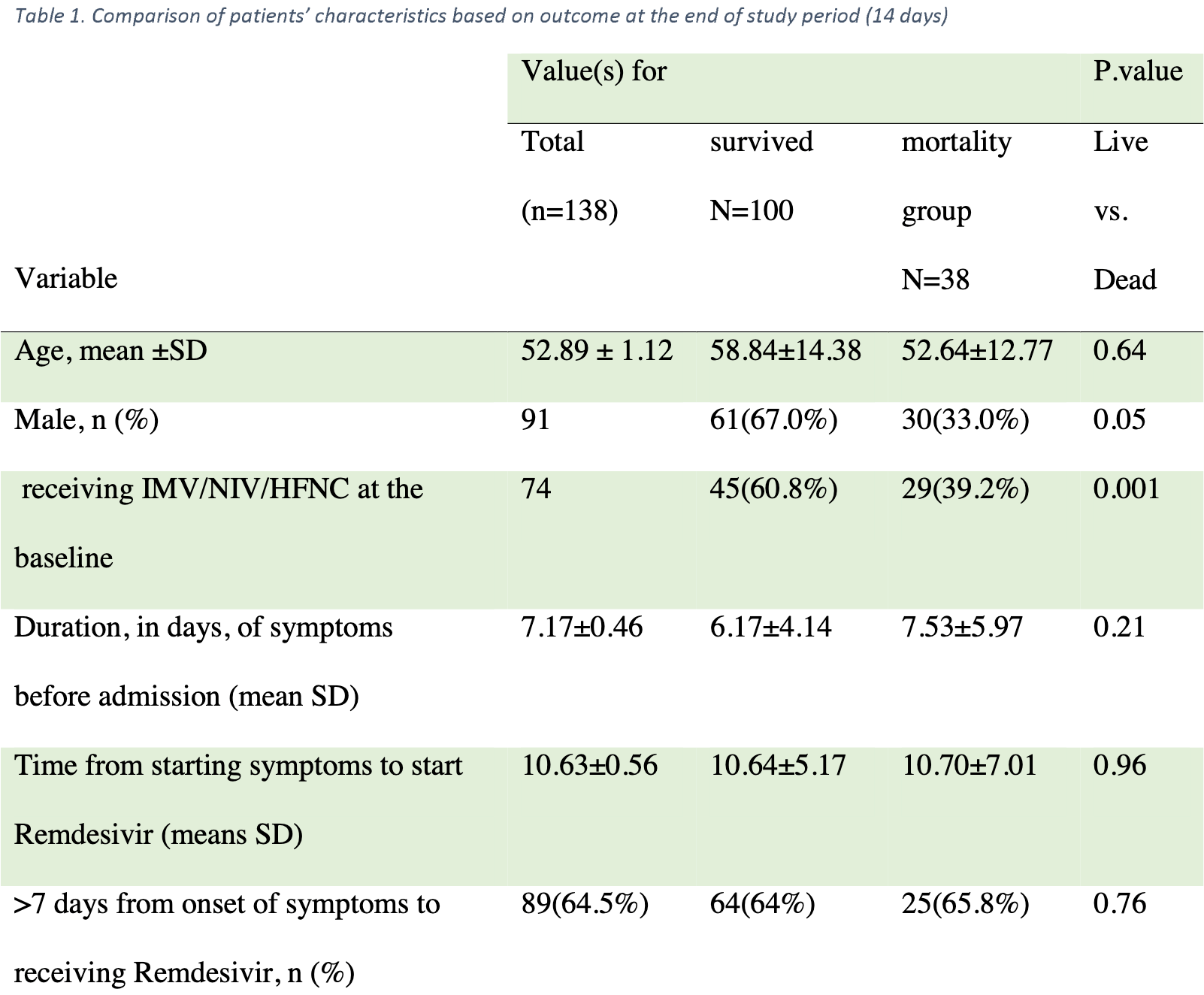
Another step toward final call on Remdesivir efficacy as a treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a multicenter open-label trial
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.08.13.21261992 , Aug 2021
Single arm remdesivir trial with 145 hospitalized patients showing no statistically significant difference between "early" and "late" administration, however the treatment delays may be better described as late and very late. The text of the paper defines early and late as less than or more than 7 days from symptom onset, however the CONSORT diagram says during or after 7 days post admission.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Hosseini et al., 13 Aug 2021, preprint, 15 authors.
Abstract: medRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.13.21261992; this version posted August 13, 2021. The copyright holder for this preprint
(which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity.
It is made available under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 International license .
Title: Another step toward final call on Remdesivir efficacy as a treatment for hospitalized
COVID-19 patients: a multicenter open-label trial
Running title: Remdesivir efficacy in COVID-19 treatment
Authors:
Hamed Hosseini1, Anahita Sadeghi2, Payam Tabarsi3, Azin Etemadimanesh4, Ilad Alavi
Darazam3, Nasser Aghdami4, Saeed Kalantari5, Mehrdad Hasibi4, Azar Hadadi4, Farhang
Babamahmoodi6, Mansooreh Momen-Heravi7, Ahmad Hormati8,9, Yunes Panahi10, Rozita
Khodashahi11, Mohammadreza Salehi4*
1. Center for Research and Training in Skin Disease and Leprosy, Tehran University of
Medical Sciences.
2. Department of Internal Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
3. Department of Infectious Disease, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences,
Tehran, Iran.
4. Department of Infectious Disease, Tehran University of Medical Science, Tehran, Iran.
5. Antimicrobial Resistance Research Center, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,
Iran
6. Antimicrobial Resistance Research Center, Communicable Diseases Institute,
Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran
7. Department of infectious diseases, faculty of medicine, Kashan university of medical
sciences, Kashan, Iran.
8. Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disease Research Center, Oom university of medical
sciences, Iran.
NOTE: This preprint reports new research that has not been certified by peer review and should not be used to guide clinical practice.
medRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.13.21261992; this version posted August 13, 2021. The copyright holder for this preprint
(which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity.
It is made available under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 International license .
9. Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases Research Center, Iran university of medical sciences,
Tehran, Iran.
10. Pharmacotherapy Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Baqiyatallah University of Medical
Sciences, Tehran, Iran
11. Department of Infectious disease and tropical medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Mashhad
university of medical sciences, Mashhad, Iran.
Corresponding author:
Mohammadreza Salehi M.D., Department of Infectious Disease, Tehran University of Medical
Sciences. Imam Khomeini hospital complex, Gharib St., Tehran, Iran. Email:
salehi.mohamad3@gmail.com , ORCID: 0000-0002-1987-5929, Cellphone: +989123159842
Declaration of interests:
Hereby, all authors of this study declare no conflict of interests before, during, and after the
study was done.
Acknowledgments:
Our sincere thanks to Professor Reza Malekzadeh who coordinated and supervised the project.
We express our gratitude to the Digestive Diseases Research Institute (DDRI), Tehran University
of Medical Sciences. Conducting the study would not have been possible without the efforts of
the DDRI team. The authors also would like to express their gratitude for all care workers and
patients in study hospitals. This study has been funded and supported by Tehran University of
Medical Sciences (TUMS); Grant no. 99-1-97-47143.
medRxiv preprint doi:..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.08.13.21261992",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.13.21261992",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>After emerging the global pandemic of SARS-CoV2 some preliminary studies demonstrated the efficacy of antiviral treatments. But shortly thereafter, inconsistencies in the results of further clinical trials raised doubts on the efficacy of these agents. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effect of Remdesivir on hospitalized COVID-19 patients’ outcomes.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Material and methods</jats:title><jats:p>This study was an open-label, single-armed, clinical trial on hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19 who had progressive respiratory symptoms despite receiving standard care. All patients received Remdesivir and their characteristics, outcomes, time of treatment initiation, and respiratory support stages during hospitalization were registered and followed up for 14 days.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>145 patients with the mean age of 52.89 ± 1.12 years enrolled in this study, 38 (26.2%) died at the end of 14 days period. The mean time interval from the onset of the symptoms to antiviral treatment was 10.63±0.56 days. Thirty deceased patients (78.9%) were men, showing 2.8 times higher mortality chance compared to women (OR<jats:sub>adj</jats:sub>=2.77; 95%CI=1.08-7.09). The type of respiratory support on the first day of treatment initiation showed a significantly lower mortality chance in patients receiving O<jats:sub>2</jats:sub>only than those who needed non-invasive and/or mechanical ventilation (OR<jats:sub>adj</jats:sub>=3.91; 95%CI=1.64-9.32). The start time (early vs late administration) and duration (less or more than 7 days) of antiviral treatment had no statistically significant association with mortality or ventilation escalation among the patients (p-value > 0.05).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>In this study, we showed that Remdesivir probably is not effective on the outcome of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
13
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2368-6749",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hosseini",
"given": "Hamed",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9564-4631",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sadeghi",
"given": "Anahita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8932-5420",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tabarsi",
"given": "Payam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6923-0133",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Etemadimanesh",
"given": "Azin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4440-335X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Darazam",
"given": "Ilad Alavi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5390-7878",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aghdami",
"given": "Nasser",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9896-4139",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kalantari",
"given": "Saeed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8120-6400",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hasibi",
"given": "Mehrdad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5080-6887",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hadadi",
"given": "Azar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4239-9569",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Babamahmoodi",
"given": "Farhang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8528-8271",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Momen-Heravi",
"given": "Mansooreh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1322-1318",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hormati",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2504-8356",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Panahi",
"given": "Yunes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6514-7308",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Khodashahi",
"given": "Rozita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1987-5929",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Salehi",
"given": "Mohammadreza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-13T20:15:19Z",
"timestamp": 1628885719000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-07T10:29:03Z",
"timestamp": 1673087343000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-14T09:52:51Z",
"timestamp": 1692006771192
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
13
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.08.13.21261992",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
13
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic",
"first-page": "157",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta bio-medica: Atenei Parmensis",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.1",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-2911",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.3",
"unstructured": "Jalili, M. , et al., Characteristics and mortality of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Iran: a National Retrospective Cohort Study. Annals of internal medicine, 2020."
},
{
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.4",
"unstructured": "Cascella, M. , et al., Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus (COVID-19), in Statpearls [internet]. 2020, StatPearls Publishing."
},
{
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.5",
"unstructured": "Organization, W.H. , Solidarity” clinical trial for COVID-19 treatments. World Health Organization (WHO). Situation reports. Geneva: WHO. [Accessed: 5 Apr 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/global-research-on-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov/solidarity-clinical-trial-for-covid-19-treatments, 2020."
},
{
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.6",
"unstructured": "Saint-Raymond, A. , et al., Remdesivir emergency approvals: a comparison of the US, Japanese, and EU systems. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology, 2020: p. 1–7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NE-JMoa2007016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cegh.2020.07.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.8",
"unstructured": "Frediansyah, A. , et al., Remdesivir and its antiviral activity against COVID-19: A systematic review. Clinical epidemiology and global health, 2020."
},
{
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.9",
"unstructured": "Wang, Y. , et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebocontrolled, multicentre trial. The Lancet, 2020."
},
{
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.10",
"unstructured": "Pan, H. , et al., Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19; interim WHO SOLIDARITY trial results. MedRxiv, 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104285",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.11",
"unstructured": "Li, C. , Y. Yang , and L. Ren , Genetic evolution analysis of 2019 novel coronavirus and coronavirus from other species. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 2020: p. 104285."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.12",
"unstructured": "Sheahan, T.P. , et al., Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Science translational medicine, 2017. 9(396)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2187",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.13",
"unstructured": "Elsawah, H.K. , et al., Efficacy and safety of remdesivir in hospitalized Covid-19 patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis including network meta-analysis. Reviews in medical virology, 2020: p. e2187."
},
{
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.14",
"unstructured": "Madsen, L.W. , Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008570",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.02.17.20024166",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021081607550690000_2021.08.13.21261992v1.16",
"unstructured": "Liu, Y. , et al., Clinical features and progression of acute respiratory distress syndrome in coronavirus disease 2019. MedRxiv, 2020."
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.08.13.21261992"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Another step toward final call on Remdesivir efficacy as a treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a multicenter open-label trial",
"type": "posted-content"
}