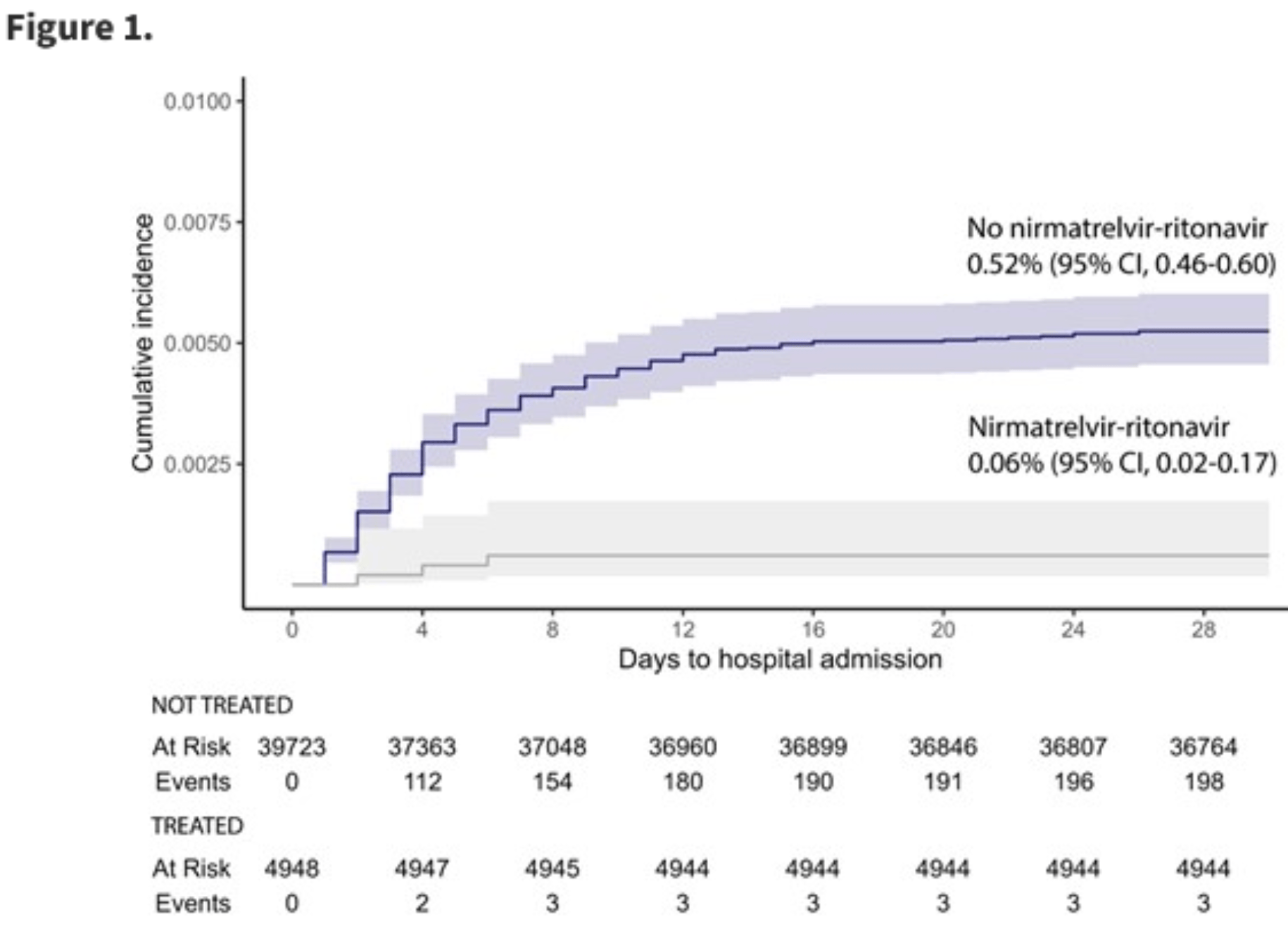
COVID-19 hospitalization risk after outpatient nirmatrelvir/ritonavir use, January to August 2022, North Carolina
et al., Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dkae042, Feb 2024
EHR retrospective 44,671 patients with 4,948 receiving paxlovid, showing lower hospitalization with treatment.
Confounding by treatment propensity. This study analyzes a population
where only a fraction of eligible patients received the treatment. Patients
receiving treatment may be more likely to follow other recommendations, more
likely to receive additional care, and more likely to use additional
treatments that are not tracked in the data (e.g., nasal/oral hygiene1,2, vitamin D3, etc.) — either because the physician
recommending paxlovid also recommended them, or
because the patient seeking out paxlovid is more
likely to be familiar with the efficacy of additional treatments and more
likely to take the time to use them.
Malden et al. confirm significant bias in the use of paxlovid, showing that treated
patients are more likely to be from affluent neighborhoods, be more health-conscious, and
have better access to care. Campion et al. also show that female patients were more
likely to receive paxlovid, and studies show that female patients are significantly more
likely to be health-conscious, for example being more likely to take additional
non-prescription treatments.
Therefore, these kind of studies may
overestimate efficacy.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid6-13. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID14. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid15. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid16. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury17 and liver injury18,19. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound20-22.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments23.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
only a fraction of eligible patients received treatment and these patients may be more likely to follow other recommendations, receive additional care, and more more likely to use additional untracked treatments such as vitamin D and nasal/oral hygiene.
|
risk of hospitalization, 84.0% lower, HR 0.16, p = 0.002, treatment 4,948, control 39,723.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
4.
Malden et al., Predictors of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir receipt among COVID-19 patients in a large US health system, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57633-7.
5.
Campion et al., Disparities in the Use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1809.
6.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
7.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
8.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
9.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
10.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
11.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
12.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
13.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
14.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
15.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
16.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
17.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
18.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
19.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
20.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
21.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Henderson et al., 21 Feb 2024, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period January 2022 - August 2022.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkae042",
"ISSN": [
"0305-7453",
"1460-2091"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkae042",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In the USA, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir is authorized for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in patients at least 12 years of age, at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objectives</jats:title>\n <jats:p>To estimate the impact of outpatient nirmatrelvir/ritonavir on COVID-19 hospitalization risk in a US healthcare system.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We conducted a cohort study using electronic health records among outpatients with a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test between January and August 2022. We evaluated the association of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir therapy with time to hospitalization by estimating adjusted HRs and assessed the impact of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir on predicted COVID-19 hospitalizations using machine-learning methods.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Among 44 671 patients, 4948 (11%) received nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, and 201 (0.4%) were hospitalized within 28 days of COVID-19 diagnosis. Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir recipients were more likely to be older, white, vaccinated, have comorbidities and reside in areas with higher average socioeconomic status. The 28 day cumulative incidence of hospitalization was 0.06% (95% CI: 0.02%–0.17%) among nirmatrelvir/ritonavir recipients and 0.52% (95% CI: 0.46%–0.60%) among non-recipients. For nirmatrelvir/ritonavir versus no therapy, the age-adjusted HR was 0.08 (95% CI: 0.03–0.26); the fully adjusted HR was 0.16 (95% CI: 0.05–0.50). In the machine-learning model, the primary features reducing predicted hospitalization risk were nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, younger age, vaccination, female gender and residence in a higher socioeconomic status area.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>COVID-19 hospitalization risk was reduced by 84% among nirmatrelvir/ritonavir recipients in a large, diverse healthcare system during the Omicron wave. These results suggest that nirmatrelvir/ritonavir remained highly effective in a setting substantially different than the original clinical trials.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2197-3149",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Henderson",
"given": "Heather I",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7764-0212",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wohl",
"given": "David A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4900-098X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fischer",
"given": "William A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"family": "Bartelt",
"given": "Luther A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4784-3227",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "van Duin",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"family": "Agil",
"given": "Deana M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"family": "Browne",
"given": "Lindsay E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Kuo-Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"family": "Moy",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"family": "Eron",
"given": "Joseph J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9032-3713",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine , 130 Mason Farm Road, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Napravnik",
"given": "Sonia",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T15:52:32Z",
"timestamp": 1708530752000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T15:52:46Z",
"timestamp": 1708530766000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"P30 AI50410"
],
"name": "University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Center for AIDS Research"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100006108",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"award": [
"TL1TR002491"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "NIH"
},
{
"award": [
"U54 CA260543"
],
"name": "NIH-funded SeroNet Serocenter of Excellence Award"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"T32 AI007001"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-22T01:03:04Z",
"timestamp": 1708563784223
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1708473600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/jac/dkae042/56726755/dkae042.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/jac/dkae042/56726755/dkae042.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"author": "CDC",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B1"
},
{
"author": "CDC",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-6306",
"article-title": "Racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19–related infections, hospitalizations, and deaths",
"author": "Mackey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "362",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B3",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "CDC",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B4"
},
{
"author": "National Institutes of Health",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B5"
},
{
"author": "Pfizer",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B7",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064498",
"article-title": "Drug interventions for prevention of COVID-19 progression to severe disease in outpatients: a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses (the LIVING project)",
"author": "Petersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e064498",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B8",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-2141",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for early COVID-19 in a large U.S. health system",
"author": "Dryden-Peterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B9",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac673",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in non-hospitalized vaccinated patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Ganatra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "563",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B10",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac687",
"article-title": "Impact of the use of oral antiviral agents on the risk of hospitalization in community COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Yip",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e26",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B11",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.221608",
"article-title": "Population-based evaluation of the effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for reducing hospital admissions and mortality from COVID-19",
"author": "Schwartz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E220",
"journal-title": "CMAJ",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B12",
"volume": "195",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2204919",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir use and severe Covid-19 outcomes during the Omicron surge",
"author": "Arbel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B13",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e342",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B14",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1213",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B15",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Real-World Effectiveness of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in Preventing Hospitalization Among Patients With COVID-19 at High Risk for Severe Disease in the United States: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study",
"author": "Zhou",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad287",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir on coronavirus disease 2019–associated hospitalization prevention: a population-based cohort study in the province of Quebec, Canada",
"author": "Kaboré",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "805",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B17",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7148e2",
"article-title": "Paxlovid associated with decreased hospitalization rate among adults with COVID-19—United States, April-September 2022",
"author": "Shah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B18",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00011-7",
"article-title": "Real-world use of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in outpatients with COVID-19 during the era of omicron variants including BA.4 and BA.5 in Colorado, USA: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Aggarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "696",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B19",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00118-4",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in preventing hospital admissions and deaths in people with COVID-19: a cohort study in a large US health-care system",
"author": "Lewnard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "806",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B20",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1214/ss/1009213726",
"article-title": "Statistical modeling: the two cultures",
"author": "Breiman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "199",
"journal-title": "Stat Sci",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B21",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"article-title": "A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation",
"author": "Charlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "J Chronic Dis",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B22",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"author": "CDC",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B23"
},
{
"author": "US Census Bureau",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B24"
},
{
"author": "Lundberg",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B25",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"author": "CDC",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7143a2",
"article-title": "Racial and ethnic disparities in outpatient treatment of COVID-19 — United States, January–July 2022",
"author": "Boehmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1359",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B27",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7143a3",
"article-title": "Notes from the field: dispensing of oral antiviral drugs for treatment of COVID-19 by zip code-level social vulnerability—United States, December 23, 2021-August 28, 2022",
"author": "Sullivan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1384",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B28",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7125e1",
"article-title": "Dispensing of oral antiviral drugs for treatment of COVID-19 by zip code–level social vulnerability—United States, December 23, 2021–May 21, 2022",
"author": "Gold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "825",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B29",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.17876",
"article-title": "Association of primary and booster vaccination and prior infection with SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 outcomes",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1415",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B30",
"volume": "328",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pgph.0000619",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence and risk factors among meat packing, produce processing, and farm workers",
"author": "Klein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0000619",
"journal-title": "PLoS Glob Public Health",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B31",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.0335",
"article-title": "COVID-19 therapeutics for nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Gandhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "617",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2024022113595098600_dkae042-B32",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jac/dkae042/7611865"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 hospitalization risk after outpatient nirmatrelvir/ritonavir use, January to August 2022, North Carolina",
"type": "journal-article"
}