Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal rinses with neutral electrolyzed water prevents COVID‑19 in front‑line health professionals: A randomized, open‑label, controlled trial in a general hospital in Mexico City
et al., Biomedical Reports, doi:10.3892/br.2021.1494, Dec 2021
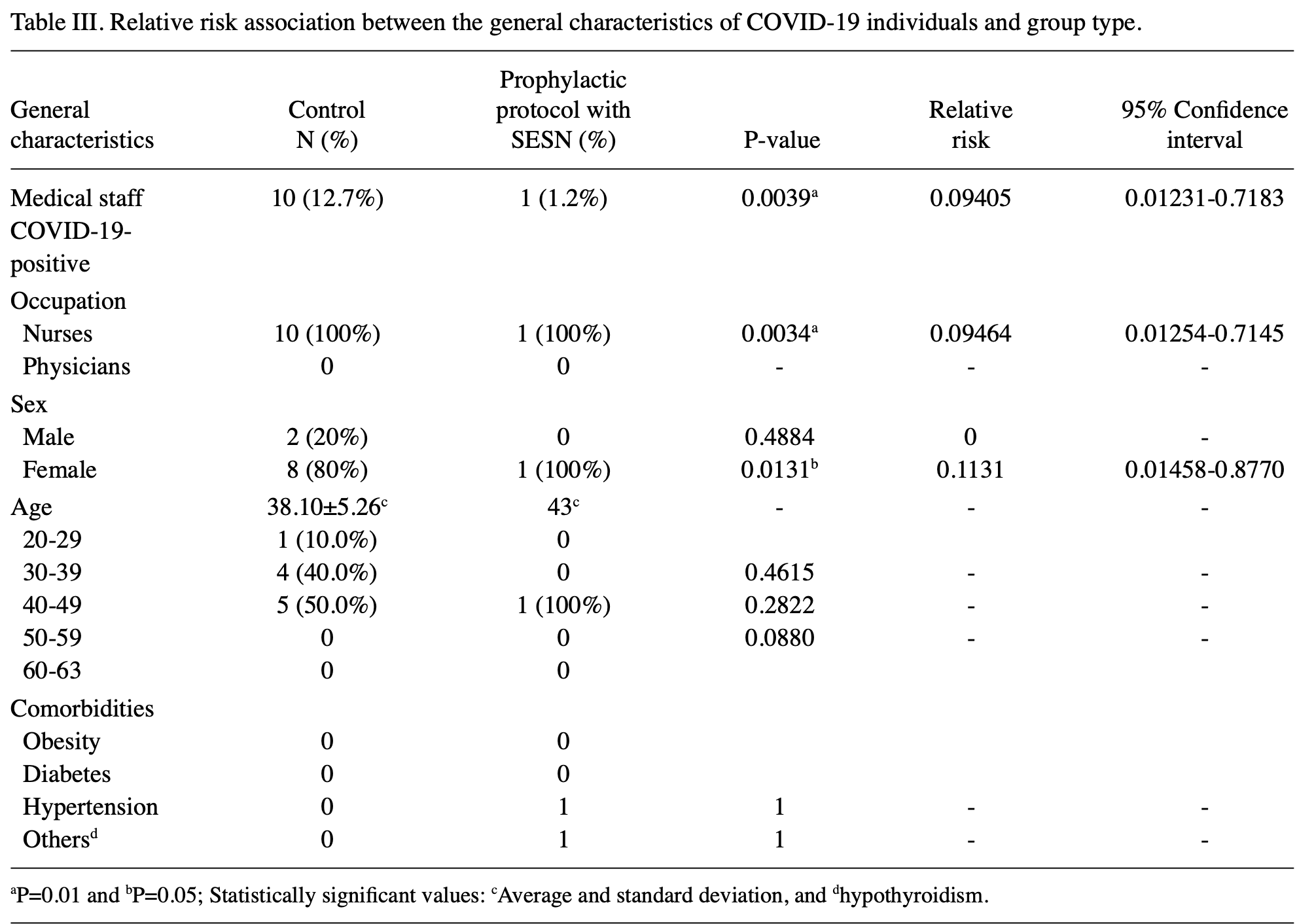
RCT 170 front-line healthcare workers in Mexico showing significantly lower COVID-19 cases with neutral electrolyzed water (SES) nasal and oral rinses. Authors hypothesize that SES inactivates viral particles through its oxidizing potential, reducing viral load in the upper respiratory tract where SARS-CoV-2 initially establishes infection. HOCl is the primary active component of neutral electrolyzed saline.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects.
|
risk of symptomatic case, 90.6% lower, RR 0.09, p = 0.004, treatment 1 of 84 (1.2%), control 10 of 79 (12.7%), NNT 8.7.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Sevinç Gül et al., Effect of oral antiseptics on the viral load of SARS-CoV-2: A randomized controlled trial, Dental and Medical Problems, doi:10.17219/dmp/150831.
2.
Panatto et al., Efficacy of the Sentinox Spray in Reducing Viral Load in Mild COVID-19 and Its Virucidal Activity against Other Respiratory Viruses: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial and an In Vitro Study, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14051033.
3.
Gutiérrez-García et al., Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal rinses with neutral electrolyzed water prevents COVID‑19 in front‑line health professionals: A randomized, open‑label, controlled trial in a general hospital in Mexico City, Biomedical Reports, doi:10.3892/br.2021.1494.
4.
Delgado-Enciso et al., Safety and efficacy of a COVID‑19 treatment with nebulized and/or intravenous neutral electrolyzed saline combined with usual medical care vs. usual medical care alone: A randomized, open‑label, controlled trial, Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10347.
Gutiérrez-García et al., 15 Dec 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Mexico, peer-reviewed, mean age 38.1, 6 authors, study period September 2020 - November 2020.
Contact: bpaz@esteripharma.com.mx.
Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal rinses with neutral electrolyzed water prevents COVID‑19 in front‑line health professionals: A randomized, open‑label, controlled trial in a general hospital in Mexico City
Biomedical Reports, doi:10.3892/br.2021.1494
The worldwide efforts that healthcare professionals are making in the COVID-19 pandemic is well known, and the high risk of illness and death that front-line staff experience on a daily basis is a reality, despite well-defined protocols for the use of personal protective equipment. In addition, it is well known that vaccination is still faraway to be achieved worldwide and that new variants are emerging, thus additional protective measures must be explored. A prospective open-label randomized controlled clinical trial was performed on front-line medical staff from the Dr. Enrique Cabrera General Hospital in México City to evaluate the effectiveness of nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal rinses with a neutral electrolyzed water, known as SES, to reduce the risk of COVID-19 disease among front-line, not vaccinated medical staff. A total of 170 volunteers were enrolled and equally divided in a control group and SES group. All members of the trial wore the adequate personal protection equipment at all times while performing their duties, as required by standard COVID-19 safety protocols. Additionally, the SES group participants followed a prophylactic protocol with SES (oral and nasal rinses, three times a day for 4 weeks). All participants were monitored for COVID-19 symptoms and disease in a time-frame of 4 weeks and the incidence of illness per group was registered. The relative risk of disease, associated with each treatment was calculated. The presence of COVID-19-positive cases, in the group that received the nasal and oral rinses with SES was 1.2%, while in the group that did not do the SES rinses (control group), it was 12.7% (P=0.0039 and RR=0.09405; 95% CI of 0.01231-0.7183). The prophylactic protocol was demonstrated as a protective factor, in more than 90%, for developing the disease, and without adverse effects. Nasal and oral rinses with SES may be an efficient alternative to reinforce the protective measures against COVID-19 disease and should be further investigated. The present clinical trial was retrospectively registered in the Cuban public registry of clinical trials (RPCEC) database (March 16, 2021; PREVECOVID-19: RPCEC00000357).
Authors' contributions RGG designed the study and conducted the data acquisition. JCDLCA performed the data acquisition. ACL performed the data analysis. IDE performed the data analysis and interpretation. NMS helped with the validation and supply of the neutral electrolyzed water used in the study. RGG, JCA and IDE confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. BAPM participated in the design of the study. All authors helped to prepare, and have read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate The present study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health of Mexico City (Reg. No. 101-010-024-2020) in accordance with the ethical international standards established in the Declaration of Helsinki. Each participant provided their written informed consent, and data was processed according to national and international data protection laws.
Patient consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors RGG, JCA and IDE declare that they have no competing interests. ACL, NMS and BPM state that they are employees at Esteripharma S.A. de C.V. company but did not participate in the decision to publish the results of the study, nor in the selection of the volunteers or in its development.
References
Bidra, Pelletier, Westover, Frank, Brown et al., Rapid in-vitro inactivation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) using povidone-iodine oral antiseptic rinse, J Prosthodont
Carrouel, Conte, Fisher, Gonçalves, Dussart et al., COVID-19: A recommendation to examine the effect of mouthrinses with β-cyclodextrin combined with citrox in preventing infection and progression, J Clin Med
Caruso, Prete, Lazzarino, Hydrogen peroxide and viral infections: A literature review with research hypothesis definition in relation to the current covid-19 pandemic, Med Hypotheses
Cegolon, Javanbakht, Mastrangelo, Nasal disinfection for the prevention and control of COVID-19: A scoping review on potential chemo-preventive agents, Int J Hyg Environ Health
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Molenkamp, Meijer et al., Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Eurosurveillance
Delgado-Enciso, Garcia, Barajas-Saucedo, Mokay-Ramírez, Meza-Robles et al., Safety and efficacy of a COVID-19 treatment with nebulized and/or intravenous neutral electrolyzed saline combined with usual medical care vs. usual medical care alone: A randomized, open-label, controlled trial, Exp Ther Med
Dubina, Gomonova, Taraskina, Vasilyeva, Sayganov, Pathogenesis-based preexposure prophylaxis associated with a low risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in healthcare workers at a designated COVID-19 hospital: A pilot study, BMC Infect Dis
Ejaz, Alsrhani, Zafar, Javed, Junaid et al., COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients, J Infect Public Health
Giarratana, Rajan, Kamala, Mendenhall, Reiner, A sprayable Acid-Oxidizing solution containing hypochlorous acid (AOS2020) efficiently and safely inactivates SARS-Cov-2: A new potential solution for upper respiratory tract hygiene, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol
Huijghebaert, Hoste, Vanham, Essentials in saline pharmacology for nasal or respiratory hygiene in times of COVID-19, Eur J Clin Pharmacol
Jogalekar, Veerabathini, Gangadaran, SARS-CoV-2 variants: A double-edged sword?, Exp Biol Med (Maywood)
Kimura, Freeman, Wessinger, Gupta, Sheng et al., Interim analysis of an open-label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non-hospitalized patients with coronavirus diesease 2019, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol
Li, Huang, Zou, Yang, Hui et al., Epidemiology of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical characteristics, risk factors, and outcomes, J Med Virol
Liu, Kang, Wang, Chu, Jen et al., Protection procedures and preventions against the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 in healthcare settings for nursing personnel: Lessons from Taiwan, Aust Crit Care
Liu, Liu, Wang, Hu, Liu et al., Analysis of the prophylactic effect of thymosin drugs on COVID-19 for 435 medical staff: A hospital-based retrospective study, J Med Virol
Meyers, Robison, Milici, Alam, Quillen et al., Lowering the transmission and spread of human coronavirus, J Med Virol
Moorman, Montazeri, Jaykus, Efficacy of neutral electrolyzed water for inactivation of human norovirus, Appl Environ Microbiol
Morita, Sano, Morimatsu, Kiura, Goto et al., Disinfection potential of electrolyzed solutions containing sodium chloride at low concentrations, J Virol Methods
O'donnell, Thomas, Stanton, Maillard, Murphy et al., Potential role of oral rinses targeting the viral lipid envelope in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Function (Oxf)
Pan, Zhang, Yang, Poon, Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples, Lancet Infect Dis
Peckham, De Gruijter, Raine, Radziszewska, Ciurtin et al., Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission, Nat Commun
Seneviratne, Balan, Ko, Udawatte, Lai et al., Efficacy of commercial mouth-rinses on SARS-CoV-2 viral load in saliva: Randomized control trial in Singapore, Infection
Sungnak, Huang, Bécavin, Berg, Queen et al., SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes, Nat Med
Takeda, Uchiumi, Matsuda, Ogawa, Acidic electrolyzed water potently inactivates SARS-CoV-2 depending on the amount of free available chlorine contacting with the virus, Biochem Biophys Res Commun
Tamaki, Bui, Ngo, Ogawa, Imai, Virucidal effect of acidic electrolyzed water and neutral electrolyzed water on avian influenza viruses, Arch Virol
To, Tsang, Leung, Tam, Wu et al., Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: An observational cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis
Wang, Zhao, Gao, Gao, Wang et al., SARS-CoV-2: Structure, biology, and structure-based therapeutics development, Front Cell Infect Microbiol
Worldometer, None, COVID Live Update
Wölfel, Corman, Guggemos, Seilmaier, Zange et al., Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019, Nature
Xu, Zhong, Deng, Peng, Dan et al., High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa, Int J Oral Sci
Yan, Daliri, Oh, New clinical applications of electrolyzed water: A review, Microorganisms
Zou, Ruan, Huang, Liang, Huang et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3892/br.2021.1494",
"ISSN": [
"2049-9434",
"2049-9442"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/br.2021.1494",
"article-number": "11",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Dr. Enrique Cabrera General Hospital, Mexico City 01620, Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Gutiérrez‑García",
"given": "Rafael",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Direction, Dr. Enrique Cabrera General Hospital, Mexico City 01620, Mexico"
}
],
"family": "De La Cerda‑Angeles",
"given": "Juan C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Research and Industrial Property, Esteripharma S.A. de C.V., Estado de México 50450, Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Cabrera‑Licona",
"given": "Ariana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Medicine, School of Medicine, Universidad de Colima, Colima 28040, Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Delgado‑Enciso",
"given": "Ivan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Direction, Esteripharma México S.A. de C.V., México City 03100, Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Mervitch‑Sigal",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Research and Industrial Property, Esteripharma S.A. de C.V., Estado de México 50450, Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Paz‑michel",
"given": "Brenda",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biomedical Reports",
"container-title-short": "Biomed Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-15T13:30:35Z",
"timestamp": 1639575035000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-02T10:19:07Z",
"timestamp": 1646216347000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-05T13:09:31Z",
"timestamp": 1754399371265
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 11,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
]
}
},
"member": "2249",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3892",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Spandidos Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.587269",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2: Structure, biology, and structure-based therapeutics development",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "724",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b1-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "key20220302121528_b2-BR-16-2-01494"
},
{
"key": "key20220302121528_b3-BR-16-2-01494"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/15353702211014146",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variants: A double-edged sword?",
"author": "Jogalekar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1721",
"journal-title": "Exp Biol Med (Maywood)",
"key": "key20220302121528_b4-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "246",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26492",
"article-title": "Analysis of the prophylactic effect of thymosin drugs on COVID-19 for 435 medical staff: A hospital-based retrospective study",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1573",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b5-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06241-1",
"article-title": "Pathogenesis-based preexposure prophylaxis associated with a low risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in healthcare workers at a designated COVID-19 hospital: A pilot study",
"author": "Dubina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "536",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "key20220302121528_b6-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113605",
"article-title": "Nasal disinfection for the prevention and control of COVID-19: A scoping review on potential chemo-preventive agents",
"author": "Cegolon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "113605",
"journal-title": "Int J Hyg Environ Health",
"key": "key20220302121528_b7-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "230",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/function/zqaa002",
"article-title": "Potential role of oral rinses targeting the viral lipid envelope in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "O'Donnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "zqaa002",
"journal-title": "Function (Oxf)",
"key": "key20220302121528_b8-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9041126",
"article-title": "COVID-19: A recommendation to examine the effect of mouthrinses with β-cyclodextrin combined with citrox in preventing infection and progression",
"author": "Carrouel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "1126",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "key20220302121528_b9-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jopr.13209",
"article-title": "Rapid in-vitro inactivation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) using povidone-iodine oral antiseptic rinse",
"author": "Bidra",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "529",
"journal-title": "J Prosthodont",
"key": "key20220302121528_b10-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109910",
"article-title": "Hydrogen peroxide and viral infections: A literature review with research hypothesis definition in relation to the current covid-19 pandemic",
"author": "Caruso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "109910",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "key20220302121528_b11-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26514",
"article-title": "Lowering the transmission and spread of human coronavirus",
"author": "Meyers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1605",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b12-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-020-01563-9",
"article-title": "Efficacy of commercial mouth-rinses on SARS-CoV-2 viral load in saliva: Randomized control trial in Singapore",
"author": "Seneviratne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "Infection",
"key": "key20220302121528_b13-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-021-03102-3",
"article-title": "Essentials in saline pharmacology for nasal or respiratory hygiene in times of COVID-19",
"author": "Huijghebaert",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1275",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b14-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms9010136",
"article-title": "New clinical applications of electrolyzed water: A review",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "136",
"journal-title": "Microorganisms",
"key": "key20220302121528_b15-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.029",
"article-title": "Acidic electrolyzed water potently inactivates SARS-CoV-2 depending on the amount of free available chlorine contacting with the virus",
"author": "Takeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "key20220302121528_b16-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "530",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AEM.00653-17",
"article-title": "Efficacy of neutral electrolyzed water for inactivation of human norovirus",
"author": "Moorman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e00653",
"journal-title": "Appl Environ Microbiol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b17-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-013-1840-2",
"article-title": "Virucidal effect of acidic electrolyzed water and neutral electrolyzed water on avian influenza viruses",
"author": "Tamaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "405",
"journal-title": "Arch Virol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b18-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2021.10347",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of a COVID-19 treatment with nebulized and/or intravenous neutral electrolyzed saline combined with usual medical care vs. usual medical care alone: A randomized, open-label, controlled trial",
"author": "Delgado-Enciso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "915",
"journal-title": "Exp Ther Med",
"key": "key20220302121528_b19-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045",
"article-title": "Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR",
"author": "Corman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "2000045",
"journal-title": "Eurosurveillance",
"key": "key20220302121528_b20-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "HyLown Consulting",
"key": "key20220302121528_b21-BR-16-2-01494"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes",
"author": "Sungnak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "key20220302121528_b22-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001737",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1177",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key20220302121528_b23-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30196-1",
"article-title": "Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: An observational cohort study",
"author": "To",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "key20220302121528_b24-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x",
"article-title": "High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Int J Oral Sci",
"key": "key20220302121528_b25-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0166-0934(99)00165-2",
"article-title": "Disinfection potential of electrolyzed solutions containing sodium chloride at low concentrations",
"author": "Morita",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "163",
"journal-title": "J Virol Methods",
"key": "key20220302121528_b26-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-021-06644-5",
"article-title": "A sprayable Acid-Oxidizing solution containing hypochlorous acid (AOS2020) efficiently and safely inactivates SARS-Cov-2: A new potential solution for upper respiratory tract hygiene",
"author": "Giarratana",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3099",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b27-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aucc.2020.10.006",
"article-title": "Protection procedures and preventions against the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 in healthcare settings for nursing personnel: Lessons from Taiwan",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "182",
"journal-title": "Aust Crit Care",
"key": "key20220302121528_b28-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6",
"article-title": "Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission",
"author": "Peckham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "6317",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "key20220302121528_b29-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26424",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical characteristics, risk factors, and outcomes",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1449",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b30-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients",
"author": "Ejaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1833",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "key20220302121528_b31-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.22703",
"article-title": "Interim analysis of an open-label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non-hospitalized patients with coronavirus diesease 2019",
"author": "Kimura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1325",
"journal-title": "Int Forum Allergy Rhinol",
"key": "key20220302121528_b32-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "key20220302121528_b33-BR-16-2-01494"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30113-4",
"article-title": "Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "411",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "key20220302121528_b34-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x",
"article-title": "Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019",
"author": "Wölfel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "key20220302121528_b35-BR-16-2-01494",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/br.2021.1494"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal rinses with neutral electrolyzed water prevents COVID‑19 in front‑line health professionals: A randomized, open‑label, controlled trial in a general hospital in Mexico City",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "16"
}