Efficacy of antiseptic mouthrinses against SARS-CoV-2: A prospective randomized placebo-controlled pilot study
et al., American Journal of Otolaryngology, doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549, Jul 2022
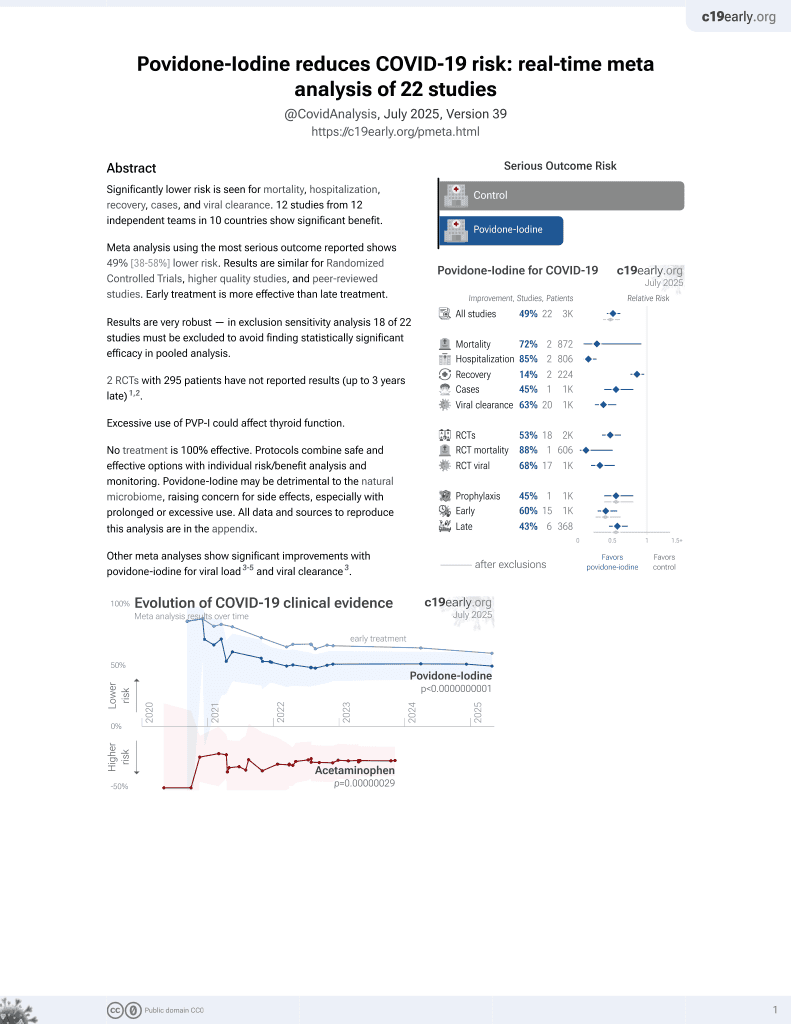
PVP-I for COVID-19
15th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.000000000016 from 22 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
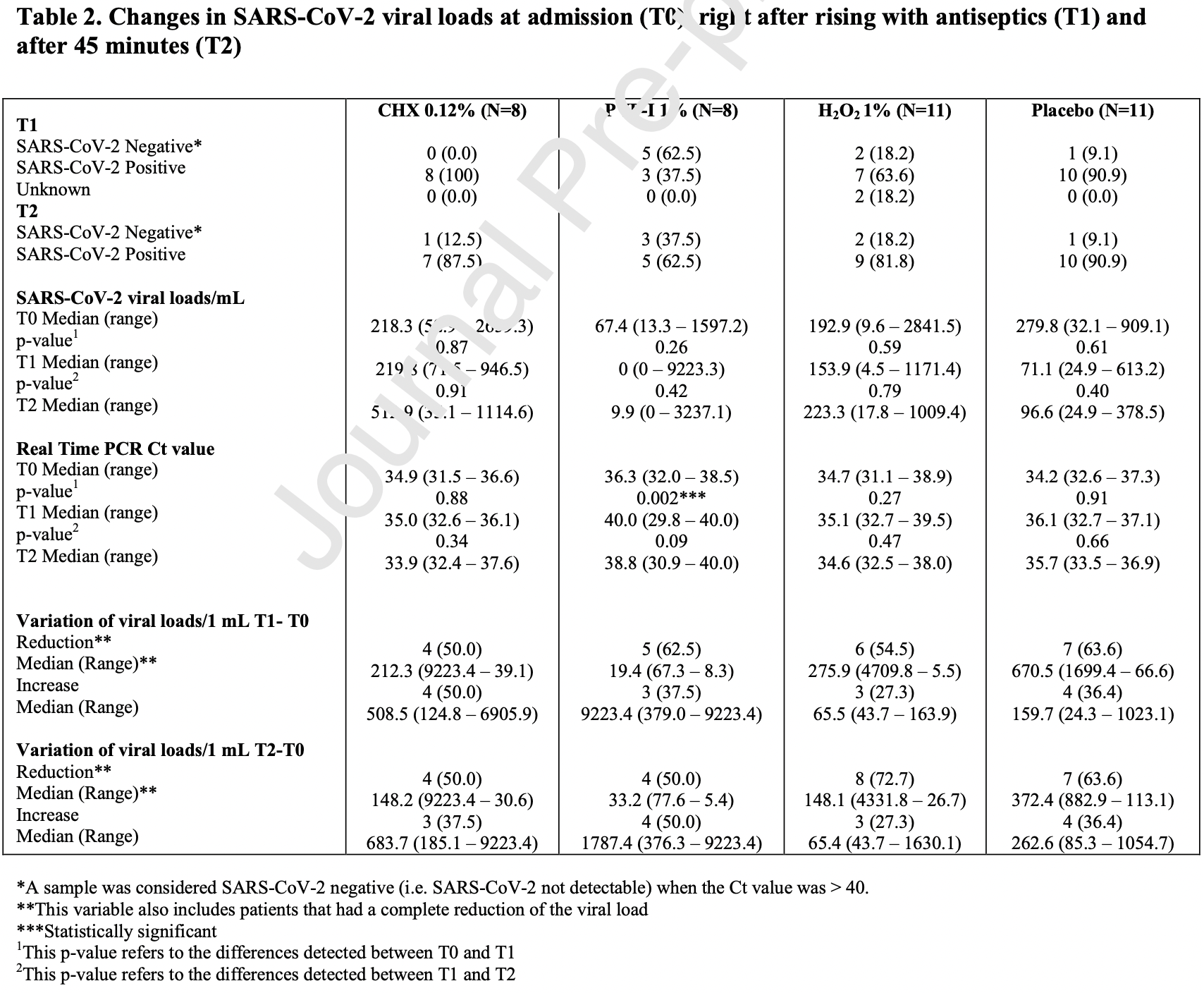
Mouthrinse RCT in Italy comparing short-term viral load after a single 60 second treatment with povidone-iodine, hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, and saline. The greatest efficacy was seen with povidone-iodine, especially for patients with low viral load at baseline.
Analysis of short-term changes in viral load using PCR may not detect
effective treatments because PCR is unable to differentiate between intact
infectious virus and non-infectious or destroyed virus particles. For example
Tarragó-Gil, Alemany perform RCTs with cetylpyridinium chloride
(CPC) mouthwash that show no difference in PCR viral load, however there was
significantly increased detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein,
indicating viral lysis. CPC inactivates SARS-CoV-2 by degrading its membrane,
exposing the nucleocapsid of the virus. To better estimate changes in viral
load and infectivity, methods like viral culture that can
differentiate intact vs. degraded virus are preferred.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
study only provides short-term viral load results.
Study covers chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, and povidone-iodine.
|
relative viral load, 57.5% better, RR 0.43, treatment 8, control 11, T2, relative fraction of median baseline viral load remaining.
|
|
relative viral load, 100% better, RR < 0.001, treatment 8, control 11, T1, relative fraction of median baseline viral load remaining.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 31.2% lower, RR 0.69, p = 0.26, treatment 5 of 8 (62.5%), control 10 of 11 (90.9%), NNT 3.5, T2.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 58.7% lower, RR 0.41, p = 0.04, treatment 3 of 8 (37.5%), control 10 of 11 (90.9%), NNT 1.9, T1.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Fantozzi et al., 28 Jul 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Italy, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period December 2020 - May 2021, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo.
Contact: umberto.romeo@uniroma1.it.
Efficacy of antiseptic mouthrinses against SARS-CoV-2: A prospective randomized placebo-controlled pilot study
American Journal of Otolaryngology, doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
When all antiseptic mouthrinses were considered, PVP-I 1% was found to be more effective in reducing the Ct Values at T1 compared to CHX 0.12% (p=0.001), the H 2 O 2 1% (p=0.027) and the placebo (p=0.001). In addition, PVP-I 1% was found to be more effective in terms of viral load reduction both at T1 (p=0.03) and at T2 (p=0.024) when compared to the placebo. No other statistically significant differences were found amongst the other rinses (Table 3 ). Interestingly, when all the negative patients were considered (at T1 and T2), the median SARS-CoV-2 viral load was 21.5 copies/mL (IQR: 4.9 -294.5), and the median Ct value was 37.8 (IQR: 34.1 -39.8).
J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
Discussion This single-blinded randomized controlled pilot study reported on the efficacy of three oral antiseptics on the reduction of oral SARS-CoV-2 viral load in the oral and oropharyngeal region. PVP-I 1% had the highest efficacy with five patients (62.5%) at T1 and three patients (37.5%) at T2 having undetectable SARS-CoV-2 viral load after the rinse, with an overall median viral load reduction of 19.4 (IQR: 67.3 -8.2) viral loads/mL at T1 (p=0.26), and 33.2 (IQR: 77.6 -5.4) viral loads/mL at T2 (p=0.42). The median Ct value in the PVP-I 1% group at T0 was 36.3 (IQR: 32.0 -38.5), followed by 40.0 (IQR: 29.8 -40.0) at T1 (p=0.002), and 38.8 (IQR: 30.9 -40.0) at T2 (p=0.09). H 2 O 2 1% showed the second highest efficacy, with six patients (54.5%) at T1, and eight patients (72.7%) at T2..
References
Bidra, Pelletier, Westover, Frank, Brown et al., Comparison of In Vitro Inactivation of SARS CoV-2 with Hydrogen Peroxide and Povidone-Iodine Oral Antiseptic Rinses, J Prosthodont, doi:10.1111/jopr.13220
Carrouel, Gonçalves, Conte, Antiviral Activity of Reagents in Mouth Rinses against SARS-CoV
Chaudhary, Melkonyan, Meethil, Estimating salivary carriage of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in nonsymptomatic people and efficacy of mouthrinse in reducing viral load: A randomized controlled trial, J Am Dent Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.adaj.2021.05.021
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045
Elmahgoub, Coll, Could certain mouthwashes reduce transmissibility of COVID-19?, Evid Based Dent, doi:10.1038/s41432-021-0172-4
Elzein, Sater, Fakhreddine, In vivo evaluation of the virucidal efficacy of chlorhexidine and povidone-iodine mouthwashes against salivary SARS-CoV-2. A randomized-controlled clinical trial, J Evid Based Dent Pract, doi:10.1016/j.jebdp.2021
Escandón, Rasmussen, Bogoch, COVID-19 false dichotomies and a comprehensive review of the evidence regarding public health, COVID-19 symptomatology, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, mask wearing, and reinfection, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06357-4
Ferrer, Barrueco, Martinez-Beneyto, Clinical evaluation of antiseptic mouth rinses to reduce salivary load of SARS-CoV-2, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-03461-y
Goralnick, Kaufmann, Gawande, Mass-Vaccination Sites -An Essential Innovation to Curb the Covid-19 Pandemic, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMp2102535
Gottsauner, Michaelides, Schmidt, A prospective clinical pilot study on the effects of a hydrogen peroxide mouthrinse on the intraoral viral load of SARS-CoV-2, Clin Oral Investig, doi:10.1007/s00784-020-03549-1
Huang, Huang, Use of chlorhexidine to eradicate oropharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26954
Huang, Pérez, Kato, SARS-CoV-2 infection of the oral cavity and saliva, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01296-8
Komine, Yamaguchi, Okamoto, Yamamoto, Virucidal activity of oral care products against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, J Oral Maxillofac Surgery, doi:10.1016/j.ajoms.2021
Kowalski, Sanabria, Ridge, COVID-19 pandemic: Effects and evidence-based recommendations for otolaryngology and head and neck surgery practice, Head Neck, doi:10.1002/hed.26164
Lamas, Dios, Rodríguez, Is povidone iodine mouthwash effective against SARS-CoV-2? First in vivo tests, Oral Dis, doi:10.1111/odi.13526
Leung, Transmissibility and transmission of respiratory viruses, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00535-6
Li, Campbell, Kulkarni, The temporal association of introducing and lifting non-pharmaceutical interventions with the time-varying reproduction number (<em>R</em>) of SARS-CoV-2: a modelling study across 131 countries, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30785-4
Meister, Brüggemann, Todt, Virucidal Efficacy of Different Oral Rinses Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa471
Meselson, Droplets and Aerosols in the Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2009324
Muñoz-Basagoiti, Perez-Zsolt, León, CoV-J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f Journal Pre-proof
Palla, Callahan, What is the rate of COVID-19 infection in a population seeking oral health care?, J Am Dent Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.adaj.2021.02.009
Seneviratne, Balan, Ko, Efficacy of commercial mouth-rinses on SARS-CoV-2 viral load in saliva: randomized control trial in Singapore, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-020-01563-9
To, Tsang, Yip, Consistent Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Saliva. Clin Infect J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f Journal Pre-proof Dis an Off, Publ Infect Dis Soc Am, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa149
Xu, Li, Gan, Du, Yao, Salivary Glands: Potential Reservoirs for COVID-19 Asymptomatic Infection, J Dent Res, doi:10.1177/0022034520918518
Xu, Zhong, Deng, High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa, Int J Oral Sci, doi:10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549",
"ISSN": [
"0196-0709"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549",
"alternative-id": [
"S0196070922001764"
],
"article-number": "103549",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Efficacy of antiseptic mouthrinses against SARS-CoV-2: A prospective randomized placebo-controlled pilot study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "American Journal of Otolaryngology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fantozzi",
"given": "Paolo Junior",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pampena",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pierangeli",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliveto",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sorrentino",
"given": "Leonardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Di Vanna",
"given": "Domenico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pampena",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lazzaro",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gentilini",
"given": "Elio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mastroianni",
"given": "Claudio Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D'Ettorre",
"given": "Gabriella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Polimeni",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Romeo",
"given": "Umberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Villa",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "American Journal of Otolaryngology",
"container-title-short": "American Journal of Otolaryngology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-28T01:49:22Z",
"timestamp": 1658972962000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-28T01:49:54Z",
"timestamp": 1658972994000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-28T02:11:58Z",
"timestamp": 1658974318624
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656633600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0196070922001764?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0196070922001764?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "103549",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2009324",
"article-title": "Droplets and aerosols in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Meselson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2063",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0010",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00535-6",
"article-title": "Transmissibility and transmission of respiratory viruses",
"author": "Leung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "528",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0015",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06357-4",
"article-title": "COVID-19 false dichotomies and a comprehensive review of the evidence regarding public health, COVID-19 symptomatology, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, mask wearing, and reinfection",
"author": "Escandón",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "710",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0020",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30785-4",
"article-title": "The temporal association of introducing and lifting non-pharmaceutical interventions with the time-varying reproduction number (R) of SARS-CoV-2: a modelling study across 131 countries",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "193",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0025",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2102535",
"article-title": "Mass-vaccination sites — an essential innovation to curb the Covid-19 pandemic",
"author": "Goralnick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0030",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hed.26164",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic: effects and evidence-based recommendations for otolaryngology and head and neck surgery practice",
"author": "Kowalski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1259",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Head Neck",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0035",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.adaj.2021.02.009",
"article-title": "What is the rate of COVID-19 infection in a population seeking oral health care?",
"author": "Palla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "448",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Am Dent Assoc",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0040",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0022034520918518",
"article-title": "Salivary glands: potential reservoirs for COVID-19 asymptomatic infection",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "989",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0045",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01296-8",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection of the oral cavity and saliva",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "892",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0050",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x",
"article-title": "High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Oral Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0055",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa149",
"article-title": "Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva",
"author": "To",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "841",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0060",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa471",
"article-title": "Virucidal efficacy of different oral rinses against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2",
"author": "Meister",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1289",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0065",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0022034520967933",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of reagents in mouth rinses against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Carrouel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "124",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0070",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41432-021-0172-4",
"article-title": "Could certain mouthwashes reduce transmissibility of COVID-19?",
"author": "Elmahgoub",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "82",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Dent",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0075",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.adaj.2021.05.021",
"article-title": "Estimating salivary carriage of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in nonsymptomatic people and efficacy of mouthrinse in reducing viral load: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Chaudhary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "903",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Am Dent Assoc",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0080",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"first-page": "1",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0090",
"series-title": "Clinical Management of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) When COVID-19 Disease Is Suspected. Interim Guidance, 13 March, 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0095",
"series-title": "COVID-19 Specimen Collection Guidelines",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045",
"article-title": "Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR",
"author": "Corman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Eurosurveillance",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0100",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jopr.13220",
"article-title": "Comparison of in vitro inactivation of SARS CoV-2 with hydrogen peroxide and povidone-iodine oral antiseptic rinses",
"author": "Bidra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "599",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Prosthodont",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0105",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajoms.2021.02.002",
"article-title": "Virucidal activity of oral care products against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Komine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0110",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/00220345211029269",
"article-title": "Mouthwashes with CPC reduce the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 variants in vitro",
"author": "Muñoz-Basagoiti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1265",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0115",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Is povidone iodine mouthwash effective against SARS-CoV-2? First in vivo tests",
"author": "Martínez Lamas",
"journal-title": "Oral Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0120",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00784-020-03549-1",
"article-title": "A prospective clinical pilot study on the effects of a hydrogen peroxide mouthrinse on the intraoral viral load of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Gottsauner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3707",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Clin Oral Investig",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0125",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jebdp.2021.101584",
"article-title": "In vivo evaluation of the virucidal efficacy of chlorhexidine and povidone-iodine mouthwashes against salivary SARS-CoV-2. A randomized-controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Elzein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Evid Based Dent Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0130",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26954",
"article-title": "Use of chlorhexidine to eradicate oropharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4370",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0135",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-03461-y",
"article-title": "Clinical evaluation of antiseptic mouth rinses to reduce salivary load of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Ferrer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24392",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0140",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-020-01563-9",
"article-title": "Efficacy of commercial mouth-rinses on SARS-CoV-2 viral load in saliva: randomized control trial in Singapore",
"author": "Seneviratne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "305",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103549_bb0145",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0196070922001764"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Otorhinolaryngology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of antiseptic mouthrinses against SARS-CoV-2: A prospective randomized placebo-controlled pilot study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}