Effects of Ivermectin-azithromycin-cholecalciferol combined therapy on COVID-19 infected patients: A proof of concept study
et al., Biomedical Research, 31:5, Aug 2020
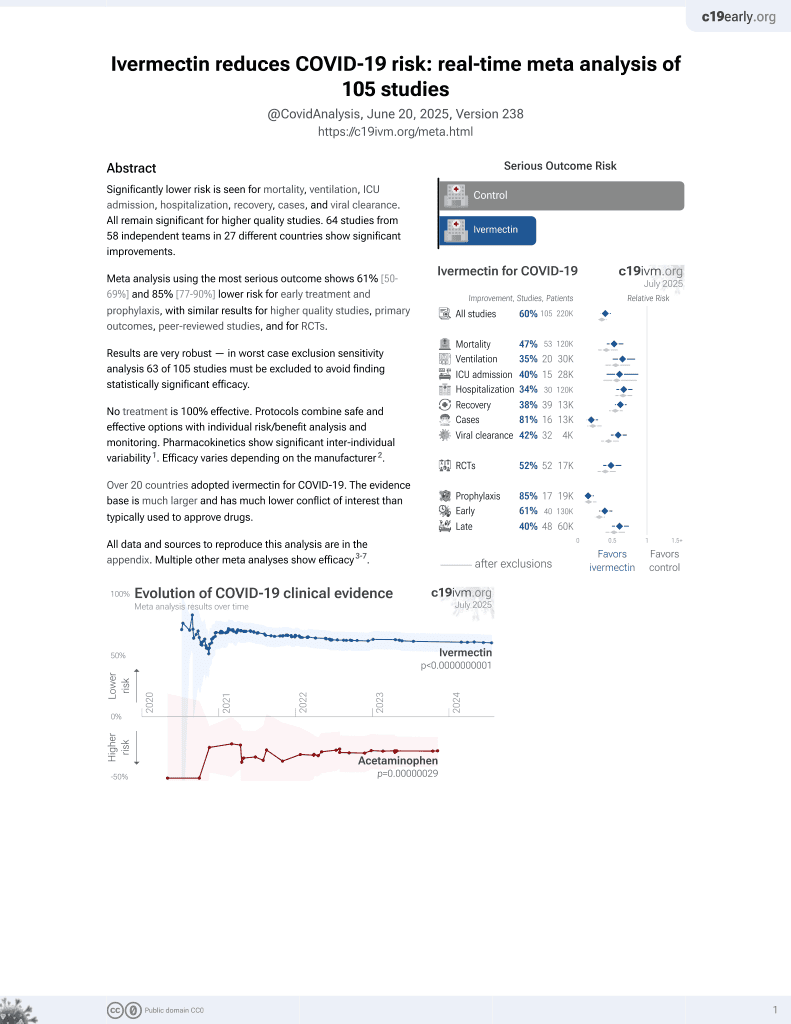
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Small study with 28 patients treated with ivermectin + AZ + cholecalciferol and 7 control patients.
All treated patients were PCR- at day 10 while all control patients remained PCR+. The mean duration of symptoms was 3 days in the treatment group and 10 days in the control group.
This is the 3rd of 106 COVID-19 controlled studies for ivermectin, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
53 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.000000087.
Study covers vitamin D and ivermectin.
|
recovery time, 70.0% lower, relative time 0.30, p < 0.001, treatment 28, control 7.
|
|
risk of viral+ at day 10, 97.2% lower, RR 0.03, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 28 (0.0%), control 7 of 7 (100.0%), NNT 1.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Espitia-Hernandez et al., 15 Aug 2020, retrospective, Mexico, peer-reviewed, mean age 45.1, 5 authors, dosage 6mg days 1-2, 8-9, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with azithromycin and cholecalciferol) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Effects of Ivermectin-azithromycin-cholecalciferol combined therapy on COVID-19 infected patients: A proof of concept study
References
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Choudhary, Sharma, Potential use of hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin and azithromycin drugs in fighting COVID-19: trends, scope and relevance, Microbes Infect
Damle, Vourvahis, Wang, Leaney, Corrigan, Clinical Pharmacology Perspectives on the Antiviral Activity of Azithromycin and Use in COVID-19, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Dasgupta, Sen, Bakshi, Dasgupta, Manna et al., Nsp7 and Spike Glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 are envisaged as Potential Targets of Vitamin D and Ivermectin
Derendorfhjijoaa, Excessive lysosomal ion-trapping of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin
Hribar, Cobbold, Church, Potential Role of Vitamin D in the Elderly to Resist COVID-19 and to Slow Progression of Parkinson's disease, Brain Sciences
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging ClinExp Res
Kirchdoerfer, Ward, Structure of the SARS-CoV NSP12 polymerase bound to NSP7 and NSP8 co-factors2019, Nat commun
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, Jones, Zheng et al., The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application, Ann Intern Med
Lee, Park, Kwon, Ham, Kim et al., Decreased lung function is associated with elevated ferritin but not iron or transferrin saturation in 42,927 healthy Korean men: A cross-sectional study, PLOS ONE
Sohrabi, Alsafi, Neill, Khan, Kerwan et al., World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19), Int J Surg
Sun, Lu, Xu, Sun, Bjjomv, Understanding of COVID-19 based on current evidence
Ulrich, Pillat, CD147 as a Target for COVID-19 Treatment: Suggested Effects of Azithromycin and Stem Cell Engagement, Stem Cell Rev Rep
Xydakis, Dehgani-Mobaraki, Holbrook, Geisthoff, Bauer et al., Smell and taste dysfunction in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Infect Dis
Zheng, Yang, Hu, Li, Wang et al., Vitamin D attenuates lung injury via stimulating epithelial repair, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits TGF-β induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition, Biochem Pharmacol
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, The Lancet