High-Dose Convalescent Plasma for Treatment of Severe COVID-19
et al., Emerging Infectious Diseases, doi:10.3201/eid2803.212299, Mar 2022
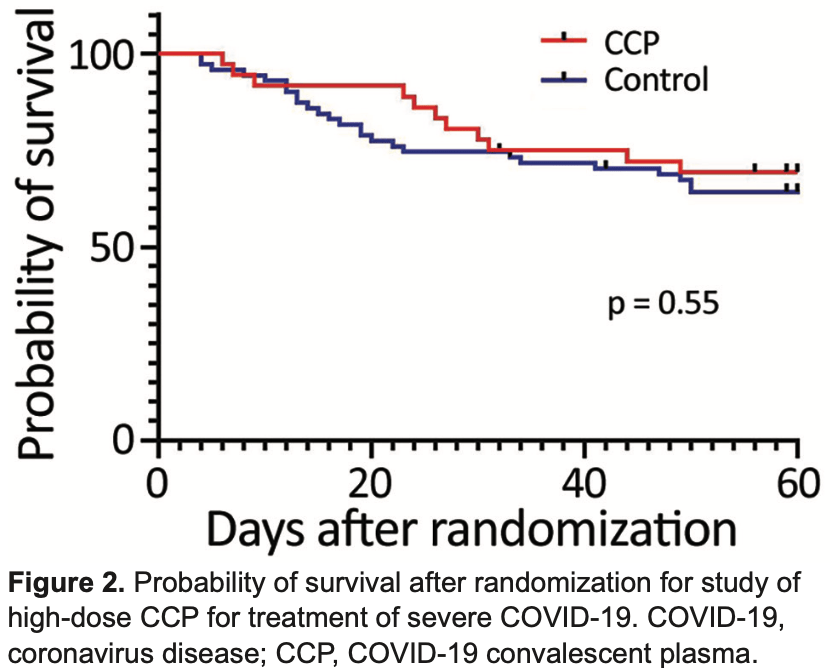
RCT 110 hospitalized patients in Brazil, showing no significant difference in outcomes with high-dose convalescent plasma.
|
risk of death, 13.2% lower, RR 0.87, p = 0.67, treatment 11 of 36 (30.6%), control 25 of 71 (35.2%), NNT 21, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 12.3% lower, RR 0.88, p = 0.81, treatment 8 of 36 (22.2%), control 18 of 71 (25.4%), NNT 32, day 30.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
De Santis et al., 31 Mar 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 23 authors, average treatment delay 9.0 days.
High-Dose Convalescent Plasma for Treatment of Severe COVID-19
Emerging Infectious Diseases, doi:10.3201/eid2803.212299
C linical signs and symptoms of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) are pleomorphic, varying from none (asymptomatic) to life-threatening. Typical signs/ symptoms are fever, dry cough, dyspnea, fatigue, myalgia, anosmia, and ageusia (1). Radiography or computed tomography of the chest usually reveals bilateral pulmonary ground-glass opacifi cations, mainly in posterior and peripheral areas of the lungs (2). The most common laboratory test alterations are lymphopenia and elevated serum concentrations of infl ammatory biomarkers and D-dimers (3). Risk factors for unfavorable outcomes are older age, concurrent conditions, and perhaps but of lesser importance, blood type A (4,5). Thus far, there is no consensual agreement about specifi c therapy for this disease, despite several attempts to develop one (3,6). More recently, antiviral agents such as MK-4482/EIDD-2801 and PF-07321332 seem to be promising (7,8). In the past, passive antibody transfer by plasma or serum transfusion has been used clinically to treat other infectious diseases, including Ebola, infl uenza A, severe acute respiratory syndrome, and Middle East respiratory syndrome, as well as . The presence of antiviral antibodies, in patient serum or in COVID-19 convalescent plasma (CCP), has been associated with more favorable clinical outcomes (14). Thus, CCP seems to be an attractive therapy because it is a potential source of neutralizing antibodies (15, 16) . The fi rst case series reported from China suggested favorable outcomes for 5 patients receiving undergoing mechanical ventilation who received CCP on days 10-22 after hospital admission (17). Also in China, 10 critically ill patients received 200 mL of CCP with a neutralizing antibody titer of >640, which resulted in undetectable viral load and clinical improvement for 7 of the 10 patients (18). In a nonrandomized
About the Author Dr. De Santis is a clinical hematologist at the University of São Paulo. His research interests include blood transfusion and cellular therapy, such as laboratory support for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
References
Abani, Abbas, Abbas, Abbas, Abbasi et al., Group. Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7
Address For ; Gil, Santis, Rua Tenente Catão Roxo
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Chatterjee, Bhatnagar et al., Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate COVID-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial), BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3939
Arabi, Hajeer, Luke, Raviprakash, Balkhy et al., Feasibility of using convalescent plasma immunotherapy for MERS-CoV infection, Saudi Arabia, Emerg Infect Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2209.151164
Avendaño-Solá, Ramos-Martínez, Muñez-Rubio, Ruiz-Antorán, De Molina et al., 19 Study Group. A multicenter randomized open-label clinical trial for convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI152740
Bloch, Shoham, Casadevall, Sachais, Shaz et al., Deployment of convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI138745
Bégin, Callum, Jamula, Cook, Heddle et al., CONCOR-1 Study Group. Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an openlabel, randomized controlled trial, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01488-2
Casadevall, Scharff, Serum therapy revisited: animal models of infection and development of passive antibody therapy, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.38.8.1695
Chung, Bernheim, Mei, Zhang, Huang et al., CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), Radiology, doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200230
Cox, Wolf, Plemper, Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets, Nat Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2
Duan, Liu, Li, Zhang, Yu et al., Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2004168117
Garibaldi, Oliveira, Fonseca, Auxiliadora-Martins, Miranda et al., Histo-blood group A is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, Transfus Med, doi:10.1111/tme.12796
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19
Hung, To, Lee, Lee, Yan, Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciq106
Izda, Jeffries, Sawalha, COVID-19: a review of therapeutic strategies and vaccine candidates, Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108634
Joyner, Carter, Senefeld, Klassen, Mills et al., Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031893
Körper, Weiss, Zickler, Wiesmann, Zacharowski et al., Trial Group. Results of the CAPSID randomized trial for high-dose convalescent plasma in patients with severe COVID-19, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI152264
Lee, Adhikari, Kwon, Teo, Siemieniuk et al., Anti-Ebola therapy for patients with Ebola virus disease: a systematic review, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-019-3980-9
Li, Zhang, Hu, Tong, Zheng et al., Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.10044
Libster, Marc, Wappner, Coviello, Bianchi et al., Fundación INFANT-COVID-19 Group. Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe COVID-19 in older adults, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2033700
O'donnell, Grinsztejn, Cummings, Justman, Lamb et al., A randomized double-blind controlled trial of convalescent plasma in adults with severe COVID-19, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI150646
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, Aschenbrenner, Avery et al., An oral SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abl4784
Piechotta, Iannizzi, Chai, Valk, Kimber et al., Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub4/full
Roback, Guarner, Convalescent plasma to treat COVID-19: possibilities and challenges, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4940
Rosenthal, Cao, Gundrum, Sianis, Safo, Risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality in a us national sample of patients with COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.29058
Roubinian, TACO and TRALI: biology, risk factors, and prevention strategies, Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program), doi:10.1182/asheducation-2018.1.585
Sekine, Arns, Fabro, Cipolatt, Machado et al., Study Group. Convalescent plasma for COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: an openlabel, randomised clinical trial, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.01471-2021
Shen, Wang, Zhao, Yang, Li et al., Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4783
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, Beruto, Vallone et al., Study Group. A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in COVID-19 severe pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031304
Stadlbauer, Amanat, Chromikova, Jiang, Strohmeier et al., SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans: a detailed protocol for a serological assay, antigen production, and test setup, Curr Protoc Microbiol, doi:10.1002/cpmc.100
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
Wendel, Kutner, Machado, Fontão-Wendel, Bub et al., Screening for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in convalescent plasma in Brazil: preliminary lessons from a voluntary convalescent donor program, Transfusion, doi:10.1111/trf.16065
Yokoyama, Wendel, Bonet-Bub, Fachini, Dametto et al., COVID-19 convalescent plasma cohort study: evaluation of the association between both donor and recipient neutralizing antibody titers and patient outcomes, Transfusion, doi:10.1111/trf.16573
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2803.212299",
"ISSN": [
"1080-6040",
"1080-6059"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2803.212299",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Santis",
"given": "Gil C.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliveira",
"given": "Luciana Correa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garibaldi",
"given": "Pedro M.M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Almado",
"given": "Carlos E.L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Croda",
"given": "Julio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arcanjo",
"given": "Ghislaine G.A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliveira",
"given": "Érika A.F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tonacio",
"given": "Adriana C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Langhi",
"given": "Dante M.",
"sequence": "additional",
"suffix": "Jr."
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bordin",
"given": "José O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilio",
"given": "Renato N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palma",
"given": "Leonardo C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Elaine V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haddad",
"given": "Simone K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prado",
"given": "Benedito P.A.",
"sequence": "additional",
"suffix": "Jr."
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pontelli",
"given": "Marjorie Cornejo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomes",
"given": "Rogério",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miranda",
"given": "Carlos H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martins",
"given": "Maria Auxiliadora",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Covas",
"given": "Dimas T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arruda",
"given": "Eurico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fonseca",
"given": "Benedito A.L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calado",
"given": "Rodrigo T.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Emerging Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-31T20:17:38Z",
"timestamp": 1643660258000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-23T17:05:39Z",
"timestamp": 1645635939000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-09T09:32:21Z",
"timestamp": 1673256741890
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 10,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
}
},
"member": "1822",
"original-title": [],
"page": "548-555",
"prefix": "10.3201",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108634",
"article-title": "COVID-19: A review of therapeutic strategies and vaccine candidates.",
"author": "Izda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108634",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R1",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2020200230",
"article-title": "CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV).",
"author": "Chung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "202",
"journal-title": "Radiology",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R2",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial.",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R3",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tme.12796",
"article-title": "Histo-blood group A is a risk factor for severe COVID-19.",
"author": "Garibaldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "tme.12796",
"journal-title": "Transfus Med",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study.",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R5",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R6",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2",
"article-title": "Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets.",
"author": "Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R7",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R8",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-019-3980-9",
"article-title": "Anti-Ebola therapy for patients with Ebola virus disease: a systematic review.",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "376",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R9",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.38.8.1695",
"article-title": "Serum therapy revisited: animal models of infection and development of passive antibody therapy.",
"author": "Casadevall",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1695",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R10",
"volume": "38",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciq106",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection.",
"author": "Hung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "447",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R11",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2209.151164",
"article-title": "Feasibility of using convalescent plasma immunotherapy for MERS-CoV infection, Saudi Arabia.",
"author": "Arabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1554",
"journal-title": "Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R12",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4940",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma to treat COVID-19: possibilities and challenges.",
"author": "Roback",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1561",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R13",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.16573",
"article-title": "COVID-19 convalescent plasma cohort study: Evaluation of the association between both donor and recipient neutralizing antibody titers and patient outcomes.",
"author": "Yokoyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2295",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R14",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI138745",
"article-title": "Deployment of convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Bloch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2757",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R15",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpmc.100",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans: a detailed protocol for a serological assay, antigen production, and test setup.",
"author": "Stadlbauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e100",
"journal-title": "Curr Protoc Microbiol",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R16",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4783",
"article-title": "Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma.",
"author": "Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1582",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R17",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2004168117",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Duan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9490",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R18",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031893",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from COVID-19.",
"author": "Joyner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1015",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R19",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"article-title": "Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R20",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"article-title": "PlasmAr Study Group. A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in COVID-19 severe pneumonia.",
"author": "Simonovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R21",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R22",
"unstructured": "Piechotta V, Iannizzi C, Chai KL, Valk SJ, Kimber C, Dorando E, Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID‐19: a living systematic review [cited 2021 Dec 3]. https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub4/full"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/asheducation-2018.1.585",
"article-title": "TACO and TRALI: biology, risk factors, and prevention strategies.",
"author": "Roubinian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "585",
"journal-title": "Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program)",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R23",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.16065",
"article-title": "Screening for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in convalescent plasma in Brazil: Preliminary lessons from a voluntary convalescent donor program.",
"author": "Wendel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2938",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R24",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.29058",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality in a us national sample of patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Rosenthal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2029058",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R25",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI152740",
"article-title": "A multicenter randomized open-label clinical trial for convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia.",
"author": "Avendaño-Solá",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e152740",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R26",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI150646",
"article-title": "A randomized double-blind controlled trial of convalescent plasma in adults with severe COVID-19.",
"author": "O’Donnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "150646",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R27",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI152264",
"article-title": "Results of the CAPSID randomized trial for high-dose convalescent plasma in patients with severe COVID-19.",
"author": "Körper",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e152264",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R28",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01471-2021",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma for COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: an open-label, randomised clinical trial.",
"author": "Sekine",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2101471",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial).",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m3939",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R30",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial.",
"author": "Abani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2049",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R31",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01488-2",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an open-label, randomized controlled trial.",
"author": "Bégin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2012",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R32",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"article-title": "Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe COVID-19 in older adults.",
"author": "Libster",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "610",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.3201/eid2803.212299-202202172242-R33",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/28/3/21-2299_article.htm"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Epidemiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "High-Dose Convalescent Plasma for Treatment of Severe COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "28"
}