Convalescent plasma for COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: an open-label, randomised clinical trial
et al., European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.01471-2021, PLACOVID, NCT04547660, Jul 2021
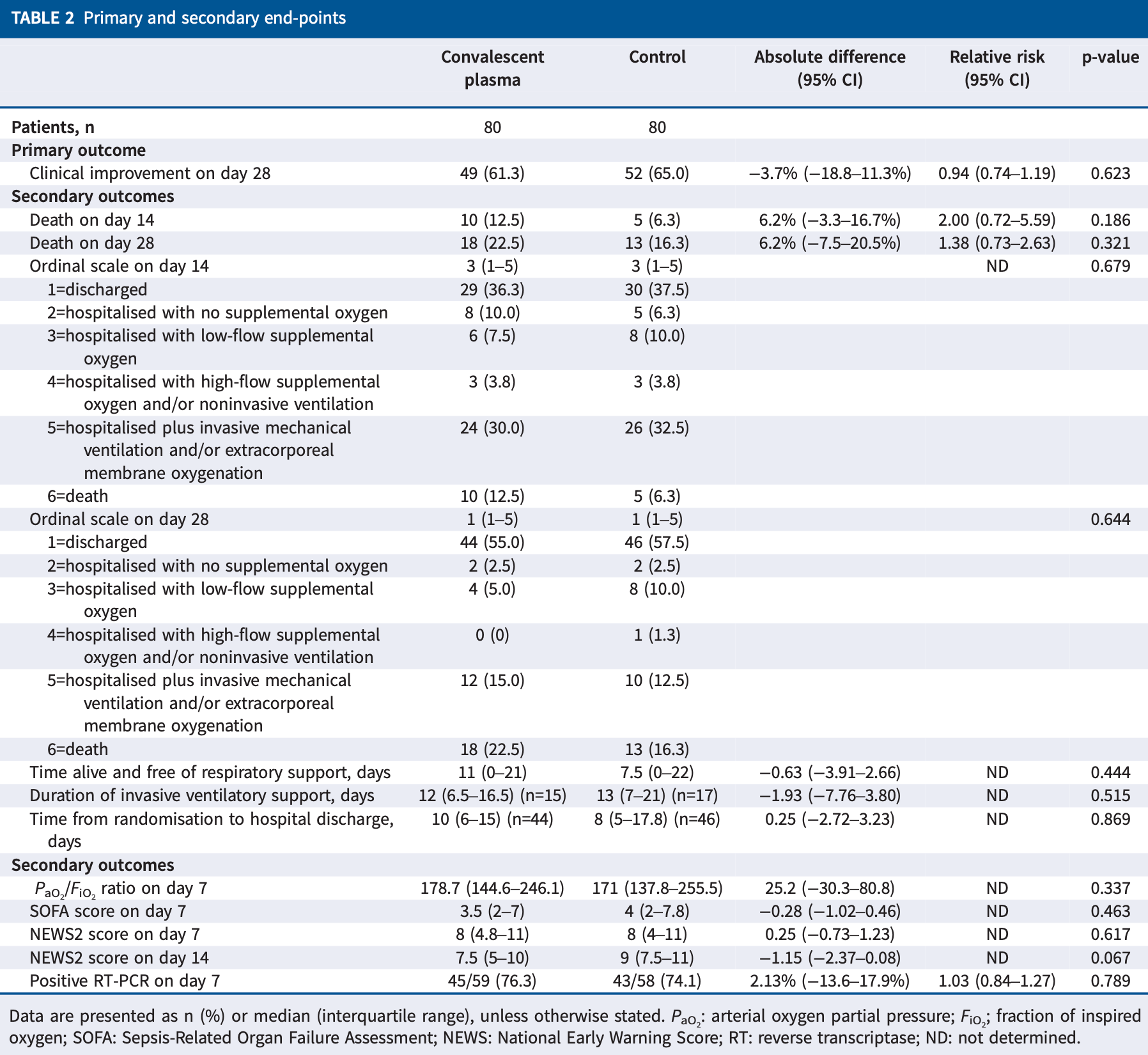
RCT 160 hospitalized patients in Brazil, showing no significant difference in outcomes with convalescent plasma.
|
risk of death, 38.5% higher, RR 1.38, p = 0.42, treatment 18 of 80 (22.5%), control 13 of 80 (16.2%), day 28.
|
|
risk of death, 100% higher, RR 2.00, p = 0.28, treatment 10 of 80 (12.5%), control 5 of 80 (6.2%), day 14.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 10.7% higher, RR 1.11, p = 0.74, treatment 31 of 80 (38.8%), control 28 of 80 (35.0%), day 28.
|
|
hospitalization time, 66.7% higher, relative time 1.67, p = 0.87, treatment 80, control 80.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sekine et al., 8 Jul 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 28 authors, study period 15 July, 2020 - 10 December, 2020, average treatment delay 10.0 days, trial NCT04547660 (history) (PLACOVID).
Contact: azavascki@hcpa.edu.br.
Convalescent plasma for COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: an open-label, randomised clinical trial
European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.01471-2021
In this open-label, randomised clinical trial, two infusions of convalescent plasma therapy plus standard of care compared to standard of care did not result in higher proportion of clinical improvement on day 28 in patients with severe COVID-19 https://bit.ly/2TXuB6S
References
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate COVID-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial), BMJ
Casadevall, Pirofski, The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19, J Clin Invest
Gottlieb, Nirula, Chen, Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Horby, Estcourt, Peto, Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Janiaud, Axfors, Schmitt, Association of convalescent plasma treatment with clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA
Joyner, Bruno, Klassen, Safety update: COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 20,000 hospitalized patients, Mayo Clin Proc
Joyner, Carter, Senefeld, Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Li, Zhang, Hu, Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Libster, Marc, Wappner, Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults, N Engl J Med
Lundgren, Grund, Barkauskas, A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Rosner, Fundamentals of Biostatistics
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Wendel, Kutner, Machado, Screening for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in convalescent plasma in Brazil: preliminary lessons from a voluntary convalescent donor program, Transfusion
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01471-2021",
"ISSN": [
"0903-1936",
"1399-3003"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01471-2021",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The effects of convalescent plasma (CP) therapy in hospitalised patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) remain uncertain. This study investigates the effect of CP on clinical improvement in these patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This is an investigator-initiated, randomised, parallel arm, open-label, superiority clinical trial. Patients were randomly (1:1) assigned to two infusions of CP plus standard of care (SOC) or SOC alone. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients with clinical improvement 28 days after enrolment.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 160 (80 in each arm) patients (66.3% critically ill, 33.7% severely ill) completed the trial. The median (interquartile range (IQR)) age was 60.5 (48–68) years; 58.1% were male and the median (IQR) time from symptom onset to randomisation was 10 (8–12) days. Neutralising antibody titres >1:80 were present in 133 (83.1%) patients at baseline. The proportion of patients with clinical improvement on day 28 was 61.3% in the CP+SOC group and 65.0% in the SOC group (difference −3.7%, 95% CI −18.8–11.3%). The results were similar in the severe and critically ill subgroups. There was no significant difference between CP+SOC and SOC groups in pre-specified secondary outcomes, including 28-day mortality, days alive and free of respiratory support and duration of invasive ventilatory support. Inflammatory and other laboratory marker values on days 3, 7 and 14 were similar between groups.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>CP+SOC did not result in a higher proportion of clinical improvement on day 28 in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 compared to SOC alone.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1183/13993003.01471-2021"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7140-4980",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sekine",
"given": "Leo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arns",
"given": "Beatriz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fabro",
"given": "Bruna R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cipolatt",
"given": "Murillo M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6974-5092",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Machado",
"given": "Rafael R.G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durigon",
"given": "Edison L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parolo",
"given": "Edino",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pellegrini",
"given": "José Augusto S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Viana",
"given": "Marina V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schwarz",
"given": "Patrícia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lisboa",
"given": "Thiago C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3386-713X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dora",
"given": "José Miguel S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Portich",
"given": "Julia P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paz",
"given": "Alessandra A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Silla",
"given": "Lucia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balsan",
"given": "Almeri M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schirmer",
"given": "Felipe da-Silva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Franz",
"given": "Juliana P.M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "da-Silveira",
"given": "Luciana M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Breunig",
"given": "Raquel C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petersen",
"given": "Viviana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sosnoski",
"given": "Monalisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mesquita",
"given": "Nanci F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Volpato",
"given": "Fabiana Caroline Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sganzerla",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Falavigna",
"given": "Maicon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosa",
"given": "Regis G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5331-4837",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zavascki",
"given": "Alexandre P.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Respiratory Journal",
"container-title-short": "Eur Respir J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"ersjournals.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-08T17:05:27Z",
"timestamp": 1625763927000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-10T09:30:23Z",
"timestamp": 1644485423000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001807",
"award": [
"2016/20045-7",
"2020/06409-1"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo"
},
{
"name": "Instituto Cultural Floresta"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004263",
"award": [
"16/2551-0000242-8"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-14T10:50:02Z",
"timestamp": 1673693402972
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 32,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625702400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1183/13993003.01471-2021",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "81",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2101471",
"prefix": "10.1183",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "European Respiratory Society (ERS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI138003",
"article-title": "The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19",
"author": "Casadevall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1545",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.3",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031893",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.028",
"article-title": "Safety update: COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 20,000 hospitalized patients",
"author": "Joyner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1888",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.5",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00897-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.16065",
"article-title": "Screening for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in convalescent plasma in Brazil: preliminary lessons from a voluntary convalescent donor program",
"author": "Wendel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2938",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.10",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.11",
"unstructured": "Rosner B . Fundamentals of Biostatistics. 7th edn. Boston, Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning, 2011."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.2747",
"article-title": "Association of convalescent plasma treatment with clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Janiaud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1185",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.12",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"article-title": "Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "632",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.14",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033130",
"article-title": "A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Lundgren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022021001300718000_59.2.2101471.15",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 15,
"references-count": 15,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://erj.ersjournals.com/lookup/doi/10.1183/13993003.01471-2021"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Convalescent plasma for COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: an open-label, randomised clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/ers-crossmark-policy",
"volume": "59"
}