Effectiveness of Paxlovid in the treatment of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection in children with hematologic malignancies: a retrospective cohort study
et al., Translational Cancer Research, doi:10.21037/tcr-24-70, Aug 2024
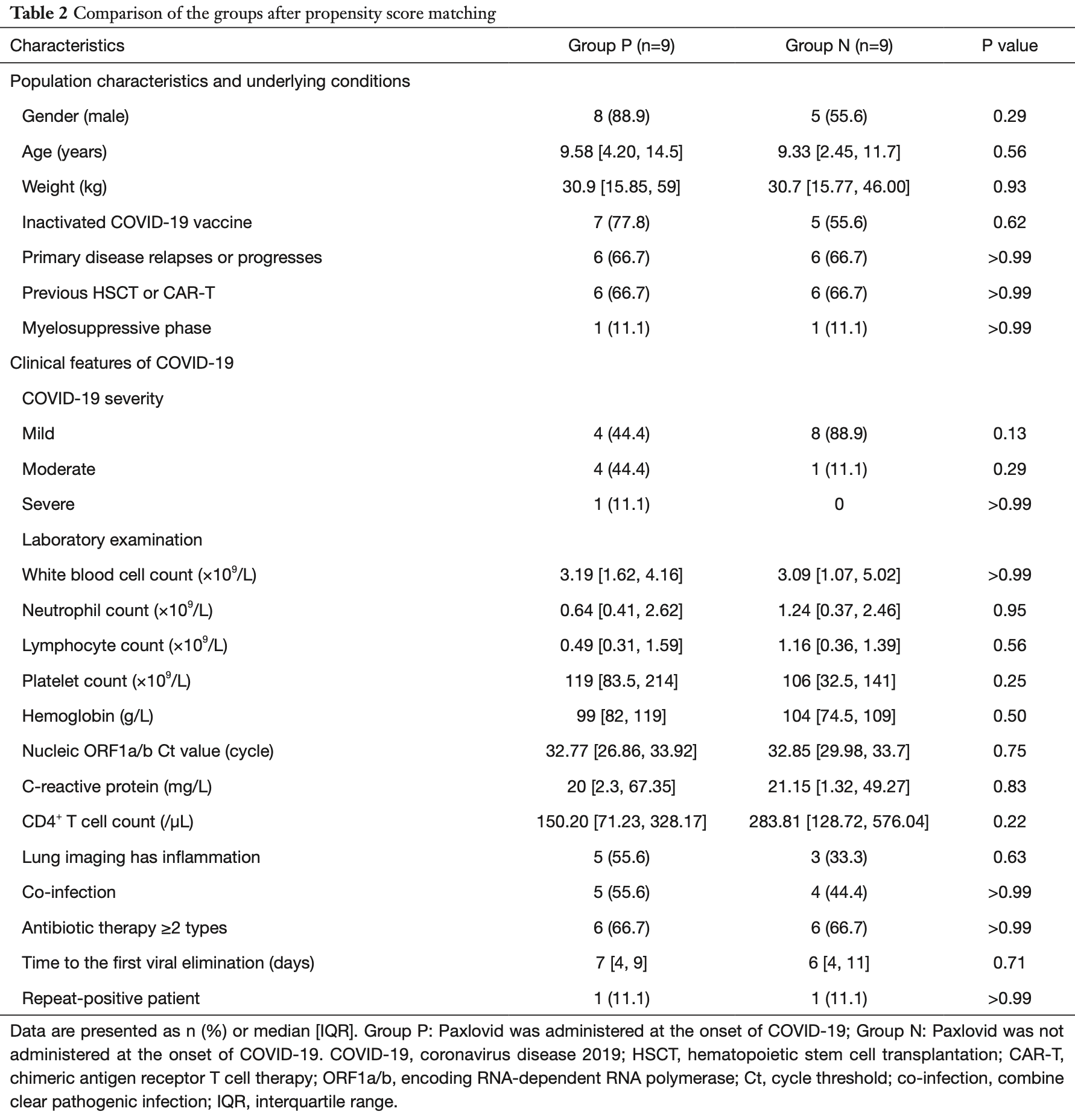
Retrospective 42 children with hematologic malignancies (HMs) and SARS-CoV-2 omicron infection showing no significant difference in clinical outcomes or viral clearance with paxlovid after propensity score matching.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
|
time to viral-, 16.7% higher, relative time 1.17, p = 0.71, treatment 9, control 9, propensity score matching.
|
|
rebound, 105.0% higher, OR 2.05, p = 0.57, treatment 21, control 21, adjusted per study, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Deng et al., 31 Aug 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 1 December, 2022 - 1 March, 2023.
Contact: caoqing@scmc.com.cn.
Effectiveness of Paxlovid in the treatment of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection in children with hematologic malignancies: a retrospective cohort study
Translational Cancer Research, doi:10.21037/tcr-24-70
Background: Patients with hematologic malignancies (HMs) may be immunocompromised after receiving anti-tumor therapy. Those who also have the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus infection face many challenges, including a lack of effective antiviral drugs. This study aimed to investigate the clinical features of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection in children with HMs, and the effectiveness of Paxlovid. Methods: A retrospective, non-randomized study was conducted on pediatric patients with HMs infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant who had been admitted to the Shanghai Children's Medical Center, Shanghai, China from December 1, 2022 to March 1, 2023. The Paxlovid-treated group (Group P) comprised 21 patients, and the non-Paxlovid-treated group (Group N) comprised 21 patients. The patients' demographic data, clinical features, and therapeutic outcomes were collected. Statistical tests were used to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and related factors. Results: The clinical course of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection for most of the children with HMs was non-severe (97.6%), and only one child progressed to severe disease (2.4%). The most common symptoms were fever (66.7%) and cough (52.4%). Compared with the children in Group N, those in Group P had worse clinical characteristics, including those who previously underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) or chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell treatment (71.4% vs. 28.6%, P=0.005), and those in the myelosuppressive phase (57.1% vs. 4.8%, P<0.001). Most of the children in Group P were treated with more than two types of antibiotics (76.2% vs. 42.9%, P=0.02). The patients treated with Paxlovid within 5 days of diagnosis had a median viral clearance time of 5 days [interquartile range (IQR), 4-8 days], which was significantly shorter than that of the patients who were not treated with Paxlovid (P=0.03). There were no significant differences in the clinical outcomes between the two groups after the propensity score matching (PSM) analyses. Eight patients (19%) had repeat-positive (re-positive) test results. No factor was found to be statistically significant in predicting re-positive test results based on the binary logistic regression analysis. Conclusions: Administering Paxlovid within 5 days of the diagnosis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection in children may effectively shorten the clearance time of the virus, but there is still the possibility the patients may have re-positive test results.
References
Cesaro, Mikulska, Hirsch, Update of recommendations for the management of COVID-19 in patients with haematological malignancies, haematopoietic cell transplantation and CAR T therapy, from the 2022 European Conference on Infections in Leukaemia (ECIL 9), Leukemia
Chien, Peterson, Young, Outcomes of breakthrough COVID-19 infections in patients with hematologic malignancies, Blood Adv
Haeusler, Ammann, Carlesse, SARS-CoV-2 in children with cancer or after haematopoietic stem cell transplant: An analysis of 131 patients, Eur J Cancer
Hall, Teh, COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients With Cancer and Patients Receiving HSCT or CAR-T Therapy: Immune Response, Real-World Effectiveness, and Implications for the Future, J Infect Dis
Hashmi, Bodea, Patni, COVID-19 in Pediatric Patients With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia or Lymphoma, JAMA Netw Open
Ichikawa, Tamura, Takahata, Prolonged shedding of viable SARS-CoV-2 in immunocompromised patients with haematological malignancies: A prospective study, Br J Haematol
Katsuya, Yoshida, Takashima, Immunogenicity after vaccination of COVID-19 vaccines in patients with cancer: a prospective, single center, observational study, Int J Clin Oncol
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Effectiveness of Paxlovid in Reducing Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Mortality in High-Risk Patients, Clin Infect Dis
New, Cham, Smith, Effects of antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents on postvaccination SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections, antibody response, and serological cytokine profile, J Immunother Cancer
Saravolatz, Depcinski, Sharma, Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Oral Coronavirus Disease 2019 Antiviral Drugs, Clin Infect Dis
Wekking, Senevirathne, Pearce, The impact of COVID-19 on cancer patients, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21037/tcr-24-70",
"ISSN": [
"2218-676X",
"2219-6803"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr-24-70",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Xiaoxia",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Yuelian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Wenjuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qin",
"given": "Xia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cao",
"given": "Qing",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Translational Cancer Research"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"amegroups.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-12T07:11:30Z",
"timestamp": 1723446690000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-29T07:54:35Z",
"timestamp": 1724918075000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-30T00:39:13Z",
"timestamp": 1724978353632
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2218-676X"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2219-6803"
}
],
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/download/88997/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8611",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4219-4230",
"prefix": "10.21037",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "AME Publishing Company",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/88997/html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Transl Cancer Res"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Effectiveness of Paxlovid in the treatment of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection in children with hematologic malignancies: a retrospective cohort study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/ame_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "13"
}