Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab in preventing hospitalization and mortality in high-risk patients with COVID-19 in the United States: A cohort study from the Mayo Clinic electronic health records
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0304822, Jul 2024
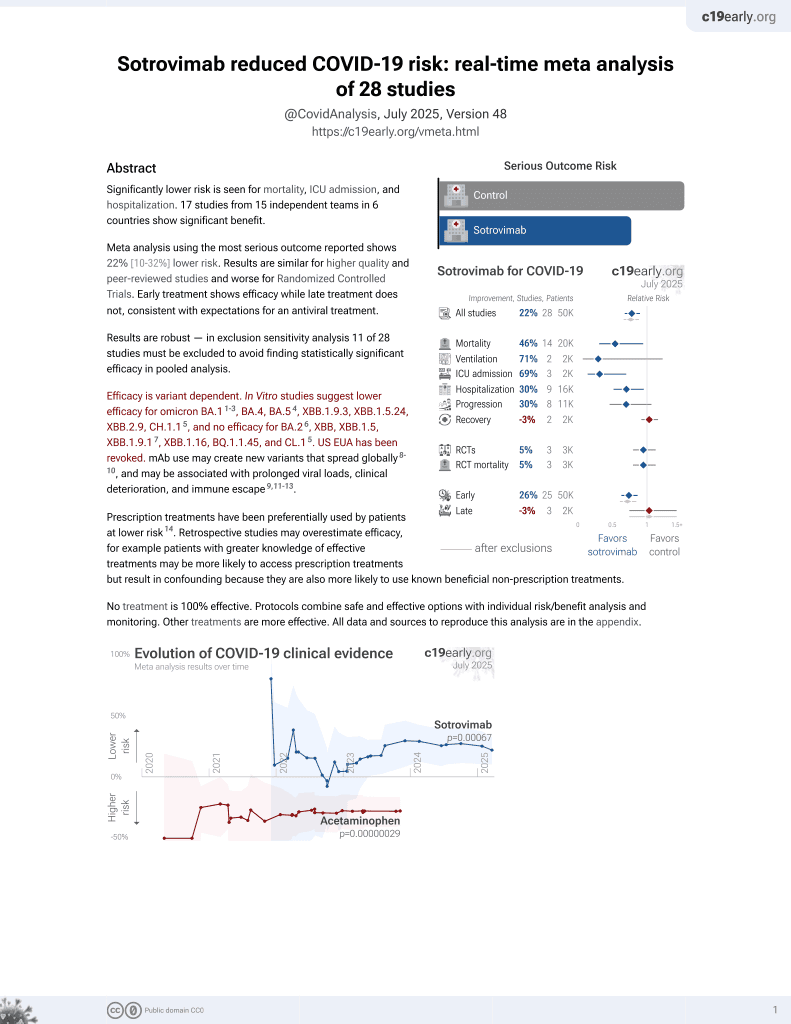
Sotrovimab for COVID-19
45th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2022, now with p = 0.00048 from 29 studies, recognized in 42 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 35,485 high-risk COVID-19 outpatients showing lower ICU admission and respiratory support with sotrovimab. There was no significant difference for hospitalization.
Confounding by treatment propensity. This study analyzes a population
where only a fraction of eligible patients received the treatment. Patients
receiving treatment may be more likely to follow other recommendations, more
likely to receive additional care, and more likely to use additional
treatments that are not tracked in the data (e.g., nasal/oral hygiene1,2, vitamin D3, etc.) — either because the physician
recommending sotrovimab also recommended them, or
because the patient seeking out sotrovimab is more
likely to be familiar with the efficacy of additional treatments and more
likely to take the time to use them.
Therefore, these kind of studies may
overestimate efficacy.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro studies predict lower efficacy for BA.14-6, BA.4, BA.57, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.2.9, CH.1.18, and no efficacy for BA.29, XBB, XBB.1.5, ХВВ.1.9.110, XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1.45, and CL.18. US EUA has been revoked.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments11.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
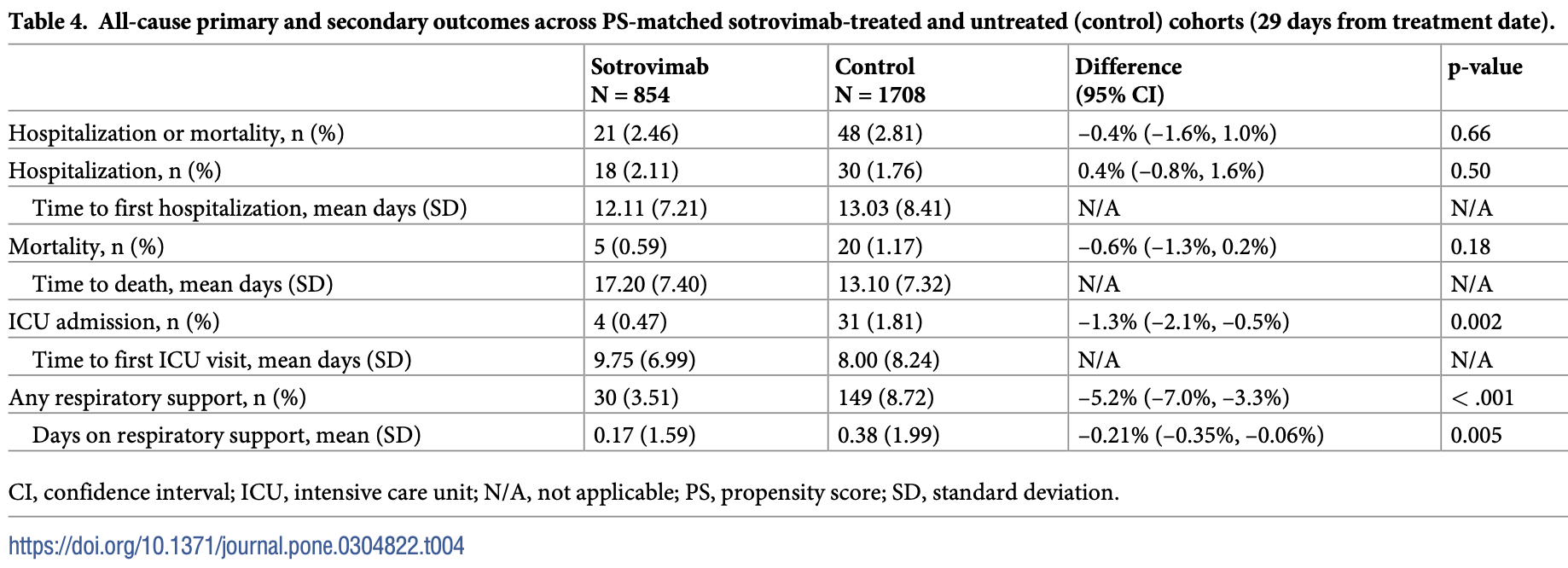
risk of death, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.20, treatment 5 of 854 (0.6%), control 20 of 1,708 (1.2%), NNT 171, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of death/hospitalization, 12.5% lower, RR 0.88, p = 0.70, treatment 21 of 854 (2.5%), control 48 of 1,708 (2.8%), NNT 285, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 74.2% lower, RR 0.26, p = 0.006, treatment 4 of 854 (0.5%), control 31 of 1,708 (1.8%), NNT 74, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 59.5% lower, RR 0.41, p < 0.001, treatment 30 of 854 (3.5%), control 148 of 1,708 (8.7%), NNT 19, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 20.0% higher, RR 1.20, p = 0.54, treatment 18 of 854 (2.1%), control 30 of 1,708 (1.8%), propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
4.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
5.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
6.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
7.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
8.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
9.
Zhou et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 Variant Evades Neutralization by Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.02.15.480166.
Bell et al., 16 Jul 2024, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, study period 26 May, 2021 - 23 April, 2022.
Contact: christopher.f.bell@gsk.com, nic@nference.net.
Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab in preventing hospitalization and mortality in high-risk patients with COVID-19 in the United States: A cohort study from the Mayo Clinic electronic health records
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0304822
Background To describe outcomes of high-risk patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treated with sotrovimab, other monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), or antivirals, and patients who did not receive early COVID-19 treatment. We also evaluate the comparative effectiveness of sotrovimab versus no treatment in preventing severe clinical outcomes.
Methods This observational retrospective cohort study analyzed Mayo Clinic electronic health records. Non-hospitalized adult patients diagnosed with COVID-19 from May 26, 2021 and April 23, 2022 and at high risk of COVID-19 progression were eligible. The primary outcome was 29-day all-cause hospitalization and/or death. Outcomes were described for patients treated with sotrovimab, other mAbs, or antivirals, and eligible but untreated patients, and compared between sotrovimab-treated and propensity score (PS)-matched untreated cohorts.
Results We included 35,485 patients (sotrovimab, 1369; other mAbs, 6488; antivirals, 133; high-risk untreated, 27,495). A low proportion of patients treated with sotrovimab (n = 33/1369, 2.4%), other mAbs (n = 147/6488, 2.3%), or antivirals (n = 2/133, 1.5%) experienced allcause hospitalization or death. Among high-risk untreated patients, the percentage of allcause hospitalization or death was 3.3% (n = 910/27,495). In the PS-matched analysis, 2.5% (n = 21/854) of sotrovimab-treated patients experienced all-cause hospitalization and/ or death versus 2.8% (n = 48/1708) of untreated patients (difference, -0.4%; p = 0.66).
References
Aggarwal, Beaty, Bennett, Carlson, Davis et al., Real-world evidence of the neutralizing monoclonal antibody sotrovimab for preventing hospitalization and mortality in COVID-19 outpatients, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac206
Aggarwal, Beaty, Bennett, Carlson, Mayer et al., Change in effectiveness of sotrovimab for preventing hospitalization and mortality for at-risk COVID-19 outpatients during an Omicron BA.1 and BA.1.1-predominant phase, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.10.002
Bierle, Ganesh, Wilker, Hanson, Moehnke et al., Impact of social and cultural factors on the decision to consent for monoclonal antibody treatment among high-risk patients with mild-moderate COVID-19, J Prim Care Comm Health, doi:10.1177/21501327211019282
Bolze, Luo, White, Cirulli, Wyman et al., SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta rapidly displaced variant Alpha in the United States and led to higher viral loads, Cell Rep Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100564
Cheng, Reyes, Satram, Birch, Gibbons et al., Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the early treatment of COVID-19 during SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron waves in the USA, Infect Dis Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-022-00755-0
Drysdale, Gibbons, Singh, Rolland, Lavoie et al., Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection during Omicron BA.2 subvariant predominance: a systematic literature review
Ganesh, Pawlowski, Horo, Arndt, Arndt et al., Intravenous bamlanivimab use associates with reduced hospitalization in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI151697
Ganesh, Philpot, Bierle, Anderson, Arndt et al., Real-world clinical outcomes of bamlanivimab and casirivimab-imdevimab among high-risk patients with mild to moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab377
Gsk, GSK and Vir Biotechnology announce sotrovimab (VIR-7831) receives Emergency Use Authorization from the US FDA for treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in high-risk adults and paediatric patients
Henry, Lippi, Chronic kidney disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Int Urol Nephrol, doi:10.1007/s11255-020-02451-9
Kip, Mccreary, Collins, Minnier, Snyder et al., Evolving real-world effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19: a cohort study, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M22-1286
Kompaniyets, Pennington, Goodman, Rosenblum, Belay et al., Underlying medical conditions and severe illness among 540,667 adults hospitalized with COVID-19, March 2020-March 2021, Prev Chronic Dis, doi:10.5888/pcd18.210123
Lambrou, Shirk, Steele, Paul, Paden et al., Genomic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants: predominance of the Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (B.1.1.529) variants-United States, June 2021, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7106a4
Ma, Shirk, Lambrou, Hassell, Zheng et al., Genomic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants: circulation of Omicron lineages-United States, January 2022-May 2023, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7224a2
O'horo, Cerhan, Cahn, Bauer, Temesgen et al., Outcomes of COVID-19 with the Mayo Clinic model of care and research, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.12.006
O'horo, Challener, Speicher, Bosch, Seville et al., Effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies in preventing severe COVID-19 with emergence of the Delta variant, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.12.002
Ou, Zhu, Li, Zhong, Li, Risk factors of severe cases with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Epidemiol Infect, doi:10.1017/S095026882000179X
Patel, Yarwood, Levick, Gibbons, Drysdale et al., Characteristics and outcomes of patients with COVID-19 at high-risk of disease progression receiving sotrovimab, oral antivirals or no treatment in England
Razonable, Aloia, Anderson, Anil, Arndt et al., A framework for outpatient infusion of antispike monoclonal antibodies to high-risk patients with mild-to-moderate Coronavirus Disease-19: the Mayo Clinic Model, Mayo Clinic Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.03.010
Razonable, Ganesh, Bierle, Clinical prioritization of antispike monoclonal antibody treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.11.017
Razonable, Horo, Challener, Arndt, Arndt et al., Curbing the Delta surge: clinical outcomes after treatment with bamlanivimab-etesevimab, casirivimab-imdevimab, or sotrovimab for mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2022.06.015
Razonable, Horo, Hanson, Arndt, Speicher et al., Comparable outcomes for bebtelovimab and ritonavir-boosted mirmatrelvir treatment in high-risk patinets with Coronavirus Disease-2019 during Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 BA.2 Omicron epoch, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac346
Razonable, Pawlowski, Horo, Arndt, Arndt et al., Casirivimab-imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102
Razonable, Tulledge-Scheitel, Hanson, Arndt, Speicher et al., Real-world clinical outcomes of bebtelovimab and sotrovimab treatment of high-risk persons with coronavirus disease 2019 during the Omicron epoch, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac411
Reyes, Cheng, Gibbons, Birch, Patel et al., Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the early treatment of COVID-19 in the US, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.congress-2022.4407
Young-Xu, Korves, Zwain, Satram, Drysdale et al., Effectiveness of sotrovimab in preventing COVID-19-related hospitalizations or deaths among U.S. veterans
Zheng, Green, Tazare, Curtis, Fisher et al., Comparative effectiveness of sotrovimab and molnupiravir for prevention of severe covid-19 outcomes in patients in the community: observational cohort study with the OpenSAFELY platform, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071932
Zhou, Chi, Lv, Wang, Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3377
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0304822",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304822",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"sec001\">\n<jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n<jats:p>To describe outcomes of high-risk patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treated with sotrovimab, other monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), or antivirals, and patients who did not receive early COVID-19 treatment. We also evaluate the comparative effectiveness of sotrovimab versus no treatment in preventing severe clinical outcomes.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec002\">\n<jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n<jats:p>This observational retrospective cohort study analyzed Mayo Clinic electronic health records. Non-hospitalized adult patients diagnosed with COVID-19 from May 26, 2021 and April 23, 2022 and at high risk of COVID-19 progression were eligible. The primary outcome was 29-day all-cause hospitalization and/or death. Outcomes were described for patients treated with sotrovimab, other mAbs, or antivirals, and eligible but untreated patients, and compared between sotrovimab-treated and propensity score (PS)-matched untreated cohorts.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec003\">\n<jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n<jats:p>We included 35,485 patients (sotrovimab, 1369; other mAbs, 6488; antivirals, 133; high-risk untreated, 27,495). A low proportion of patients treated with sotrovimab (n = 33/1369, 2.4%), other mAbs (n = 147/6488, 2.3%), or antivirals (n = 2/133, 1.5%) experienced all-cause hospitalization or death. Among high-risk untreated patients, the percentage of all-cause hospitalization or death was 3.3% (n = 910/27,495). In the PS-matched analysis, 2.5% (n = 21/854) of sotrovimab-treated patients experienced all-cause hospitalization and/or death versus 2.8% (n = 48/1708) of untreated patients (difference, –0.4%; p = 0.66). Significantly fewer sotrovimab-treated patients required intensive care unit admission (0.5% vs 1.8%; difference, –1.3%; p = 0.002) or respiratory support (3.5% vs 8.7%; difference, –5.2%; p < 0.001).</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec004\">\n<jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n<jats:p>There was no significant difference in the proportion of sotrovimab-treated and PS-matched untreated patients experiencing 29-day all-cause hospitalization or mortality, although significantly fewer sotrovimab-treated patients required intensive care unit admission or respiratory support.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6413-2537",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Bell",
"given": "Christopher F.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibbons",
"given": "Daniel C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drysdale",
"given": "Myriam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Birch",
"given": "Helen J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lloyd",
"given": "Emily J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Vishal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carpenter",
"given": "Corinne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2083-944X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Carlson",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calay",
"given": "Ediz S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puranik",
"given": "Arjun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wagner",
"given": "Tyler E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0880-4498",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "O’Horo",
"given": "John C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Razonable",
"given": "Raymund R.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T17:25:47Z",
"timestamp": 1721150747000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T17:26:04Z",
"timestamp": 1721150764000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Taie",
"given": "Anmar",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"name": "GSK and Vir Biotechnology, Inc"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-17T00:25:59Z",
"timestamp": 1721175959236
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1721088000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304822",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0304822",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"key": "pone.0304822.ref001",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard [Internet]. 2023 November 8 [cited 2023 November 15]. https://covid19.who.int/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3377",
"article-title": "Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19)",
"author": "Y Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3377",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref002",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S095026882000179X",
"article-title": "Risk factors of severe cases with COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"author": "M Ou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e175",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Infect",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref003",
"volume": "148",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11255-020-02451-9",
"article-title": "Chronic kidney disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "BM Henry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1193",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int Urol Nephrol",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref004",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5888/pcd18.210123",
"article-title": "Underlying medical conditions and severe illness among 540,667 adults hospitalized with COVID-19, March 2020–March 2021",
"author": "L Kompaniyets",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E66",
"journal-title": "Prev Chronic Dis",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref005",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "pone.0304822.ref006",
"unstructured": "U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Emergency Use Authorizations for drugs and non-vaccine biological products [Internet]. 2023 November 9 [cited 2023 November 15]. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/emergency-use-authorizations-drugs-and-non-vaccine-biological-products."
},
{
"key": "pone.0304822.ref007",
"unstructured": "GSK. GSK and Vir Biotechnology announce sotrovimab (VIR-7831) receives Emergency Use Authorization from the US FDA for treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in high-risk adults and paediatric patients [Internet]. 2021 May 26 [cited 2023 November 15]. https://www.gsk.com/en-gb/media/press-releases/gsk-and-vir-biotechnology-announce-sotrovimab-vir-7831-receives-emergency-use-authorization-from-the-us-fda/."
},
{
"key": "pone.0304822.ref008",
"unstructured": "U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA updates sotrovimab Emergency Use Authorization [Internet]. 2022 April 5 [cited 2023 November 15]. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-updates-sotrovimab-emergency-use-authorization."
},
{
"key": "pone.0304822.ref009",
"unstructured": "Medicines & Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. Summary of product characteristics for Xevudy [Internet]. 2022 March 28 [cited 2023 November 15]. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/regulatory-approval-of-xevudy-sotrovimab/summary-of-product-characteristics-for-xevudy."
},
{
"key": "pone.0304822.ref010",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency. Xevudy [Internet]. 2023 October 13 [cited 2023 November 15]. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/xevudy."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-022-00755-0",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the early treatment of COVID-19 during SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron waves in the USA",
"author": "MM Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "607",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref011",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-1286",
"article-title": "Evolving real-world effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19: a cohort study",
"author": "KE Kip",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "496",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref012",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the early treatment of COVID-19 in the US",
"author": "C Reyes",
"first-page": "4407",
"issue": "suppl 66",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref013",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.03.09.23287034",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "#cr-split#-pone.0304822.ref014.1",
"unstructured": "Drysdale M, Gibbons DC, Singh M, Rolland C, Lavoie L, Skingsley A, et al. Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection during Omicron BA.2 subvariant predominance: a systematic literature review. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 medRxiv 2023.03.09.23287034 [posted 2023 March 10"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-pone.0304822.ref014.2",
"unstructured": "cited 2023 November 15]: [42 p.] http://medrxiv.org/content/early/2023/03/10/2023.03.09.23287034.abstract"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2022-071932",
"article-title": "Comparative effectiveness of sotrovimab and molnupiravir for prevention of severe covid-19 outcomes in patients in the community: observational cohort study with the OpenSAFELY platform",
"author": "B Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e071932",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref015",
"volume": "379",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7106a4",
"article-title": "Genomic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants: predominance of the Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (B.1.1.529) variants—United States, June 2021–January 2022",
"author": "AS Lambrou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "206",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref016",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7224a2",
"article-title": "Genomic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants: circulation of Omicron lineages—United States, January 2022–May 2023",
"author": "KC Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "651",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref017",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac411",
"article-title": "Real-world clinical outcomes of bebtelovimab and sotrovimab treatment of high-risk persons with coronavirus disease 2019 during the Omicron epoch",
"author": "RR Razonable",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofac411",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref018",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.03.010",
"article-title": "A framework for outpatient infusion of antispike monoclonal antibodies to high-risk patients with mild-to-moderate Coronavirus Disease-19: the Mayo Clinic Model",
"author": "RR Razonable",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1250",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clinic Proc",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref019",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI151697",
"article-title": "Intravenous bamlanivimab use associates with reduced hospitalization in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19",
"author": "R Ganesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e151697",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref020",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab377",
"article-title": "Real-world clinical outcomes of bamlanivimab and casirivimab-imdevimab among high-risk patients with mild to moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "R Ganesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1278",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref021",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.12.002",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies in preventing severe COVID-19 with emergence of the Delta variant",
"author": "JC O’Horo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref022",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102",
"article-title": "Casirivimab-imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19",
"author": "RR Razonable",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101102",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref023",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiac346",
"article-title": "Comparable outcomes for bebtelovimab and ritonavir-boosted mirmatrelvir treatment in high-risk patinets with Coronavirus Disease-2019 during Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 BA.2 Omicron epoch",
"author": "RR Razonable",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1683",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref024",
"volume": "226",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.11.017",
"article-title": "Clinical prioritization of antispike monoclonal antibody treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19",
"author": "RR Razonable",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "26",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref025",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/21501327211019282",
"article-title": "Impact of social and cultural factors on the decision to consent for monoclonal antibody treatment among high-risk patients with mild-moderate COVID-19",
"author": "DM Bierle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Prim Care Comm Health",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref026",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiac206",
"article-title": "Real-world evidence of the neutralizing monoclonal antibody sotrovimab for preventing hospitalization and mortality in COVID-19 outpatients",
"author": "NR Aggarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2129",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref027",
"volume": "226",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.10.002",
"article-title": "Change in effectiveness of sotrovimab for preventing hospitalization and mortality for at-risk COVID-19 outpatients during an Omicron BA.1 and BA.1.1-predominant phase",
"author": "NR Aggarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "310",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref028",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2022.06.015",
"article-title": "Curbing the Delta surge: clinical outcomes after treatment with bamlanivimab-etesevimab, casirivimab-imdevimab, or sotrovimab for mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "RR Razonable",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1641",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref029",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.12.30.22284063",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "#cr-split#-pone.0304822.ref030.1",
"unstructured": "Young-Xu Y, Korves C, Zwain G, Satram S, Drysdale M, Reyes C, et al. Effectiveness of sotrovimab in preventing COVID-19-related hospitalizations or deaths among U.S. veterans. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 medRxiv 2022.12.30.22284063 [posted 2022 December 30"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-pone.0304822.ref030.2",
"unstructured": "cited 2023 November 15]: [26 p.] http://medrxiv.org/content/early/2022/12/30/2022.12.30.22284063.abstract"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.11.28.22282808",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "#cr-split#-pone.0304822.ref031.1",
"unstructured": "Patel V, Yarwood MJ, Levick B, Gibbons DC, Drysdale M, Kerr W, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with COVID-19 at high-risk of disease progression receiving sotrovimab, oral antivirals or no treatment in England. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 medRxiv 2022.11.28.22282808 [posted 2022 November 29"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-pone.0304822.ref031.2",
"unstructured": "cited 2023 November 15]: [38 p.] http://medrxiv.org/content/early/2022/11/29/2022.11.28.22282808.abstract"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.12.006",
"article-title": "Outcomes of COVID-19 with the Mayo Clinic model of care and research",
"author": "JC O’Horo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "601",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref032",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100564",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta rapidly displaced variant Alpha in the United States and led to higher viral loads",
"author": "A Bolze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100564",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "pone.0304822.ref033",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "pone.0304822.ref034",
"unstructured": "U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA limits use of certain monoclonal antibodies to treat COVID-19 due to the Omicron variant [Internet]. 2022 January 24 [cited 2023 November 15]. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-limits-use-certain-monoclonal-antibodies-treat-covid-19-due-omicron."
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304822"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab in preventing hospitalization and mortality in high-risk patients with COVID-19 in the United States: A cohort study from the Mayo Clinic electronic health records",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "19"
}