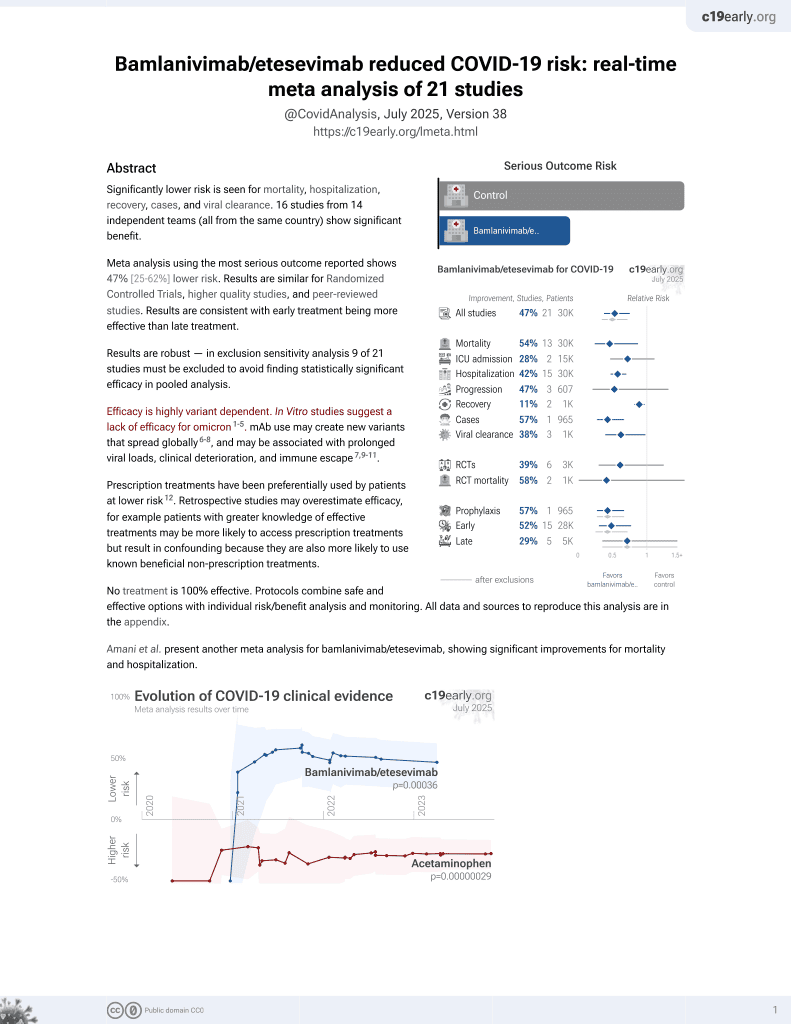
Intravenous bamlanivimab use associates with reduced hospitalization in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19
et al., Journal of Clinical Investigation, doi:10.1172/JCI151697, Oct 2021
25th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2021, now with p = 0.00049 from 22 studies, recognized in 11 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
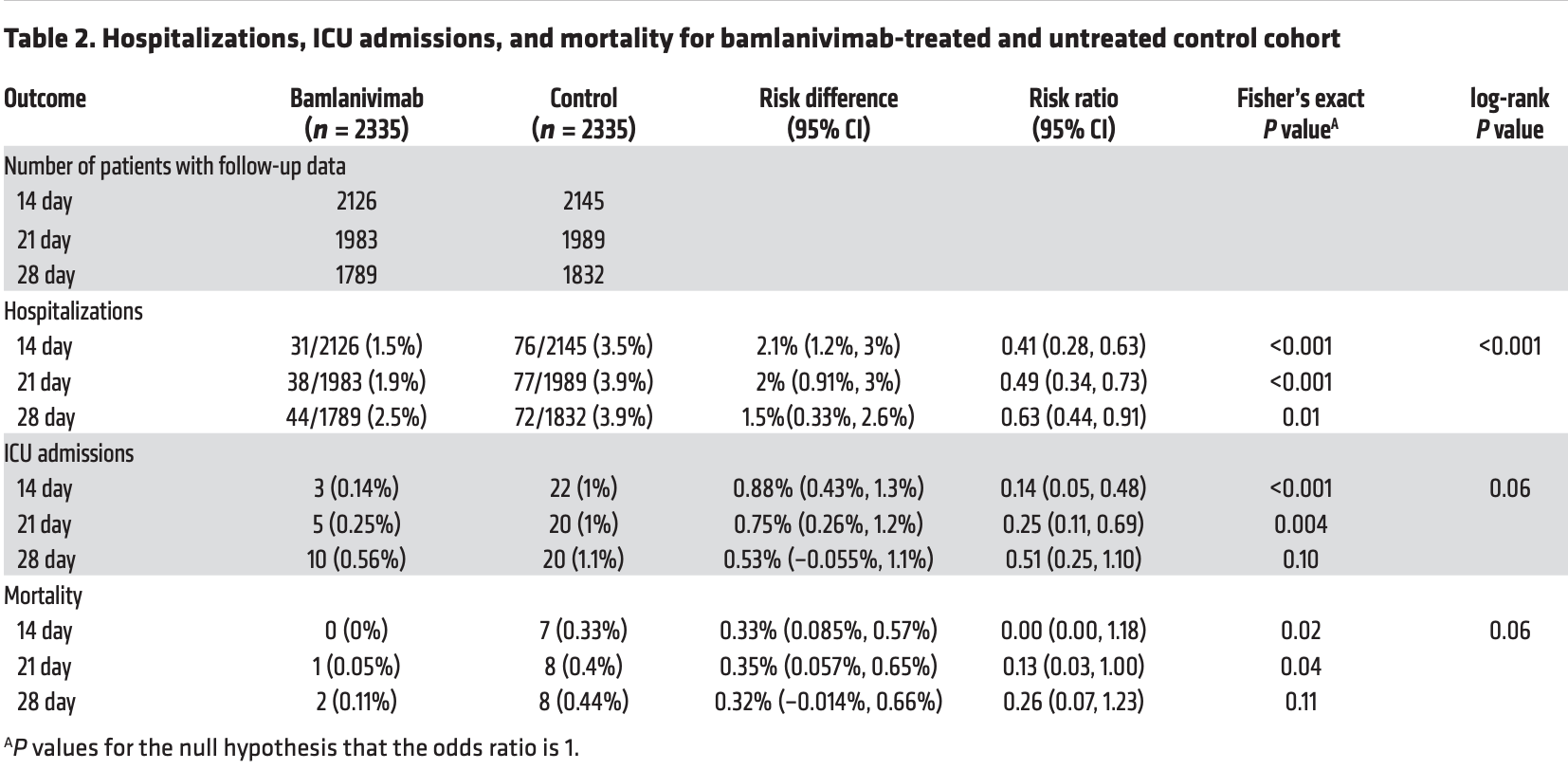
Retrospective 2,335 bamlanivimab patients and 2,335 PSM controls in the USA, showing significantly lower hospitalization with treatment.
Confounding by treatment propensity. This study analyzes a population
where only a fraction of eligible patients received the treatment. Patients
receiving treatment may be more likely to follow other recommendations, more
likely to receive additional care, and more likely to use additional
treatments that are not tracked in the data (e.g., nasal/oral hygiene6,7, vitamin D8, etc.) — either because the physician
recommending bamlanivimab/etesevimab also recommended them, or
because the patient seeking out bamlanivimab/etesevimab is more
likely to be familiar with the efficacy of additional treatments and more
likely to take the time to use them.
Therefore, these kind of studies may
overestimate efficacy.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments9.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 74.4% lower, RR 0.26, p = 0.11, treatment 2 of 1,789 (0.1%), control 8 of 1,832 (0.4%), NNT 308, day 28.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 48.8% lower, RR 0.51, p = 0.10, treatment 10 of 1,789 (0.6%), control 20 of 1,832 (1.1%), NNT 188, day 28.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 37.4% lower, RR 0.63, p = 0.01, treatment 44 of 1,789 (2.5%), control 72 of 1,832 (3.9%), NNT 68, day 28, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Ganesh et al., 1 Oct 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 63.0, 20 authors.
Intravenous bamlanivimab use associates with reduced hospitalization in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19
Journal of Clinical Investigation, doi:10.1172/jci151697
Clinical data to support the use of bamlanivimab for the treatment of outpatients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) are needed. 2335 Patients who received single-dose bamlanivimab infusion between November 12, 2020, and February 17, 2021, were compared with a propensity-matched control of 2335 untreated patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 at Mayo Clinic facilities across 4 states. The primary outcome was the rate of hospitalization at days 14, 21, and 28. The median age of the population was 63 years; 47.3% of the bamlanivimab-treated cohort were 65 years or more; 49.3% were female and 50.7% were male. High-risk characteristics included hypertension (54.2%), BMI greater than or equal to 35 (32.4%), diabetes mellitus (26.5%), chronic lung disease (25.1%), malignancy (16.6%), and renal disease (14.5%). Patients who received bamlanivimab had lower all-cause hospitalization rates at days 14 (1.5% vs. 3.5%; risk ratio [RR], 0.41), 21 (1.9% vs. 3.9%; RR, 0.49), and 28 (2.5% vs. 3.9%; RR, 0.63). Secondary exploratory outcomes included lower intensive care unit (ICU) admission rates at days 14 (0.14% vs. 1%; RR, 0.14), 21 (0.25% vs.1%; RR, 0.25), and 28 (0.56% vs.1.1%; RR. 0.51) and lower […] Clinical Medicine Virology
Author contributions RG, CFP, and RRR conceived and designed the study. CFP, PJL, AP, AJV, JCO, RG, ADB, and RRR acquired, analyzed, or interpreted data. RG, CFP, and RRR drafted the manuscript. All authors critically revised the manuscript. CFP, PJL, AP, AJV, JCO, RG, and RRR performed statistical analysis. SJB, JJL, MDB, ADB, and DMB provided administrative, technical, or material support. RO, LLS, SMTS, CGW, SNH, DMB, RG, LLA, RFA, AH, and RRR supervised the project.
References
Austin, Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples, Stat Med, doi:10.1002/sim.3697
Bariola, Impact of bamlanivimab monoclonal antibody treatment on hospitalization and mortality among non-hospitalized adults with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab254
Bhimraj, Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19
Bierle, Influence of social and cultural factors on the decision to consent for monoclonal antibody treatment among high-risk patients with mild-moderate COVID-19, J Prim Care Community Health
Caliendo, Kopeinig, Some practical guidance for the implementation of propensity score matching, J Econ Surv, doi:10.1111/j.1467-6419.2007.00527.x
Cardinal, Aitken, ANOVA for the Behavioral Sciences Researcher
Chen, SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody LY-CoV555 in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2029849
Crane, Telemedicine consultations and follow-up of patients with COVID-19, Mayo Clin Proc
Feaster, Modeling site effects in the design and analysis of multi-site trials, Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse, doi:10.3109/00952990.2011.600386
Ganesh, Managing patients in the COVID-19 pandemic: a virtual multidisciplinary approach, Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes, doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2020.12.003
Jones, of SARS-CoV-2 infection, doi:10.1101/2020.09.30.318972
Kumar, Real-world experience of bamlanivimab for COVID-19: a case-control study
Razonable, A framework for outpatient infusion of anti-spike monoclonal antibodies to, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.03.010
Richardson, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Seabold, Perktold, Statsmodels: econometric and statistical modeling with Python, doi:10.25080/Majora-92bf1922-011
Stuart, Prognostic score-based balance measures can be a useful diagnostic for propensity score methods in comparative effectiveness research, J Clin Epidemiol
Tian, Evaluating large-scale propensity score performance through real-world and synthetic data experiments, Int J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/dyy120
Tulledge-Scheitel, A mobile unit overcomes the challenges to monoclonal antibody infusion for COVID-19 in skilled care facilities, J Am Geriatr Soc, doi:10.1111/jgs.17090
Virtanen, SciPy 1.0: fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python, Nat Methods, doi:10.1038/s41592-019-0686-2
Vora, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with COVID-19
Yetmar, Monoclonal antibody therapy for COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab255
Zhou, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci151697",
"ISSN": [
"1558-8238"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/jci151697",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1172/JCI151697"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6877-1712",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ganesh",
"given": "Ravindra",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2781-7507",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pawlowski",
"given": "Colin F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O’Horo",
"given": "John C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arndt",
"given": "Lori L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4723-689X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Arndt",
"given": "Richard F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "Sarah J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3337-5645",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bierle",
"given": "Dennis M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borgen",
"given": "Molly Destro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "Sara N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3414-0832",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Heyliger",
"given": "Alexander",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Larsen",
"given": "Jennifer J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lenehan",
"given": "Patrick J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orenstein",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puranik",
"given": "Arjun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Speicher",
"given": "Leigh L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tulledge-Scheitel",
"given": "Sidna M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venkatakrishnan",
"given": "A.J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilker",
"given": "Caroline G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7796-7680",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Badley",
"given": "Andrew D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5248-0227",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Razonable",
"given": "Raymund R.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of Clinical Investigation"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-19T16:12:14Z",
"timestamp": 1629389534000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-30T18:25:22Z",
"timestamp": 1633026322000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000871",
"award": [
"NA"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Mayo Clinic"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-13T15:49:43Z",
"timestamp": 1639410583854
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1558-8238"
}
],
"issue": "19",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "19",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.jci.org/articles/view/151697/files/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "232",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1172",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Clinical Investigation",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "An EUA for bamlanivimab-a monoclonal antibody for COVID-19",
"first-page": "880",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "An EUA for bamlanivimab etesevimab for COVID-19",
"first-page": "49",
"issue": "1621",
"journal-title": "Med Lett Drugs Ther",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "An EUA for casirivimab imdevimab for COVID-19",
"first-page": "201",
"issue": "1614",
"journal-title": "Med Lett Drugs Ther",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.30.318972",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "B4",
"unstructured": "Jones BE, et al. LY-CoV555, a rapidly isolated potent neutralizing antibody, provides protection in a non-human primate model of SARS-CoV-2 infection [preprint]. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.30.318972 Posted on bioRxiv October 9, 2020"
},
{
"key": "B5",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA revokes emergency use authorization for monoclonal antibody bamlanivimab. News release. U.S. Food and Drug Administration; April 16, 2021. Accessed April 24, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-revokes-emergency-use-authorization-monoclonal-antibody-bamlanivimab"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2029849",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.03.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B7"
},
{
"key": "B8",
"unstructured": "Bhimraj A, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. https://www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/covid-19-guideline-treatment-and-management/ Updated June 25, 2021. Accessed January 30, 2021"
},
{
"key": "B9",
"unstructured": "National Institutes of Health. The COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel’s Statement on the Emergency Use Authorization of Bamlanivimab for the Treatment of COVID-19. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/statement-on-bamlanivimab-eua/ Updated August 4, 2021. Accessed January 30, 2021"
},
{
"key": "B10",
"unstructured": "Vora S. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with COVID-19. https://pids.org/2020/11/19/sars-cov-2-neutralizing-antibody-ly-cov555-in-outpatients-with-covid-19/ Updated November 19, 2020. Accessed January 30, 2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab254",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/21501327211019282",
"article-title": "Influence of social and cultural factors on the decision to consent for monoclonal antibody treatment among high-risk patients with mild-moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Bierle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Prim Care Community Health",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Real-world experience of bamlanivimab for COVID-19: a case-control study",
"author": "Kumar",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "B13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab255",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgs.17090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.051",
"article-title": "Telemedicine consultations and follow-up of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Crane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S33",
"issue": "9S",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2020.12.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1467-6419.2007.00527.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyy120",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.3697",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.01.013",
"article-title": "Prognostic score-based balance measures can be a useful diagnostic for propensity score methods in comparative effectiveness research",
"author": "Stuart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S84",
"issue": "8 Suppl",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/00952990.2011.600386",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.25080/Majora-92bf1922-011",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "B25",
"unstructured": "Seabold S, Perktold J. Statsmodels: econometric and statistical modeling with Python. Paper presented at: 9th Python in Science Conference; June 28–July 3, 2010; Austin, Texas, USA. Accessed August 16, 2021. https://doi.org/10.25080/Majora-92bf1922-011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41592-019-0686-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B26"
},
{
"key": "B27",
"unstructured": "lifelines. Version 0.26.0. Cam Davidson-Pilon; 2021. Accessed August 16, 2021. https://github.com/CamDavidsonPilon/lifelines"
},
{
"key": "B28"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Intravenous bamlanivimab use associates with reduced hospitalization in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "131"
}