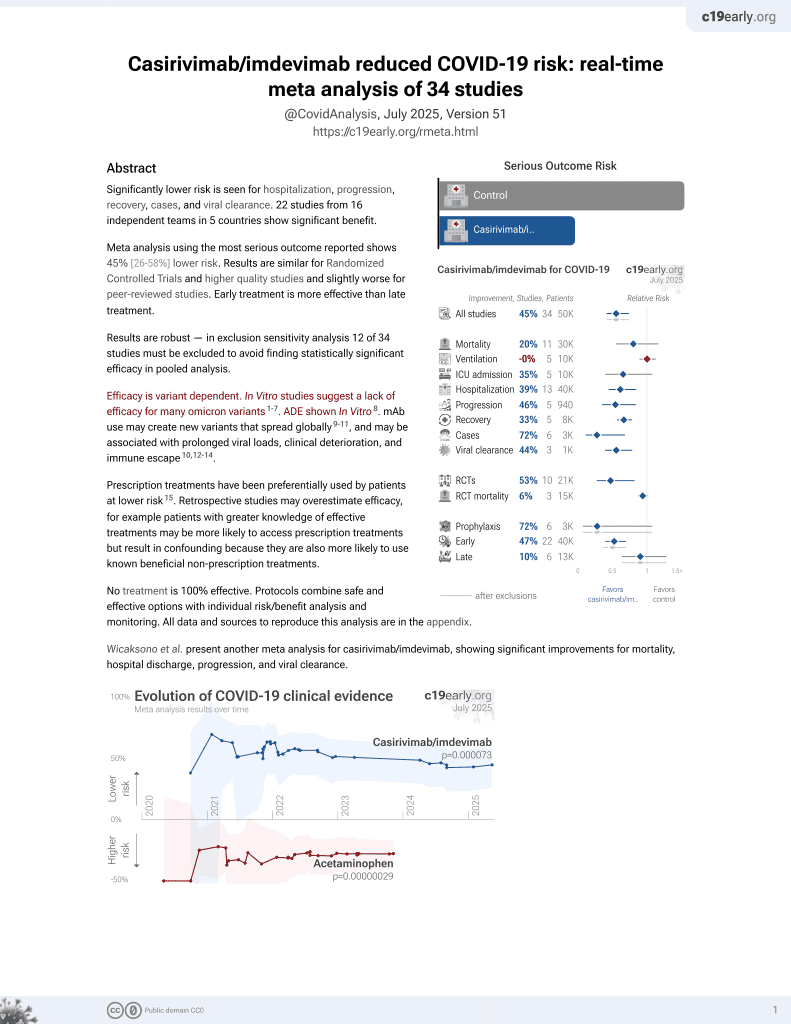
Casirivimab–Imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102, Oct 2021
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
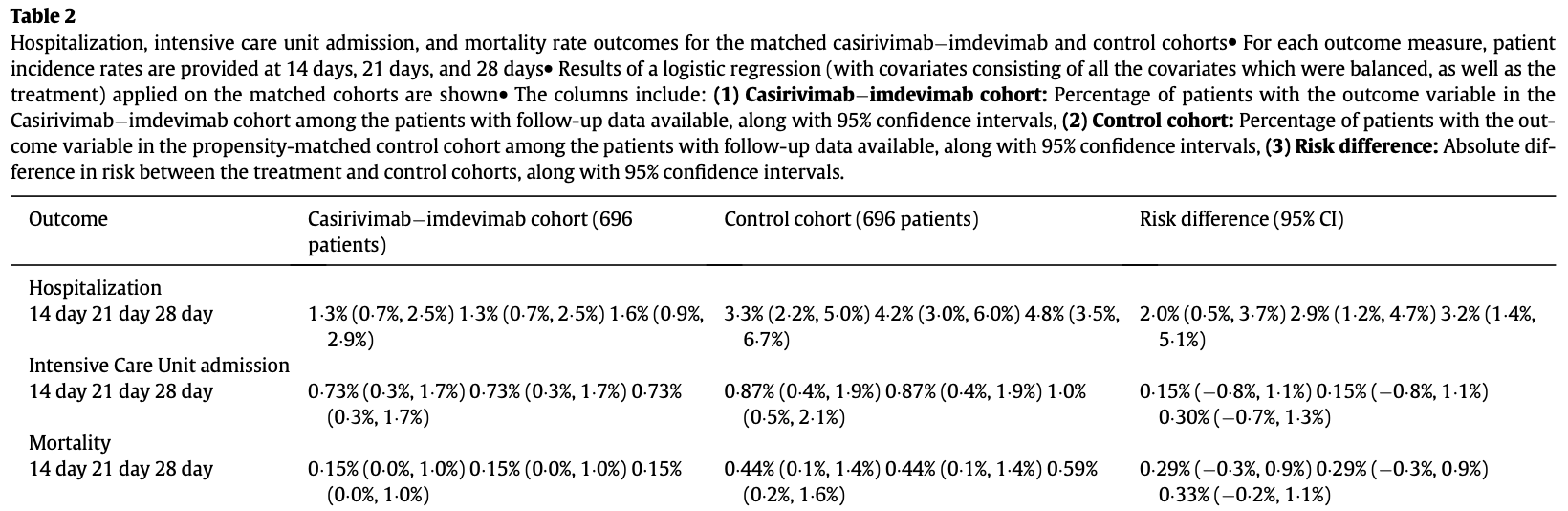
Retrospective 696 patients treated with casirivimab/imdevimab, and 696 matched controls, showing lower hospitalization with treatment. Authors only included patients with documented followup, which is likely to disproportionately bias the control group towards patients with worse outcomes.
Confounding by treatment propensity. This study analyzes a population
where only a fraction of eligible patients received the treatment. Patients
receiving treatment may be more likely to follow other recommendations, more
likely to receive additional care, and more likely to use additional
treatments that are not tracked in the data (e.g., nasal/oral hygiene1,2, vitamin D3, etc.) — either because the physician
recommending casirivimab/imdevimab also recommended them, or
because the patient seeking out casirivimab/imdevimab is more
likely to be familiar with the efficacy of additional treatments and more
likely to take the time to use them.
Therefore, these kind of studies may
overestimate efficacy.
.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants4-10.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments11.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 75.0% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.37, treatment 1 of 696 (0.1%), control 4 of 696 (0.6%), NNT 232.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 28.6% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.77, treatment 5 of 696 (0.7%), control 7 of 696 (1.0%), NNT 348.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 0.001, treatment 11 of 696 (1.6%), control 33 of 696 (4.7%), NNT 32.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
4.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
5.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
6.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
7.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
8.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
9.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
Razonable et al., 31 Oct 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 18 authors, study period 4 December, 2020 - 9 April, 2021.
Contact: razonable.raymund@mayo.edu.
Casirivimab–Imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19
EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102
Background: Real-world clinical data to support the use of casirivimabÀimdevimab for the treatment of outpatients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) is needed. This study aimed to assess the outcomes of casirivimabÀimdevimab treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19. Methods: A retrospective cohort of 696 patients who received casirivimabÀimdevimab between December 4, 2020 and April 9, 2021 was compared to a propensity-matched control of 696 untreated patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 at Mayo Clinic sites in Arizona, Florida, Minnesota, and Wisconsin. Primary outcome was rate of hospitalization at days 14, 21 and 28 after infusion. Findings: The median age of the antibody-treated cohort was 63 years (interquartile range, 52À71); 45¢5% were 65 years old; 51.4% were female. High-risk characteristics were hypertension (52.4%), body mass index 35 (31.0%), diabetes mellitus (24.6%), chronic lung disease (22.1%), chronic renal disease (11.4%), congestive heart failure (6.6%), and compromised immune function (6.7%). Compared to the propensitymatched untreated control, patients who received casirivimabÀimdevimab had significantly lower all-cause hospitalization rates at day 14 (1.3% vs 3.3%; Absolute Difference: 2.0%; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.5À3.7%), day 21 (1.3% vs 4.2%; Absolute Difference: 2.9%; 95% CI: 1.2À4.7%), and day 28 (1.6% vs 4.8%; Absolute Difference: 3.2%; 95% CI: 1.4À5.1%). Rates of intensive care unit admission and mortality at days 14, 21 and 28 were similarly low for antibody-treated and untreated groups. Interpretation: Among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19, casirivimabÀimdevimab treatment was associated with a significantly lower rate of hospitalization. Funding: Mayo Clinic.
Funding
Mayo Clinic
Contributors Concept and Design: Razonable, Pawlowski, Ganesh Acquisition, Analysis, or Interpretation of Data: Razonable, Pawlowski, Lenehan, Puranik, Venkatakrishnan, O'Horo, Badley, Ganesh Drafting of the Manuscript:
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102.
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -final report, N Engl J Med
Bhimraj, Morgan, Schumaker, Infectious diseases society of America guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19
Caliendo, Kopeinig, Some practical guidance for the implementation of propensity score matching, J Econ Surv
Chen, Nirula, Heller, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Crane, Ganesh, Post, Jacobson, Telemedicine consultations and followup of patients with COVID-19, Mayo Clin Proc
Davidson-Pilon, Kalderstam, Zivich, CamDavidsonPilon/lifelines: v0. 21.3. Zenodo
Ganesh, Salonen, Bhuiyan, Managing patients in the COVID-19 pandemic: a virtual multidisciplinary approach, Mayo Clinic Proc: Innovat, Qual Outcomes
Garcia-Vidal, Cozar-Llisto, Meira, Trends in mortality of hospitalised COVID-19 patients: a single centre observational cohort study from Spain, Lancet Reg Health Eur
Group, Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Horwitz, Jones, Cerfolio, Trends in COVID-19 risk-adjusted mortality rates, J Hosp Med
Hosmer, Lemeshow, May, Applied survival analysis: regression modeling of time-to-event data
Huang, Yang, Xu, Xu, Liu, Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19, Acta Pharmacol Sin
Nih, Anti, SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies
O'horo, Cerhan, Cahn, Outcomes of COVID-19 with the mayo clinic model of care and research
Razonable, Aloia, Anderson, A framework for outpatient infusion of anti-spike monoclonal antibodies to high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19: the mayo clinic model
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA
Tian, Schuemie, Suchard, Evaluating large-scale propensity score performance through real-world and synthetic data experiments, Int J Epidemiol
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102",
"ISSN": [
"2589-5370"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102",
"alternative-id": [
"S2589537021003825"
],
"article-number": "101102",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5248-0227",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Razonable",
"given": "Raymund R.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pawlowski",
"given": "Colin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Horo",
"given": "John C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arndt",
"given": "Lori L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4723-689X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Arndt",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bierle",
"given": "Dennis M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borgen",
"given": "Molly Destro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2517-638X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "Sara N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hedin",
"given": "Michelle C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lenehan",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puranik",
"given": "Arjun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seville",
"given": "Maria T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Speicher",
"given": "Leigh L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tulledge-Scheitel",
"given": "Sidna M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venkatakrishnan",
"given": "AJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilker",
"given": "Caroline G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Badley",
"given": "Andrew D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganesh",
"given": "Ravindra",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"container-title-short": "EClinicalMedicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-30T11:00:58Z",
"timestamp": 1630321258000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-25T21:24:45Z",
"timestamp": 1635197085000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100007048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Mayo Clinic"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004337",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Roche"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100005564",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Gilead Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-20T05:19:10Z",
"timestamp": 1684559950727
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 93,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1628726400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537021003825?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537021003825?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101102",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "An EUA for bamlanivimab-a monoclonal antibody for COVID-19",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0001",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "An EUA for casirivimab and imdevimab for COVID-19",
"first-page": "201",
"issue": "1614",
"journal-title": "Med Lett Drugs Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0002",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "An EUA for bamlanivimab and etesevimab for COVID-19",
"first-page": "49",
"issue": "1621",
"journal-title": "Med Lett Drugs Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0003",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4",
"article-title": "Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1141",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol Sin",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0004",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0005",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0006",
"unstructured": "Bhimraj A, Morgan R, Schumaker AH, et al. Infectious diseases society of America guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19. Available at: https://www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/covid-19-guideline-treatment-and-management/. Accessed 05/10/ 2021."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0007",
"unstructured": "NIH. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies. Available at: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/anti-sars-cov-2-antibody-products/anti-sars-cov-2-monoclonal-antibodies/. Accessed May 10, 2021."
},
{
"author": "Razonable",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0008",
"series-title": "A framework for outpatient infusion of anti-spike monoclonal antibodies to high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19: the mayo clinic model",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1467-6419.2007.00527.x",
"article-title": "Some practical guidance for the implementation of propensity score matching",
"author": "Caliendo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Econ Surv",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0009",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyy120",
"article-title": "Evaluating large-scale propensity score performance through real-world and synthetic data experiments",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2005",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int J Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0010",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "Hosmer",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0011",
"series-title": "Applied survival analysis: regression modeling of time-to-event data",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0012",
"unstructured": "Davidson-Pilon C, Kalderstam J, Zivich P, et al. CamDavidsonPilon/lifelines: v0. 21.3. Zenodo 2019."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area",
"author": "Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2052",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0013",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0014",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2029849",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0015",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Telemedicine consultations and follow-up of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Crane",
"issue": "9s",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0016",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Managing patients in the COVID-19 pandemic: a virtual multidisciplinary approach",
"author": "Ganesh",
"first-page": "118",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clinic Proc: Innovat, Qual Outcomes",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0017",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "O'Horo",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0018",
"series-title": "Outcomes of COVID-19 with the mayo clinic model of care and research",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0019",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19 - preliminary report",
"author": "Group",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0020",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Trends in mortality of hospitalised COVID-19 patients: a single centre observational cohort study from Spain",
"author": "Garcia-Vidal",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health Eur",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0021",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12788/jhm.3552",
"article-title": "Trends in COVID-19 risk-adjusted mortality rates",
"author": "Horwitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Hosp Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0022",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102_bib0023",
"unstructured": "Medicine JHU. Coronavirus resource center. Available at: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/. Accessed 06/02/ 2021."
}
],
"reference-count": 23,
"references-count": 23,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2589537021003825"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Casirivimab–Imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "40"
}