Frequency of Severe Vitamin D Deficiency and its Association with Mortality in Patients with Corona virus Disease
et al., Pakistan J. Med. Heal. Sci., 14:4, Dec 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
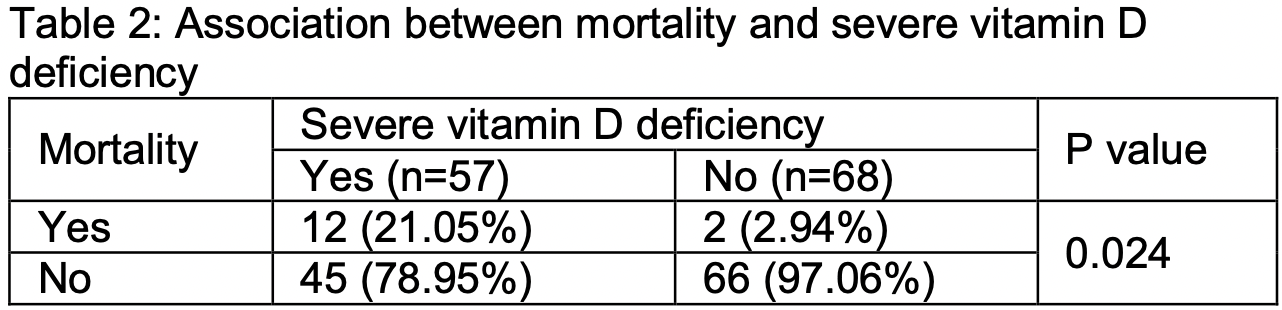
Prospective study of 125 severe COVID-19 patients in Pakistan, showing significantly higher mortality with vitamin D deficiency.
This is the 36th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of death, 86.0% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.02, high D levels (≥25nmol/L) 2 of 68 (2.9%), low D levels (<25nmol/L) 12 of 57 (21.1%), NNT 5.5.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ansari et al., 31 Dec 2020, prospective, Pakistan, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 31 August, 2020.
Frequency of Severe Vitamin D Deficiency and its Association with Mortality in Patients with Corona virus Disease
Aim: To determine the frequency of severe vitamin D deficiency and its association with mortality in patients presented with Covid-19.
References
Asghar, Kazmi, Ahmed, Akram, Khan et al., Clinical Profiles, Characteristics, and Outcomes of the First 100 Admitted COVID-19 Patients in Pakistan: a single-center retrospective study in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Karachi, Cureus
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Shah, Kandiah et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad Med J
Biesalski, Vitamin D deficiency and co-morbidities in COVID-19 patients -a fatal relationship?, NFS J
Carpagnano, Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J Endocrinol Invest
Cucinotta, Vanelli, WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic, Acta Biomedica: Atenei Parmensis
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, Nicolo et al., 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Forrest, Stuhldreher, Prevalence and correlates of vitamin D deficiency in US adults, Nutr Res
Garg, Kim, Whitaker, 'halloran, Cummings et al., Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019: COVID-NET, 14 States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Gheblawi, Wang, Viveiros, Nguyen, Zhong et al., Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2, Circulation Res
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Gruber-Bzura, Vitamin D and Influenza-Prevention or Therapy?, Int J Molecular Sci
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Huotari, Herzig, Vitamin D and living in northern latitudes -an endemic risk area for vitamin D deficiency, Int J Circumpolar Health
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res
Lamers, Beumer, Van Der Vaart, Knoops, Puschhof et al., SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human gut enterocytes, Science
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Pazoki, Kafan et al., Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS ONE
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Ortega, Serrano, Pujol, Rangel, Role of changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the interaction with the human ACE2 receptor: An in silico analysis, EXCLI journal
Owah, Fan, Dennett, Hagtvedt, Straube, Vitamin D levels and deficiency with different occupations: a systematic review, BMC Public Health
Panarese, Shahini, COVID-19, and vitamin D, Aliment Pharm Ther
Umhau, Casting sunlight on an epidemic: is vitamin D a critical host factor to prevent COVID-19?, Med Page Today
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respiratory Med
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury via regulation of the reninangiotensin system, Molecular Med Reports
