Efficacy of Favipiravir in treatment of mild & moderate COVID-19 infection in Nepal: a multi-center, randomized, open-labelled, phase III clinical trial
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.12.109, Mar 2022
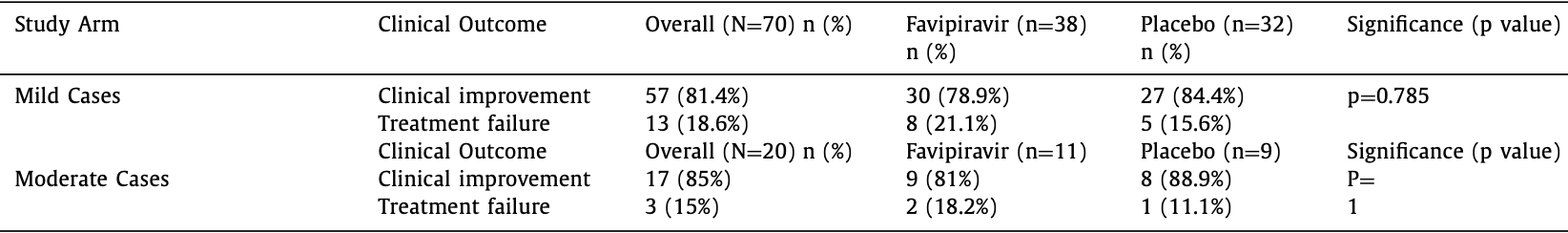
Preliminary report for an RCT in Nepal with 38 favipiravir patients and 32 control patients, showing no significant differences. There were no serious side effects.
Potential risks of favipiravir include kidney injury1-3, liver injury2-5, cardiovascular events5,6, pulmonary toxicity6,7, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, embryotoxicity, and the creation of dangerous variants8-14.
|
risk of no improvement, 40.4% higher, RR 1.40, p = 0.57, treatment 10 of 38 (26.3%), control 6 of 32 (18.8%), all.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 36.3% higher, RR 1.36, p = 0.75, treatment 8 of 27 (29.6%), control 5 of 23 (21.7%), mild cases.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 63.6% higher, RR 1.64, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 11 (18.2%), control 1 of 9 (11.1%), moderate cases.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Abdulaziz et al., Clinical Features and Prognosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospital-Admitted Patients with COVID-19 in Egypt: A Single-Center Experience, Mansoura Medical Journal, doi:10.58775/2735-3990.1433.
2.
Ülger et al., Experimental evaluation of favipiravir (T-705)-induced liver and kidney toxicity in rats, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115472.
3.
El-Fetouh et al., Experimental Studies on Some Drugs Used in Covid-19 Treatment (Favipiravir and Dexamethasone) in Albino Rats, Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research, 13:10, www.advetresearch.com/index.php/AVR/article/view/1635.
4.
Almutairi et al., Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study, Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed8020129.
5.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
6.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
7.
Ülger (B) et al., Evaluation of the effects of favipiravir (T-705) on the lung tissue of healty rats: An experimental study, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115235.
8.
Zhirnov et al., Favipiravir: the hidden threat of mutagenic action, Journal of microbiology, epidemiology and immunobiology, doi:10.36233/0372-9311-114.
9.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
10.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
11.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
12.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
Adhikari et al., 1 Mar 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Nepal, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period May 2020 - October 2020.
High SARS-CoV-2 attack rates among asymptomatic hospital workers from Ecuador
International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.12.107
Purpose: To determine the SARS-CoV-2 risk of infection in Ecuadorian hospital. This study aims to describe the SARS-CoV-2 attacks rate and viral loads among patient care workers and other staff from Ecuadorian hospitals during the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic. Methods & Materials: : Study design and setting. We carried out a cross-sectional study to describe the attack rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection among patient care workers (physicians, nurses and nursing assistants) and other healthcare personnel (administrative and services staff) from 9 hospitals of the Andean and Costal Regions of Ecuador from May to October 2020. Sample collection, RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis using the CDC protocol. The samples were processed in the BSL2 certified molecular biology laboratory at Universidad de Las Americas. Nasopharyngeal swabs were collected on 0.5mL TE pH 8 buffer for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis by RT-qPCR following an adapted version of the CDC protocol. Statistical analysis. Chi cuadrado with the statistic program SPSS Results: A total of 1243 patient care workers and 428 of other healthcare staff were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The SARS-CoV-2 attack rate was 12% (145/1243) for patient care workers and 19% (80/428) for other healthcare personnel, being this difference statistically significant (p < 0.05). For each hospital, the following SARS-CoV-2 attack rates were obtained for patient care workers and other staff: 35% and 50% in "Hogar ABEI", 21% and 26% in "Clínica Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe", 15% and 18% in "Hospital de Atención Integral al Adulto Mayor", 5% and 11% in "Hospital de Especialidades Eugenio Espejo", 12% and 22% in "Hospital Geriátrico Dr. Bolívar Arguello", 13% and 22% in "Hospital Dr. Gustavo Domínguez", 22% and 12% in "Hospital General Dr. Napoleón Dávila", 9% and 14% in "Hospital Pablo Arturo" and 5% and 13% in "Hospital San Francisco de Quito". Moreover, we found 47 individuals (19 among patient care workers and 28 among other staff) with viral loads larger than 10 8 copies/mL that may be considered super spreaders.
Conclusion: Ecuadorian hospital workers at a high-risk group for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Regular SARS-CoV-2 testing should be mandatory for this group as even asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 super spreaders can be detected.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.12.109",
"ISSN": [
"1201-9712"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2021.12.109",
"alternative-id": [
"S1201971221010018"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adhikari",
"given": "P.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koirala",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bista",
"given": "N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maleku",
"given": "K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Das",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhandari",
"given": "K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adhikari",
"given": "N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rawal",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandit",
"given": "K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gyawali",
"given": "P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pant",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"International Journal of Infectious Diseases"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-28T23:44:43Z",
"timestamp": 1646091883000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-28T23:44:44Z",
"timestamp": 1646091884000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-01T00:12:48Z",
"timestamp": 1646093568973
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1201-9712"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1646092800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1639267200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971221010018?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971221010018?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "S45-S46",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": null
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"International Journal of Infectious Diseases"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Efficacy of Favipiravir in treatment of mild & moderate COVID-19 infection in Nepal: a multi-center, randomized, open-labelled, phase III clinical trial"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "116"
}