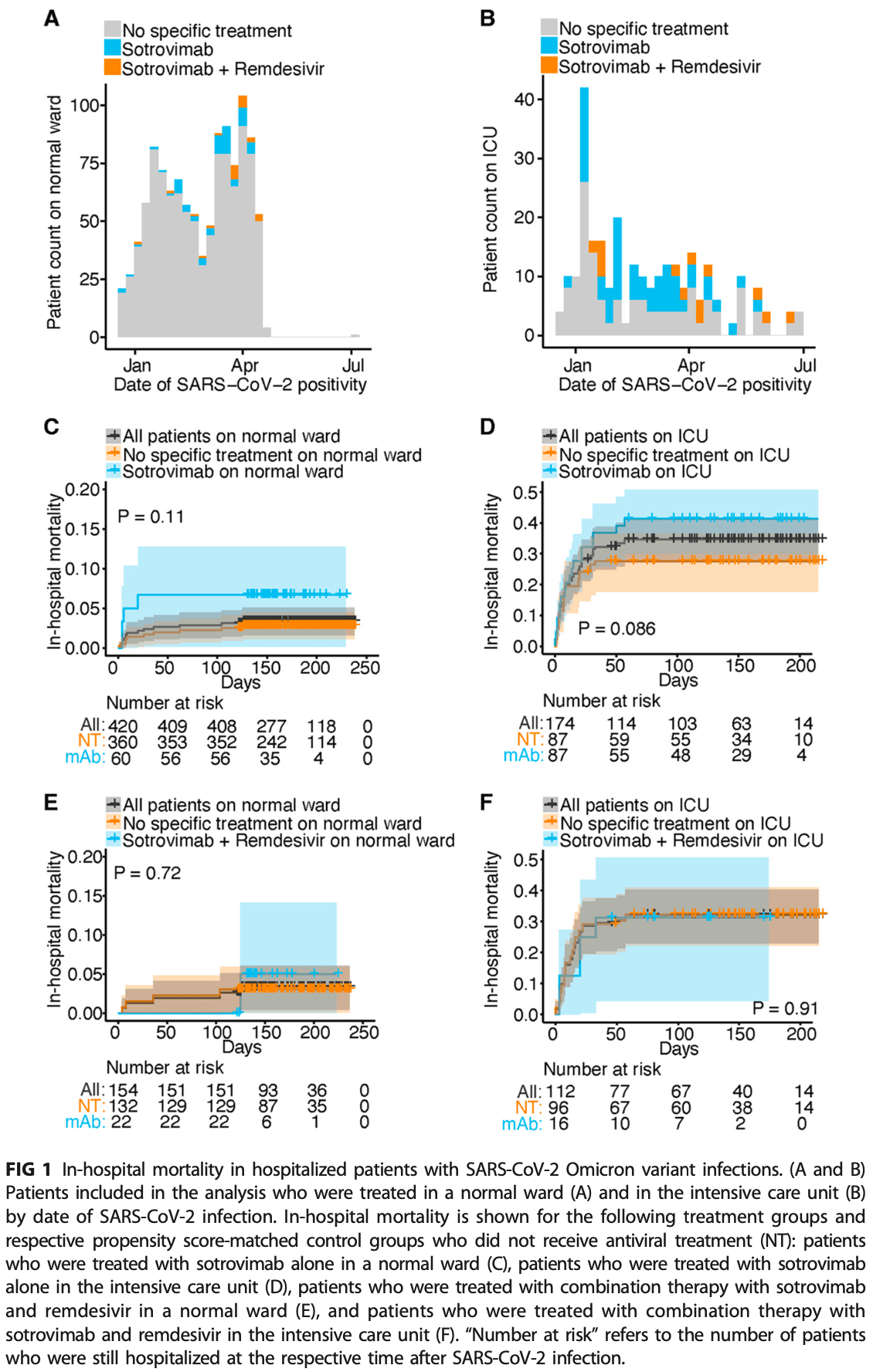
Sotrovimab in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Infection: a Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study
et al., Microbiology Spectrum, doi:10.1128/spectrum.04103-22, Dec 2022
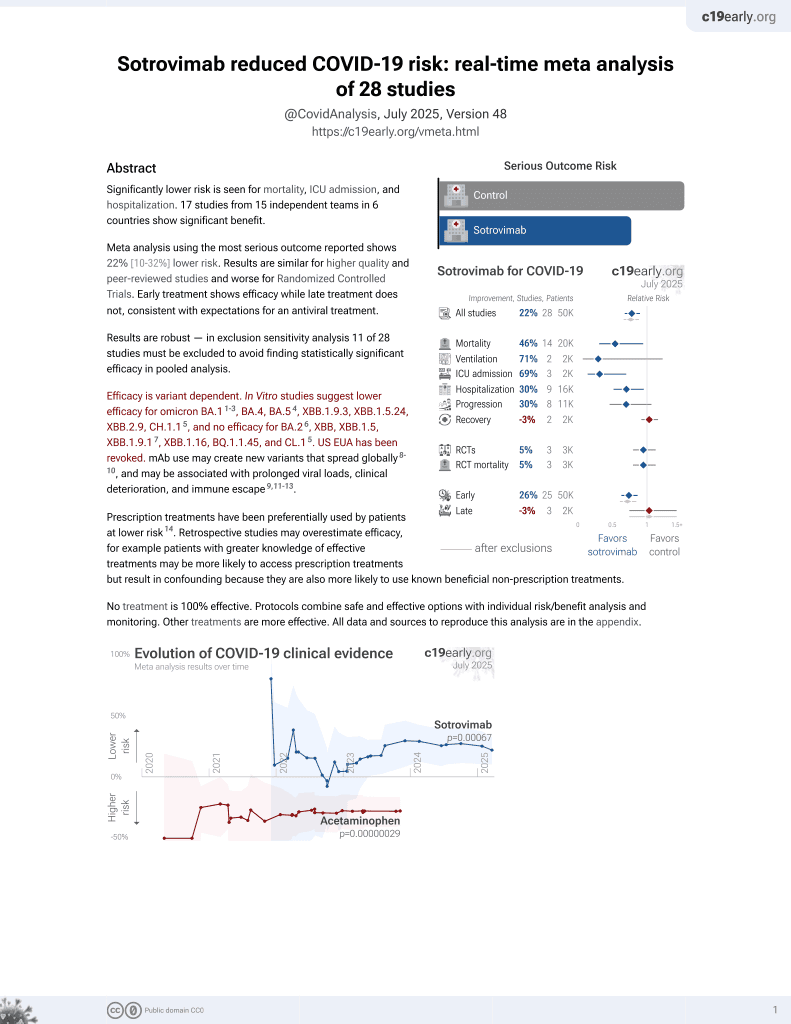
Sotrovimab for COVID-19
45th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2022, now with p = 0.00048 from 29 studies, recognized in 42 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
PSM retrospective 1,254 hospitalized patients in Germany, 147 treated with sotrovimab, showing higher mortality with sotrovimab, without statistical significance.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro studies predict lower efficacy for BA.11-3, BA.4, BA.54, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.2.9, CH.1.15, and no efficacy for BA.26, XBB, XBB.1.5, ХВВ.1.9.17, XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1.45, and CL.15. US EUA has been revoked.
|
risk of death, 140.0% higher, RR 2.40, p = 0.12, treatment 4 of 60 (6.7%), control 10 of 360 (2.8%), non-ICU, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of death, 50.0% higher, RR 1.50, p = 0.08, treatment 36 of 87 (41.4%), control 24 of 87 (27.6%), ICU, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Woo et al., 8 Dec 2022, retrospective, Germany, peer-reviewed, 13 authors.
Sotrovimab in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Infection: a Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study
Microbiology Spectrum, doi:10.1128/spectrum.04103-22
In vitro data suggest the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab may have lost inhibitory capability against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant. We aimed to provide real-life data on clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients. We retrospectively analyzed patients who were treated at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Germany, between December 2021 and June 2022. Out of all 1,254 patients, 185 were treated with sotrovimab: 147 patients received sotrovimab monotherapy, and 38 received combination treatment with sotrovimab and remdesivir. We compared in-hospital mortality for the different treatment regimens for patients treated on regular wards and the intensive care unit separately and performed propensity score matching by age, sex, comorbidities, immunosuppression, and additional dexamethasone treatment to select patients who did not receive antiviral treatment for comparison. No difference in in-hospital mortality was observed between any of the treatment groups and the respective control groups. These findings underline that sotrovimab adds no clinical benefit for hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infections. IMPORTANCE This study shows that among hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection at risk of disease progression, treatment with sotrovimab alone or in combination with remdesivir did not decrease in-hospital mortality. These real-world clinical findings in combination with previous in vitro data about lacking neutralizing activity of sotrovimab against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant do not support sotrovimab as a treatment option in these patients.
References
Bmj, Update to living WHO guideline on drugs for COVID-19, BMJ, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252
Brehm, Heyer, Roedl, Jarczak, Nierhaus et al., Patient characteristics and clinical course of COVID-19 patients treated at a German tertiary center during the first and second waves in the year 2020, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10112274
Brehm, Pfefferle, Possel, Karolyi, Zoufaly et al., Clinical efficacy and in vitro neutralization capacity of monoclonal antibodies for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 delta and omicron variants, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27916
Brehm, Van Der Meirschen, Hennigs, Roedl, Jarczak et al., Comparison of clinical characteristics and disease outcome of COVID-19 and seasonal influenza, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85081-0
Cao, Wang, Jian, Song, Yisimayi et al., Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3
Dejnirattisai, Huo, Zhou, Zahradník, Supasa et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Casal, Moya et al., Early treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107934
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Casal, Moya et al., Effect of sotrovimab on hospitalization or death among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.2832
Iketani, Liu, Guo, Liu, Chan et al., Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4
Nörz, Grunwald, Olearo, Fischer, Aepfelbacher et al., Evaluation of a fully automated high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 multiplex qPCR assay with built-in screening functionality for del-HV69/70-and N501Y variants such as B.1.1.7, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104894
Nörz, Grunwald, Tang, Olearo, Günther et al., Rapid automated screening for SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 lineage variants (Delta/ Kappa) through a versatile toolset of qPCR-based SNP detection, Diagnostics, doi:10.3390/diagnostics11101818
Nörz, Grunwald, Tang, Weinschenk, Günther et al., Clinical evaluation of a fully-automated high-throughput multiplex screening-assay to detect and differentiate the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1, Omicron), doi:10.3390/v14030608
Piccicacco, Zeitler, Ing, Montero, Faughn et al., Real-world effectiveness of early remdesivir and sotrovimab in the highest-risk COVID-19 outpatients during the Omicron surge, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkac256
Takashita, Yamayoshi, Simon, Van Bakel, Sordillo et al., Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against Omicron BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5 subvariants, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2207519
Vangeel, Chiu, Jonghe, Maes, Slechten et al., Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and other variants of concern, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252
Who, WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/spectrum.04103-22",
"ISSN": [
"2165-0497"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.04103-22",
"abstract": "<jats:p>\n This study shows that among hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection at risk of disease progression, treatment with sotrovimab alone or in combination with remdesivir did not decrease in-hospital mortality. These real-world clinical findings in combination with previous\n <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic>\n data about lacking neutralizing activity of sotrovimab against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant do not support sotrovimab as a treatment option in these patients.\n </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/spectrum.04103-22"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-10-08"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-11-17"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-12-08"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Neuroimmunology and Multiple Sclerosis (INIMS), Center for Molecular Neurobiology Hamburg (ZMNH), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Woo",
"given": "Marcel S.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1737-161X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I. Department of Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
},
{
"name": "German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Lübeck-Borstel-Riems, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Brehm",
"given": "Thomas Theo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Intensive Care Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Fischer",
"given": "Marlene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I. Department of Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Heyer",
"given": "Andreas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Intensive Care Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Wichmann",
"given": "Dominic",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I. Department of Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Jordan",
"given": "Sabine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4001-7192",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Medical Microbiology, Virology and Hygiene, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Nörz",
"given": "Dominik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Lübeck-Borstel-Riems, Hamburg, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Medical Microbiology, Virology and Hygiene, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Lütgehetmann",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I. Department of Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
},
{
"name": "German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Lübeck-Borstel-Riems, Hamburg, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Infection Research and Vaccine Development (IIRVD), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Addo",
"given": "Marylyn M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I. Department of Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
},
{
"name": "German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Lübeck-Borstel-Riems, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Lohse",
"given": "Ansgar W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I. Department of Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
},
{
"name": "German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Lübeck-Borstel-Riems, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Schmiedel",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Intensive Care Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Kluge",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I. Department of Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany"
},
{
"name": "German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Lübeck-Borstel-Riems, Hamburg, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Schulze zur Wiesch",
"given": "Julian",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Microbiology Spectrum",
"container-title-short": "Microbiol Spectr",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-08T14:01:43Z",
"timestamp": 1670508103000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-08T14:01:45Z",
"timestamp": 1670508105000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jhaveri",
"given": "Tulip A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-08T14:43:58Z",
"timestamp": 1670510638301
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1670457600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1670457600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/spectrum.04103-22",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/spectrum.04103-22",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_3_3_2_2",
"unstructured": "WHO. 2022. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27916",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2207519",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_7_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_3_8_2",
"unstructured": "European Commission. 2022. Union Register of medicinal products for human use. ECUrompfhuAa. https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1562.htm."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.2832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107934",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10112274",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85081-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac256",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_13_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_3_14_2",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency. 2022. Veklury. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/veklury."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o2224",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14030608",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics11101818",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104894",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_19_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/spectrum.04103-22"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Cell Biology",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Genetics",
"General Immunology and Microbiology",
"Ecology",
"Physiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Sotrovimab in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Infection: a Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page"
}