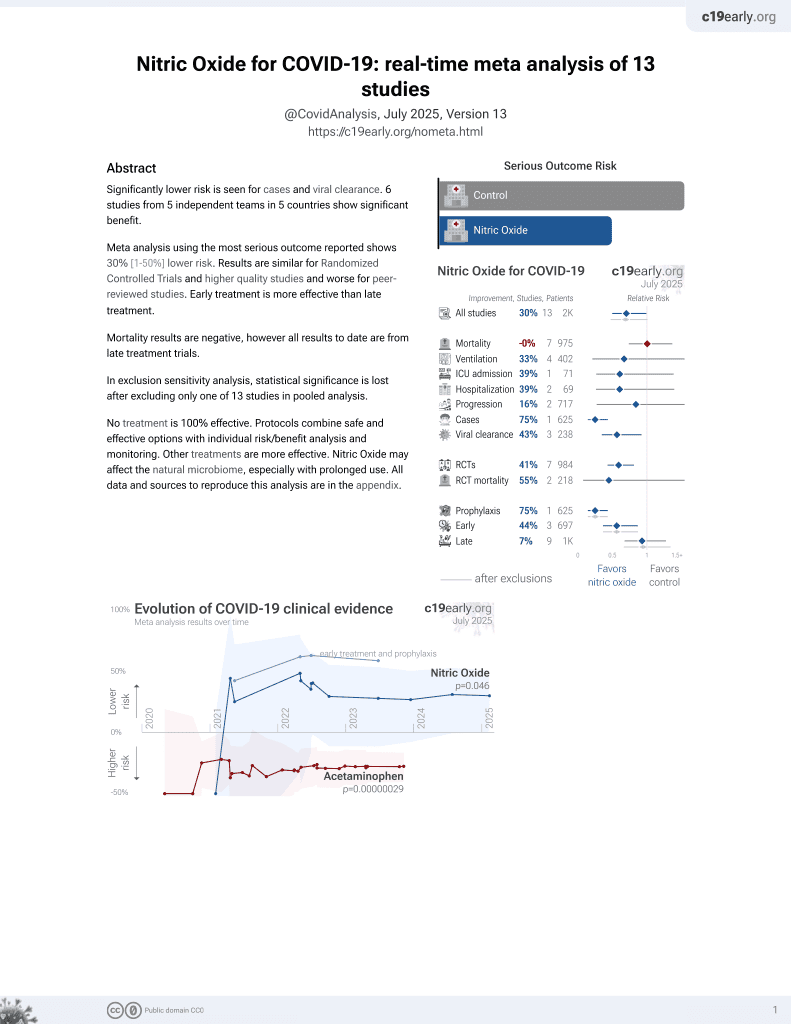
A safety evaluation of intermittent high-dose inhaled nitric oxide in viral pneumonia due to COVID-19: a randomised clinical study
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-68055-w, Jul 2024
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
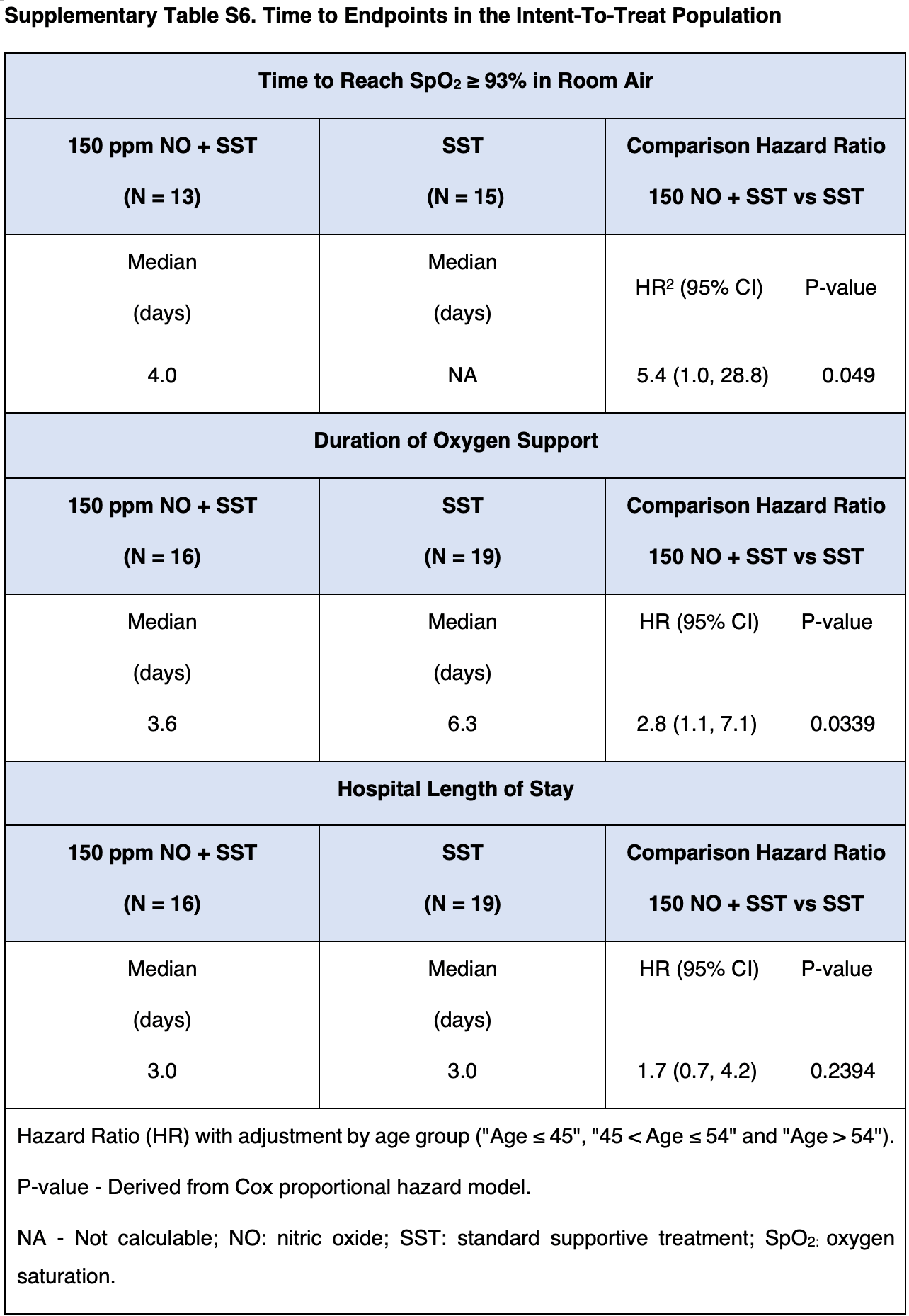
RCT 35 hospitalized patients with viral pneumonia (34 with COVID-19) showing improved recovery with high-dose inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) treatment. The treatment group received intermittent inhalations of 150 ppm iNO for 40 minutes, 4 times daily for up to 7 days. The treatment group had significantly reduced oxygen support duration and a greater number of patients reaching oxygen saturation ≥93%. There was also a trend towards earlier hospital discharge in the iNO group, without statistical significance. The study was terminated early. There was no ICU admission or mortality in either group.
|
oxygen support time, 64.3% lower, HR 0.36, p = 0.03, treatment 16, control 19, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
time to SpO2≥93, 81.5% lower, HR 0.19, p = 0.049, treatment 16, control 19, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
hospitalization time, 41.2% lower, HR 0.59, p = 0.24, treatment 16, control 19, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Wolak et al., 26 Jul 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, Israel, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: talyaw@szmc.org.il.
A safety evaluation of intermittent high-dose inhaled nitric oxide in viral pneumonia due to COVID-19: a randomised clinical study
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-68055-w
High-dose inhaled Nitric Oxide (iNO) has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, vasodilator, and antimicrobial properties, resulting in improved arterial oxygenation as well as a beneficial therapeutic effect on lower respiratory tract infections. This study evaluated the safety and efficacy of 150-ppm intermittent iNO administered with a novel iNO-generator, for treating adults hospitalised for viral pneumonia. In this prospective, open-label, multicenter study, subjects aged 18-80, diagnosed with viral pneumonia received either standard supportive treatment alone (Control-Group) or combined with iNO for 40 min, 4 times per day up to 7 days (Treatment-Group). Out of 40 recruited subjects, 35 were included in the intention-to-treat population (34 with COVID-19). Adverse Events rate was similar between the groups (56.3% vs. 42.1%; respectively). No treatment-related adverse events were reported, while 2 serious adverse events were accounted for by underlying pre-existing conditions. Among the Treatment-Group, oxygen support duration was reduced by 2.7 days (Hazard Ratio = 2.8; p = 0.0339), a greater number of subjects reached oxygen saturation ≥ 93% within hospitalisation period (Hazard Ratio = 5.4; p = 0.049), and a trend for earlier discharge was demonstrated. Intermittent 150-ppm iNO-treatment is well-tolerated, safe, and beneficial compared to usual care for spontaneously breathing hospitalised adults diagnosed with COVID-19 viral pneumonia. For over 25 years, inhaled Nitric Oxide (iNO) therapy has been used as a rescue treatment to improve arterial oxygenation in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome 1,2 , a major complication of Viral Pneumonia (VP). Nitric Oxide (NO) is a gas produced from arginine in mammalian cells by three NO synthase (NOS) enzymes: neuronal, endothelial, and inducible NO synthase (iNOS) 3 . Endogenous NO is an endothelium-derived relaxing factor that plays key roles in vascular signalling and blood flow regulation, induces vasodilation, and host defence against various microbial pathogens including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites 4-6 . Following infection or cytokine stimulation, pulmonary iNOS expression is upregulated in macrophages and neutrophils, which play an important protective role against infectious organisms 7 . At high doses, NO demonstrates antimicrobial properties against a variety of infectious microorganisms. Pre-clinical and clinical evidence suggests iNO presents favourable clinical applications as a treatment of lung infections, due to multiple therapeutic properties including the potential reduction in microbial load [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] . VP is a serious threat to global health, especially after the outbreak of the coronavirus disease during 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Approximately 6 million cases of community-acquired pneumonia occur annually, with over 20% requiring hospitalisation 15 and a similar percentage presenting severe-critical pneumonia 16 . Along with the severe acute..
Author contributions Prof. TW supervised the study at her site, and has also drafted, reviewed, and revised the manuscript. Drs. DD, YS, AR and Prof. AG coordinated and supervised the study at their respective sites, and were responsible for the conduct of the study according to the study protocol under stringent GCP rules, with the ongoing monitoring of a contract research organization (CRO). They also performed data acquisition and interpretation and critically reviewed the manuscript. Ms. MS was in charge of treatment aspects at respective site. Prof. AT conceptualized and designed the study, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Competing interests Because of the perception of a conflict of interest and in the interest of full transparency, we are disclosing the relationships between Profs. Talya Wolak, Asher Tal, Alon Grossman and Dr. Dror Dicker and Beyond Air Inc. All four authors have signed contracts with the company. Prof Wolak received payment including traveling fees for attending a conference and all payments were made through her affiliated institution. Prof. Tal bought stocks, received a stock option grant, and consulting fees. Drs. Dicker and Grossman received payment through their affiliated institutions.
Additional information
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10...
References
Achangwa, Collateral impact of public health and social measures on respiratory virus activity during the COVID-19 pandemic 2020-2021, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14051071
Ader, Remdesivir plus standard of care versus standard of care alone for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (DisCoVeRy): A phase 3, randomised, controlled, open-label trial, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00485-0
Adusumilli, Zhang, Friedman, Friedman, Harnessing nitric oxide for preventing, limiting and treating the severe pulmonary consequences of COVID-19, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2020.07.003
Akaberi, Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro, Redox Biol
Akerström, Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005
Alqahtani, Inhaled nitric oxide for clinical management of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph191912803
Bentur, Pilot study to test inhaled nitric oxide in cystic fibrosis patients with refractory Mycobacterium abscessus lung infection, J. Cyst. Fibros, doi:10.1016/j.jcf.2019.05.002
Bogdan, Nitric oxide and the immune response, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/ni1001-907
Buchanan, Li, Hendrickson, Bhargava, Roychoudhury, Assessing adverse events in clinical trials during the era of the COVID-19 pandemic, J. Biopharmaceut. Stat, doi:10.1080/10543406.2023.2170398
Darwish, Miller, Kain, Liles, Inhaled nitric oxide therapy fails to improve outcome in experimental severe influenza, Int. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.7150/ijms.3880
Di Fenza, High-dose inhaled nitric oxide in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19: A multicenter phase 2 trial, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202304-0637OC
Fang, Antimicrobial reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: Concepts and controversies, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/nrmicro1004
Feng, Impact of COVID-19 outbreaks and interventions on influenza in China and the United States, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23440-1
Flume, Inhaled nitric oxide for adults with pulmonary non-tuberculous mycobacterial infection, Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2022.107069
Freeman, Leigh, Pneumonia, None
Garren, Nitric oxide and viral infection: Recent developments in antiviral therapies and platforms, Appl. Mater Today, doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100887
Goldbart, Inhaled nitric oxide for the treatment of acute bronchiolitis: A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate dose response, Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc, doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202103-348OC
Goldbart, Inhaled nitric oxide therapy in acute bronchiolitis: A multicenter randomized clinical trial, correction appears in Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-66433-8
Gottlieb, Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116846
Hajian, Pulmonary vascular effects of pulsed inhaled nitric oxide in COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension, Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon Dis, doi:10.2147/COPD.S106480
Hu, Overview of viral pneumonia associated with influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, and coronavirus, and therapeutics based on natural products of medicinal plants, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.630834
Ichinose, Roberts, Zapol, Inhaled nitric oxide: A selective pulmonary vasodilator: Current uses and therapeutic potential, Circulation, doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62
Kamenshchikov, Berra, Carroll, therapeutic effects of inhaled nitric oxide therapy in COVID-19 patients, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020369
Kanda, Indirect impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the incidence of non-COVID-19 infectious diseases: A regionwide, patient-based database study in Japan, Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2022.10.018
Keyaerts, Growth kinetics of SARS-coronavirus in vero E6 cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun
Lisi, Zelikin, Chandrawati, Nitric oxide to fight viral infections, Adv. Sci
Liu, Zhou, Yang, The cytokine storm of severe influenza and development of immunomodulatory therapy, Cell Mol. Immunol, doi:10.1038/cmi.2015.74
Lolascon, Recommendations for diagnosis and treatment of methemoglobinemia, Am. J. Hematol, doi:10.1002/ajh.26340
Majumdar, Eurich, Gamble, Senthilselvan, Marrie, Oxygen saturations less than 92% are associated with major adverse events in outpatients with pneumonia: A population-based cohort study, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciq076
Mayorga, Overview of nitrogen dioxide effects on lung with emphasis on military, relevance, Toxicology, doi:10.1016/0300-483x(94)90097-3
Nathan, Reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the relationship between mammalian hosts and microbial pathogens, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
Pagliano, Characteristics of viral pneumonia in the COVID-19 era: An update, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-021-01603-y
Ragab, The COVID-19 cytokine storm; What we know so far, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446
Regev-Shoshani, Gaseous nitric oxide reduces influenza infectivity in vitro, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2013.03.007
Ricciardolo, Multiple roles of nitric oxide in the airways, Thorax, doi:10.1136/thorax.58.2.175
Rossaint, Lewandowski, Zapol, Our paper 20 years later: Inhaled nitric oxide for the acute respiratory distress syndrome-discovery, current understanding, and focused targets of future applications, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-014-3458-6
Safaee, High concentrations of nitric oxide inhalation therapy in pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Obstet. Gynecol, doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004128
Safaee, Inhaled high dose nitric oxide is a safe and effective respiratory treatment in spontaneous breathing hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2021.08.003
Schulz, Altman, Moher, Consort Group, CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.c332
Sorbo, High doses of inhaled nitric oxide as an innovative antimicrobial strategy for lung infections, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10071525
Srivastava, Assessment of nitric oxide (NO) potential to mitigate COVID-19 severity, Virusdisease, doi:10.1007/s13337-021-00702-6
Tal, Nitric oxide inhalations in bronchiolitis: A pilot, randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial, Pediatr Pulmonol, doi:10.1002/ppul.23905
Tin Tin Htar, Yerramalla, Moïsi, Swerdlow, The burden of respiratory syncytial virus in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Epidemiol. Infect, doi:10.1017/S0950268820000400
Valsecchi, High-dose inhaled nitric oxide for the treatment of spontaneously breathing pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia, Obstet. Gynecol, doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004847
Wang, Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
Wiegand, Antimicrobial effects of nitric oxide in murine models of Klebsiella pneumonia, Redox. Biol
Wiegand, Rescue treatment with high-dose gaseous nitric oxide in spontaneously breathing patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019, Crit. Care Explor, doi:10.1097/CCE.0000000000000277
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72,314 cases from the Chinese Center for disease control and prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Zhao, Inhaled nitric oxide: can it serve as a savior for COVID-19 and related respiratory and cardiovascular diseases?, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277552
Åkerström, Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: Viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected, Virology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-68055-w",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-68055-w",
"alternative-id": [
"68055"
],
"article-number": "17201",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "7 March 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "19 July 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "26 July 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "Because of the perception of a conflict of interest and in the interest of full transparency, we are disclosing the relationships between Profs. Talya Wolak, Asher Tal, Alon Grossman and Dr. Dror Dicker and Beyond Air Inc. All four authors have signed contracts with the company. Prof Wolak received payment including traveling fees for attending a conference and all payments were made through her affiliated institution. Prof. Tal bought stocks, received a stock option grant, and consulting fees. Drs. Dicker and Grossman received payment through their affiliated institutions."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolak",
"given": "Talya",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dicker",
"given": "D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shifer",
"given": "Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grossman",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rokach",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shitrit",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tal",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-27T00:03:07Z",
"timestamp": 1722038587000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-27T00:15:10Z",
"timestamp": 1722039310000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Beyond Air Inc."
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-28T00:19:25Z",
"timestamp": 1722125965374
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1721952000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1721952000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-68055-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-68055-w",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-68055-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR1",
"unstructured": "Ichinose, F., Roberts, J. D. Jr. & Zapol, W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide: A selective pulmonary vasodilator: Current uses and therapeutic potential. Circulation. 109, 3106–3111. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62 (2004)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-014-3458-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR2",
"unstructured": "Rossaint, R., Lewandowski, K. & Zapol, W. M. Our paper 20 years later: Inhaled nitric oxide for the acute respiratory distress syndrome—discovery, current understanding, and focused targets of future applications. Intensive Care Med. 40, 1649–1658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-014-3458-6 (2014)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.07.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR3",
"unstructured": "Adusumilli, N. C., Zhang, D., Friedman, J. M. & Friedman, A. J. Harnessing nitric oxide for preventing, limiting and treating the severe pulmonary consequences of COVID-19. Nitric Oxide. 103, 4–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2020.07.003 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni1001-907",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR4",
"unstructured": "Bogdan, C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2, 907–916. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1001-907 (2001)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro1004",
"author": "FC Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "820",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "68055_CR5",
"unstructured": "Fang, F. C. Antimicrobial reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: Concepts and controversies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2(10), 820–832. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1004 (2004).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/COPD.S106480",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR6",
"unstructured": "Hajian, B. et al. Pulmonary vascular effects of pulsed inhaled nitric oxide in COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon Dis. 11, 1533–1541. https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S106480 (2016)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.58.2.175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR7",
"unstructured": "Ricciardolo, F. L. Multiple roles of nitric oxide in the airways. Thorax. 58, 175–182. https://doi.org/10.1136/thorax.58.2.175 (2003)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10071525",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR8",
"unstructured": "Sorbo, L. D. et al. High doses of inhaled nitric oxide as an innovative antimicrobial strategy for lung infections. Biomedicines. 10, 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071525 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202304-0637OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR9",
"unstructured": "Di Fenza, R. et al. High-dose inhaled nitric oxide in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19: A multicenter phase 2 trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 208, 1293–1304. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202304-0637OC (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2022.107069",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR10",
"unstructured": "Flume, P. A. et al. Inhaled nitric oxide for adults with pulmonary non-tuberculous mycobacterial infection. Respir. Med. 206, 107069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2022.107069 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcf.2019.05.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR11",
"unstructured": "Bentur, L. et al. Pilot study to test inhaled nitric oxide in cystic fibrosis patients with refractory Mycobacterium abscessus lung infection. J. Cyst. Fibros. 19, 225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcf.2019.05.002 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR12",
"unstructured": "Akerström, S. et al. Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 79, 1966–1969. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005 (2005)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"author": "S Åkerström",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology.",
"key": "68055_CR13",
"unstructured": "Åkerström, S. et al. Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: Viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected. Virology. 395, 1–9 (2009).",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100887",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR14",
"unstructured": "Garren, M. R. et al. Nitric oxide and viral infection: Recent developments in antiviral therapies and platforms. Appl. Mater Today. 22, 100887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100887 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.630834",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR15",
"unstructured": "Hu, Z. et al. Overview of viral pneumonia associated with influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, and coronavirus, and therapeutics based on natural products of medicinal plants. Front. Pharmacol. 12: 630834. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.630834 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR16",
"unstructured": "Wu, Z. & McGoogan, J. M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72,314 cases from the Chinese Center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 323,1239–1242. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2648 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268820000400",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR17",
"unstructured": "Tin Tin Htar, M., Yerramalla, M. S., Moïsi, J. C. & Swerdlow, D. L. The burden of respiratory syncytial virus in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Infect. 148: e48. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268820000400 (2020)."
},
{
"key": "68055_CR18",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD). Preliminary Estimated Influenza Illnesses, Medical visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths in the United States – 2021–2022 influenza seasonhttps://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/burden/2021-2022.htm#:~:text=The%20overall%20burden%20of%20influenza,flu%20deaths%20 (2022)."
},
{
"key": "68055_CR19",
"unstructured": "U.S. Food and Drug Administration, The Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH). LungFit® PH - P200044 https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/recently-approved-devices/lungfit-ph-p200044 (2022)."
},
{
"key": "68055_CR20",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency. INOmax nitric chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/overview/inomax-epar-summary-public_en.pdf (2011)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/AOG.0000000000004847",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR21",
"unstructured": "Valsecchi, C. et al. High-dose inhaled nitric oxide for the treatment of spontaneously breathing pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia. Obstet. Gynecol. 140, 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000004847 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2021.08.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR22",
"unstructured": "Safaee, F. B. et al. Inhaled high dose nitric oxide is a safe and effective respiratory treatment in spontaneous breathing hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Nitric Oxide. 11, 7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2021.08.003 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/AOG.0000000000004128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR23",
"unstructured": "Safaee, F. B. et al. High concentrations of nitric oxide inhalation therapy in pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Obstet. Gynecol. 136, 1109–1113; https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000004128 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000277",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR24",
"unstructured": "Wiegand, S. B. et al. Rescue treatment with high-dose gaseous nitric oxide in spontaneously breathing patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019. Crit. Care Explor. 2, e0277. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCE.0000000000000277 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10020369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR25",
"unstructured": "Kamenshchikov, N. O., Berra, L. & Carroll, R. W. therapeutic effects of inhaled nitric oxide therapy in COVID-19 patients. Biomedicines. 10, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020369 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.23905",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR26",
"unstructured": "Tal, A. et al. Nitric oxide inhalations in bronchiolitis: A pilot, randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial. Pediatr Pulmonol. 53, 95–102.https://doi.org/10.1002/ppul.23905 (2018)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-66433-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR27",
"unstructured": "Goldbart, A. et al. Inhaled nitric oxide therapy in acute bronchiolitis: A multicenter randomized clinical trial [published correction appears in Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 14;10(1):17640]. Sci. Rep. 10, 9605. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66433-8 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1513/AnnalsATS.202103-348OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR28",
"unstructured": "Goldbart, A. et al. Inhaled nitric oxide for the treatment of acute bronchiolitis: A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate dose response. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 20, 236–244. https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.202103-348OC (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2013.03.007",
"author": "G Regev-Shoshani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide.",
"key": "68055_CR29",
"unstructured": "Regev-Shoshani, G. et al. Gaseous nitric oxide reduces influenza infectivity in vitro. Nitric Oxide. 31, 48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2013.03.007 (2013).",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734",
"author": "D Akaberi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "68055_CR30",
"unstructured": "Akaberi, D. et al. Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro. Redox Biol. 37, 101734 (2020).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.02.085",
"author": "E Keyaerts",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1147",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "68055_CR31",
"unstructured": "Keyaerts, E. et al. Growth kinetics of SARS-coronavirus in vero E6 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 329, 1147–2115 (2005).",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101826",
"author": "SB Wiegand",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Redox. Biol.",
"key": "68055_CR32",
"unstructured": "Wiegand, S. B. et al. Antimicrobial effects of nitric oxide in murine models of Klebsiella pneumonia. Redox. Biol. 39, 101826 (2021).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR33",
"unstructured": "Gottlieb, R. L. et al. Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 305–315. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2116846 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10543406.2023.2170398",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR34",
"unstructured": "Buchanan, J., Li, M., Hendrickson, B., Bhargava, P., & Roychoudhury S. Assessing adverse events in clinical trials during the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Biopharmaceut. Stat. 33, 466–475. https://doi.org/10.1080/10543406.2023.2170398 (2023)."
},
{
"key": "68055_CR35",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Nitrogen Dioxide https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/10102440.html (2018)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0300-483x(94)90097-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR36",
"unstructured": "Mayorga, M. Overview of nitrogen dioxide effects on lung with emphasis on military. relevance, Toxicology. 89, 175–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483x(94)90097-3 (1994)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.26340",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR37",
"unstructured": "Lolascon, A. et al. Recommendations for diagnosis and treatment of methemoglobinemia. Am. J. Hematol. 96, 1666–1678. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.26340 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-021-01603-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR38",
"unstructured": "Pagliano, P. et al. Characteristics of viral pneumonia in the COVID-19 era: An update. Infection. 49, 607–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-021-01603-y (2021)."
},
{
"key": "68055_CR39",
"unstructured": "Freeman, A. M. & Leigh, Jr T. R. Viral Pneumonia. (StatPearls, 2022). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513286/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR40",
"unstructured": "Wang, M. et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 30, 269–271. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00485-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR41",
"unstructured": "Ader, F. et al. Remdesivir plus standard of care versus standard of care alone for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (DisCoVeRy): A phase 3, randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 22, 209–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00485-0 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13337-021-00702-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR42",
"unstructured": "Srivastava, S., et al. Assessment of nitric oxide (NO) potential to mitigate COVID-19 severity. Virusdisease. 32, 589–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-021-00702-6 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph191912803",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR43",
"unstructured": "Alqahtani, J. S. et al. Inhaled nitric oxide for clinical management of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 19, 12803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912803 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.97.16.8841",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "68055_CR44",
"unstructured": "Nathan, C. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the relationship between mammalian hosts and microbial pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 97, 8841–8848."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202003895",
"author": "F Lisi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2003895",
"journal-title": "Adv. Sci.",
"key": "68055_CR45",
"unstructured": "Lisi, F., Zelikin, A. N. & Chandrawati, R. Nitric oxide to fight viral infections. Adv. Sci. 8, 2003895 (2021).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277552",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR46",
"unstructured": "Zhao, Y. et al. Inhaled nitric oxide: can it serve as a savior for COVID-19 and related respiratory and cardiovascular diseases? Front. Microbiol. 14, 1277552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277552 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijms.3880",
"author": "I Darwish",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "68055_CR47",
"unstructured": "Darwish, I., Miller, C., Kain, K. C. & Liles, W. C. Inhaled nitric oxide therapy fails to improve outcome in experimental severe influenza. Int. J. Med. Sci. 9, 157–162. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.3880 (2012).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23440-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR48",
"unstructured": "Feng, L. et al. Impact of COVID-19 outbreaks and interventions on influenza in China and the United States. Nat. Commun. 12, 3249. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23440-1 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.puhe.2022.10.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR49",
"unstructured": "Kanda, N. et al. Indirect impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the incidence of non-COVID-19 infectious diseases: A region-wide, patient-based database study in Japan. Public Health. 214, 20–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2022.10.018 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cmi.2015.74",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR50",
"unstructured": "Liu, Q., Zhou, Y. H. & Yang, Z. Q. The cytokine storm of severe influenza and development of immunomodulatory therapy. Cell Mol. Immunol. 13, 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.74 (2016)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR51",
"unstructured": "Ragab, D. et al. The COVID-19 cytokine storm; What we know so far. Front. Immunol. 11, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14051071",
"author": "C Achangwa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1071",
"journal-title": "Viruses.",
"key": "68055_CR52",
"unstructured": "Achangwa, C. et al. Collateral impact of public health and social measures on respiratory virus activity during the COVID-19 pandemic 2020–2021. Viruses. 14, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051071 (2022).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.c332",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "68055_CR53",
"unstructured": "Schulz, K. F., Altman, D. G., Moher, D. & CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ. 340, c332. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c332 (2010)."
},
{
"key": "68055_CR54",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciq076",
"author": "SR Majumdar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "325",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "68055_CR55",
"unstructured": "Majumdar, S. R., Eurich, D. T., Gamble, J. M., Senthilselvan, A. & Marrie, T. J. Oxygen saturations less than 92% are associated with major adverse events in outpatients with pneumonia: A population-based cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 52(3), 325–331. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciq076 (2011).",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2011"
}
],
"reference-count": 55,
"references-count": 55,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-68055-w"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A safety evaluation of intermittent high-dose inhaled nitric oxide in viral pneumonia due to COVID-19: a randomised clinical study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "14"
}