Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A rapid systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
et al., Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.3906, Dec 2023
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
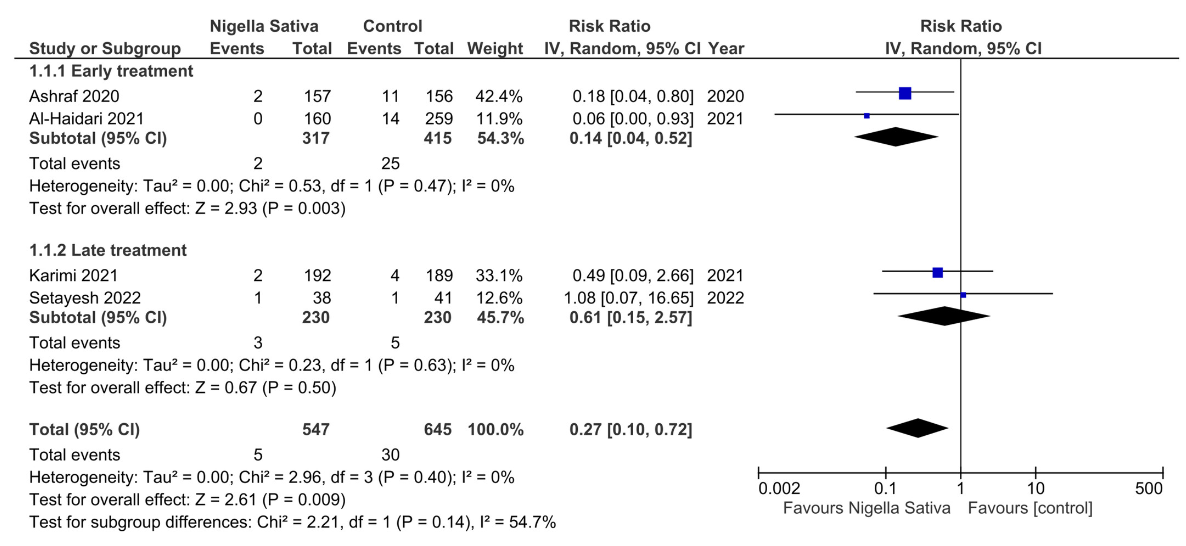
Systematic review and meta analysis of seven RCTs showing significantly lower mortality (RR 0.27) and improved viral clearance (RR 0.62) with nigella sativa treatment in COVID-19 patients. The mortality benefit was greater with early treatment within 5 days of symptom onset.
3 meta-analyses show significant improvements with nigella sativa for mortality1-3,
progression3, and
viral clearance2.
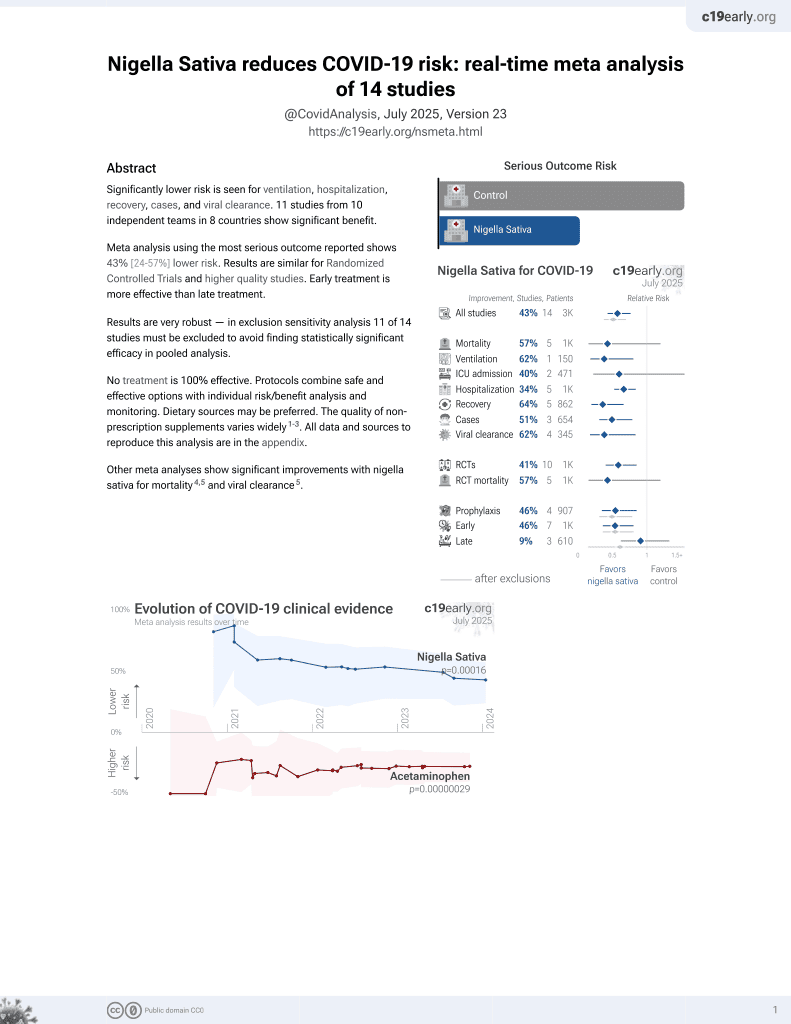
Currently there are 14 nigella sativa for COVID-19 studies, showing 57% lower mortality [-20‑85%], 62% lower ventilation [19‑82%], 40% lower ICU admission [-61‑78%], 34% lower hospitalization [16‑47%], and 51% fewer cases [21‑69%].
|
risk of death, 73.0% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.009.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 74.0% lower, RR 0.26, p = 0.15.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 52.0% lower, OR 0.48, p = 0.10, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 38.0% lower, RR 0.62, p = 0.04.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Kow et al., The effect of Nigella sativa on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized trials, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7743.
Umer et al., 27 Dec 2023, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A rapid systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
doi:10.1002/fsn3.3906
Nigella sativa is an herbal therapy for various afflictions. It has some potential to be a promising option as an efficacious treatment for COVID-19 patients that can contribute to global healthcare as a relatively cheap therapy but evidence of its use from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) is limited. Therefore, to explore the effect of N. sativa in combating COVID-19, we undertook this meta-analysis. We searched several databases to retrieve all RCTs investigating N. sativa for the treatment of COVID-19 as compared to placebo or standard care. We used RevMan 5.4 for all analyses with risk ratio (RR) or odds ratio (OR) as the effect measures. We included a total of seven RCTs in this review. N. sativa significantly reduced the risk of allcause mortality in patients with COVID-19 compared to the control group (RR 0.27, 95% CI: 0.10 to 0.72; I 2 = 0%). N. sativa significantly reduced the rate of viral PCR positivity (RR 0.62, 95% CI: 0.39 to 0.97; I 2 = 0%). We did not find any significant difference in the risk of hospitalization (RR 0.26, 95% CI: 0.04 to 1.54; I 2 = 0%) and the rate of no recovery (OR 0.48, 95% CI: 0.20 to 1.15; I 2 = 84%) between the two groups. N. sativa is an easily available herbal medicine that may decrease the risk of mortality and improve virological clearance in COVID-19 patients. However, our results are limited by the small number of RCTs available. Further large-scale RCTs are needed to better understand the anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects of N. sativa in COVID-19 patients.
S U PP O RTI N G I N FO R M ATI O N Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section at the end of this article.
References
Agarwal, Rochwerg, Lamontagne, Siemieniuk, Agoritsas et al., A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379
Ali, Al-Haidari, Faiq, Ghareeb, Clinical trial of black seeds against COVID -19 in Kirkuk City/Iraq, Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, doi:10.37506/IJFMT.V15I3.15825
Ashraf, Ashraf, Ashraf, Imran, Kalsoom et al., Honey and Nigella sativa against COVID-19 in Pakistan (HNS-COVID-PK): A multicenter placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7640
Bencheqroun, Ahmed, Kocak, Villa, Barrera et al., A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ThymoQuinone formula (TQF) for treating outpatient SARS-CoV-2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/PATHOGENS11050551
Borczuk, Yantiss, The pathogenesis of coronavirus-19 disease, Journal of Biomedical Science, doi:10.1186/S12929-022-00872-5
Bordoni, Fedeli, Nasuti, Maggi, Papa et al., Antioxidant and antiinflammatory properties of Nigella sativa oil in human pre-adipocytes, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/ANTIOX8020051
Cheema, Sohail, Fatima, Shahid, Shahzil et al., Quercetin for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2427
Fatima, Azeem, Saeed, Shahid, Cheema, Efficacy and safety of molnupiravir for COVID-19 patients, European Journal of Internal Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2022.05.024
Gholamnezhad, Boskabady, Hosseini, Effect of Nigella sativa on immune response in treadmill exercised rat, BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1186/1472-6882-14-437/FIGURES/8
Hosseinzadeh, Tavakkoli, Mahdian, Razavi, Review on clinical trials of black seed (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, Thymoquinone, Journal of Pharmacopuncture, doi:10.3831/KPI.2017.20.021
Islam, Hossain, Sarker, Ferdous, Hannan et al., Revisiting pharmacological potentials of Nigella sativa seed: A promising option for COVID-19 prevention and cure, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/PTR.6895
Jakhmola Mani, Sehgal, Dogra, Saxena, Pande Katare, Deciphering underlying mechanism of Sars-CoV-2 infection in humans and revealing the therapeutic potential of bioactive constituents from Nigella sativa to combat COVID19: In-silico study, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1839560
Karimi, Zarei, Soleymani, Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Asadi et al., Efficacy of Persian medicine herbal formulations (capsules and decoction) compared to standard care in patients with COVID-19, a multicenter open-labeled, randomized, controlled clinical trial, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7277
Khazdair, Ghafari, Sadeghi, Possible therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and its thymoquinone on COVID-19, Pharmaceutical Biology, doi:10.1080/13880209.2021.1931353
Koshak, Koshak, Mobeireek, Badawi, Wali et al., Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19: An open-label randomized controlled clinical trial, Complementary Therapies in Medicine, doi:10.1016/J.CTIM.2021.102769
Koshak, Koshak, Nigella sativa L as a potential phytotherapy for coronavirus disease 2019: A mini review of in silico studies, Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental, doi:10.1016/J.CURTHERES.2020.100602
Kow, Ramachandram, Hasan, The effect of Nigella sativa on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7743
Lorenzo-Redondo, Ozer, Hultquist, Covid-19: Is omicron less lethal than delta?, BMJ, doi:10.1136/BMJ.O1806
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/BMJ.N71
Said, Abdulbaset, El-Kholy, Besckales, Sabri et al., The effect of Nigella sativa and vitamin D3 supplementation on the clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial, Integrative Medicine Research, doi:10.1016/J.IMR.2022.100869
Shafiee, Athar, Shahid, Ghafoor, Ayyan et al., Curcumin for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7724
Swamy, Tan, Cytotoxic and immunopotentiating effects of ethanolic extract of Nigella sativa L. seeds, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(98)00241-4
Umer, Black cumin seed essential oil, as a potent analgesic and antiinflammatory drug, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/PTR.1390