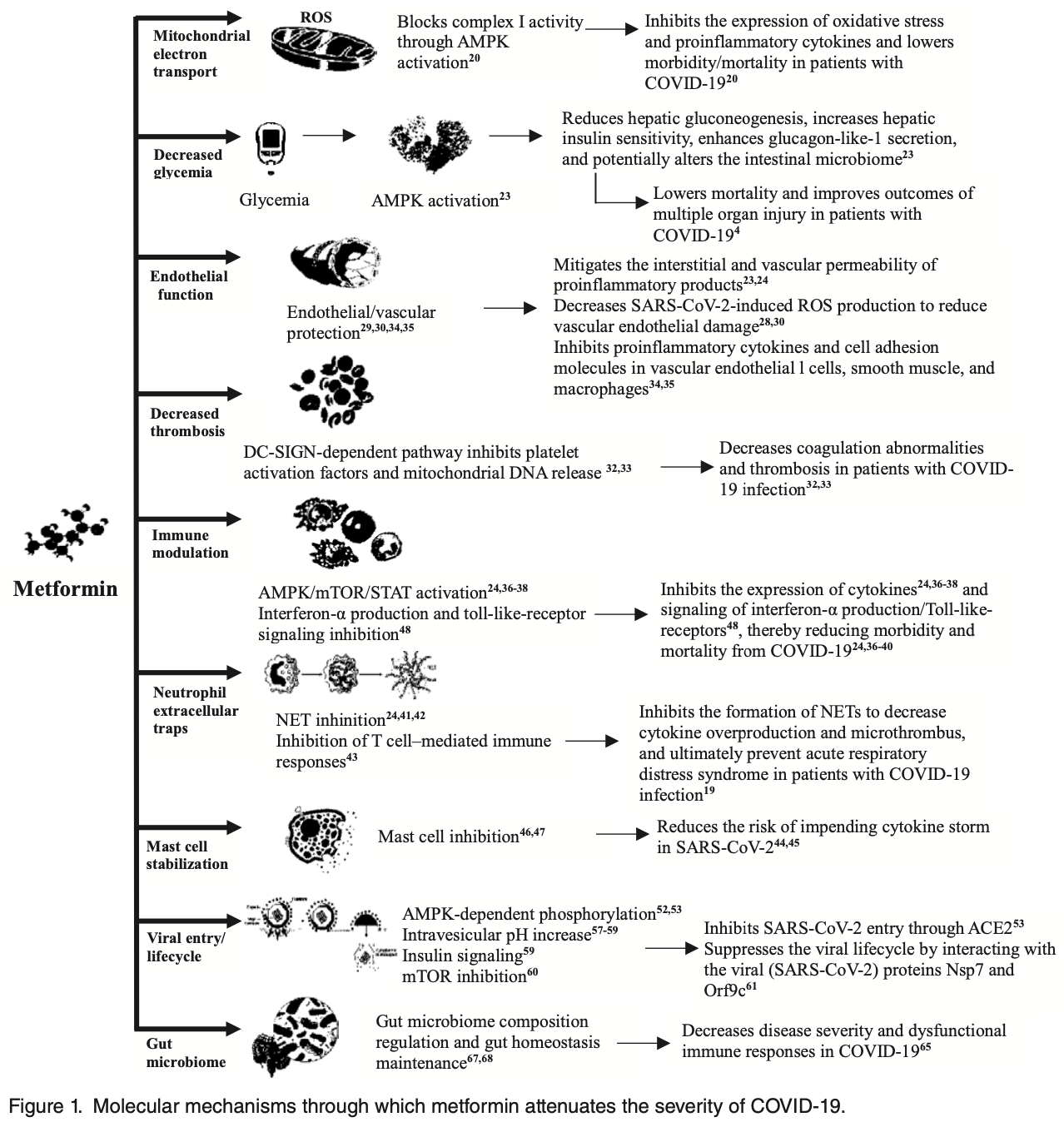
Metformin and Coronavirus Disease 2019: A New Deal for an Old Drug
, K., 內科學誌, doi:10.6314/JIMT.202308_34(4).04, Aug 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of metformin for COVID-19, particularly in patients with preexisting type 2 diabetes. Author summarizes the evidence that metformin has broad anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antiviral, and endothelial protective effects, in addition to its glucose lowering properties. These pleiotropic mechanisms may underlie observational data showing reduced morbidity and mortality in metformin-treated diabetic COVID-19 patients compared to those not on metformin. The molecular pathways inhibited by metformin, including AMPK, mTOR, cytokine signaling, neutrophil extracellular traps, and viral entry receptors, are implicated in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Author notes that metformin is contraindicated with kidney dysfunction or respiratory distress, requiring close monitoring if administered to hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
1.
Monsalve et al., NETosis: A key player in autoimmunity, COVID-19, and long COVID, Journal of Translational Autoimmunity, doi:10.1016/j.jtauto.2025.100280.
2.
Halabitska et al., Metformin in Antiviral Therapy: Evidence and Perspectives, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16121938.
3.
Plowman et al., Anti-Inflammatory Potential of the Anti-Diabetic Drug Metformin in the Prevention of Inflammatory Complications and Infectious Diseases Including COVID-19: A Narrative Review, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms25105190.
4.
De Jesús-González et al., A Dual Pharmacological Strategy against COVID-19: The Therapeutic Potential of Metformin and Atorvastatin, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms12020383.
5.
Halma et al., Exploring autophagy in treating SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-related pathology, Endocrine and Metabolic Science, doi:10.1016/j.endmts.2024.100163.
6.
Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a Protein as a Therapeutic Target against COVID-19 and Long-Term Post-Infection Effects, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens13010075.
7.
Gomaa et al., Pharmacological evaluation of vitamin D in COVID-19 and long COVID-19: recent studies confirm clinical validation and highlight metformin to improve VDR sensitivity and efficacy, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01383-x.
Tseng et al., 1 Aug 2023, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
Metformin and Coronavirus Disease 2019: A New Deal for an Old Drug
doi:10.6314/JIMT.202308_34(4).04
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has posed a remarkable global challenge as a previously unrecognized viral infection with high infectivity. The high prevalence of diabetes makes it one of the most common comorbidities observed in patients with COVID-19 infection. Studies have suggested that diabetes is associated with unfavorable COVID-19-related outcomes. Lower mortality rates have been observed among individuals with good glycemic control than among those with poor glycemic control, and glycemic management may affect the prognoses and outcomes of COVID-19 infection. Several studies have demonstrated that COVID-19 infection contributes to hyperglycemia, metabolic dysfunction, and increased microvascular complications and thrombotic events against the backdrop of aberrant endothelial function. Metformin, the most prescribed oral antidiabetic medication, exhibits multiple beneficial effects beyond its glucose-lowering functions, such as anti-infection, anti-inflammation, immunomodulation, anti-hypertension, preventive effects on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and heart failure. Hence, metformin may share similar mechanisms of these pleiotropic benefits or contribute to the reduced morbidity/mortality in COVID-19 infection. Therefore, metformin is a feasible candidate drug for repurposing to address the rising number of patients with COVID-19 infection who have diabetes. This review article presents a summary of the multiple potential mechanisms through which metformin produces beneficial therapeutic effects and summarizes real-world data supporting the repurposing of metformin for use in patients with COVID-19 who have type 2 diabetes.
References
Akbari, Tabrizi, Lankarani, The role of cytokine profile and lymphocyte subsets in the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis, Life Sci
Al-Ibrahimi, Nihad, Metformin improves overall survival of COVID 19 Iraqi patients with type 2 diabetes, Int J Diabetes Clin Res
Apicella, Campopiano, Mantuano, Mazoni, Coppelli et al., COVID-19 in people with diabetes: understanding the reasons for worse outcomes, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Bornstein, Rubino, Khunti, Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Cameron, Morrison, Levin, Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status, Circ Res
Cani, Bibiloni, Knauf, Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice, Diabetes
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia
Chen, Gong, Wang, Guo, Effects of hypertension, diabetes and coronary heart disease on COVID-19 diseases severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis, medRxiv
Chen, Guo, Qiu, Zhang, Deng et al., Immunomodulatory and antiviral activity of metformin and its potential implications in treating coronavirus disease 2019 and lung injury, Front Immunol
Chen, Sang, Jiang, Longitudinal hematologic and immunologic variations associated with the progression of COVID-19 patients in China, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes Care
Chen, Zou, Tang, Metformin corrects RAGE overexpression caused signaling dysregulation and NF-κB targeted gene change, Int J Clin Exp Med
Cheng, Liu, Li, Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
Conti, Caraffa, Tetè, Mast cells activated by SARS-CoV-2 release histamine which increases IL-1 levels causing cytokine storm and inflammatory reaction in COVID-19, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Might, Ovalle et al., Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes, Front Endocrinol
Cure, Cure, Comment on "Should anti-diabetic medications be reconsidered amid COVID-19 pandemic?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Dhar, Mohanty, Gut Microbiota and Covid-19-possible link and implications, Virus Res
Ding, Zhou, Ling, Metformin in cardiovascular diabetology: a focused review of its impact on endothelial function, Theranostics
Drucker, Coronavirus infections and type 2 diabetesshared pathways with therapeutic implications, Endocr Rev
Eaton, Merkulova, Brown, The H + -ATPase (V-AT-Pase): from proton pump to signaling complex in health and disease, Am J Physiol Cell Physiol
Esam, A proposed mechanism for the possible therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Francesco, Vella, Belfiore, COVID-19 and diabetes: the importance of controlling RAGE, Front Endocrinol
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci
Ghany, Palacio, Dawkins, Metformin is associated with lower hospitalizations, mortality and severe coronavirus infection among elderly medicare minority patients in 8 states in USA, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Giannarelli, Aragona, Coppelli, Prato, Reducing insulin resistance with metformin: the evidence today, Diabetes Metab
Gong, Goswami, Giacomini, Altman, Klein, Metformin pathways: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, Pharmacogenet Genomics
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, A SARS-CoV-2-human protein-protein interaction map reveals drug targets and potential drug-repurposing, Nature
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obes Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Ibrahim, Monaco, Sims, Not so sweet and simple: impacts of SARS-CoV-2 on the β cell, Islets
Ingraham, Lotfi-Emran, Thielen, Immunomodulation in COVID-19, Lancet Respir Med
Isoda, Young, Zirlik, Metformin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-κB in human vascular wall cells, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol
Karam, Morris, Bramante, mTOR inhibition in COVID-19: a commentary and review of efficacy in RNA viruses, J Med Virol
Kim, You, Regulation of organelle function by metformin, IUBMB Life
Korytkowski, Antinori-Lent, Drincic, A pragmatic approach to inpatient diabetes management during the COVID-19 pandemic, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Kritas, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Mast cells contribute to coronavirus-induced inflammation: new anti-inflammatory strategy, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents
Kruglikov, Shah, Scherer, Obesity and diabetes as comorbidities for COVID-19: Underlying mechanisms and the role of viral-bacterial interactions, Elife
Lally, Tsoukas, Halladay, Neill, Gravenstein et al., Metformin is associated with decreased 30-day mortality among nursing home residents infected with SARS-CoV2, J Am Med Dir Assoc
Levi, Thachil, Iba, Levy, Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Haematol
Li, Liu, Zhang, SARS-CoV-2 and viral sepsis: observations and hypotheses, Lancet
Liao, Liu, Yuan, Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19, Nat Med
Lim, Bae, Kwon, Nauck, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management, Nat Rev Endocrinol
Lisco, Tullio, Giagulli, Guastamacchia, Pergola et al., Hypothesized mechanisms explaining poor prognosis in type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19: a review, Endocrine
Lu, Leu, Metformin and risk of deep vein thrombosis: a nonrandomized, pair-matched cohort study, J Am Coll Cardiol
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Ma, Holt, COVID-19 and diabetes, Diabet Med
Mackey, Ayyadurai, Pohl, Costa, Li et al., Sexual dimorphism in the mast cell transcriptome and the pathophysiological responses to immunological and psychological stress, Biol Sex Differ
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Covid-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Menegazzo, Scattolini, Cappellari, The antidiabetic drug metformin blunts NETosis in vitro and reduces circulating NETosis biomarkers in vivo, Acta Diabetol
Mulchandani, Lyngdoh, Kakkar, Deciphering the COVID-19 cytokine storm: systematic review and metaanalysis, Eur J Clin Invest
Nanditha, Raghavan, Misra, Management of hyperglycemia in COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 syndromeproposed guidelines for India, J Assoc Physicians India
Nath, Khan, Paintlia, Singh, Hoda et al., Metformin attenuated the autoimmune disease of the central nervous system in animal models of multiple sclerosis, J Immunol
Oscanoa, Amado, Vidal, Savarino, Romero-Ortuno, Metformin therapy and severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a meta-analysis, Clin Diabetol
Pollak, The effects of metformin on gut microbiota and the immune system as research frontiers, Diabetologia
Prestes, Rocha, Miranda, Teixeira, Simoes-E-Silva, The anti-inflammatory potential of ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis: evidence from basic and clinical research, Curr Drug Targets
Rena, Hardie, Pearson, The mechanisms of action of metformin, Diabetologia
Saenwongsa, Nithichanon, Chittaganpitch, Metformin-induced suppression of IFN-alpha via mTORC1 signaling following seasonal vaccination is associated with impaired antibody responses in type 2 diabetes, Sci Rep
Samuel, Varghese, Bu¨sselberg, Therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19: reasoning for its protective role, Trends Microbiol
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Singh, Singh, Is metformin ahead in the race as a repurposed host-directed therapy for patients with diabetes and COVID-19?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Triggle, Ding, Metformin is not just an anti-hyperglycemic drug but also has protective effects on the vascular endothelium, Acta Physiol(Oxf)
Tsai, Clemente-Casares, Zhou, Insulin receptor-mediated stimulation boosts T Cell immunity during inflammation and infection, Cell Metab
Tseng, Metformin and helicobacter pylori infection in patients with type 2 diabetes, Diabetes Care
Tseng, Metformin and risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in diabetes patients, Diabetes Metab
Tseng, Metformin and risk of hypertension in Taiwanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, J Am Heart Assoc
Tseng, Metformin decreases risk of tuberculosis infection in type 2 diabetes patients, J Clin Med
Tseng, Metformin use is associated with a lower risk of hospitalization for heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cohort analysis, J Am Heart Assoc
Tseng, Metformin use is associated with a lower risk of inflammatory bowel disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, J Crohns Colitis
Ursini, Russo, Pellino, Metformin and autoimmunity: a new deal of an old drug, Front Immunol
Varghese, Samuel, Liskova, Kubatka, Büsselberg, Diabetes and coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): Molecular mechanism of metformin intervention and the scientific basis of drug repurposing, PLoS Pathog
Veras, Pontelli, Silva, SARS-CoV-2-triggered neutrophil extracellular traps mediate COVID-19 pathology, J ExMed
Wang, Gheblawi, Oudit, Angiotensin converting enzyme 2: a double-edged sword, Circulation
Wang, Huang, Metformin inhibits IgE-and Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated mast cell activation in vitro and in vivo, Eur J Immunol
Wu, Esteve, Tremaroli, Metformin alters the gut microbiome of individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to the therapeutic effects of the drug, Nat Med
Xin, Wei, Ji, Metformin uniquely prevents thrombosis by inhibiting platelet activation and mtDNA Release, Sci Rep
Yang, Lin, Ji, Guo, Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes, Acta Diabetol
Yeoh, Zuo, Lui, Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19, Gut
Zhang, Dong, Martin, AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in endothelium mitigates pulmonary hypertension, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zhu, She, Cheng, Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and preexisting type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
Zuo, Liu, Zhang, Depicting SARSCoV-2 Faecal Viral Activity in association with gut microbiota composition in patients with COVID-19, Gut
Zuo, Yalavarthi, Shi, Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19, JCI Insight
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.6314/JIMT.202308_34(4).04",
"URL": "",
"abstract": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has posed a remarkable global challenge as a previously unrecognized viral infection with high infectivity. The high prevalence of diabetes makes it one of the most common comorbidities observed in patients with COVID-19 infection. Studies have suggested that diabetes is associated with unfavorable COVID-19-related outcomes. Lower mortality rates have been observed among individuals with good glycemic control than among those with poor glycemic control, and glycemic management may affect the prognoses and outcomes of COVID-19 infection. Several studies have demonstrated that COVID-19 infection contributes to hyperglycemia, metabolic dysfunction, and increased microvascular complications and thrombotic events against the backdrop of aberrant endothelial function. Metformin, the most prescribed oral antidiabetic medication, exhibits multiple beneficial effects beyond its glucose-lowering functions, such as anti-infection, anti-inflammation, immunomodulation, anti-hypertension, preventive effects on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and heart failure. Hence, metformin may share similar mechanisms of these pleiotropic benefits or contribute to the reduced morbidity/mortality in COVID-19 infection. Therefore, metformin is a feasible candidate drug for repurposing to address the rising number of patients with COVID-19 infection who have diabetes. This review article presents a summary of the multiple potential mechanisms through which metformin produces beneficial therapeutic effects and summarizes real-world data supporting the repurposing of metformin for use in patients with COVID-19 who have type 2 diabetes.",
"author": [
{
"literal": "Kuo-Bin Tseng"
}
],
"container-title": "內科學誌",
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
"2023",
"8",
"1"
]
]
},
"language": "",
"page-first": "286",
"title": "Metformin and Coronavirus Disease 2019: A New Deal for an Old Drug",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "34"
}
