Evaluating the Efficacy of Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin to Prevent Hospitalization or Death in Persons With COVID-19
et al., NCT04358068, NCT04358068, Jul 2020
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Early terminated NIAID RCT for HCQ. Patients >60 were only in the HCQ arm. 57% of patients were high risk in the HCQ arm vs. 22% for control. Treatment started up to 20 days after symptoms.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
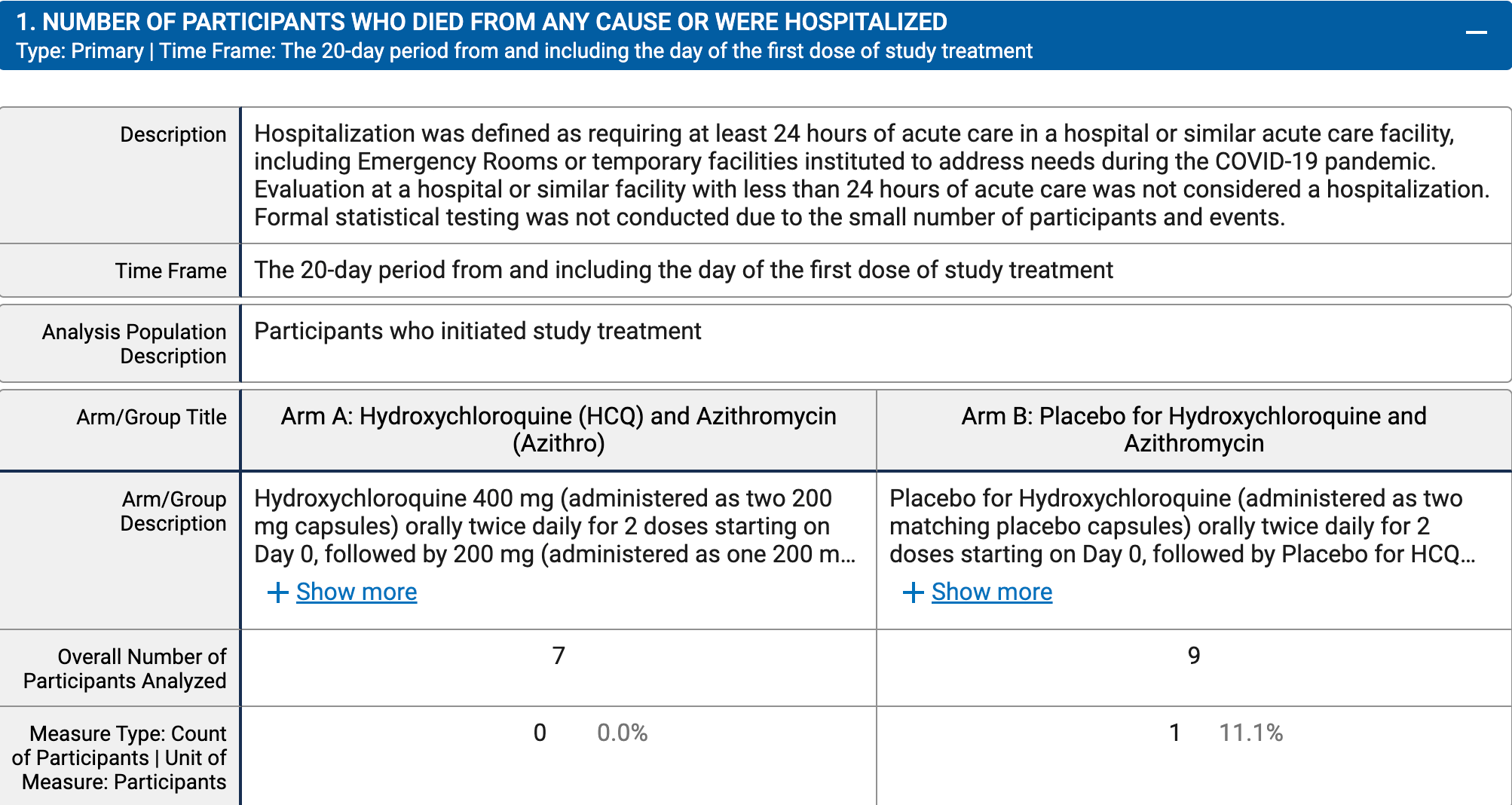
risk of hospitalization, 64.0% lower, RR 0.36, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 7 (0.0%), control 1 of 9 (11.1%), NNT 9.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
recovery time, 10.0% higher, relative time 1.10, treatment 7, control 9.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Smith et al., 8 Jul 2020, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, preprint, 1 author, average treatment delay 5.0 days, dosage 400mg bid day 1, 200mg bid days 2-7, trial NCT04358068 (history).
