Early antiviral and supervisory dexamethasone treatment improve clinical outcomes of nonsevere COVID-19 patients
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000031681, Nov 2022
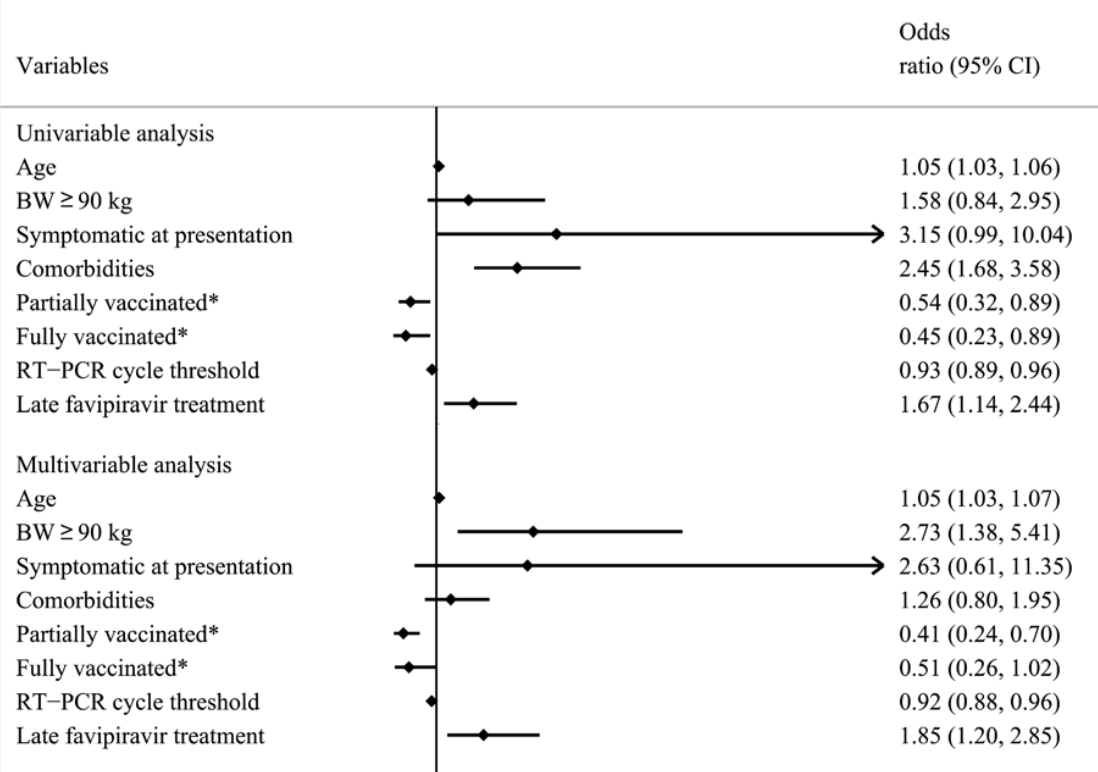
Retrospective 1,940 outpatients in Thailand, showing lower risk of clinical deterioration with early vs. late favipiravir treatment.
Potential risks of favipiravir include kidney injury1-3, liver injury2-5, cardiovascular events5,6, pulmonary toxicity6,7, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, embryotoxicity, and the creation of dangerous variants8-14.
1.
Abdulaziz et al., Clinical Features and Prognosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospital-Admitted Patients with COVID-19 in Egypt: A Single-Center Experience, Mansoura Medical Journal, doi:10.58775/2735-3990.1433.
2.
Ülger et al., Experimental evaluation of favipiravir (T-705)-induced liver and kidney toxicity in rats, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115472.
3.
El-Fetouh et al., Experimental Studies on Some Drugs Used in Covid-19 Treatment (Favipiravir and Dexamethasone) in Albino Rats, Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research, 13:10, www.advetresearch.com/index.php/AVR/article/view/1635.
4.
Almutairi et al., Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study, Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed8020129.
5.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
6.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
7.
Ülger (B) et al., Evaluation of the effects of favipiravir (T-705) on the lung tissue of healty rats: An experimental study, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115235.
8.
Zhirnov et al., Favipiravir: the hidden threat of mutagenic action, Journal of microbiology, epidemiology and immunobiology, doi:10.36233/0372-9311-114.
9.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
10.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
11.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
12.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
Sitasuwan et al., 11 Nov 2022, retrospective, Thailand, peer-reviewed, mean age 42.1, 23 authors, study period July 2021 - November 2021.
Contact: thanet.chs@mahidol.ac.th.
Early antiviral and supervisory dexamethasone treatment improve clinical outcomes of nonsevere COVID-19 patients
Medicine, doi:10.1097/md.0000000000031681
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of early antiviral treatment in preventing clinical deterioration in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infected (COVID-19) patients in home isolation and to share our experiences with the ambulatory management of nonsevere COVID-19 patients. This retrospective study included mild COVID-19 adult patients confirmed by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. They received care via an ambulatory management strategy between July 2021 and November 2021. Demographic data, clinical progression, and outcomes were collected. Both descriptive and inferential statistics were performed to illustrate the cohort's characteristic and outcomes of the study. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression models were employed to investigate the associations between clinical factors and disease progression. A total of 1940 patients in the Siriraj home isolation system met the inclusion criteria. Their mean age was 42.1 ± 14.9 years, with 14.2% older than 60 years, 54.3% female, and 7.1% with a body weight ≥ 90 kg. Only 115 patients (5.9%) had deterioration of clinical symptoms. Two-thirds of these could be managed at home by dexamethasone treatment under physician supervision; however, 38 of the 115 patients (2.0% of the study cohort) needed hospitalization. Early favipiravir outpatient treatment (≤ 5 days from onset of symptoms) in nonsevere COVID-19 patients was significantly associated with a lower rate of symptom deterioration than late favipiravir treatment (50 [4.6%] vs 65 [7.5%] patients, respectively; P = .008; odds ratio 1.669; 95% confidence interval, 1.141-2.441). The unfavorable prognostic factors for symptom deterioration were advanced age, body weight ≥ 90 kg, unvaccinated status, higher reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction cycle threshold, and late favipiravir treatment. The early delivery of essential treatment, including antiviral and supervisory dexamethasone, to ambulatory nonsevere COVID-19 patients yielded favorable outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic in Thailand. Abbreviations: ARI = acute respiratory infection, CI = confidence interval, COVID-19 = coronavirus disease 2019, IQR = interquartile range, OR = odds ratio, RT-PCR = reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, Si-home = Siriraj home isolation system.
References
Ayaz, Dizman, Metan, Out-patient management of patients with COVID-19 on home isolation, Infez Med
Baughman, Hirschberg, Lucas, Pandemic care through collaboration: lessons from a COVID-19 field hospital, J Am Med Dir Assoc
Cai, Yang, Liu, Experimental treatment with Favipiravir for COVID-19: an open-label control study, Engineering
Cdc, Team, Preliminary estimates of the prevalence of selected underlying health conditions among patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 -United States, February 12, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Chuah, Chow, Hor, Efficacy of early treatment with favipiravir on disease progression among high risk COVID-19 patients: a randomized, open-label clinical trial, Clin Infect Dis
Delang, Abdelnabi, Neyts, Favipiravir as a potential countermeasure against neglected and emerging RNA viruses, Antiviral Res
Doi, Hibino, Hase, A prospective, randomized, open-label trial of early versus late favipiravir therapy in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Fujii, Ibe, Ishigo, Early favipiravir treatment was associated with early defervescence in non-severe COVID-19 patients, J Infect Chemother
Gallo Marin, Aghagoli, Lavine, Predictors of COVID-19 severity: a literature review, Rev Med Virol
Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Ivashchenko, Dmitriev, Vostokova, AVIFAVIR for treatment of patients with moderate Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): interim results of a phase II/III multicenter randomized clinical trial, Clin Infect Dis
Izzedine, Jhaveri, Perazella, COVID-19 therapeutic options for patients with kidney disease, Kidney Int
Kwok, Adam, Ho, Obesity: a critical risk factor in the COVID-19 pandemic, Clin Obes
Long, Chavez, Carius, Clinical update on COVID-19 for the emergency and critical care clinician: Medical management, Am J Emerg Med
Mccullough, Kelly, Ruocco, Pathophysiological basis and rationale for early outpatient treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, Am J Med
Procter, Ross, Pickard, Clinical outcomes after early ambulatory multidrug therapy for high-risk SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, Rev Cardiovasc Med
Rao, Manissero, Steele, A systematic review of the clinical utility of cycle threshold values in the context of COVID-19, Infect Dis Ther
Shinkai, Tsushima, Tanaka, Efficacy and safety of favipiravir in moderate COVID-19 pneumonia patients without oxygen therapy: a randomized, phase III clinical trial, Infect Dis Ther
Shiraki, Sato, Sakai, Antiviral therapy for COVID-19: derivation of optimal strategy based on past antiviral and favipiravir experiences, Pharmacol Therap
Udwadia, Singh, Barkate, Efficacy and safety of favipiravir, an oral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, in mild-to-moderate COVID-19: A randomized, comparative, open-label, multicenter, phase 3 clinical trial, Int J Infect Dis
Yu, Rohli, Yang, Impact of obesity on COVID-19 patients, J Diabetes Complications
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/md.0000000000031681",
"ISSN": [
"1536-5964"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000031681",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sitasuwan",
"given": "Tullaya",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phisalprapa",
"given": "Pochamana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Srivanichakorn",
"given": "Weerachai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Washirasaksiri",
"given": "Chaiwat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Auesomwang",
"given": "Chonticha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinmanee",
"given": "Rungsima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sayabovorn",
"given": "Naruemit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chayakulkeeree",
"given": "Methee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phoompoung",
"given": "Pakpoom",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayurasakorn",
"given": "Korapat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sookrung",
"given": "Nitat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tungtrongchitr",
"given": "Anchalee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wanitphakdeedecha",
"given": "Rungsima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muangman",
"given": "Saipin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Senawong",
"given": "Sansnee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tangjittipokin",
"given": "Watip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanpawitayakul",
"given": "Gornmigar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woradetsittichai",
"given": "Diana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nimitpunya",
"given": "Pongpol",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kositamongkol",
"given": "Chayanis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nopmaneejumruslers",
"given": "Cherdchai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vamvanij",
"given": "Visit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaisathaphol",
"given": "Thanet",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-17T14:09:58Z",
"timestamp": 1668694198000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-18T07:05:33Z",
"timestamp": 1668755133000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-18T07:41:55Z",
"timestamp": 1668757315773
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "45",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "45",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000031681",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e31681",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.09.003",
"article-title": "Pandemic care through collaboration: lessons from a COVID-19 field hospital.",
"author": "Baughman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1563",
"journal-title": "J Am Med Dir Assoc",
"key": "R1-20221118",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Out-patient management of patients with COVID-19 on home isolation.",
"author": "Ayaz",
"first-page": "351",
"journal-title": "Infez Med",
"key": "R3-20221118",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.03.036",
"article-title": "Clinical update on COVID-19 for the emergency and critical care clinician: Medical management.",
"author": "Long",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "158",
"journal-title": "Am J Emerg Med",
"key": "R5-20221118",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.03.003",
"article-title": "Favipiravir as a potential countermeasure against neglected and emerging RNA viruses.",
"author": "Delang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "R7-20221118",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00517-4",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of favipiravir in moderate COVID-19 pneumonia patients without oxygen therapy: a randomized, phase III clinical trial.",
"author": "Shinkai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2489",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "R8-20221118",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.142",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of favipiravir, an oral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, in mild-to-moderate COVID-19: A randomized, comparative, open-label, multicenter, phase 3 clinical trial.",
"author": "Udwadia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "R9-20221118",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiac.2021.04.013",
"article-title": "Early favipiravir treatment was associated with early defervescence in non-severe COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Fujii",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1051",
"journal-title": "J Infect Chemother",
"key": "R10-20221118",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eng.2020.03.007",
"article-title": "Experimental treatment with Favipiravir for COVID-19: an open-label control study.",
"author": "Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1192",
"journal-title": "Engineering",
"key": "R11-20221118",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6913e2",
"article-title": "Preliminary estimates of the prevalence of selected underlying health conditions among patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 - United States, February 12-March 28, 2020.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "382",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "R12-20221118",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108121",
"article-title": "Antiviral therapy for COVID-19: derivation of optimal strategy based on past antiviral and favipiravir experiences.",
"author": "Shiraki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108121",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Therap",
"key": "R13-20221118",
"volume": "235",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"article-title": "Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1330",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R14-20221118",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R15-20221118",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.07.003",
"article-title": "Pathophysiological basis and rationale for early outpatient treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection.",
"author": "McCullough",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Am J Med",
"key": "R16-20221118",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2020.03.015",
"article-title": "COVID-19 therapeutic options for patients with kidney disease.",
"author": "Izzedine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1297",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "R17-20221118",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1176",
"article-title": "AVIFAVIR for treatment of patients with moderate Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): interim results of a phase II/III multicenter randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Ivashchenko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "R18-20221118",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01897-20",
"article-title": "A prospective, randomized, open-label trial of early versus late favipiravir therapy in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Doi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01897-20",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "R19-20221118",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31083/j.rcm.2020.04.260",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes after early ambulatory multidrug therapy for high-risk SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection.",
"author": "Procter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "611",
"journal-title": "Rev Cardiovasc Med",
"key": "R20-20221118",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2146",
"article-title": "Predictors of COVID-19 severity: a literature review.",
"author": "Gallo Marin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "R21-20221118",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab962",
"article-title": "Efficacy of early treatment with favipiravir on disease progression among high risk COVID-19 patients: a randomized, open-label clinical trial.",
"author": "Chuah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e432",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "R22-20221118",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107817",
"article-title": "Impact of obesity on COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107817",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes Complications",
"key": "R23-20221118",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cob.12403",
"article-title": "Obesity: a critical risk factor in the COVID-19 pandemic.",
"author": "Kwok",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e12403",
"journal-title": "Clin Obes",
"key": "R24-20221118",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00324-3",
"article-title": "A systematic review of the clinical utility of cycle threshold values in the context of COVID-19.",
"author": "Rao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "573",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "R25-20221118",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000031681"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Early antiviral and supervisory dexamethasone treatment improve clinical outcomes of nonsevere COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "101"
}