The role of thymoquinone, a major constituent of Nigella sativa, in the treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases
et al., Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13553, Jul 2021
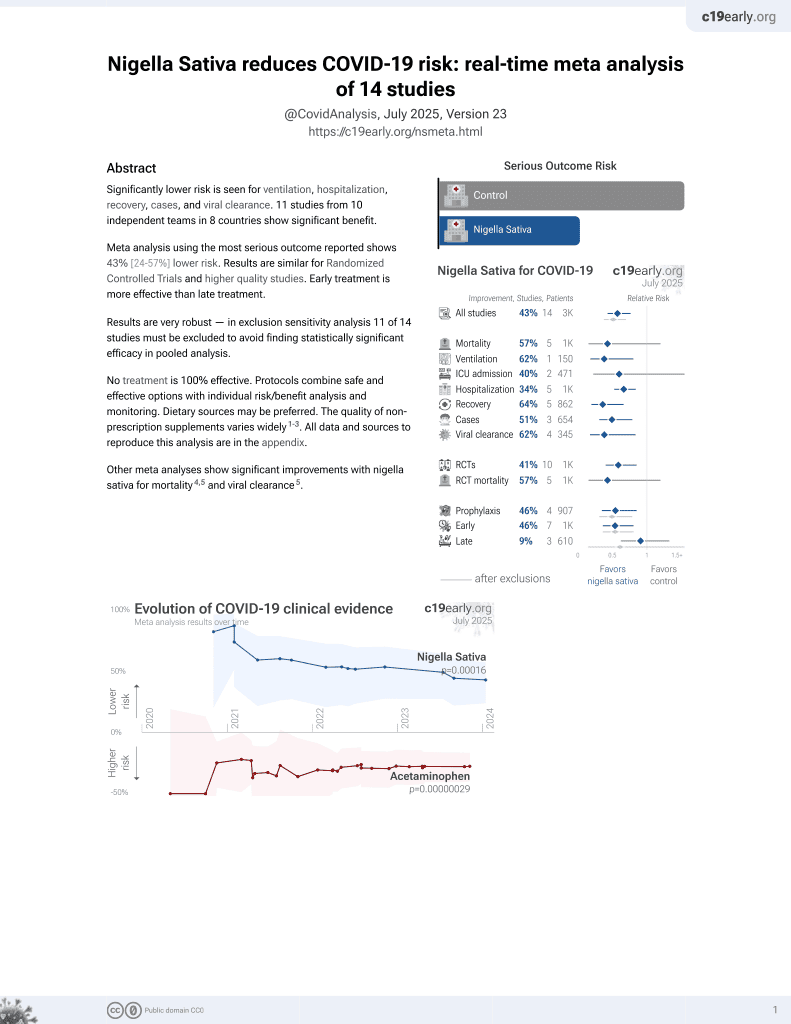
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the pharmacological properties of nigella sativa and thymoquinone and application for a variety of diseases, focusing on recent studies of the anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties that are promising for diseases including COVID-19.
1.
Alsalahi et al., Immune stimulatory effect of Nigella sativa in healthy animal models: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27390.
2.
Donzelli, A., Neglected Effective Early Therapies against COVID-19: Focus on Functional Foods and Related Active Substances. A Review, MDPI AG, doi:10.20944/preprints202312.1178.v1.
3.
Cyril et al., Nigella sativa and its chemical constituents: pre-clinical and clinical evidence for their potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01385-9.
4.
Al-Gabri et al., Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone and Its Nanoformulations in Pulmonary Injury: A Comprehensive Review, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S314321.
5.
Ahmad et al., The potential role of thymoquinone in preventing the cardiovascular complications of COVID-19, Vascular Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.vph.2021.106899.
6.
Shad et al., The role of thymoquinone, a major constituent of Nigella sativa, in the treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases, Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13553.
Shad et al., 23 Jul 2021, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
The role of thymoquinone, a major constituent of Nigella sativa , in the treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13553
Nigella sativa (N. sativa) is an annual flowering plant that has been used as a traditional remedy for many centuries. The seed possesses a large variety of compounds with thymoquinone (TQ) considered its major but not sole bioactive constituent. Supercritical fluid extraction, geographical location, and oxidative status of N. sativa produces the highest yield of essential oil content including TQ. Thymoquinone is lipophilic, heat and light sensitive with low oral bioavailability and rapid elimination that have significantly inhibited its pharmacological development. Novel developments in nanoparticulate-based oral administration, nasal spray and transdermal delivery may allow the clinical development of N. sativa and TQ as therapeutic agents. Animal and human studies indicate a potential role of N. sativa seed oil and TQ for a diverse range of disease processes including hypertension, dyslipidaemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, arthritis, asthma, bacterial and viral infections, neurological and dermatological disorders, as it belongs to the group of pan-assay interference compounds. This review outlines the pharmacological properties of N. sativa and TQ and their potential wide application for a large variety of human diseases. The paper will focus on recent studies of the anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties that make N. sativa and TQ promising therapeutic agents targeting contemporary inflammatory and infectious diseases including Covid 19.
epilepsy and dermatological disorders due to its non-specific binding to multiple biological targets. The non-specificity of TQ can be reduced by combining it with the other fractions present in the extract.
References
Abdelwahab, Sheikh, Taha, Thymoquinone-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: preparation, gastroprotection, in vitro toxicity, and pharmacokinetic properties after extravascular administration, Int J Nanomed
Ahmad, Abbasi, Shahid, Gul, Abbasi, Molecular docking, simulation and MM-PBSA studies of nigella sativa compounds: a computational quest to identify potential natural antiviral for COVID-19 treatment, J Biomol Struct Dyn
Ahmad, Husain, Mujeeb, A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: a miracle herb, Asian Pac J Trop Biomed
Ahmad, Rehman, Ahmad, Alkharfy, Covid-19 and thymoquinone: connecting the dots, Phytother Res
Akbar, Nigella sativa (black seeds): panacea or hyperbole? A critical review of experimental and clinical observations, Aust J Herb Naturop Med
Akhondian, Kianifar, Raoofziaee, Moayedpour, Toosi et al., The effect of thymoquinone on intractable pediatric seizures (pilot study), Epilepsy Res
Ali, Parveen, Ali, Links between the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) recommened foods and disease management: a review in the light of modern superfoods, Int J Health Sci (Qassim)
Aljabre, Alakloby, Randhawa, Dermatological effects of Nigella sativa, J Dermatol Dermatol Surg
Alkharfy, Ahmad, Khan, Shagha, Pharmacokinetic plasma behaviors of intravenous and oral bioavailability of thymoquinone in a rabbit model, Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet
Alrashedi, Ali, Ali, Khan, Impact of thymoquinone on cyclosporine A pharmacokinetics and toxicity in rodents, J Pharm Pharmacol
Amin, Hosseinzadeh, Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and Its active constituent, thymoquinone: an overview on the analgesic and antiinflammatory effects, Planta Med
Ashraf, Rao, Kaneez, Nigella sativa extract as a potent antioxidant for petrochemical-induced oxidative stress, J Chromatogr Sci
Atanasov, Zotchev, Dirsch, Supuran, International Natural Product Sciences Taskforce, Supuran CT. Natural products in drug discovery: advances and opportunities, Nat Rev Drug Discov
Azizi, Ghorat, Rakhshani, Comparison of the effect of topical use of Nigella Sativa oil and diclofenac gel on osteoarthritis pain in older people: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial, J Herbal Med
Bamosa, Kaatabi, Lebdaa, Elq, Al-Sultanb, Effect of Nigella sativa seeds on the glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Indian J Physiol Pharmacol
Bordoni, Fedeli, Nasuti, Antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory properties of Nigella sativa oil in human preadipocytes, Antioxidants
Boskabady, Mohsenpoor, Takaloo, Antiasthmatic effect of Nigella sativa in airways of asthmatic patients, Phytomedicine
Chaieb, Kouidhi, Jrah, Mahdouani, Bakhrouf, Antibacterial activity of Thymoquinone, an active principle of Nigella sativa and its potency to prevent bacterial biofilm formation, BMC Complement Altern Med
Chowdhury, Hossain, Mostofa, Akbor, Sayeed, Therapeutic potential of thymoquinone in glioblastoma treatment: targeting major gliomagenesis signaling pathways, Biomed Res Int
Dajani, Shahwan, Dajani, Overview of the preclinical pharmacological properties of Nigella sativa (black seeds): a complementary drug with historical and clinical significance, J Physiol Pharamcol
Disi, Anwar, Eid, Anti-hypertensive herbs and their mechanisms of action: part I, Front Pharmacol
Dutra, De Melo, Chelucci, Chin, Santos, The paradigma of the interference in assays for natural products, Biochem Pharmacol
Fahmy, Noor, Mohammed, Elsayed, Radwan, Nigella sativa as an anti-inflammatory and promising remyelinating agent in the cortex and hippocampus of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis-induced rats, J Basic Appl Zool
Farkhondeh, Samarghandian, Shahri, Samini, The neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone: a review, Dose Response
Forouzanfar, Bazzaz, Hosseinzadeh, Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its constituent (thymoquinone): a review on antimicrobial effects, Iran J Basic Med Sci
Fouad, Sharaf, Abdelghany, Sayed, Neuromodulatory effect of thymoquinone in attenuating glutamate-mediated neurotoxicity targeting the amyloidogenic and apoptotic pathways, Front Neurol
Gharby, Harhar, Guillaume, Chemical investigation of Nigella sativa L. seed oil produced in Morocco, J Saudi Soc Agric Sci
Glaser, Holzgrabe, Focus on PAINS: false friends in the quest for selective anti-protozoal lead structures from Nature?, MedChemComm
Goyal, Prajapati, Gore, Therapeutic potential and pharmaceutical development of thymoquinone: a multitargeted molecule of natural origin, Front Pharmacol
Hadi, Kheirouri, Alizadeh, Khabbazi, Hosseini, Effects of Nigella sativa oil extract on inflammatory cytokine response and oxidative stress status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, Avicenna J Phytomed
Hamdan, Idrus, Mokhtar, Effects of Nigella Sativa on type-2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Hanafy, Hatem, Studies on the antimicrobial activity of Nigella sativa seed (black cumin), J Ethnopharmacol
Haq, Lobo, Al-Tufail, Rama, St, Immunomodulatory effect of Nigella sativa proteins fractionated by ion exchange chromatography, Int J Immunopharmacol
Haq, Michniak-Kohn, Effects of solvents and penetration enhancers on transdermal delivery of thymoquinone: permeability and skin deposition study, Drug Deliv
Hossein, Haj-Allahyari, Anti-inflammatory effect of alcoholic extract of Nigella sativa L on bovine fibroblastlike synoviocyte and THP-1, Int J Contemp Research Rev
Ikhsan, Hiedayati, Maeyama, Nurwidya, Nigella sativa as an anti-inflammatory agent in asthma, BMC Res Notes
Jakaria, Cho, Haque, Neuropharmacological potential and delivery prospects of thymoquinone for neurological disorders, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Javanbakht, Hobbenaghi, Hosseini, Histopathological investigation of neuroprotective effects of Nigella sativa on motor neurons anterior horn spinal cord after sciatic nerve crush in rats, Pathol Biol
Karimi, Aghasizadeh, Razavi, Taghiabadi, Protective effects of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Nigella sativa L. and Portulaca oleracea L. on free radical induced hemolysis of RBCs, Daru
Kulyar, Li, Mehmood, Waqas, Li et al., Potential influence of Nagella sativa (Black cumin) in reinforcing immune system: a hope to decelerate the COVID-19 pandemic, Phytomedicine
Maideen, Prophetic medicine-Nigella Sativa (Black cumin seeds) -Potential herb for COVID-19?, J Pharmacopuncture
Mani, Sehgal, Dogra, Saxena, Pande, Deciphering underlying mechanism of Sars-CoV-2 infection in humans and revealing the therapeutic potential of bioactive constituents from Nigella sativa to combat COVID19: in-silico study, J Biomol Struct Dyn
Mazaheri, Torbati, Azadmard-Damirchi, Savage, A comprehensive review of the physicochemical, quality and nutritional properties of Nigella sativa oil, Food Rev Int
Mendonca, Soliman, Flavonoids activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 as a hypothesis approach for the prevention and modulation of SARS-CoV-2 infection severity, Antioxidants
Moslemi, Nokhandani, Otaghsaraei, Moghadamnia, Kazemi et al., Management of chemo/ radiation-induced oral mucositis in patients with head and neck cancer: a review of the current literature, Radiother Oncol
Nelson, Dahlin, Bisson, Graham, Pauli et al., The essential medicinal chemistry of curcumin, J Med Chem
Newman, Cragg, Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019, J Nat Prod
Nikakhlagh, Rahim, Aryani, Syahpoush, Brougerdnya et al., Herbal treatment of allergic rhinitis: the use of Nigella sativa, Am J Otolaryngol
Pop, Trifa, Popolo, Nigella sativa: Valuable perspective in the management of chronic diseases, Iran J Basic Med Sci
Ragab, Salah Eldin, Taeimah, Khattab, Salem, The COVID-19 cytokine storm; what we know so far, Front Immunol
Rahman, Potential benefits of combination of Nigella sativa and Zn supplements to treat COVID-19, J Herb Med
Rao, Al-Marzouqi, Fatima, Ashraf, Adem, Comparative evaluation of SFE and solvent extraction methods on the yield and composition of black seeds (Nigella sativa), J Liq Chrom Relat Tech
Rezaeian, Amoushahi, Effect of Nigella sativa nasal spray on the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis without a nasal polyp, Allergy Rhinol
Sahak, Kabir, Abbas, Draman, Hashim et al., The role of Nigella sativa and its active constituents in learning and memory, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Salea, Widjojokusumo, Hartanti, Veriansyah, Tjandrawinata, Supercritical fluid carbon dioxide extraction of Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds using taguchi method and full factorial design, Biochem Comp
Salehi, Quispe, Imran, Nigella plants -traditional uses, bioactive phytoconstituents, preclinical and clinical studies, Front Pharmacol
Salem, Bamosa, Qutub, Effect of Nigella sativa supplementation on lung function and inflammatory mediators in partly controlled asthma: a randomized controlled trial, Ann Saudi Med
Seadawy, Gad, Elhoseny, In vitro: natural compounds (Thymol, Carvacol, Hesperidine, and Thymoquinone) against SARS-CoV2 strain isolated from Egyptian patients, bioRxiv
Seghatoleslam, Alipour, Shafieian, The effects of Nigella sativa on neural damage after pentylenetetrazole induced seizures in rats, J Tradit Complement Med
Shanmugam, Arfuso, Kumar, Modulation of diverse oncogenic transcription factors by thymoquinone, an essential oil compound isolated from the seeds of Nigella sativa Linn, Pharmacol Res
Singh, Gupta, Verma, Mishra, Pal, An evaluation of the efficacy of ethanolic extract of Nigella sativa L. (Kalonji) on the clinical parameters of moderate-to-severe gingivitis: a split-mouth clinical study, Ayu
Sommer, Försterling, Naber, Thymoquinone: shield and sword against SARS-CoV-2, Precis Nanomed
Taka, Mazzio, Goodman, Anti-inflammatory effects of thymoquinone in activated BV-2 microglial cells, J Neuroimmunol
Tavakkoli, Mahdian, Razavi, Hosseinzadeh, Review on clinical trials of black seed (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, thymoquinone, J Pharmacopuncture
Tekeoglu, Dogan, Ediz, Budancamanak, Demirel, Effects of thymoquinone (volatile oil of black cumin) on rheumatoid arthritis in rat models, Phytother Res
Tiwary, Sapra, Jain, Innovations in transdermal drug delivery: formulations and techniques, Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul
Ulasli, Gurses, Bayraktar, The effects of Nigella sativa (Ns), Anthemis hyalina (Ah) and Citrus sinensis (Cs) extracts on the replication of coronavirus and the expression of TRP genes family, Mol Biol Rep
Xu, Liu, Xiao, Computational and experimental studies reveal that thymoquinone blocks the entry of coronaviruses into in vitro cells, Infect Dis Ther
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1440-1681.13553",
"ISSN": [
"0305-1870",
"1440-1681"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.13553",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p><jats:italic>Nigella sativa</jats:italic> (<jats:italic>N</jats:italic>. <jats:italic>sativa</jats:italic>) is an annual flowering plant that has been used as a traditional remedy for many centuries. The seed possesses a large variety of compounds with thymoquinone (TQ) considered its major but not sole bioactive constituent. Supercritical fluid extraction, geographical location, and oxidative status of <jats:italic>N. sativa</jats:italic> produces the highest yield of essential oil content including TQ. Thymoquinone is lipophilic, heat and light sensitive with low oral bioavailability and rapid elimination that have significantly inhibited its pharmacological development. Novel developments in nanoparticulate‐based oral administration, nasal spray and transdermal delivery may allow the clinical development of <jats:italic>N. sativa</jats:italic> and TQ as therapeutic agents. Animal and human studies indicate a potential role of <jats:italic>N. sativa</jats:italic> seed oil and TQ for a diverse range of disease processes including hypertension, dyslipidaemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, arthritis, asthma, bacterial and viral infections, neurological and dermatological disorders, as it belongs to the group of pan‐assay interference compounds. This review outlines the pharmacological properties of <jats:italic>N. sativa</jats:italic> and TQ and their potential wide application for a large variety of human diseases. The paper will focus on recent studies of the anti‐inflammatory and antiviral properties that make <jats:italic>N. sativa</jats:italic> and TQ promising therapeutic agents targeting contemporary inflammatory and infectious diseases including Covid 19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/1440-1681.13553"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-06-15"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-07-14"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-08-18"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Technology Sydney Sydney Australia"
},
{
"name": "Australian Catholic University Sydney Australia"
},
{
"name": "University of Health Sciences"
},
{
"name": "ISRA University"
}
],
"family": "Fatima Shad",
"given": "Kaneez",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Technology Sydney Sydney Australia"
},
{
"name": "Ingham Institute for Applied Medical Research"
},
{
"name": "A Health Step Clinic Sydney Australia"
}
],
"family": "Soubra",
"given": "Wissam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ingham Institute for Applied Medical Research"
},
{
"name": "Department of Neurophysiology Liverpool Hospital Liverpool Australia"
},
{
"name": "South Western Sydney Clinical School University of New South Wales Sydney Australia"
}
],
"family": "Cordato",
"given": "Dennis John",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology",
"container-title-short": "Clin Exp Pharma Physio",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-23T19:14:35Z",
"timestamp": 1627067675000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-29T04:30:49Z",
"timestamp": 1693283449000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T08:26:13Z",
"timestamp": 1715588773893
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 23,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1629244800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/1440-1681.13553",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/1440-1681.13553",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/1440-1681.13553",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1445-1453",
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
18
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its constituent (thymoquinone): a review on antimicrobial effects",
"author": "Forouzanfar F",
"first-page": "929",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Iran J Basic Med Sci",
"key": "e_1_2_8_2_1",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2017.00656",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/87559129.2018.1563793",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_4_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Overview of the preclinical pharmacological properties of Nigella sativa (black seeds): a complementary drug with historical and clinical significance",
"author": "Dajani EZ",
"first-page": "801",
"journal-title": "J Physiol Pharamcol",
"key": "e_1_2_8_5_1",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Links between the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) recommened foods and disease management: a review in the light of modern superfoods",
"author": "Ali SA",
"first-page": "61",
"journal-title": "Int J Health Sci (Qassim)",
"key": "e_1_2_8_6_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Chemical investigation of Nigella sativa L. seed oil produced in Morocco",
"author": "Gharby S",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "J Saudi Soc Agric Sci",
"key": "e_1_2_8_7_1",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-020-00114-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2017.11.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.625386",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox8020051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jobaz.2014.08.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7243/2052-9341-1-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/chrsci/49.4.321",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/1209801",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10717544.2018.1523256",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2152656718800059",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3831/KPI.2017.20.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4172/2167-0501.1000e183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C5MD00481K",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13318-014-0207-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jphp.12943",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_24_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and Its active constituent, thymoquinone: an overview on the analgesic and anti‐inflammatory effects",
"author": "Amin B",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Planta Med",
"key": "e_1_2_8_25_1",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1559325818761455",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S44108",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/187221107779814087",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10826070701540100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fneur.2018.00236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_30_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Nigella sativa: Valuable perspective in the management of chronic diseases",
"author": "Pop RM",
"first-page": "699",
"journal-title": "Iran J Basic Med Sci",
"key": "e_1_2_8_31_1",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153277",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15520/ijcrr/2018/9/02/428",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.2143",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0192-0561(99)00010-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11033-014-3019-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jneuroim.2015.06.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_37_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Protective effects of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Nigella sativa L. and Portulaca oleracea L. on free radical induced hemolysis of RBCs",
"author": "Karimi G",
"first-page": "295",
"journal-title": "Daru",
"key": "e_1_2_8_38_1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Molecular docking, simulation and MM‐PBSA studies of nigella sativa compounds: a computational quest to identify potential natural antiviral for COVID‐19 treatment",
"author": "Ahmad S",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn",
"key": "e_1_2_8_39_1",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60075-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.patbio.2013.03.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtcme.2015.06.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13104-018-3858-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/4010629",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1472-6882-11-29",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0378-8741(91)90047-H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6793",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_47_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Thymoquinone: shield and sword against SARS‐CoV‐2",
"author": "Sommer AP",
"first-page": "541",
"journal-title": "Precis Nanomed",
"key": "e_1_2_8_48_1",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Deciphering underlying mechanism of Sars‐CoV‐2 infection in humans and revealing the therapeutic potential of bioactive constituents from Nigella sativa to combat COVID19: in‐silico study",
"author": "Jakhmola Mani R",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn",
"key": "e_1_2_8_49_1",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9080659",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00400-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hermed.2020.100382",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_53_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3831/KPI.2020.23.3.179",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_54_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Nigella sativa (black seeds): panacea or hyperbole? A critical review of experimental and clinical observations",
"author": "Akbar S",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Aust J Herb Naturop Med",
"key": "e_1_2_8_55_1",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Anti‐hypertensive herbs and their mechanisms of action: part I",
"author": "Al Disi SS",
"first-page": "323",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "e_1_2_8_56_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph16244911",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_57_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of Nigella sativa seeds on the glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus",
"author": "Bamosa AO",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "Indian J Physiol Pharmacol",
"key": "e_1_2_8_58_1",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2010.01.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_59_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5144/0256-4947.2017.64",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_60_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjoto.2010.07.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_61_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of Nigella sativa oil extract on inflammatory cytokine response and oxidative stress status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Hadi V",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "Avicenna J Phytomed",
"key": "e_1_2_8_62_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hermed.2019.100259",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_63_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2016/6075679",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_64_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2010.10.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_65_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdds.2015.04.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_66_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ayu.AYU_68_18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_67_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.radonc.2016.04.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_68_1"
},
{
"article-title": "In vitro: natural compounds (Thymol, Carvacol, Hesperidine, and Thymoquinone) against SARS‐CoV2 strain isolated from Egyptian patients",
"author": "Seadawy MG",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "e_1_2_8_69_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 68,
"references-count": 68,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1440-1681.13553"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The role of thymoquinone, a major constituent of <i>Nigella sativa</i>, in the treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "48"
}