Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone and Its Nanoformulations in Pulmonary Injury: A Comprehensive Review
et al., International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S314321, Jul 2021
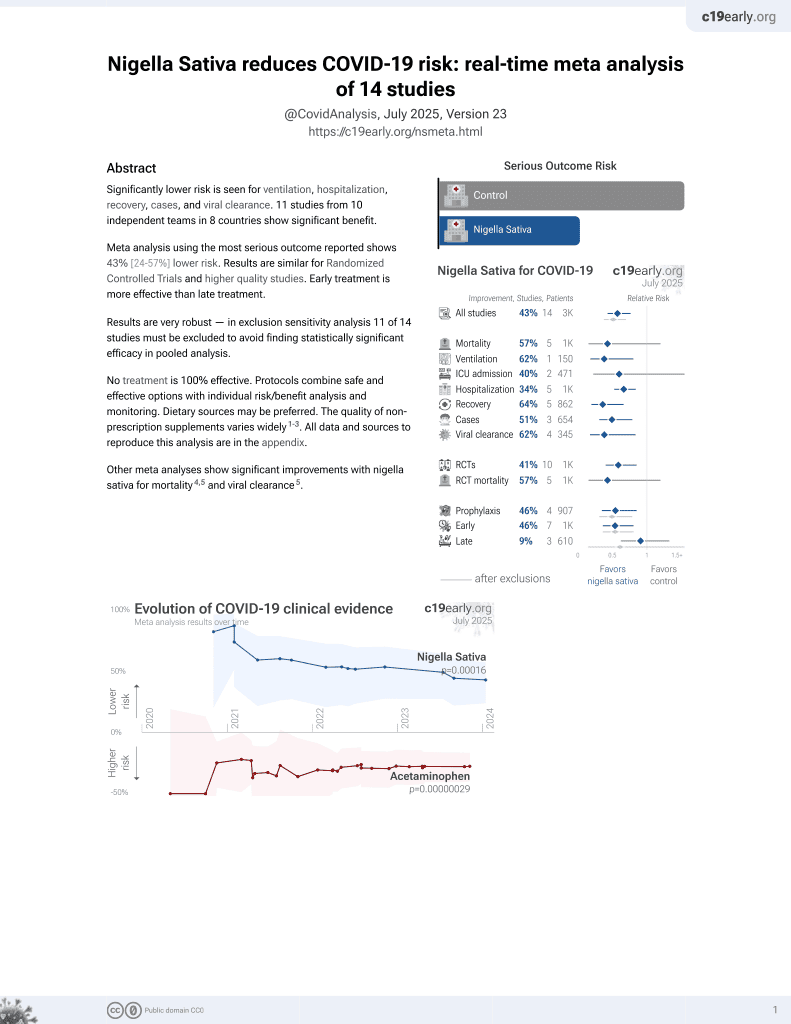
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of thymoquinone (a component of nigella sativa) research, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antineoplastic properties, application to lung conditions, and the potential advantages of nanoformulations on drug solubility, cellular absorption, and drug delivery to lung tissue target sites.
1.
Alsalahi et al., Immune stimulatory effect of Nigella sativa in healthy animal models: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27390.
2.
Donzelli, A., Neglected Effective Early Therapies against COVID-19: Focus on Functional Foods and Related Active Substances. A Review, MDPI AG, doi:10.20944/preprints202312.1178.v1.
3.
Cyril et al., Nigella sativa and its chemical constituents: pre-clinical and clinical evidence for their potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01385-9.
4.
Al-Gabri et al., Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone and Its Nanoformulations in Pulmonary Injury: A Comprehensive Review, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S314321.
5.
Ahmad et al., The potential role of thymoquinone in preventing the cardiovascular complications of COVID-19, Vascular Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.vph.2021.106899.
6.
Shad et al., The role of thymoquinone, a major constituent of Nigella sativa, in the treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases, Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13553.
Al-Gabri et al., 27 Jul 2021, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone and Its Nanoformulations in Pulmonary Injury: A Comprehensive Review
International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/ijn.s314321
As a crucial organ, the lung is exposed to various harmful agents that may induce inflammation and oxidative stress, which may cause chronic or acute lung injury. Nigella sativa, also known as black seed, has been widely used to treat various diseases and is one of the most extensively researched medicinal plants. Thymoquinone (TQ) is the main component of black seed volatile oil and has been proven to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antineoplastic properties. The potential therapeutic properties of TQ against various pulmonary disorders have been studied in both in vitro and in vivo studies. Furthermore, the application of nanotechnology may increase drug solubility, cellular absorption, drug release (sustained or control), and drug delivery to lung tissue target sites. As a result, fabricating TQ as nanoparticles (NPs) is a potential therapeutic approach against a variety of lung diseases. In this current review, we summarize recent findings on the efficacy of TQ and its nanotypes in lung disorders caused by immunocompromised conditions such as cancer, diabetes, gastric ulcers, and other neurodegenerative diseases. It is concluded that TQ nanoparticles with antiinflammatory, antioxidant, antiasthma, and antitumor activity may be safely applied to treat lung disorders. However, more research is required before TQ nanoparticles can be used as pharmaceutical preparations in human studies.
Author Contributions All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
References
Abdelwahab, Sheikh, Taha, Thymoquinoneloaded nanostructured lipid carriers: preparation, gastroprotection, in vitro toxicity, and pharmacokinetic properties after extravascular administration, Int J Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S44108
Abu-Dahab, Odeh, Ismail, Azzam, Bawab, Preparation, characterization and antiproliferative activity of thymoquinone-beta-cyclodextrin self-assembling nanoparticles, Pharmazie, doi:10.1691/ph.2013.3033
Abukhader, Khan, Thymoquinone and nanoparticles: a promising approach for the clinical trials, J Bionanosci, doi:10.1166/jbns.2017.1447
Ahmad, Ahmad, Alam, Samim, Iqbal et al., Quantification and evaluation of thymoquinone loaded mucoadhesive nanoemulsion for treatment of cerebral ischemia, Int J Biol Macromol, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.019
Ahmad, Kaus, Hamid, Synthesis and characterization of PLGA-PEG thymoquinone nanoparticles and its cytotoxicity effects in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells, Cancer Biology and Advances in Treatment, doi:10.1007/5584_2018_302
Al-Gabri, Ali, Hamed, Pathological study on the role of thymoquinone in experimentally induced acute lung injury in rats, Zagazig Vet J, doi:10.21608/ZVJZ.2017.7948
Al-Gabri, Qaid, El-Shaer, Ali, Abudabos, Thymoquinone ameliorates pulmonary vascular damage induced by Escherichia coli-derived lipopolysaccharide via cytokine downregulation in rats, Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, doi:10.1007/s11356-019-05229-4
Al-Qadi, Grenha, Carrión-Recio, Seijo, Remuñán-López, Microencapsulated chitosan nanoparticles for pulmonary protein delivery: in vivo evaluation of insulin-loaded formulations, J Control Release, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.08.008
Alam, Khan, Mustafa, Development and evaluation of thymoquinone-encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles for nose-tobrain targeting: a pharmacoscintigraphic study, Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S35329
Ali, Akter, Mei, Zheng, Tania et al., Thymoquinone in autoimmune diseases: therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111157
Ammar, Gameil, Shawky, Nader, Comparative evaluation of anti-inflammatory properties of thymoquinone and curcumin using an asthmatic murine model, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2011.10.013
Anderson, Ho, Brackett, Finkelstein, Laffel, Parental involvement in diabetes management tasks: relationships to blood glucose monitoring adherence and metabolic control in young adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, J Pediatr, doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(97)70352-4
Armstrong, Medford, Uppington, Expression of functional toll-like receptor-2 and-4 on alveolar epithelial cells, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, doi:10.1165/rcmb.2004-0078OC
Asti, Ruggieri, Porzio, Chiusaroli, Melillo et al., Lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in mice. I. concomitant evaluation of inflammatory cells and haemorrhagic lung damage, Pulm Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1006/pupt.2000.0231
Babu, Templeton, Munshi, Ramesh, Nanoparticlebased drug delivery for therapy of lung cancer: progress and challenges, J Nanomater, doi:10.1155/2013/863951
Badary, Hamza, Tikamdas, Thymoquinone: a promising natural compound with potential benefits for COVID-19 prevention and cure, Drug Des Devel Ther, doi:10.2147/DDDT.S308863
Barnawi, Tran, Roscioli, Pro-phagocytic effects of thymoquinone on cigarette smoke-exposed macrophages occur by modulation of the sphingosine-1-phosphate signalling system, COPD, doi:10.3109/15412555.2016.1153614
Basavaraj, Betageri, Can formulation and drug delivery reduce attrition during drug discovery and development-review of feasibility, benefits and challenges, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2013.12.003
Bauer, Laccone, Rolfs, Trinucleotide repeat expansion in SCA17/TBP in white patients with Huntington's disease-like phenotype, J Med Genet, doi:10.1136/jmg.2003.015602
Beutler, Rietschel, Innate immune sensing and its roots: the story of endotoxin, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri1004
Bhattacharya, Ahir, Patra, PEGylated-thymoquinonenanoparticle mediated retardation of breast cancer cell migration by deregulation of cytoskeletal actin polymerization through miR-34a, Biomaterials, doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.01.007
Cai, Mcclafferty, Benson, COVID-19: catastrophic cause of acute lung injury, South Dakota Med
Caroff, Karibian, Structure of bacterial lipopolysaccharides, Carbohydr Res, doi:10.1016/j.carres.2003.07.010
Chakraborty, Boer, Selomulya, Plebanski, Sg, Insights into endotoxin-mediated lung inflammation and future treatment strategies, Expert Rev Respir Med, doi:10.1080/17476348.2018.1523009
Chakraborty, Royce, Plebanski, Selomulya, Glycine microparticles loaded with functionalized nanoparticles for pulmonary delivery, Int J Pharm, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118654
Chakraborty, Royce, Pm, Wadhwa, Haghi et al., Use of biologics in the treatment of asthma, COPD, ACOS, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S314321
Chakraborty, Royce, Selomulya, Plebanski, A novel approach for non-invasive lung imaging and targeting lung immune cells, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21051613
Cingi, Eskiizmir, Burukoğlu, Erdoğmuş, Ural et al., The histopathological effect of thymoquinone on experimentally induced rhinosinusitis in rats, Am J Rhinol Allergy, doi:10.2500/ajra.2011.25.3703
Coker, Laurent, Shahzeidi, Transforming growth factors-beta 1,-beta 2, and-beta 3 stimulate fibroblast procollagen production in vitro but are differentially expressed during bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis, Am J Pathol
Colnaghi, Carpenter, Volker, Driscoll, The consequences of structural genomic alterations in humans: genomic disorders, genomic instability and cancer, Semin Cell Dev Biol, doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.07.010
Darakhshan, Pour, Colagar, Sisakhtnezhad, Shaterzadeh et al., Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of thymoquinone, Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1871529X18666180212114816
Dehghani, Hashemi, Entezari, Mohsenifar, The comparison of anticancer activity of thymoquinone and nanothymoquinone on human breast adenocarcinoma, Iran J Pharm Res, doi:10.1007/s11051-014-2821-4
Dinarello, Proinflammatory cytokines, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.118.2.503
Ding, Getz, Wheeler, Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature07423
El Gazzar, El Mezayen, Marecki, Nicolls, Canastar et al., Anti-inflammatory effect of thymoquinone in a mouse model of allergic lung inflammation, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2006.02.004
El-Ashmawy, Khedr, Ebeid, Salem, Zidan et al., Enhanced anticancer effect and reduced toxicity of doxorubicin in combination with thymoquinone released from poly-N -acetyl glucosamine nanomatrix in mice bearing solid Ehrlish carcinoma, Eur J Pharm Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2017.09.012
El-Far, Korshom, Mandour, El-Bessoumy, El-Sayed, Hepatoprotective efficacy of Nigella sativa seeds dietary supplementation against lead acetate-induced oxidative damage in rabbit-purification and characterization of glutathione peroxidase, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.044
El-Hack, Alagawany, Farag, Tiwari, Karthik et al., Nutritional, healthical and therapeutic efficacy of black cumin (Nigella sativa) in animals, poultry and humans, Int J Pharmacol, doi:10.3923/ijp.2016.232.248
El-Hakim, Sagheer, Khafaga, Batiha, Arif et al., Nigella sativa supplementation in ruminant diets: production, health, and environmental perspectives, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-48798-0_17
El-Mahdy, Zhu, Wang, Wani, Wani, Thymoquinone induces apoptosis through activation of caspase-8 and mitochondrial events in p53-null myeloblastic leukemia HL-60 cells, Int J Cancer, doi:10.1002/ijc.21205
Elmowafy, Samy, Raslan, Enhancement of bioavailability and pharmacodynamic effects of thymoquinone via nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) formulation, AAPS PharmSciTech, doi:10.1208/s12249-015-0391-0
Erdurmus, Yagci, Yilmaz, Inhibitory effects of topical thymoquinone on corneal neovascularization, Cornea, doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e31804f5a45
Fahmy, Ahmed, El-Moselhy, Asfour, Alhakamy, Thymoquinone loaded zein nanoparticles improves the cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells, Int J Pharmacol, doi:10.3923/ijp.2020.554.561
Fahmy, Alaofi, Awan, Alqarni, Alhakamy, Optimization of thymoquinone-loaded coconut oil nanostructured lipid carriers for the management of ethanol-induced ulcer, AAPS PharmSciTech, doi:10.1208/s12249-020-01693-1
Feinberg, Ohlsson, Henikoff, The epigenetic progenitor origin of human cancer, Nat Rev Genet, doi:10.1038/nrg1748
Gado, Ellakany, Elbestawy, Herbal medicine additives as powerful agents to control and prevent avian influenza virus in poultry-a review, Ann Anim Sci, doi:10.2478/aoas-2019-0043
Gali-Muhtasib, Diab-Assaf, Boltze, Thymoquinone extracted from black seed triggers apoptotic cell death in human colorectal cancer cells via a p53-dependent mechanism, Int J Oncol, doi:10.3892/ijo.25.4.857
Ganea, Fakayode, Losso, Van Nostrum, Sabliov et al., Delivery of phytochemical thymoquinone using molecular micelle modified poly (D, L lactide-coglycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles, Nanotechnology, doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/28/285104
Gavhane, Yadav, Loss of orally administered drugs in GI tract, Saudi Pharm J, doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2012.03.005
Gazzar, Mezayen, Nicolls, Dreskin, Thymoquinone attenuates proinflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-activated mast cells by modulating NF-kappaB nuclear transactivation, Biochim Biophys Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.01.002
George, Jin, Wohlford-Lenane, Endotoxin responsiveness and subchronic grain dust-induced airway disease, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.2.L203
Gordon, Balmes, Fine, Sheppard, Airway oedema and obstruction in guinea pigs exposed to inhaled endotoxin, Br J Ind Med, doi:10.1136/oem.48.9.629
Gothai, Ganesan, Park, Fakurazi, Choi et al., Natural phyto-bioactive compounds for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: inflammation as a target, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu8080461
Goyal, Prajapati, Gore, Therapeutic potential and pharmaceutical development of thymoquinone: a multitargeted molecule of natural origin, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00656
Grenha, Seijo, Remunán-López, Microencapsulated chitosan nanoparticles for lung protein delivery, Eur J Pharm Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2005.04.009
Hainaut, Hernandez, Robinson, IARC Database of p53 gene mutations in human tumors and cell lines: updated compilation, revised formats and new visualisation tools, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/26.1.205
Havlik, Kokoska, Vasickova, Valterova, Chemical composition of essential oil from the seeds of Nigella arvensis L. and assessment of its actimicrobial activity, Flavour Fragr J, doi:10.1002/ffj.1713
Hele, First siena international conference on animal models of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 2001 Sept-30-Oct 2; Certosa di Pontignano, University of Siena, Italy, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/rr161
Hendrickson, Matthay, Viral pathogens and acute lung injury: investigations inspired by the SARS epidemic and the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic, Semin Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1055/s-0033-1351122
Hirohashi, Morrison, Low-dose lipopolysaccharide (LPS) pretreatment of mouse macrophages modulates LPS-dependent interleukin-6 production in vitro, Infect Immun, doi:10.1128/iai.64.3.1011-1015.1996
Huang, Hu, Huang, Nanomaterial applications for neurological diseases and central nervous system injury, Prog Neurobiol, doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.07.003
Hui, Azhar, Madani, The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health-The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009
Hutson, Church, Clay, Miller, Holgate, Early and late-phase bronchoconstriction after allergen challenge of nonanesthetized guinea pigs, Am Rev Respir Dis, doi:10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.548
Irigaray, Newby, Clapp, Lifestyle-related factors and environmental agents causing cancer: an overview, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2007.10.006
Ismail, Ismail, Azmi, Thymoquinone-rich fraction nanoemulsion (TQRFNE) decreases Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels by modulating APP processing, up-regulating IDE and LRP1, and down-regulating BACE1 and RAGE in response to high fat/ cholesterol diet-induced rats, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.074
Kalam, Raish, Ahmed, Oral bioavailability enhancement and hepatoprotective effects of thymoquinone by self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system, Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, doi:10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.088
Kaneko, Takashima, Suzuki, Yamana, Effects of theophylline on chronic inflammatory lung injury induced by LPS exposure in guinea pigs, Allergol Int, doi:10.2332/allergolint.O-07-490
Kanter, Effects of Nigella sativa seed extract on ameliorating lung tissue damage in rats after experimental pulmonary aspirations, Acta Histochem, doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2008.10.008
Kazan, Yesil-Celiktas, Zhang, Fabrication of thymoquinone-loaded albumin nanoparticles by microfluidic particle synthesis and their effect on planarian regeneration, Macromol Biosci, doi:10.1002/mabi.201900182
Keyhanmanesh, Boskabady, Khamneh, Doostar, Effect of thymoquinone on the lung pathology and cytokine levels of ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1016/s1734-1140(10)70351-0
Khattabi, Talib, Alqdeimat, The effect of polymer length on the in vitro characteristics of a drug loaded and targeted silica nanoparticles, Saudi Pharmaceut J, doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2018.05.010
Khedoe, Wong, Wagenaar, The effect of PPEinduced emphysema and chronic LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation on therosclerosis development in APOE*3-LEIDEN mice, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080196
Kobayashi, Exposure to diesel exhaust aggravates nasal allergic reaction in guinea pigs, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.162.2.9809035
Kolhar, Anselmo, Gupta, Using shape effects to target antibody-coated nanoparticles to lung and brain endothelium, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1308345110
Kulyar, Li, Mehmood, Waqas, Li et al., Potential influence of Nagella sativa (Black cumin) in reinforcing immune system: a hope to decelerate the COVID-19 pandemic, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153277
Kumar, Ilavarasan, Jayachandran, Anti-diabetic activity of Syzygium cumini and its isolated compound against streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, J Med Plants Res, doi:10.5897/JMPR.9000093
Lebda, El-Far, Noreldin, Elewa, Jaouni et al., Protective effects of miswak (Salvadora persica) against experimentally induced gastric ulcers in rats, Oxid Med Cell Longev, doi:10.1155/2018/6703296
Lee, Loo, Traini, Young, Inhalation of nanoparticle-based drug for lung cancer treatment: advantages and challenges, Asian J Pharm Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2015.08.009
Li, Ma, Acute respiratory failure in COVID-19: is it "typical" ARDS?, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-02911-9
Liu, Gong, Fu, Solid lipid nanoparticles for pulmonary delivery of insulin, Int J Pharm, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.01.008
Mahapatro, Singh, Biodegradable nanoparticles are excellent vehicle for site directed in vivo delivery of drugs and vaccines, J Nanobiotechnol, doi:10.1186/1477-3155-9-55
Malcolmson, Embleton, Dry powder formulations for pulmonary delivery, Pharmaceut Sci Tech Today, doi:10.1016/S1461-5347(98)00099-6
Mcgettrick, Neill, Regulators of TLR4 signaling by endotoxins, Subcell Biochem, doi:10.1007/978-90-481-9078-2_7
Nemmar, Al-Salam, Zia, Contrasting actions of diesel exhaust particles on the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems and the effects of thymoquinone, Br J Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01442.x
Ng, Saiful Yazan, Yap, Hafiza, How et al., Thymoquinone-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier exhibited cytotoxicity towards breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7) and cervical cancer cell lines (HeLa and SiHa), Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2015/263131
Nihei, Suzuki, Aoki, Development of a novel nanoparticle formulation of thymoquinone with a cold wet-milling system and its pharmacokinetic analysis, Int J Pharmaceut, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.07.038
Odeh, Ismail, Abu-Dahab, Bawab, Thymoquinone in liposomes: a study of loading efficiency and biological activity towards breast cancer, Drug Deliv, doi:10.3109/10717544.2012.727500
Onclinx, Maertelaer, Gustin, Gevenois, Elastaseinduced pulmonary emphysema in rats: comparison of computed density and microscopic morphometry, Radiology, doi:10.1148/radiol.2413051456
Ong, Saiful Yazan, Ng, Thymoquinone loaded in nanostructured lipid carrier showed enhanced anticancer activity in 4T1 tumor-bearing mice, Nanomedicine, doi:10.2217/nnm-2017-0322
Parratt, Nitric oxide in sepsis and endotoxaemia, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/41.suppl_1.31
Paul, Chakrabarty, Ghosh, Targeting cellular microtubule by phytochemical apocynin exhibits autophagy-mediated apoptosis to inhibit lung carcinoma progression and tumorigenesis, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153152
Pillai, Akhter, Morris, Super aqueous solubility of albendazole in β-cyclodextrin for parenteral application in cancer therapy, J Cancer, doi:10.7150/jca.17301
Piñeiro-Carrero, Piñeiro, None, Liver. Pediatrics
Pourgholamhossein, Sharififar, Rasooli, Thymoquinone effectively alleviates lung fibrosis induced by paraquat herbicide through down-regulation of pro-fibrotic genes and inhibition of oxidative stress, Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.etap.2016.06.019
Raetz, Whitfield, Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins, Annu Rev Biochem, doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135414
Rajput, Puvvada, Kumar, Overcoming akt induced therapeutic resistance in breast cancer through siRNA and thymoquinone encapsulated multilamellar gold niosomes, Mol Pharm, doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00692
Ramachandran, Thangarajan, A novel therapeutic application of solid lipid nanoparticles encapsulated thymoquinone (TQ-SLNs) on 3-nitroproponic acid induced Huntington's diseaselike symptoms in wistar rats, Chem Biol Interact, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2016.05.020
Ramachandran, Thangarajan, Thymoquinone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles counteracts 3-Nitropropionic acid induced motor impairments and neuroinflammation in rat model of Huntington's disease, Metab Brain Dis, doi:10.1007/s11011-018-0252-0
Rani, Dahiya, Dhingra, Dilbaghi, Kim et al., Improvement of antihyperglycemic activity of nano-thymoquinone in rat model of type-2 diabetes, Chem Biol Interact, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.006
Rathore, Rathbone, Chellappan, Nanocarriers: more than tour de force for thymoquinone, Expert Opin Drug Deliv, doi:10.1080/17425247.2020.1730808
Saghir, Gabri, Khafaga, Thymoquinone-PLGA-PVA nanoparticles ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats via regulation of inflammatory cytokines and iNOS signaling, Animals, doi:10.3390/ani9110951
Sairazi, Sirajudeen, Natural products and their bioactive compounds: neuroprotective potentials against neurodegenerative diseases, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2020/6565396
Savov, Brass, Berman, Mcelvania, Schwartz, Fibrinolysis in LPS-induced chronic airway disease, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00102.2003
Seigneuric, Markey, Nuyten, From nanotechnology to nanomedicine: applications to cancer research, Curr Mol Med, doi:10.2174/156652410792630634
Sezen, Kucuk, Özer, Assessment of the effects of levosimendan and thymoquinone on lung injury after myocardial ischemia reperfusion in rats, Drug Des Devel Ther, doi:10.2147/DDDT.S160092
Shaarani, Hamid, Kaus, The Influence of pluronic F68 and F127 nanocarrier on physicochemical properties, in vitro release, and antiproliferative activity of thymoquinone drug, Pharmacognosy Res, doi:10.4103/0974-8490.199774
Shapiro, The macrophage in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.160.supplement_1.9
Singh, Ahmad, Akhter, Nanocarrier based formulation of thymoquinone improves oral delivery: stability assessment, in vitro and in vivo studies, Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.08.038
Soni, Kaur, Tikoo, Dual drug-loaded paclitaxel-thymoquinone nanoparticles for effective breast cancer therapy, J Nanopart Res, doi:10.1007/s11051-014-2821-4
Stolk, Rudolphus, Davies, Induction of emphysema and bronchial mucus cell hyperplasia by intratracheal instillation of lipopolysaccharide in the hamster, J Pathol, doi:10.1002/path.1711670314
Suddek, Ashry, Gameil, Thymoquinone attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced pulmonary injury in rats, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-012-0160-6
Taborsky, Kunt, Kloucek, Lachman, Zeleny et al., Identification of potential sources of thymoquinone and related compounds in Asteraceae, Cupressaceae, Lamiaceae, and Ranunculaceae families, Cent Eur J Chem, doi:10.2478/s11532-012-0114-2
Tong, Bi, Zhu, Keratinocyte growth factor-2 is protective in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats, Respir Physiol Neurobiol, doi:10.1016/j.resp.2014.06.011
Ulfa, Sholikhah, Utomo, Editors, Synthesis of thymoquinone derivatives and its activity analysis: in-silico approach
Ulich, Yi, Yin, Smith, Remick, Intratracheal administration of endotoxin and cytokines: VII. The soluble interleukin-1 receptor and the soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor II (p80) inhibit acute inflammation, Clin Immunol Immunopathol, doi:10.1006/clin.1994.1117
Van Rijt, Bein, Meiners, Medical nanoparticles for next generation drug delivery to the lungs, Eur Respir Soc, doi:10.1183/09031936.00212813
Ventola, The nanomedicine revolution: part 1: emerging concepts, P T
Vernooy, Dentener, Van Suylen, Buurman, Wouters, Long-term intratracheal lipopolysaccharide exposure in mice results in chronic lung inflammation and persistent pathology, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, doi:10.1165/ajrcmb.26.1.4652
Vogelzang, Van Der Gulden, Folgering, Endotoxin exposure as a major determinant of lung function decline in pig farmers, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.157.1.9703087
Ware, Matthay, The acute respiratory distress syndrome, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJM200005043421806
Xiao, Zhu, Bu, Li, Zhou et al., Evaluation of neuroprotective effect of thymoquinone nanoformulation in the rodent cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model, Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2016/2571060
Xiao, Zhu, Zhang, Emodin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury, involving the inactivation of NF-κB in mice, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms151119355
Yogyakarta, None, doi:10.1063/1.4978175
Younus, Molecular and Therapeutic Actions of Thymoquinone: Actions of Thymoquinone
Zhang, Shen, Nagai, Prolonged hypoglycemic effect of insulin-loaded polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles after pulmonary administration to normal rats, Int J Pharm, doi:10.1016/s0378-5173(01)00614-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2147/ijn.s314321",
"ISSN": [
"1178-2013"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S314321",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Gabri",
"given": "Naif A",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saghir",
"given": "Sultan AM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Hashedi",
"given": "Sallah A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9721-4360",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "El-Far",
"given": "Ali H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khafaga",
"given": "Asmaa F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3247-5898",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Swelum",
"given": "Ayman A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-wajeeh",
"given": "Abdullah S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9294-015X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mousa",
"given": "Shaker A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2831-8534",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Abd El-Hack",
"given": "Mohamed E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naiel",
"given": "Mohammed AE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8189-7088",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "El-Tarabily",
"given": "Khaled A",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Nanomedicine",
"container-title-short": "IJN",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-27T05:50:06Z",
"timestamp": 1627365006000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-05T15:36:58Z",
"timestamp": 1672933018000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-07T20:15:25Z",
"timestamp": 1715112925718
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 12,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625097600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.dovepress.com/getfile.php?fileID=72104",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.dovepress.com/getfile.php?fileID=72104",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"page": "5117-5131",
"prefix": "10.2147",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.resp.2014.06.011",
"author": "Tong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Respir Physiol Neurobiol",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms151119355",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19355",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM200005043421806",
"author": "Ware",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1334",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "342",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.548",
"author": "Hutson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "548",
"journal-title": "Am Rev Respir Dis",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "137",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00102.2003",
"author": "Savov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "L940",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/rr161",
"author": "Hele",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Respir Res",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.162.2.9809035",
"author": "Kobayashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "352",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"author": "Coker",
"first-page": "981",
"journal-title": "Am J Pathol",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "150",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2413051456",
"author": "Onclinx",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "763",
"journal-title": "Radiology",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "241",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/oem.48.9.629",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "629",
"journal-title": "Br J Ind Med",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "48",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/clin.1994.1117",
"author": "Ulich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol Immunopathol",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "72",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3923/ijp.2016.232.248",
"author": "Abd El-Hack",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "232",
"journal-title": "Int J Pharmacol",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-48798-0_17",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13",
"volume-title": "Black Cumin (Nigella sativa) Seeds: Chemistry, Technology, Functionality, and Applications. Food Bioactive Ingredients",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2478/aoas-2019-0043",
"author": "Gado",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Ann Anim Sci",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.044",
"author": "El-Far",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "711",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1477-3155-9-55",
"author": "Mahapatro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "J Nanobiotechnol",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.00212813",
"author": "van Rijt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "765",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir Soc",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/863951",
"author": "Babu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "863951",
"journal-title": "J Nanomater",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajps.2015.08.009",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "481",
"journal-title": "Asian J Pharm Sci",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1461-5347(98)00099-6",
"author": "Malcolmson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "394",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceut Sci Tech Today",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2005.04.009",
"author": "Grenha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "427",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharm Sci",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1308345110",
"author": "Kolhar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10753",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.01.008",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "333",
"journal-title": "Int J Pharm",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0378-5173(01)00614-7",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Int J Pharm",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.08.008",
"author": "Al-Qadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "J Control Release",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ani9110951",
"author": "Saghir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "951",
"journal-title": "Animals",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.carres.2003.07.010",
"author": "Caroff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2431",
"journal-title": "Carbohydr Res",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "338",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri1004",
"author": "Beutler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "169",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135414",
"author": "Raetz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "635",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Biochem",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/pupt.2000.0231",
"author": "Asti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "61",
"journal-title": "Pulm Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/rcmb.2004-0078OC",
"author": "Armstrong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "241",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-90-481-9078-2_7",
"author": "McGettrick",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Subcell Biochem",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.118.2.503",
"author": "Dinarello",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "503",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/iai.64.3.1011-1015.1996",
"author": "Hirohashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1011",
"journal-title": "Infect Immun",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "64",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/41.suppl_1.31",
"author": "Parratt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "ref35",
"volume": "41",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0033-1351122",
"author": "Hendrickson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Semin Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009",
"author": "Hui",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "264",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "ref37",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02911-9",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "198",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Cai",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "South Dakota Med",
"key": "ref39",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.160.supplement_1.9",
"author": "Shapiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S29",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "160",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"key": "ref41",
"volume-title": "Targeting Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases Using Advanced Drug Delivery Systems",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/ajrcmb.26.1.4652",
"author": "Vernooy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol",
"key": "ref42",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.2.L203",
"author": "George",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "L203",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "280",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2332/allergolint.O-07-490",
"author": "Kaneko",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Allergol Int",
"key": "ref44",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1711670314",
"author": "Stolk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "349",
"journal-title": "J Pathol",
"key": "ref45",
"volume": "167",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.157.1.9703087",
"author": "Vogelzang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref46",
"volume": "157",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0080196",
"author": "Khedoe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e80196",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref47",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2478/s11532-012-0114-2",
"author": "Taborsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1899",
"journal-title": "Cent Eur J Chem",
"key": "ref48",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ffj.1713",
"author": "Havlik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "713",
"journal-title": "Flavour Fragr J",
"key": "ref49",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2017.00656",
"author": "Goyal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "656",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ref50",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "ref51",
"volume-title": "Molecular and Therapeutic Actions of Thymoquinone: Actions of Thymoquinone",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01442.x",
"author": "Nemmar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1871",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "ref52",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21608/ZVJZ.2017.7948",
"author": "Al-Gabri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "Zagazig Vet J",
"key": "ref53",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-019-05229-4",
"author": "Al-Gabri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "18465",
"journal-title": "Environ Sci Pollut Res Int",
"key": "ref54",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.etap.2016.06.019",
"author": "Pourgholamhossein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "340",
"journal-title": "Environ Toxicol Pharmacol",
"key": "ref55",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/15412555.2016.1153614",
"author": "Barnawi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "653",
"journal-title": "COPD",
"key": "ref56",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1734-1140(10)70351-0",
"author": "Keyhanmanesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "910",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "ref57",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-012-0160-6",
"author": "Suddek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "427",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "ref58",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2006.02.004",
"author": "El Gazzar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1135",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "ref59",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111157",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111157",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "ref60",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.01.002",
"author": "El Gazzar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "556",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta",
"key": "ref61",
"volume": "1770",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2015/263131",
"author": "Ng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "263131",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res Int",
"key": "ref62",
"volume": "2015",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2500/ajra.2011.25.3703",
"author": "Cingi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e268",
"journal-title": "Am J Rhinol Allergy",
"key": "ref63",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.acthis.2008.10.008",
"author": "Kanter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "393",
"journal-title": "Acta Histochem",
"key": "ref64",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/ICO.0b013e31804f5a45",
"author": "Erdurmus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Cornea",
"key": "ref65",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DDDT.S160092",
"author": "Sezen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1347",
"journal-title": "Drug Des Devel Ther",
"key": "ref66",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2013.12.003",
"author": "Basavaraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B",
"key": "ref67",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/jca.17301",
"author": "Pillai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "913",
"journal-title": "J Cancer",
"key": "ref68",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mabi.201900182",
"author": "Kazan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1900182",
"journal-title": "Macromol Biosci",
"key": "ref69",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsps.2012.03.005",
"author": "Gavhane",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "331",
"journal-title": "Saudi Pharm J",
"key": "ref70",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1166/jbns.2017.1447",
"author": "AbuKhader",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "258",
"journal-title": "J Bionanosci",
"key": "ref71",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.4978175",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref72",
"unstructured": "Ulfa SM, Sholikhah S, Utomo EP, editors. Synthesis of thymoquinone derivatives and its activity analysis: in-silico approach. Proceedings of the International Conference on Chemistry, Chemical Process and Engineering (IC3PE); Yogyakarta, Indonesia; AIP Publishing LLC; 2017. doi:10.1063/1.4978175."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/156652410792630634",
"author": "Seigneuric",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "640",
"journal-title": "Curr Mol Med",
"key": "ref73",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "Ventola",
"first-page": "512",
"journal-title": "P T",
"key": "ref74",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DDDT.S308863",
"author": "Badary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1819",
"journal-title": "Drug Des Devel Ther",
"key": "ref75",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17425247.2020.1730808",
"author": "Rathore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "479",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Drug Deliv",
"key": "ref76",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrg1748",
"author": "Feinberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Genet",
"key": "ref77",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.07.010",
"author": "Colnaghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "875",
"journal-title": "Semin Cell Dev Biol",
"key": "ref78",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2007.10.006",
"author": "Irigaray",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "640",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "ref79",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature07423",
"author": "Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1069",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref80",
"volume": "455",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/26.1.205",
"author": "Hainaut",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "ref81",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijo.25.4.857",
"author": "Gali-Muhtasib",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "857",
"journal-title": "Int J Oncol",
"key": "ref82",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijc.21205",
"author": "El-Mahdy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Int J Cancer",
"key": "ref83",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3923/ijp.2020.554.561",
"author": "Fahmy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "554",
"journal-title": "Int J Pharmacol",
"key": "ref84",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1088/0957-4484/21/28/285104",
"author": "Ganea",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "285104",
"journal-title": "Nanotechnology",
"key": "ref85",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/10717544.2012.727500",
"author": "Odeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "371",
"journal-title": "Drug Deliv",
"key": "ref86",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1691/ph.2013.3033",
"author": "Abu-Dahab",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "939",
"journal-title": "Pharmazie",
"key": "ref87",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11051-014-2821-4",
"author": "Soni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "J Nanopart Res",
"key": "ref88",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11051-014-2821-4",
"author": "Dehghani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "539",
"journal-title": "Iran J Pharm Res",
"key": "ref89",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.01.007",
"author": "Bhattacharya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Biomaterials",
"key": "ref90",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/5584_2018_302",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref91",
"volume-title": "Cancer Biology and Advances in Treatment",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00692",
"author": "Rajput",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4214",
"journal-title": "Mol Pharm",
"key": "ref92",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2017.09.012",
"author": "El-Ashmawy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "525",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharm Sci",
"key": "ref93",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/nnm-2017-0322",
"author": "Ong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1567",
"journal-title": "Nanomedicine",
"key": "ref94",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0022-3476(97)70352-4",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr",
"key": "ref95",
"volume": "130",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5897/JMPR.9000093",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "246",
"journal-title": "J Med Plants Res",
"key": "ref96",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu8080461",
"author": "Gothai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "461",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref97",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.006",
"author": "Rani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Chem Biol Interact",
"key": "ref98",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/6703296",
"author": "Lebda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6703296",
"journal-title": "Oxid Med Cell Longev",
"key": "ref99",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S44108",
"author": "Abdelwahab",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2163",
"journal-title": "Int J Nanomedicine",
"key": "ref100",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1208/s12249-020-01693-1",
"author": "Fahmy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "AAPS PharmSciTech",
"key": "ref101",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.113.S3.1097",
"author": "Piñeiro-Carrero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1097",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "ref102",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.08.038",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "822",
"journal-title": "Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces",
"key": "ref103",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1208/s12249-015-0391-0",
"author": "Elmowafy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "663",
"journal-title": "AAPS PharmSciTech",
"key": "ref104",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.088",
"author": "Kalam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl",
"key": "ref105",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/6565396",
"author": "Mohd Sairazi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6565396",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "ref106",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S35329",
"author": "Alam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5705",
"journal-title": "Int J Nanomed",
"key": "ref107",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2016/2571060",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2571060",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res Int",
"key": "ref108",
"volume": "2016",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.07.003",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "Prog Neurobiol",
"key": "ref109",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.019",
"author": "Ahmad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "ref110",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.074",
"author": "Ismail",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "780",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "ref111",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jmg.2003.015602",
"author": "Bauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "230",
"journal-title": "J Med Genet",
"key": "ref112",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbi.2016.05.020",
"author": "Ramachandran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "Chem Biol Interact",
"key": "ref113",
"volume": "256",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11011-018-0252-0",
"author": "Ramachandran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1459",
"journal-title": "Metab Brain Dis",
"key": "ref114",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153277",
"author": "Kulyar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "153277",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "ref115",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17476348.2018.1523009",
"author": "Chakraborty",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "941",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Respir Med",
"key": "ref116",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21051613",
"author": "Chakraborty",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1613",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "ref117",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2011.10.013",
"author": "Ammar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2232",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "ref118",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153152",
"author": "Paul",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "153152",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "ref119",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118654",
"author": "Chakraborty",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118654",
"journal-title": "Int J Pharm",
"key": "ref120",
"volume": "570",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2015.03.011",
"author": "Darakhshan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "138",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "ref121",
"volume": "95–96",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871529X18666180212114816",
"author": "Shaterzadeh-Yazdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets",
"key": "ref122",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.07.038",
"author": "Nihei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "455",
"journal-title": "Int J Pharmaceut",
"key": "ref123",
"volume": "511",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0974-8490.199774",
"author": "Shaarani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Pharmacognosy Res",
"key": "ref124",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsps.2018.05.010",
"author": "Khattabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1022",
"journal-title": "Saudi Pharmaceut J",
"key": "ref125",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 125,
"references-count": 125,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.dovepress.com/therapeutic-potential-of-thymoquinone-and-its-nanoformulations-in-pulm-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-IJN"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone and Its Nanoformulations in Pulmonary Injury: A Comprehensive Review",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "Volume 16"
}