Nutritional Status and Selenium Biomarkers in COVID-19
et al., Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144, Feb 2026
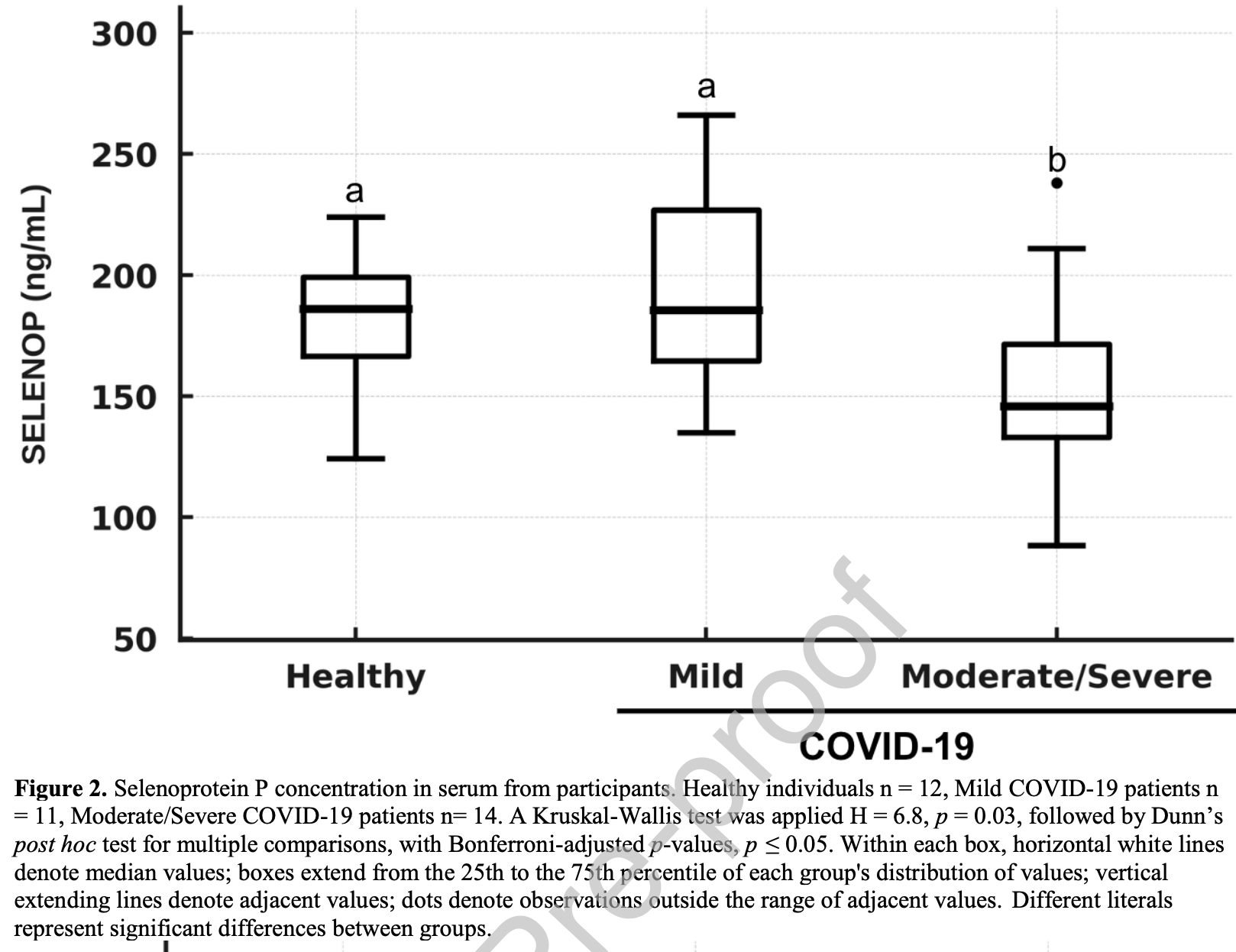
Cross-sectional study of 95 COVID-19 patients and 29 healthy controls examining selenium status and nutritional factors. Patients with moderate/severe COVID-19 had lower selenoprotein P levels compared to mild cases, despite adequate dietary selenium intake across all groups.
Roldán-Bretón et al., 12 Feb 2026, retrospective, Mexico, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period June 2020 - October 2020.
Contact: renata.roldan@uabc.edu.mx, nutrois@gmail.com, gabriela.leija@uabc.edu.mx, maria.navarro.ibarra@uabc.edu.mx, gonzaleza1@uabc.edu.mx, esther.mejia86@uabc.edu.mx.
Nutritional Status and Selenium Biomarkers in COVID-19
Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144
The Coronavirus Disease 2019 , caused by SARS-CoV-2, causes severe systemic effects. The oxidative mechanism of COVID-19 is characterized by excessive production of reactive oxygen species within infected cells, contributing to oxidative stress, cellular damage, and inflammation. Clinical features, dietary intake, and micronutrients influence infection severity. Selenium is an essential micronutrient that plays a crucial role in modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. These responses are closely associated with COVID-19 severity and progression. This study was conducted in northern Mexico between June and October 2020. Participants included adults aged 18 years and older with healthy and PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. We found that patients with COVID-19 exhibited a higher prevalence of overweight or obesity, although there were no significant differences in BMI or by age. Body composition analysis revealed that female COVID-19 patients had significantly higher fat mass and lower fat-free mass compared to healthy females. Dietary analysis showed both groups had elevated caloric intake, characterized by high consumption of total fats, saturated fats, and added sugars, concurrent with inadequate fiber and vitamin D intake. COVID-19 patients had selenium intake within recommendations. However, Selenoprotein P was lower in moderate/severe COVID-19 patients. Serum albumin and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) were significantly reduced in COVID-19 patients, potentially suggesting systemic inflammation. This study highlights the importance of assessing nutritional status and dietary patterns to understand their potential role in disease progression and recovery, emphasizing the relevance of essential nutrients in maintaining health during infections and the need for further research to linking selenium, inflammation, and clinical outcomes.
Author Contributions All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by NRRB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by NRRB and MEML. DRP, MJNI, AAGR and AGLM commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-forprofit sectors.
Competing Interests RBNR receives a CONACYT grant number 2021-000018-02NACF-06760 to pursue doctoral studies. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Declaration of interests ☐ The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. ☒ The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Maria Esther Mejia Leon reports was provided by Autonomous University of Baja California. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Avery, Hoffmann, Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Immunity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10091203
Avery, Hoffmann, Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Immunity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10091203
Beck, Nelson, Shi, Selenium deficiency increases the pathology of an influenza virus infection, FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol
Beck, Nelson, Shi, Selenium deficiency increases the pathology of an influenza virus infection, FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol
Becker, Martitz, Renko, Hypoxia reduces and redirects selenoprotein biosynthesis, Met Integr Biometal Sci, doi:10.1039/c4mt00004h
Chambliss, Aljehani, Tran, Immune biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease severity in an urban, hospitalized population, Pract Lab Med, doi:10.1016/j.plabm.2023.e00323
Devaux, Rolain, Raoult, ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome, J Microbiol Immunol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015
Doaei, Mardi, Zare, Role of micronutrients in the modulation of immune system and platelet activating factor in patients with COVID-19; a narrative review, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1207237
Ezquivel, Romero, Esparza, Implementation of the Nutritional Health Promotion Center in University Students of the Faculty of Mexicali Medicine, Curr Dev Nutr, doi:10.1093/cdn/nzaa043_043
Filippini, Urbano, Grill, Human serum albumin-bound selenium (Se-HSA) in serum and its correlation with other selenium species, J Trace Elem Med Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127266
Godos, Giampieri, Micek, Effect of Brazil Nuts on Selenium Status, Blood Lipids, and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11020403
Golin, Tinkov, Aschner, Relationship between selenium status, selenoproteins and COVID-19 and other inflammatory diseases: A critical review, J Trace Elem Med Biol Organ Soc Miner Trace Elem GMS, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127099
Golin, Tinkov, Aschner, Relationship between selenium status, selenoproteins and COVID-19 and other inflammatory diseases: A critical review, J Trace Elem Med Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127099
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Risk Factors Associated With Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in Intensive Care Units in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539
Haratake, Hongoh, Miyauchi, Albumin-Mediated Selenium Transfer by a Selenotrisulfide Relay Mechanism, Inorg Chem, doi:10.1021/ic800310j
Haratake, Hongoh, Miyauchi, Albumin-Mediated Selenium Transfer by a Selenotrisulfide Relay Mechanism, Inorg Chem, doi:10.1021/ic800310j
Heller, Sun, Hackler, Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764
Hourani, Alkhatib, Shami, Energy and macronutrient intakes in Jordan: a population study
Kagawa, Influence of Nutritional Intakes in Japan and the United States on COVID-19 Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030633
Khatiwada, Subedi, A Mechanistic Link Between Selenium and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Curr Nutr Rep, doi:10.1007/s13668-021-00354-4
Khatiwada, Subedi, A Mechanistic Link Between Selenium and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Curr Nutr Rep, doi:10.1007/s13668-021-00354-4
Kieliszek, Błażejak, Selenium: Significance, and outlook for supplementation, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.11.012
Kieliszek, Selenium-Fascinating Microelement, Properties and Sources in Food, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules24071298
Kozlov, Ivanova, Grechko, Involvement of Oxidative Stress and the Innate Immune System in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Diseases, doi:10.3390/diseases9010017
Laing, Petrovic, Lachat, Course and Survival of COVID-19 Patients with Comorbidities in Relation to the Trace Element Status at Hospital Admission, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103304
Lehane, Levy, Erglis, Colorimetric quantitation of albumin in microliter volumes of serum, Ann Clin Lab Sci
Lopez, Murillo, Neciosup, Rios, Hypoalbuminemia as a predicator of mortality of sepsis from COVID-19. Hospital II Chocope, Rev Fac Med Humana, doi:10.25176/RFMH.v21i1.3437
Lucijanić, Stojić, Atić, Clinical and prognostic significance of Creactive protein to albumin ratio in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients : Data on 2309 patients from a tertiary center and validation in an independent cohort, Wien Klin Wochenschr, doi:10.1007/s00508-021-01999-5
Lucijanić, Stojić, Atić, Clinical and prognostic significance of Creactive protein to albumin ratio in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, Wien Klin Wochenschr, doi:10.1007/s00508-021-01999-5
Maggini, Pierre, Calder, Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10101531
Maggini, Pierre, Calder, Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10101531
Meng, Li, Liu, The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clin Nutr Edinb Scotl, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008
Minich, Selenium Metabolism and Biosynthesis of Selenoproteins in the Human Body, Biochem Biokhimiia, doi:10.1134/S0006297922140139
Moghaddam, Heller, Sun, Selenium Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality Risk from COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072098
Pincemail, Cavalier, Charlier, Oxidative Stress Status in COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in Intensive Care Unit for Severe Pneumonia. A Pilot Study, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10020257
Sattar, Valabhji, Obesity as a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19: Summary of the Best Evidence and Implications for Health Care, Curr Obes Rep, doi:10.1007/s13679-021-00448-8
Shahbaz, Fatima, Basharat, Role of vitamin C in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, AIMS Microbiol, doi:10.3934/microbiol.2022010
Simopoulos, Genetic Variation, Diet, Inflammation, and the Risk for COVID-19, Lifestyle Genomics, doi:10.1159/000513886
Skesters, Kustovs, Lece, Selenium, selenoprotein P, and oxidative stress levels in SARS-CoV-2 patients during illness and recovery, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-022-00925-z
Suárez, Quezada, Ruiz, De Jesús, Epidemiología de COVID-19 en México: del 27 de febrero al 30 de abril de 2020, Rev Clin Esp, doi:10.1016/j.rce.2020.05.007
Tinggi, Selenium: its role as antioxidant in human health, Environ Health Prev Med, doi:10.1007/s12199-007-0019-4
Tomaszewska, Rustecka, Lipińska-Opałka, The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 and the Impact of Pandemic Restrictions on Vitamin D Blood Content, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.836738
Tomo, Saikiran, Banerjee, Paul, Selenium to selenoproteins -role in COVID-19, EXCLI J, doi:10.17179/excli2021-3530
Vj, Velasco, Redondo-Flórez, Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15122749
Voelkle, Gregoriano, Neyer, Prevalence of Micronutrient Deficiencies in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19: An Observational Cohort Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14091862
Wang, Huang, Sun, SARS-CoV-2 suppresses mRNA expression of selenoproteins associated with ferroptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and DNA synthesis
Who, Healthy diet
Xu, Gong, Sun, Impact of Selenium Deficiency on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Phagocytosis in Mouse Macrophages, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-019-01775-7
Xu, Gong, Sun, Impact of Selenium Deficiency on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Phagocytosis in Mouse Macrophages, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-019-01775-7
Younesian, Khodabakhshi, Abdolahi, Decreased Serum Selenium Levels of COVID-19 Patients in Comparison with Healthy Individuals, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-02797-w
Zhang, Yu, Zhao, Albumin Infusion May Improve the Prognosis of Critical COVID-19 Patients with Hypoalbuminemia in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Infect Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S383818
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144",
"ISSN": [
"0899-9007"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144",
"alternative-id": [
"S0899900726000535"
],
"article-number": "113144",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Nutritional Status and Selenium Biomarkers in COVID-19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nutrition"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2026 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2037-933X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Roldán-Bretón",
"given": "Nuria Renata",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8051-9432",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Reyes-Pavón",
"given": "Diana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8543-5676",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Leija-Montoya",
"given": "Ana Gabriela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8051-6928",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Navarro-Ibarra",
"given": "María Jossé",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1867-958X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "González-Rascón",
"given": "Anna Arely",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3387-4858",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mejía-León",
"given": "María Esther",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-12T16:44:12Z",
"timestamp": 1770914652000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-13T16:09:41Z",
"timestamp": 1770998981000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-13T17:05:54Z",
"timestamp": 1771002354699,
"version": "3.50.1"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1769904000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1769904000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 12,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1770940800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900726000535?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900726000535?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "113144",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome",
"author": "Devaux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "425",
"journal-title": "J Microbiol Immunol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0002",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diseases9010017",
"article-title": "Involvement of Oxidative Stress and the Innate Immune System in SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Kozlov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0003",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"article-title": "Risk Factors Associated With Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in Intensive Care Units in Lombardy, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0004",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14091862",
"article-title": "Prevalence of Micronutrient Deficiencies in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19: An Observational Cohort Study",
"author": "Voelkle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1862",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0005",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13668-021-00354-4",
"article-title": "A Mechanistic Link Between Selenium and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Khatiwada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Curr Nutr Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0006",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2023.1207237",
"article-title": "Role of micronutrients in the modulation of immune system and platelet activating factor in patients with COVID-19; a narrative review",
"author": "Doaei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0007",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.836738",
"article-title": "The Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19 and the Impact of Pandemic Restrictions on Vitamin D Blood Content",
"author": "Tomaszewska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0008",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-021-02797-w",
"article-title": "Decreased Serum Selenium Levels of COVID-19 Patients in Comparison with Healthy Individuals",
"author": "Younesian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0009",
"volume": "200",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00508-021-01999-5",
"article-title": "Clinical and prognostic significance of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients : Data on 2309 patients from a tertiary center and validation in an independent cohort",
"author": "Lucijanić",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "Wien Klin Wochenschr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0010",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127266",
"article-title": "Human serum albumin-bound selenium (Se-HSA) in serum and its correlation with other selenium species",
"author": "Filippini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Trace Elem Med Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0011",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ic800310j",
"article-title": "Albumin-Mediated Selenium Transfer by a Selenotrisulfide Relay Mechanism",
"author": "Haratake",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6273",
"journal-title": "Inorg Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0012",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-019-01775-7",
"article-title": "Impact of Selenium Deficiency on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Phagocytosis in Mouse Macrophages",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0013",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1134/S0006297922140139",
"article-title": "Selenium Metabolism and Biosynthesis of Selenoproteins in the Human Body",
"author": "Minich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S168",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biokhimiia",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0014",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764",
"article-title": "Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker",
"author": "Heller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0015",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2012.11.012",
"article-title": "Selenium: Significance, and outlook for supplementation",
"author": "Kieliszek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "713",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0016",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10091203",
"article-title": "Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Immunity",
"author": "Avery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1203",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0017",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10101531",
"article-title": "Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course",
"author": "Maggini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0018",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Selenium deficiency increases the pathology of an influenza virus infection",
"author": "Beck",
"first-page": "1481",
"journal-title": "FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0019",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-022-00925-z",
"article-title": "Selenium, selenoprotein P, and oxidative stress levels in SARS-CoV-2 patients during illness and recovery",
"author": "Skesters",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0020",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Implementation of the Nutritional Health Promotion Center in University Students of the Faculty of Mexicali Medicine",
"author": "Ezquivel",
"first-page": "192",
"journal-title": "Curr Dev Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0023",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Al Hourani",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0025"
},
{
"article-title": "Colorimetric quantitation of albumin in microliter volumes of serum",
"author": "Lehane",
"first-page": "122",
"journal-title": "Ann Clin Lab Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0027",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13103304",
"article-title": "Course and Survival of COVID-19 Patients with Comorbidities in Relation to the Trace Element Status at Hospital Admission",
"author": "Du Laing",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3304",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0028",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10020257",
"article-title": "Oxidative Stress Status in COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in Intensive Care Unit for Severe Pneumonia",
"author": "Pincemail",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "A Pilot Study. Antioxidants",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0029",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S383818",
"article-title": "Albumin Infusion May Improve the Prognosis of Critical COVID-19 Patients with Hypoalbuminemia in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6039",
"journal-title": "Infect Drug Resist",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0030",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rce.2020.05.007",
"article-title": "Epidemiología de COVID-19 en México: del 27 de febrero al 30 de abril de 2020",
"author": "Suárez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "463",
"journal-title": "Rev Clin Esp",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0031",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules24071298",
"article-title": "Selenium–Fascinating Microelement, Properties and Sources in Food",
"author": "Kieliszek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0032",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-019-01775-7",
"article-title": "Impact of Selenium Deficiency on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Phagocytosis in Mouse Macrophages",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0033",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10091203",
"article-title": "Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Immunity",
"author": "Avery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0034",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Selenium deficiency increases the pathology of an influenza virus infection",
"author": "Beck",
"first-page": "1481",
"journal-title": "FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0035",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10101531",
"article-title": "Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course",
"author": "Maggini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0036",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13679-021-00448-8",
"article-title": "Obesity as a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19: Summary of the Best Evidence and Implications for Health Care",
"author": "Sattar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "282",
"journal-title": "Curr Obes Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0037",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14030633",
"article-title": "Influence of Nutritional Intakes in Japan and the United States on COVID-19 Infection",
"author": "Kagawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "633",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0038",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000513886",
"article-title": "Genetic Variation, Diet, Inflammation, and the Risk for COVID-19",
"author": "Simopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Lifestyle Genomics",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0039",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15122749",
"article-title": "Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review",
"author": "Clemente-Suárez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2749",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0040",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3934/microbiol.2022010",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin C in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Shahbaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "AIMS Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0041",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Meng",
"first-page": "2198",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr Edinb Scotl",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0042",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "A Mechanistic Link Between Selenium and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Khatiwada",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Nutr Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0043",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Relationship between selenium status, selenoproteins and COVID-19 and other inflammatory diseases: A critical review",
"author": "Golin",
"journal-title": "J Trace Elem Med Biol Organ Soc Miner Trace Elem GMS",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0044",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C4MT00004H",
"article-title": "Hypoxia reduces and redirects selenoprotein biosynthesis",
"author": "Becker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1079",
"journal-title": "Met Integr Biometal Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0045",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Selenium to selenoproteins - role in COVID-19",
"author": "Tomo",
"first-page": "781",
"journal-title": "EXCLI J",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0046",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11020403",
"article-title": "Effect of Brazil Nuts on Selenium Status, Blood Lipids, and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials",
"author": "Godos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0047",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127099",
"article-title": "Relationship between selenium status, selenoproteins and COVID-19 and other inflammatory diseases: A critical review",
"author": "Golin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Trace Elem Med Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0048",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.31.230243",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0049",
"unstructured": "Wang Y, Huang J, Sun Y, et al (2020) SARS-CoV-2 suppresses mRNA expression of selenoproteins associated with ferroptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and DNA synthesis. 2020.07.31.230243"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ic800310j",
"article-title": "Albumin-Mediated Selenium Transfer by a Selenotrisulfide Relay Mechanism",
"author": "Haratake",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6273",
"journal-title": "Inorg Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0050",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.25176/RFMH.v21i1.3437",
"article-title": "Hypoalbuminemia as a predicator of mortality of sepsis from COVID-19. Hospital II Chocope, 2020",
"author": "Lopez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Rev Fac Med Humana",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0051",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00508-021-01999-5",
"article-title": "Clinical and prognostic significance of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients",
"author": "Lucijanić",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "Wien Klin Wochenschr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0052",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12199-007-0019-4",
"article-title": "Selenium: its role as antioxidant in human health",
"author": "Tinggi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102",
"journal-title": "Environ Health Prev Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0053",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"article-title": "Immune biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease severity in an urban, hospitalized population",
"author": "Chambliss",
"journal-title": "Pract Lab Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0054",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072098",
"article-title": "Selenium Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality Risk from COVID-19",
"author": "Moghaddam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2098",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2026.113144_bib0055",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0899900726000535"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nutritional Status and Selenium Biomarkers in COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}