Therapies to Prevent Progression of COVID-19, Including Hydroxychloroquine, Azithromycin, Zinc, and Vitamin D3 With or Without Intravenous Vitamin C: An International, Multicenter, Randomized Trial
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.19902, ACTRN12620000557932, Nov 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
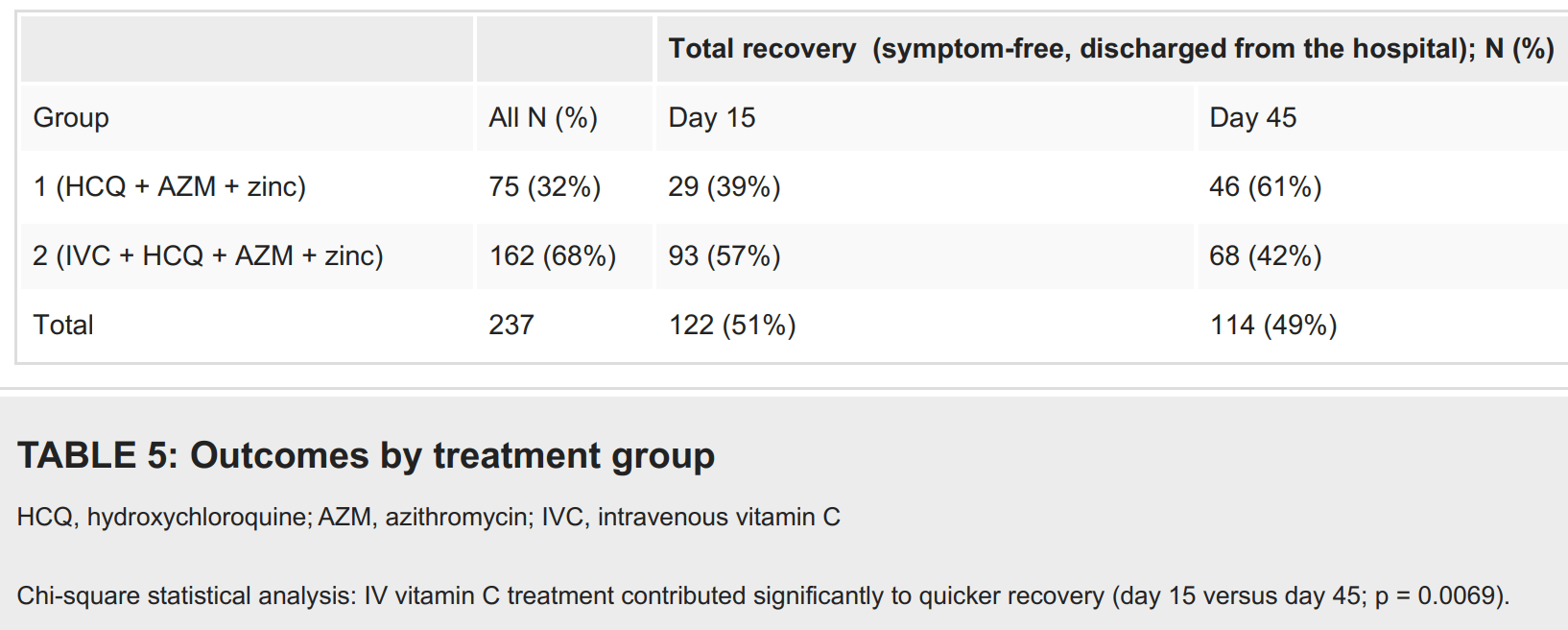
RCT 237 patients in Turkey, 162 treated with IV vitamin C in addition to HCQ/AZ/zinc/vitamin D used for all patients, showing significantly faster recovery with the addition of IV vitamin C.
97% of patients were vitamin D deficient, and lower vitamin D levels were associated with ICU admission and longer hospital stay.
Only 1 of 237 hospitalized patients died (average age 63, range 22-99) - a 70-year-old patient with heart and lung disease and severely deficient vitamin D levels (6 nmol/L). IV vitamin C (sodium ascorbate) was given as 50 mg/kg every six hours on day 1, followed by 100 mg/kg every six hours (four times daily, 400 mg/kg/day) for seven days. NCT04395768 (history).
This is the 9th of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0012.
This is the 36th of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
|
risk of no recovery, 30.6% lower, RR 0.69, p = 0.008, treatment 69 of 162 (42.6%), control 46 of 75 (61.3%), NNT 5.3, mid-recovery, day 15.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ried et al., 25 Nov 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, study period January 2021 - June 2021, average treatment delay 4.0 days, dosage 50mg/kg qid day 1, 100mg/kg qid days 2-7, trial ACTRN12620000557932.
Therapies to Prevent Progression of COVID-19, Including Hydroxychloroquine, Azithromycin, Zinc, and Vitamin D3 With or Without Intravenous Vitamin C: An International, Multicenter, Randomized Trial
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.19902
Background COVID-19 is a global pandemic. Treatment with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), zinc, and azithromycin (AZM), also known as the Zelenko protocol, and treatment with intravenous (IV) vitamin C (IVC) have shown encouraging results in a large number of trials worldwide. In addition, vitamin D levels are an important indicator of the severity of symptoms in patients with COVID-19.
Objectives Our multicenter, randomized, open-label study aimed to assess the effectiveness of HCQ, AZM, and zinc with or without IVC in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in reducing symptom severity and duration and preventing death.
Methods Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in seven participating hospitals in Turkey were screened for eligibility and randomly allocated to receive either HCQ, AZM, and zinc (group 1) or HCQ, AZM, zinc plus IV vitamin C treatment (group 2) for 14 days. The patients also received nontherapeutic levels of vitamin D3. The trial is registered on the Australian and New Zealand Clinical Trial Registry ACTRN12620000557932 and has been approved by the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).
Results A total of 237 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 aged 22-99 years (mean: 63.3 ± 15.7 years) were enrolled in the study. Almost all patients were vitamin D deficient (97%), 55% were severely vitamin D deficient (<25 nmol/L) and 42% were vitamin D deficient (<50 nmol/L); 3% had insufficient vitamin D levels (<75 nmol/L), and none had optimal vitamin D levels. Of the patients, 73% had comorbidities, including diabetes (35%), heart disease (36%), and lung disease (34%). All but one patient (99.6%; n = 236/237) treated with HCQ, AZM, and zinc with or without high-dose IV vitamin C (IVC) fully recovered. Additional IVC therapy contributed significantly to a quicker recovery (15 days versus 45 days until discharge; p = 0.0069). Side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, reported by 15%-27% of the patients, were mild to moderate and transient. No cardiac side effects were observed. Low vitamin D levels were significantly correlated with a higher probability of admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) and longer hospital stay.
References
Andreani, Bideau, Duflot, In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect, Microb Pathog, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104228
Baradaran, Ebrahimzadeh, Baradaran, Kachooei, Prevalence of comorbidities in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Bone Jt Surg, doi:10.22038/abjs.2020.47754.2346
Benskin, A basic review of the preliminary evidence that COVID-19 risk and severity is increased in vitamin D deficiency, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00513
Borsche, Glauner, Jv, COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/ml 25 (OH) D3: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.1101/2021.09.22.21263977
Bosseboeuf, Aubry, Nhan, De Pina, Rolain et al., Azithromycin inhibits the replication of Zika virus, J Antivir Antiretrovir, doi:10.4172/1948-5964.1000173
Brighthope, Am, Ried, Vitamin-D and COVID-19: time for the profession to take a stand, Adv Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.aimed.2021.01.003
Cerullo, Negro, Parimbelli, The long history of vitamin C: from prevention of the common cold to potential aid in the treatment of COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.574029
Derwand, Scholz, Does zinc supplementation enhance the clinical efficacy of 2021 Ried et al, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109815
Derwand, Scholz, Zelenko, COVID-19 outpatients: early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus lowdose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106214
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949
Hernández, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa733
Hu, Frieman, Insights from nanomedicine into chloroquine efficacy against COVID-19, Nat Nanotechnol, doi:10.1038/s41565-020-0674-9
Huang, Wang, Tan, Liu, Ni, High-dose vitamin C intravenous infusion in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025876
Mahmoodpoor, Shadvar, Sanaie, Hadipoor, Pourmoghaddam et al., Effect of vitamin C on mortality of critically ill patients with severe pneumonia in intensive care unit: a preliminary study, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06288-0
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Matin, Fouladi, Pahlevan, The sufficient vitamin D and albumin level have a protective effect on COVID-19 infection, Arch Microbiol, doi:10.1007/s00203-021-02482-5
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, Ahlenstiel, The role of zinc in antiviral immunity, Adv Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmz013
Retallack, Lullo, Arias, Zika virus cell tropism in the developing human brain and inhibition by azithromycin, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.1618029113/-/DCSupplemental
Tanriverdi, Çörtük, Yildirim, Hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin and early hospital admission are beneficial in COVID-19 patients: Turkish experience with real-life data, Turk J Med Sci, doi:10.3906/sag-2005-82
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
Travica, Ried, Bujnowski, Sali, Integrative health check reveals suboptimal levels in a number of vital biomarkers, Adv Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.aimed.2015.11.002
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Xu, Baylink, Chen, The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5
Xue, Moyer, Peng, Wu, Hannafon et al., Chloroquine is a zinc ionophore, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109180
Yang, Shen, Targeting the endocytic pathway and autophagy process as a novel therapeutic strategy in COVID-19, Int J Biol Sci, doi:10.7150/ijbs.45498
Yildiz, Senel, Kavurgaci, Ozturk, Ozturk, The prognostic significance of vitamin D deficiency in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Bratisl Lek Listy, doi:10.4149/BLL_2021_119
Zhao, Liu, Liu, High dose intravenous vitamin C for preventing the disease aggravation of moderate COVID-19 pneumonia. a retrospective propensity matched before-after study, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.638556
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.19902",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.19902",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ried",
"given": "Karin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "BinJemain",
"given": "Taufiq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sali",
"given": "Avni",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Cureus"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-25T22:55:56Z",
"timestamp": 1637880956000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-25T22:56:01Z",
"timestamp": 1637880961000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-26T06:17:42Z",
"timestamp": 1637907462596
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2168-8184"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/76496-therapies-to-prevent-progression-of-covid-19-including-hydroxychloroquine-azithromycin-zinc-and-vitamin-d3-with-or-without-intravenous-vitamin-c-an-international-multicenter-randomized-trial",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4492",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
25
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cureus, Inc.",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109815",
"article-title": "Does zinc supplementation enhance the clinical efficacy of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine to win today's battle against COVID-19?",
"author": "Derwand R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Derwand R, Scholz M. Does zinc supplementation enhance the clinical efficacy of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine to win today's battle against COVID-19?. Med Hypotheses. 2020, 142:109815. 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109815",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106214",
"article-title": "COVID-19 outpatients: early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low-dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study",
"author": "Derwand R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Derwand R, Scholz M, Zelenko V. COVID-19 outpatients: early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low-dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020, 56:106214. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106214",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.45498",
"article-title": "Targeting the endocytic pathway and autophagy process as a novel therapeutic strategy in COVID-19",
"author": "Yang N",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Sci",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Yang N, Shen HM. Targeting the endocytic pathway and autophagy process as a novel therapeutic strategy in COVID-19. Int J Biol Sci. 2020, 16:1724-31. 10.7150/ijbs.45498",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41565-020-0674-9",
"article-title": "Insights from nanomedicine into chloroquine efficacy against COVID-19",
"author": "Hu TY",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Nanotechnol",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Hu TY, Frieman M, Wolfram J. Insights from nanomedicine into chloroquine efficacy against COVID-19. Nat Nanotechnol. 2020, 15:247-9. 10.1038/s41565-020-0674-9",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Gautret P",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Gautret P, Lagier JC, Parola P, et al.. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020, 56:105949. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "HCQ for COVID- 19. real-time meta analysis of 294 studies. (2021). https://hcqmeta.com/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4172/1948-5964.1000173",
"article-title": "Azithromycin inhibits the replication of Zika virus",
"author": "Bosseboeuf E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Antivir Antiretrovir",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Bosseboeuf E, Aubry M, Nhan T, de Pina JJ, Rolain JM, Raoult D, Musso D. Azithromycin inhibits the replication of Zika virus. J Antivir Antiretrovir. 2018, 10:6-11. 10.4172/1948-5964.1000173",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1618029113/-/DCSupplemental",
"article-title": "Zika virus cell tropism in the developing human brain and inhibition by azithromycin",
"author": "Retallack H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PNAS",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Retallack H, Di Lullo E, Arias C, et al.. Zika virus cell tropism in the developing human brain and inhibition by azithromycin. PNAS. 2016, 113:14408-13. 10.1073/pnas.1618029113/-/DCSupplemental",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104228",
"article-title": "In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect",
"author": "Andreani J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Microb Pathog",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Andreani J, Le Bideau M, Duflot I, et al.. In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect. Microb Pathog. 2020, 145:104228. 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104228",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3906/sag-2005-82",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin and early hospital admission are beneficial in COVID-19 patients: Turkish experience with real-life data",
"author": "Tanriverdİ E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Turk J Med Sci",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Tanriverdİ E, Çörtük M, Yildirim BZ, et al.. Hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin and early hospital admission are beneficial in COVID-19 patients: Turkish experience with real-life data. Turk J Med Sci. 2021, 51:10-5. 10.3906/sag-2005-82",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0109180",
"article-title": "Chloroquine is a zinc ionophore",
"author": "Xue J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Xue J, Moyer A, Peng B, Wu J, Hannafon BN, Ding WQ. Chloroquine is a zinc ionophore. PLoS One. 2014, 9:e109180. 10.1371/journal.pone.0109180",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmz013",
"article-title": "The role of zinc in antiviral immunity",
"author": "Read SA",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Read SA, Obeid S, Ahlenstiel C, Ahlenstiel G. The role of zinc in antiviral immunity. Adv Nutr. 2019, 10:696-710. 10.1093/advances/nmz013",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"article-title": "Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture",
"author": "te Velthuis AJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "te Velthuis AJ, van den Worm SH, Sims AC, Baric RS, Snijder EJ, van Hemert MJ. Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6:e1001176. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.574029",
"article-title": "The long history of vitamin C: from prevention of the common cold to potential aid in the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Cerullo G",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Cerullo G, Negro M, Parimbelli M, et al.. The long history of vitamin C: from prevention of the common cold to potential aid in the treatment of COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2020, 11:574029. 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574029",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06288-0",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin C on mortality of critically ill patients with severe pneumonia in intensive care unit: a preliminary study",
"author": "Mahmoodpoor A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Mahmoodpoor A, Shadvar K, Sanaie S, Hadipoor MR, Pourmoghaddam MA, Saghaleini SH. Effect of vitamin C on mortality of critically ill patients with severe pneumonia in intensive care unit: a preliminary study. BMC Infect Dis. 2021, 21:616. 10.1186/s12879-021-06288-0",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000025876",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin C intravenous infusion in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Huang L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore)",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Huang L, Wang L, Tan J, Liu H, Ni Y. High-dose vitamin C intravenous infusion in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021, 100:e25876. 10.1097/MD.0000000000025876",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.638556",
"article-title": "High dose intravenous vitamin C for preventing the disease aggravation of moderate COVID-19 pneumonia. a retrospective propensity matched before-after study",
"author": "Zhao B",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Zhao B, Liu M, Liu P, et al.. High dose intravenous vitamin C for preventing the disease aggravation of moderate COVID-19 pneumonia. a retrospective propensity matched before-after study. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12:638556. 10.3389/fphar.2021.638556",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau AR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Martineau AR, Jolliffe DA, Hooper RL, et al.. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ. 2017, 356:i6583. 10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.00513",
"article-title": "A basic review of the preliminary evidence that COVID-19 risk and severity is increased in vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Benskin LL",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Benskin LL. A basic review of the preliminary evidence that COVID-19 risk and severity is increased in vitamin D deficiency. Front Public Health. 2020, 8:513. 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00513",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aimed.2021.01.003",
"article-title": "Vitamin-D and COVID-19: time for the profession to take a stand",
"author": "Brighthope I",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Adv Integr Med",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Brighthope I, Sali Am A, Ried K. Vitamin-D and COVID-19: time for the profession to take a stand. Adv Integr Med. 2021, 8:77-8. 10.1016/j.aimed.2021.01.003",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5",
"article-title": "The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Xu Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Xu Y, Baylink DJ, Chen CS, et al.. The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19. J Transl Med. 2020, 18:322. 10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Meta-analysis of vitamin C Covid-19 treatment studies. (2021). https.//c19vitaminc.com/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"article-title": "Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Thomas S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Thomas S, Patel D, Bittel B, et al.. Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021, 4:e210369. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4149/BLL_2021_119",
"article-title": "The prognostic significance of vitamin D deficiency in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Yildiz M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Bratisl Lek Listy",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Yildiz M, Senel MU, Kavurgaci S, Ozturk FE, Ozturk A. The prognostic significance of vitamin D deficiency in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2021, 122:744-7. 10.4149/BLL_2021_119",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00203-021-02482-5",
"article-title": "The sufficient vitamin D and albumin level have a protective effect on COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Matin S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arch Microbiol",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Matin S, Fouladi N, Pahlevan Y, et al.. The sufficient vitamin D and albumin level have a protective effect on COVID-19 infection. Arch Microbiol. 2021, 203:5153-62. 10.1007/s00203-021-02482-5",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study",
"author": "Merzon E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Merzon E, Tworowski D, Gorohovski A, Vinker S, Golan Cohen A, Green I, Frenkel-Morgenstern M. Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study. FEBS J. 2020, 287:3693-702. 10.1111/febs.15495",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa733",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hernández JL",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Hernández JL, Nan D, Fernandez-Ayala M, et al.. Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021, 106:e1343-53. 10.1210/clinem/dgaa733",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.09.22.21263977",
"article-title": "COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/ml 25 (OH) D3: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Borsche L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Borsche L, Glauner B, Mendel Jv. COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/ml 25 (OH) D3: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2021, 13:3596. 10.1101/2021.09.22.21263977",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aimed.2015.11.002",
"article-title": "Integrative health check reveals suboptimal levels in a number of vital biomarkers",
"author": "Travica N",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Adv Integr Med",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Travica N, Ried K, Bujnowski R, Sali A. Integrative health check reveals suboptimal levels in a number of vital biomarkers. Adv Integr Med. 2015, 2:135-40. 10.1016/j.aimed.2015.11.002",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22038/abjs.2020.47754.2346",
"article-title": "Prevalence of comorbidities in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Baradaran A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arch Bone Jt Surg",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Baradaran A, Ebrahimzadeh MH, Baradaran A, Kachooei AR. Prevalence of comorbidities in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2020, 8:247-55. 10.22038/abjs.2020.47754.2346",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Aerospace Engineering"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Therapies to Prevent Progression of COVID-19, Including Hydroxychloroquine, Azithromycin, Zinc, and Vitamin D3 With or Without Intravenous Vitamin C: An International, Multicenter, Randomized Trial"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}
