High Dose Intravenous Vitamin C for Preventing The Disease Aggravation of Moderate COVID-19 Pneumonia. A Retrospective Propensity Matched Before-After Study
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.638556, Apr 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
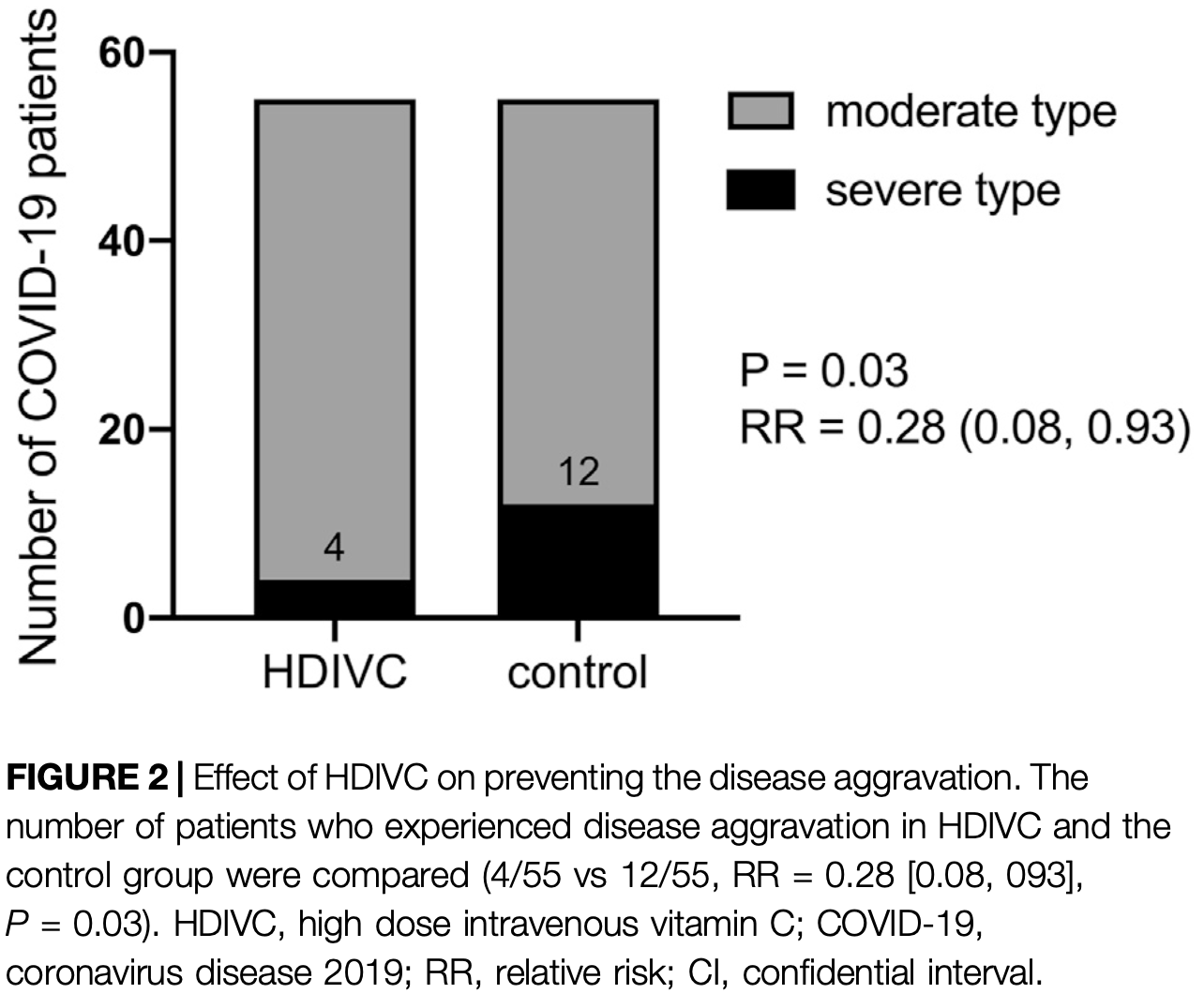
PSM retrospective 110 patients, 55 treated with high-dose IV vitamin C, showing lower progression to severe disease with treatment. Patients in each group were in different time periods, time based confounding is likely due to SOC improving over time. ChiCTR2000033050.
This is the 23rd of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
21 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0012.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
substantial confounding by time likely due to declining usage over the early stages of the pandemic when overall treatment protocols improved dramatically.
|
risk of progression, 72.0% lower, RR 0.28, p = 0.03, treatment 4 of 55 (7.3%), control 12 of 55 (21.8%), NNT 6.9, adjusted per study, PSM.
|
|
time to viral-, 7.7% higher, relative time 1.08, p = 0.79, treatment 55, control 55, PSM.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zhao et al., 22 Apr 2021, retrospective, propensity score matching, China, peer-reviewed, 15 authors, average treatment delay 4.0 days, dosage 100mg/kg days 1-7.
High Dose Intravenous Vitamin C for Preventing The Disease Aggravation of Moderate COVID-19 Pneumonia. A Retrospective Propensity Matched Before-After Study
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.638556
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is continuing to impact multiple countries worldwide and effective treatment options are still being developed. In this study, we investigate the potential of high-dose intravenous vitamin C (HDIVC) in the prevention of moderate COVID-19 disease aggravation. Methods: In this retrospective before-after case-matched clinical study, we compare the outcome and clinical courses of patients with moderate COVID-19 patients who were treated with an HDIVC protocol (intravenous injection of vitamin C, 100 mg/kg/day, 1 g/h, for 7 days from admission) during a one-month period (between March 18 and april 18, 2020, HDIVC group) with a control group treated without the HDIVC protocol during the preceding two months (January 18 to March 18, 2020). Patients in the two groups were matched in a 1:1 ratio according to age and gender.
Results: The HDIVC and control groups each comprised 55 patients. For the primary outcomes, there was a significant difference in the number of patients that evolved from moderate to severe type between the two groups (HDIVC: 4/55 vs. control: 12/55, relative risk [RR] 0.28 [0.08, 0.93], P 0.03). Compared to the control group, there was a shorter duration of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) (P 0.0004) during the first week and lower SIRS occurrence (2/21 vs 10/22, P 0.0086) on Day 7 (6-7 days after
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University school of medicine. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS BZ conceived the hypothesis and wrote the manuscript. ML and PL contributed to data collection. YP, JH, ML, YW, LX, and XQ provided supporting data and contributed intellectual input. YL and JL contribute statistical analysis. WZ and EM conceived hypothesis, provided supporting data, contributed intellectual input and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
FUNDING The
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2021.638556/ full#supplementary-material.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Anonymous, Update to living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, Bmj, doi:10.1136/bmj.m4779
Arvinte, Singh, Marik, Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a north American community hospital intensive care unit in may 2020: a pilot study, Med. Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064
Barabutis, Khangoora, Marik, Catravas, Hydrocortisone and ascorbic acid synergistically prevent and repair lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2017.07.014
Carr, Rowe, The emerging role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113286
Cerullo, Negro, Parimbelli, Pecoraro, Perna et al., The long history of vitamin C: from prevention of the common cold to potential aid in the treatment of COVID-19, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.574029
Channappanavar, Zhao, Perlman, T cell-mediated immune response to respiratory coronaviruses, Immunol. Res, doi:10.1007/s12026-014-8534-z
Cheng, Can early and high intravenous dose of vitamin C prevent and treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?, Med. Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100028
Chiscano-Camón, Ruiz-Rodriguez, Ruiz-Sanmartin, Roca, Ferrer, Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y
Fink-Neuboeck, Lindenmann, Bajric, Maier, Riedl et al., Clinical impact of interleukin 6 as a predictive biomarker in the early diagnosis of postoperative systemic inflammatory response syndrome after major thoracic surgery: a prospective clinical trial, Surgery, doi:10.1016/j.surg.2016.04.004
Fowler, Syed, Syed, Knowlson, Sculthorpe et al., Phase I safety trial of intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with severe sepsis, J. Transl Med, doi:10.1186/1479-5876-12-32
Fowler, Truwit, Hite, Morris, Dewilde et al., Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.11825
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Hemilä, Chalker, Reanalysis of the effect of vitamin C on mortality in the CITRIS-ALI trial: important findings dismissed in the trial report, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.590853
Iba, Levy, Connors, Warkentin, Thachil et al., The unique characteristics of COVID-19 coagulopathy, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03077-0
Iba, Levy, Levi, Connors, Thachil, Coagulopathy of coronavirus disease 2019, Crit. Care Med. Publish Ahead of Print, doi:10.1097/ccm.0000000000004458
Kaukonen, Bailey, Pilcher, Cooper, Bellomo, Systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria in defining severe sepsis, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415236
Mahase, Covid-19: WHO declares pandemic because of "alarming levels" of spread, severity, and inaction, Bmj, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1036
Manning, Mitchell, Appadurai, Shakya, Pierce et al., Vitamin C promotes maturation of T-cells, Antioxid. Redox Signaling, doi:10.1089/ars.2012.4988
Moskowitz, Huang, Hou, Gong, Doshi et al., Effect of ascorbic acid, corticosteroids, and thiamine on organ injury in septic shock, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.11946
Oudemans-Van Straaten, Man, -D, De Waard, Expert consensus on comprehensive treatment of coronavirus diseases in Shanghai in 2019, Chin. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2020
Sinha, Matthay, Calfee, Is a "cytokine storm" relevant to COVID-19?, JAMA Intern. Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3313
Spinelli, Pellino, COVID-19 pandemic: perspectives on an unfolding crisis, Br. J. Surg, doi:10.1002/bjs.11627
Van Gorkom, Klein Wolterink, Van Elssen, Wieten, Germeraad et al., Influence of vitamin C on lymphocytes: an overview, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox7030041
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirusinfected pneumonia in wuhan, China, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Williams, Ladva, Leon, Lopman, Tangpricha et al., Changes in micronutrient and inflammation serum biomarker concentrations after a norovirus human challenge, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqz201
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan, China, JAMA Intern. Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Xu, Fan, Wang, Zou, Yu et al., Suppressed T cell-mediated immunity in patients with COVID-19: a clinical retrospective study in Wuhan, China, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.012
Yang, Li, Li, Hon, Ng et al., Hematological findings in SARS patients and possible mechanisms (review), Int. J. Mol. Med
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., Pilot trial of highdose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Ann. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.638556",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.638556",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:bold>Background:</jats:bold> Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is continuing to impact multiple countries worldwide and effective treatment options are still being developed. In this study, we investigate the potential of high-dose intravenous vitamin C (HDIVC) in the prevention of moderate COVID-19 disease aggravation.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Methods:</jats:bold> In this retrospective before-after case-matched clinical study, we compare the outcome and clinical courses of patients with moderate COVID-19 patients who were treated with an HDIVC protocol (intravenous injection of vitamin C, 100 mg/kg/day, 1 g/h, for 7 days from admission) during a one-month period (between March 18 and april 18, 2020, HDIVC group) with a control group treated without the HDIVC protocol during the preceding two months (January 18 to March 18, 2020). Patients in the two groups were matched in a 1:1 ratio according to age and gender.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold> The HDIVC and control groups each comprised 55 patients. For the primary outcomes, there was a significant difference in the number of patients that evolved from moderate to severe type between the two groups (HDIVC: 4/55 vs. control: 12/55, relative risk [RR] = 0.28 [0.08, 0.93], <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.03). Compared to the control group, there was a shorter duration of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.0004) during the first week and lower SIRS occurrence (2/21 vs 10/22, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.0086) on Day 7 (6–7 days after admission). In addition, HDIVC group had lower C-reactive protein levels (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.005) and higher number of CD4<jats:sup>+</jats:sup> T cells from Day 0 (on admission) to Day 7 (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.04).” The levels of coagulation indicators, including activated partial thromboplastin time and D-dimer were also improved in the HDIVC compared to the control group on Day 7.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Conclusion:</jats:bold> HDIVC may be beneficial in limiting disease aggravation in the early stage of COVID-19 pneumonia, which may be related to its improvements on the inflammatory response, immune function and coagulation function. Further randomized controlled trials are required to augment these findings.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2021.638556"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Bing",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Yibing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Jun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Mengjiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yihui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "LiLi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Silei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qi",
"given": "Xing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ling",
"given": "Yun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Wenhong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mao",
"given": "Enqiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qu",
"given": "Jieming",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-22T11:55:28Z",
"timestamp": 1619092528000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-22T11:55:33Z",
"timestamp": 1619092533000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003399",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100018920",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ruijin Hospital"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-15T11:43:30Z",
"timestamp": 1702640610060
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 27,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
22
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1619049600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2021.638556/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m4779",
"article-title": "Update to living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m4779",
"journal-title": "Bmj",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064",
"article-title": "Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a north American community hospital intensive care unit in may 2020: a pilot study",
"author": "Arvinte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100064",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2017.07.014",
"article-title": "Hydrocortisone and ascorbic acid synergistically prevent and repair lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction",
"author": "Barabutis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "954",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113286",
"article-title": "The emerging role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3286",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.574029",
"article-title": "The long history of vitamin C: from prevention of the common cold to potential aid in the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Cerullo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "574029",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12026-014-8534-z",
"article-title": "T cell-mediated immune response to respiratory coronaviruses",
"author": "Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118",
"journal-title": "Immunol. Res.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100028",
"article-title": "Can early and high intravenous dose of vitamin C prevent and treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100028",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Chiscano-Camón",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "522",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.surg.2016.04.004",
"article-title": "Clinical impact of interleukin 6 as a predictive biomarker in the early diagnosis of postoperative systemic inflammatory response syndrome after major thoracic surgery: a prospective clinical trial",
"author": "Fink-Neuboeck",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "443",
"journal-title": "Surgery",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1479-5876-12-32",
"article-title": "Phase I safety trial of intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with severe sepsis",
"author": "Fowler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "J. Transl Med.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.11825",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure",
"author": "Fowler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1261",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "322",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.590853",
"article-title": "Reanalysis of the effect of vitamin C on mortality in the CITRIS-ALI trial: important findings dismissed in the trial report",
"author": "Hemilä",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "590853",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03077-0",
"article-title": "The unique characteristics of COVID-19 coagulopathy",
"author": "Iba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "360",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "24",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/ccm.0000000000004458",
"article-title": "Coagulopathy of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Iba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1358",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "B15",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1415236",
"article-title": "Systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria in defining severe sepsis",
"author": "Kaukonen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1629",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1036",
"article-title": "Covid-19: WHO declares pandemic because of “alarming levels” of spread, severity, and inaction",
"author": "Mahase",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m1036",
"journal-title": "Bmj",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2012.4988",
"article-title": "Vitamin C promotes maturation of T-cells",
"author": "Manning",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2054",
"journal-title": "Antioxid. Redox Signaling",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.11946",
"article-title": "Effect of ascorbic acid, corticosteroids, and thiamine on organ injury in septic shock",
"author": "Moskowitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "642",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B20",
"volume-title": "Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of SARS-CoV-2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-014-0460-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin C revisited",
"author": "Oudemans-van Straaten",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2020",
"article-title": "Expert consensus on comprehensive treatment of coronavirus diseases in Shanghai in 2019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Chin. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3313",
"article-title": "Is a \"cytokine storm\" relevant to COVID-19?",
"author": "Sinha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1152",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bjs.11627",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic: perspectives on an unfolding crisis",
"author": "Spinelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "785",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Surg.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox7030041",
"article-title": "Influence of vitamin C on lymphocytes: an overview",
"author": "van Gorkom",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqz201",
"article-title": "Changes in micronutrient and inflammation serum biomarker concentrations after a norovirus human challenge",
"author": "Williams",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1456",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.012",
"article-title": "Suppressed T cell-mediated immunity in patients with COVID-19: a clinical retrospective study in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e51",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Hematological findings in SARS patients and possible mechanisms (review)",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "311",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3",
"article-title": "Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensive Care",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2021.638556/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "High Dose Intravenous Vitamin C for Preventing The Disease Aggravation of Moderate COVID-19 Pneumonia. A Retrospective Propensity Matched Before-After Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "12"
}
