The prognostic significance of vitamin D deficiency in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia
et al., Bratislava Medical Journal, doi:10.4149/BLL_2021_119, Sep 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
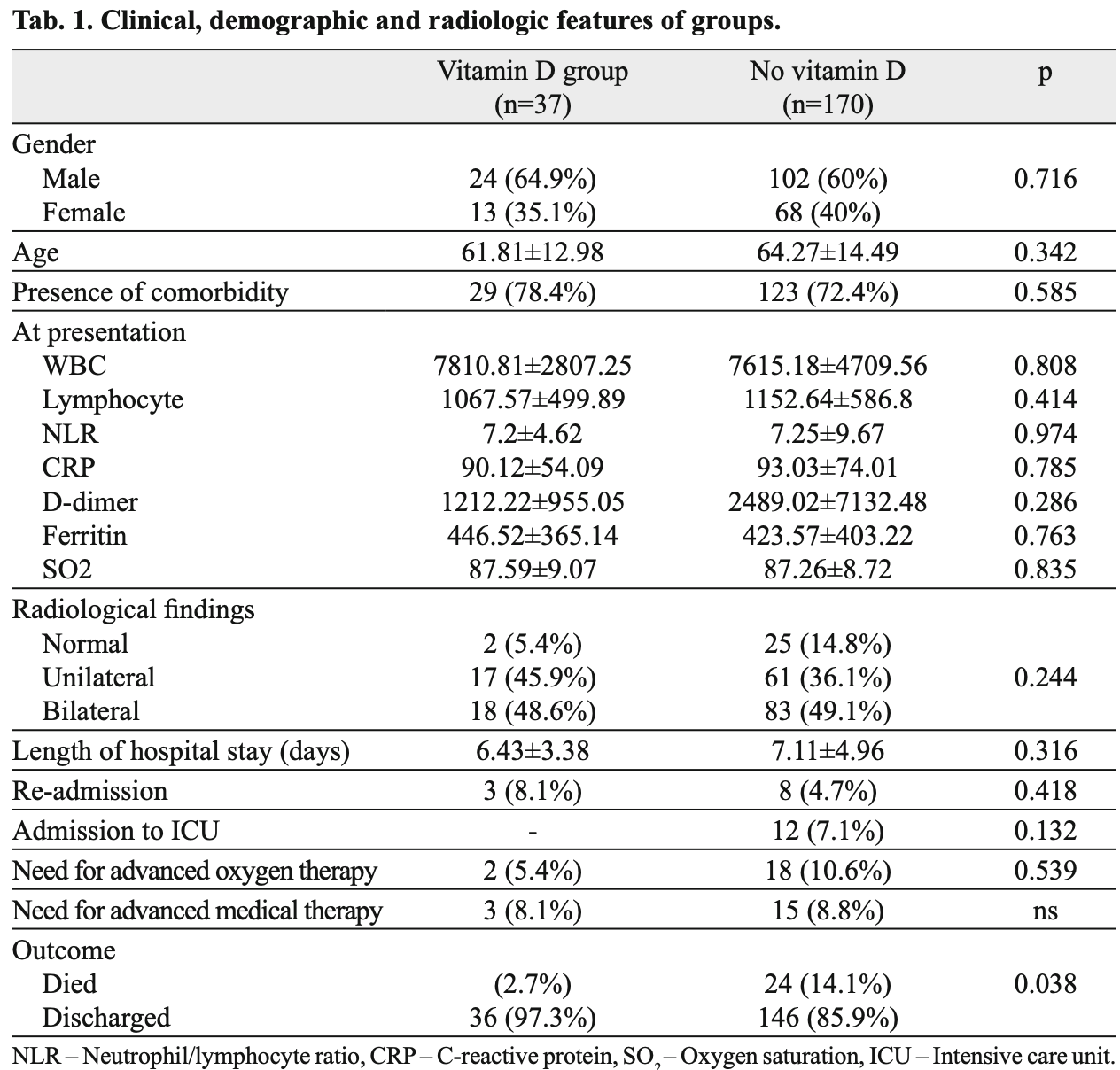
Retrospective 207 hospitalized patients in Turkey, 37 with vitamin D levels <30ng/ml treated with a single dose of 300,000IU vitamin D, showing lower mortality with treatment.
Cholecalciferol was used in this study.
Meta-analysis shows that late stage treatment with calcitriol / calcifediol (or
paricalcitol, alfacalcidol, etc.) is more effective than cholecalciferol: 66% [47‑78%] lower risk vs. 45% [34‑54%] lower risk.
Cholecalciferol requires two hydroxylation steps to become activated - first
in the liver to calcifediol, then in the kidney to calcitriol. Calcitriol,
paricalcitol, and alfacalcidol are active vitamin D analogs that do not
require conversion. This allows them to have more rapid onset of action
compared to cholecalciferol. The time delay for cholecalciferol to increase
serum calcifediol levels can be 2-3 days, and the delay for converting
calcifediol to active calcitriol can be up to 7 days.
Bolus treatment is less effective.
Pharmacokinetics and the potential side effects of high bolus doses suggest
that ongoing treatment spread over time is more appropriate.
Research has confirmed that lower dose regular treatment with vitamin D is more
effective than intermittent high-dose bolus treatment for various conditions,
including rickets and acute respiratory infections1,2. The biological mechanisms supporting these
findings involve the induction of enzymes such as 24-hydroxylase and
fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) by high-dose bolus treatments. These
enzymes play roles in inactivating vitamin D, which can paradoxically reduce
levels of activated vitamin D and suppress its activation for extended periods
post-dosage. Evidence indicates that 24-hydroxylase activity may remain
elevated for several weeks following a bolus dose, leading to reduced levels
of the activated form of vitamin D. Additionally, FGF23 levels can increase
for at least three months after a large bolus dose, which also contributes to
the suppression of vitamin D activation1.
This is the 55th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of death, 80.9% lower, RR 0.19, p = 0.04, treatment 1 of 37 (2.7%), control 24 of 170 (14.1%), NNT 8.8.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 94.5% lower, RR 0.06, p = 0.13, treatment 0 of 37 (0.0%), control 14 of 170 (8.2%), NNT 12, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
hospitalization time, 9.6% lower, relative time 0.90, p = 0.32, treatment 37, control 170.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Yildiz et al., 27 Sep 2021, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, dosage 300,000IU single dose.
The prognostic significance of vitamin D deficiency in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia
Bratislava Medical Journal, doi:10.4149/bll_2021_119
BACKGROUND: Vitamin D has anti-infl ammatory and immunomodulatory effects via the downregulation of pro-infl ammatory cytokines. We aimed to demonstrate the effect of vitamin D levels on survival in COVID-19 patients. MATERIALS AND METHODS: 207 COVID-19 patients were included in the study. Serum vitamin D levels were measured, and patients with levels < 20 ng/ml or 21 to 30 ng received a single 300.000 IU dose of vitamin D. RESULTS: Of 207 patients, 37 received vitamin D, while 170 did not. Demographic, radiologic and mean laboratory values were similar between the groups. The mean plasma vitamin D level without vitamin D support (n=170) was 50.82 ± 16.12 ng/ml (30.28 -81.35) vs. 16.98 ± 6.2 ng/ml (4.20 -28.30) in vitamin D group. The most remarkable fi nding were the mortality rates; while only 1 patient (2.7 %) died in the vitamin D group, 24 patients (14.1 %) died in no vitamin D supplementation group (p = 0.038). CONCLUSION: Although a few retrospective studies put forth a relation between vitamin D defi ciency and COVID-19 course severity there is still paucity of data about the effi cacy of vitamin supplementations in COVID-19 patients. A single 300.000 IU dose of vitamin D seems to represent a useful, practical, and safe adjunctive approach for the treatment or prevention of Fig. 1, Ref. 30).
References
Adams, Hewison, Ross, The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D, J ClinEndocrinol-Metab
Alipio, Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus-2019 (COVID-2019, SSRN Electronic J
Carnes, Quinn, Nelson, Jones, Winzenberg, Intermittent high-dose vitamin D corrects vitamin D defi ciency in adolescents: A pilot study, Eur J Clin Nutr
Cascella, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Induction of pro-infl ammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung infl ammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV2): anti-infl ammatory strategies, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, doi:10.23812/CONTI-E
Ebert, Schütze, Adamski, Vitamin D signaling is modulated on multiple levels in health and disease, Mol Cell Endocrinol
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of infl uenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hunter, Jones, IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease, Nat Immunol
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res
Jakovac, COVID-19 and vitamin D -Is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab
Jones, Jenkins, Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in infl ammatory diseases and cancer, Nat Rev Immunol
Kerget, Kerget, Kiziltunç, Koçak, Araz et al., Evaluation of the relationship of serum vitamin D levels in COVID-19 patients with clinical course and prognosis, Tuberk Toraks
Kong, Li, Effect of ANG II type I receptor antagonist and ACE inhibitor on vitamin D receptor-null mice, Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol
Kong, Zhu, Shi, VDR attenuates acute lung injury by blocking 9Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system, Mol Endocrinol
Konya, Czarnewski, Forkel, Rao, Kokkinou et al., Vitamin D downregulates the IL-23 receptor pathway in human mucosal group 3 innate lymphoid cells, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Majumder, Torabi, Saeg, Hoffman, Cirillo et al., Vitamin D Insuffi ciency is Prevalent in Severe COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2020.04.24.20075838
Mar, Gülgün, Sule, Sargin, Comparison of Different Vitamin D Replacement Modalities in Vitamin D-Defi cient Patients, Turk J Endocrinol Metab
Martineau, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mcmurray, Bartow, Mintzer, Hernandez-Frontera, 1990Micronutrient statusandimmunefunction in tuberculosis, Ann NY Acad Sci
Michael, Neil, Heike, Endocrine Society. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D defi ciency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Miroliaee, Salamzadeh, Shokouhi, Sahraei, The study of vitamin D administration effect on CRP and Interleukin-6 as prognostic biomarkers of ventilator associated pneumonia, J Crit Care
Mitchell, Vitamin-D and COVID-19: do defi cient risk a poorer outcome?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2
Nile, COVID-19: pathogenesis, cytokine storm and therapeutic potential of interferons, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev
Nonn, Peng, Feldman, Peehl, Inhibition of p38 by vitamin D reduces interleukin-6 production in normal prostate cells via mitogenactivated protein kinase phosphatase 5: implications for prostate cancer prevention by vitamin D, Cancer Res
Pascarella, Strumia, Piliego, COVID-19 diagnosis and management: a comprehensive review, J Intern Med
Prietl, Treiber, Piber, Amrein, Vitamin D and immune function, Nutrients
Teymoori-Rad, Shokri, Salimi, Marashi, The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections, Rev Med Virol
Van Etten, Mathieu, Immunoregulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: basic concepts, J Steroid BiochemMol Biol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4149/bll_2021_119",
"ISSN": [
"1336-0345"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4149/BLL_2021_119",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yildiz",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Senel",
"given": "M. U.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kavurgaci",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ozturk",
"given": "F. E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ozturk",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Bratislava Medical Journal",
"container-title-short": "BLL",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-27T16:16:03Z",
"timestamp": 1632759363000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-27T16:16:13Z",
"timestamp": 1632759373000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-24T16:15:01Z",
"timestamp": 1687623301090
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
}
},
"member": "2638",
"original-title": [],
"page": "744-747",
"prefix": "10.4149",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "AEPress, s.r.o.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.elis.sk/index.php?page=shop.product_details&flypage=flypage.tpl&product_id=7390&category_id=171&option=com_virtuemart"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Earth and Planetary Sciences",
"General Environmental Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The prognostic significance of vitamin D deficiency in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "122"
}
