Pre-hospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19
et al., European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000002013, Nov 2021
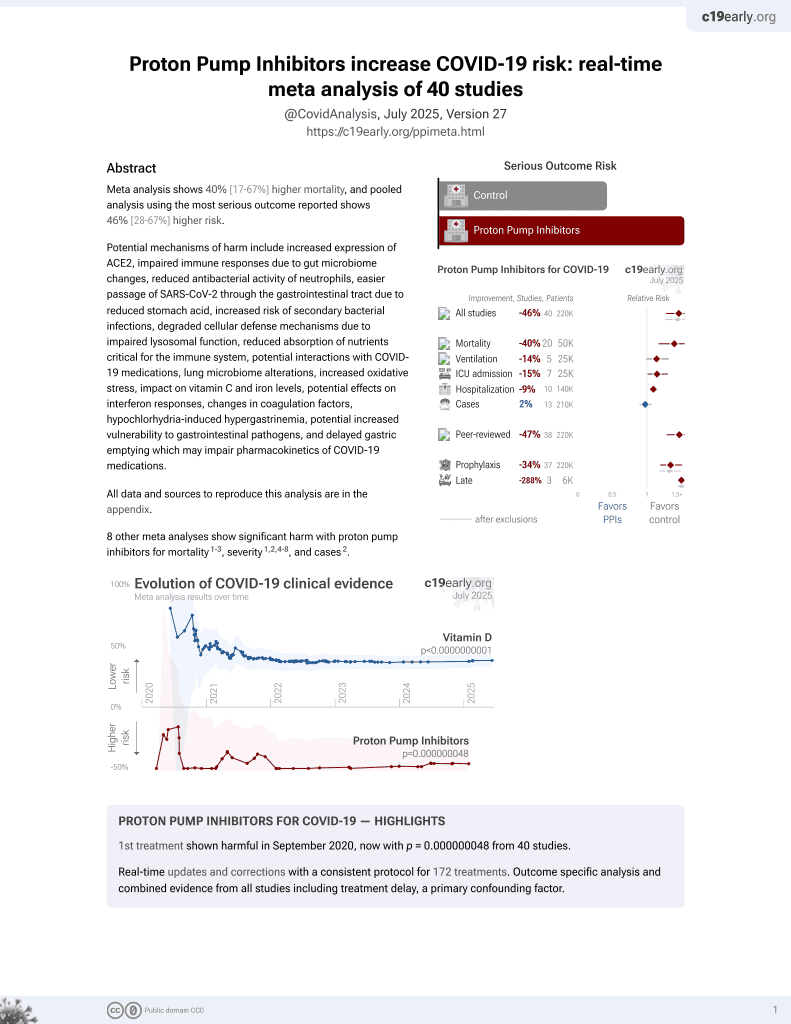
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
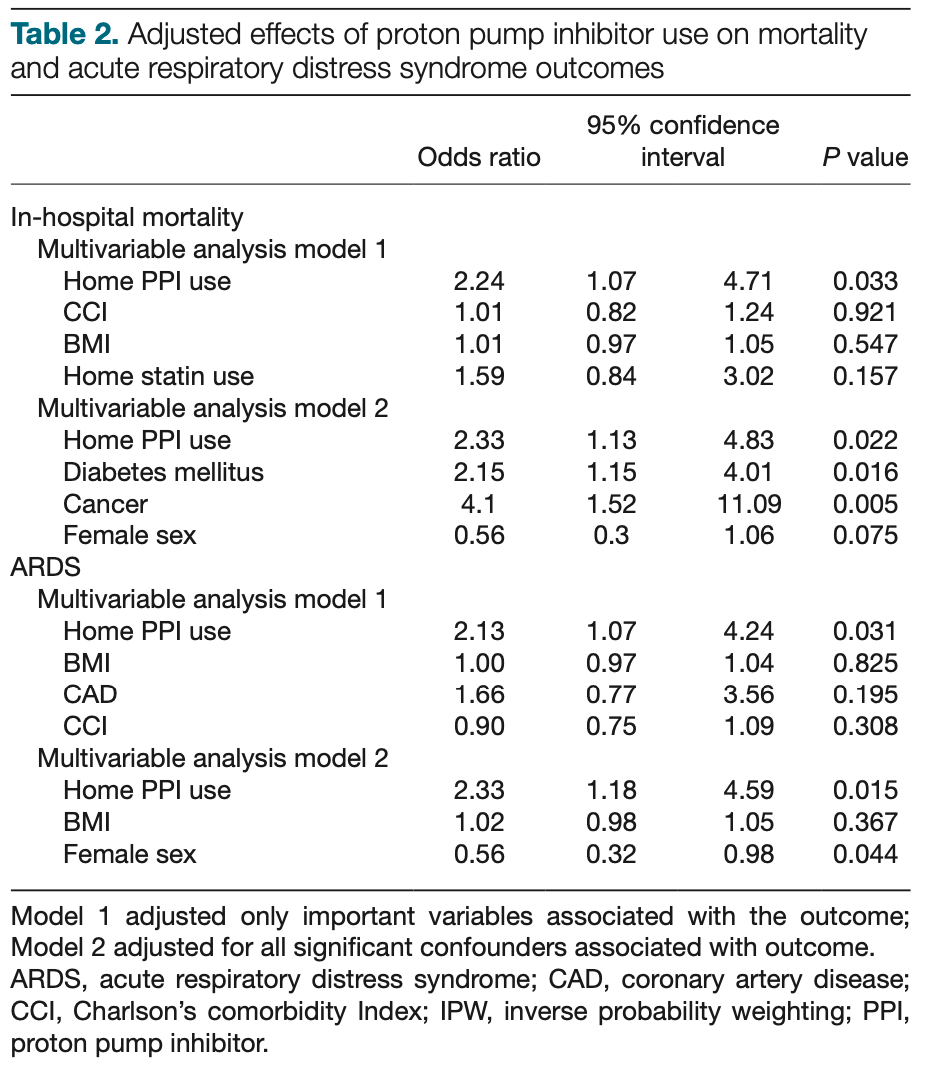
Retrospective 295 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing higher mortality and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) with pre-hospitalization proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use. Authors hypothesize that hypochlorhydria caused by PPIs may allow SARS-CoV-2 to more easily infect the gastrointestinal tract.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 92.0% higher, RR 1.92, p = 0.02, treatment 16 of 46 (34.8%), control 40 of 249 (16.1%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
ARDS, 80.1% higher, RR 1.80, p = 0.01, treatment 18 of 46 (39.1%), control 55 of 249 (22.1%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ramachandran et al., 30 Nov 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 25 April, 2020.
Contact: doc.hemant@yahoo.com.
Pre-hospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, doi:10.1097/meg.0000000000002013
Introduction Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 may escape the inactivation by gastric acid because of hypochlorhydria caused by proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which could predispose the patients to severe COVID-19. Methods We studied the association between prehospitalization PPI exposure and clinical outcomes among hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Results A total of 295 hospitalized COVID-19 patients were included in the study. 15.6% of hospitalized COVID-19 patients were on PPIs at home. Mortality among PPI-users was 2.3 times higher than non-users, along with 2.3 times higher risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome after adjusting for confounding variables. Conclusion We found that prehospitalization PPI-exposure is independently associated with worse clinical outcomes, including mortality in COVID-19 patients, regardless of the presence of cardiovascular comorbidities.
Conflicts of interest There are no conflicts of interest.
References
Almario, Chey, Spiegel, Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors, Am J Gastroenterol
Aloysius, Thatti, Gupta, Sharma, Bansal et al., COVID-19 presenting as acute pancreatitis, Pancreatology
Aziz, Perisetti, Smith, Gajendran, Bansal et al., Taste changes (dysgeusia) in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Gastroenterology
Boregowda, Aloysius, Perisetti, Gajendran, Bansal et al., Serum activity of liver enzymes is associated with higher mortality in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front Med
Buendgens, Bruensing, Matthes, Dückers, Luedde et al., Administration of proton pump inhibitors in critically ill medical patients is associated with increased risk of developing Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, J Crit Care
Cheng, Zhu, Faden, Interactions of bile acids and the gut microbiota: learning from the differences in Clostridium difficile infection between children and adults, Physiol Genomics
Darnell, Subbarao, Feinstone, Taylor, Inactivation of the coronavirus that induces severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV, J Virol Methods
Dhar, Mohanty, Gut microbiota and COVID-19-possible link and implications, Virus Res
Freedberg, Conigliaro, Wang, Tracey, Callahan et al., Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study, Gastroenterology
Gadiparthi, Perisetti, Sayana, Tharian, Inamdar et al., Gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2, Am J Gastroenterol
Goyal, Perisetti, Rehman, Singla, New and emerging therapies in treatment of Clostridium difficile infection, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Lely, Navis et al., Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J Pathol
Jackson, Goodrich, Maxan, Freedberg, Abrams et al., Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota, Gut
Johnson, Harris, Cain, Hummer, Goyal et al., pulmonary and extra-pulmonary clinical manifestations of COVID-19, Front Med
Kopel, Perisetti, Gajendran, Boregowda, Goyal, Clinical insights into the gastrointestinal manifestations of COVID-19, Dig Dis Sci
Lee, Ha, Yeniova, Moon, Kim et al., Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching, Gut
Lombardo, Foti, Ruggia, Chiecchio, Increased incidence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth during proton pump inhibitor therapy, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Luxenburger, Sturm, Biever, Rieg, Duerschmied et al., Treatment with proton pump inhibitors increases the risk of secondary infections and ARDS in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: coincidence or underestimated risk factor?, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13121
Maclaren, Reynolds, Allen, Histamine-2 receptor antagonists vs proton pump inhibitors on gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage and infectious complications in the intensive care unit, JAMA Intern Med
Mather, Seip, Mckay, Impact of famotidine use on clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Am J Gastroenterol
Miller, Gastric acidity during the first year of life, Arch Dis Child
Pan, Mu, Yang, Sun, Wang et al., Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study, Am J Gastroenterol
Perisetti, Gajendran, Boregowda, Bansal, Goyal, COVID-19 and gastrointestinal endoscopies: current insights and emergent strategies, Dig Endosc
Perisetti, Khan, Sahmoun, Newman, Meidinger, Role of Prophylactic Pre-Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) Endotracheal Intubation (ETI) in Upper Gastrointestinal Bleed (UGIB): a retrospective study: 42, Am J Gastroenterol
Price, Could the severity of COVID-19 be increased by low gastric acidity?, Crit Care
Ramachandran, Onukogu, Ghanta, Gajendran, Perisetti et al., Gastrointestinal symptoms and outcomes in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients, Dig Dis
Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson, Ferguson, Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition, JAMA
Shin, Sachs, Pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors, Curr Gastroenterol Rep
Singh, Bilal, Pakhchanian, Raiker, Kochhar et al., Impact of obesity on outcomes of patients with COVID-19 in United States: a multicenter electronic health records network study, Gastroenterology
Wu, Liu, Yang, Zhang, Zhong et al., Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods, Acta Pharm Sin B
Xiao, Tang, Zheng, Liu, Li et al., Evidence for gastrointestinal infection of SARS-CoV-2, Gastroenterology
Xie, Bowe, Li, Xian, Yan et al., Risk of death among users of proton pump inhibitors: a longitudinal observational cohort study of United States veterans, BMJ Open
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/meg.0000000000002013",
"ISSN": [
"0954-691X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0000000000002013",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Introduction</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 may escape the inactivation by gastric acid because of hypochlorhydria caused by proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which could predispose the patients to severe COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We studied the association between prehospitalization PPI exposure and clinical outcomes among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 295 hospitalized COVID-19 patients were included in the study. 15.6% of hospitalized COVID-19 patients were on PPIs at home. Mortality among PPI-users was 2.3 times higher than non-users, along with 2.3 times higher risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome after adjusting for confounding variables.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We found that prehospitalization PPI-exposure is independently associated with worse clinical outcomes, including mortality in COVID-19 patients, regardless of the presence of cardiovascular comorbidities.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Midamerica Cancer Care, West Kansas City, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Ramachandran",
"given": "Preethi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas"
}
],
"family": "Perisetti",
"given": "Abhilash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Texas Tech University, Paul L Foster School of Medicine, El Paso, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Gajendran",
"given": "Mahesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Brookdale University Hospital and Medical Center, Brooklyn, New York"
}
],
"family": "Jean-Louis",
"given": "Farla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology, Moses Taylor Hospital and Reginal Hospital of Scranton, Scranton, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Bansal",
"given": "Pardeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, Department of Molecular and Translational Medicine, Texas Tech University, Paul L Foster School of Medicine, El Paso, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Dwivedi",
"given": "Alok Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, Pennsylvania, USA"
}
],
"family": "Goyal",
"given": "Hemant",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-29T20:03:09Z",
"timestamp": 1606680189000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-16T16:13:22Z",
"timestamp": 1694880802000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-03T07:16:13Z",
"timestamp": 1719990973022
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 27,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MEG.0000000000002013",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "137-141",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.055",
"article-title": "Evidence for gastrointestinal infection of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1831",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "R1-20230916",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "R2-20230916",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/den.13693",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and gastrointestinal endoscopies: current insights and emergent strategies",
"author": "Perisetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Dig Endosc",
"key": "R3-20230916",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.003",
"article-title": "Taste changes (dysgeusia) in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Aziz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1132",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "R4-20230916",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00526",
"article-title": "pulmonary and extra-pulmonary clinical manifestations of COVID-19",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "526",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "R5-20230916",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pan.2020.05.003",
"article-title": "COVID-19 presenting as acute pancreatitis",
"author": "Aloysius",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1026",
"journal-title": "Pancreatology",
"key": "R6-20230916",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10620-020-06362-8",
"article-title": "Clinical insights into the gastrointestinal manifestations of COVID-19",
"author": "Kopel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1932",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis Sci",
"key": "R7-20230916",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000719",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Gadiparthi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1283",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "R8-20230916",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.06.006",
"article-title": "Inactivation of the coronavirus that induces severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV",
"author": "Darnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "J Virol Methods",
"key": "R9-20230916",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"article-title": "Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "Lee",
"first-page": "gutjnl-2020-322248",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "R10-20230916",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Treatment with proton pump inhibitors increases the risk of secondary infections and ARDS in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: coincidence or underestimated risk factor?",
"author": "Luxenburger",
"first-page": "10.1111/joim.13121",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "R11-20230916",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota and COVID-19- possible link and implications",
"author": "Dhar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198018",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "R12-20230916",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition",
"author": "Ranieri",
"first-page": "2526",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R13-20230916",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11894-008-0098-4",
"article-title": "Pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Shin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "528",
"journal-title": "Curr Gastroenterol Rep",
"key": "R14-20230916",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1570",
"article-title": "Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis",
"author": "Hamming",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "631",
"journal-title": "J Pathol",
"key": "R15-20230916",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.14673",
"article-title": "Histamine-2 receptor antagonists vs proton pump inhibitors on gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage and infectious complications in the intensive care unit",
"author": "MacLaren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "564",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "R16-20230916",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310861",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "749",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "R17-20230916",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2009.12.022",
"article-title": "Increased incidence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth during proton pump inhibitor therapy",
"author": "Lombardo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "504",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "R18-20230916",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.03.002",
"article-title": "Administration of proton pump inhibitors in critically ill medical patients is associated with increased risk of developing Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea",
"author": "Buendgens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "696.e11",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care",
"key": "R19-20230916",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/00000434-201310001-00042",
"article-title": "Role of Prophylactic Pre-Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) Endotracheal Intubation (ETI) in Upper Gastrointestinal Bleed (UGIB): a retrospective study: 42",
"author": "Perisetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S15",
"issue": "Supple 1",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "R20-20230916",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000001103",
"article-title": "New and emerging therapies in treatment of Clostridium difficile infection",
"author": "Goyal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "589",
"journal-title": "Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "R21-20230916",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000509774",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal symptoms and outcomes in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients",
"author": "Ramachandran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis",
"key": "R22-20230916",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00431",
"article-title": "Serum activity of liver enzymes is associated with higher mortality in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Boregowda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "431",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "R23-20230916",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798",
"article-title": "Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Almario",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1707",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "R24-20230916",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000832",
"article-title": "Impact of famotidine use on clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Mather",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1617",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "R25-20230916",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2020.02.008",
"article-title": "Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm Sin B",
"key": "R26-20230916",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"article-title": "Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Freedberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "R27-20230916",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03182-0",
"article-title": "Could the severity of COVID-19 be increased by low gastric acidity?",
"author": "Price",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "456",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R28-20230916",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/adc.17.92.198",
"article-title": "Gastric acidity during the first year of life",
"author": "Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "198",
"journal-title": "Arch Dis Child",
"key": "R29-20230916",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1942"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physiolgenomics.00034.2019",
"article-title": "Interactions of bile acids and the gut microbiota: learning from the differences in Clostridium difficile infection between children and adults",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "218",
"journal-title": "Physiol Genomics",
"key": "R30-20230916",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Impact of obesity on outcomes of patients with COVID-19 in United States: a multicenter electronic health records network study",
"author": "Singh",
"first-page": "S0016-5085(20)35067-35068",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "R31-20230916",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015735",
"article-title": "Risk of death among users of proton pump inhibitors: a longitudinal observational cohort study of United States veterans",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e015735",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "R32-20230916",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2020.07.12.20151084",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MEG.0000000000002013"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Pre-hospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "34"
}