Benefits of melatonin on mortality in severe-to-critical COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
et al., Clinics, doi:10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638, PROSPERO CRD42023466646, Jan 2025
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.0000000099 from 19 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
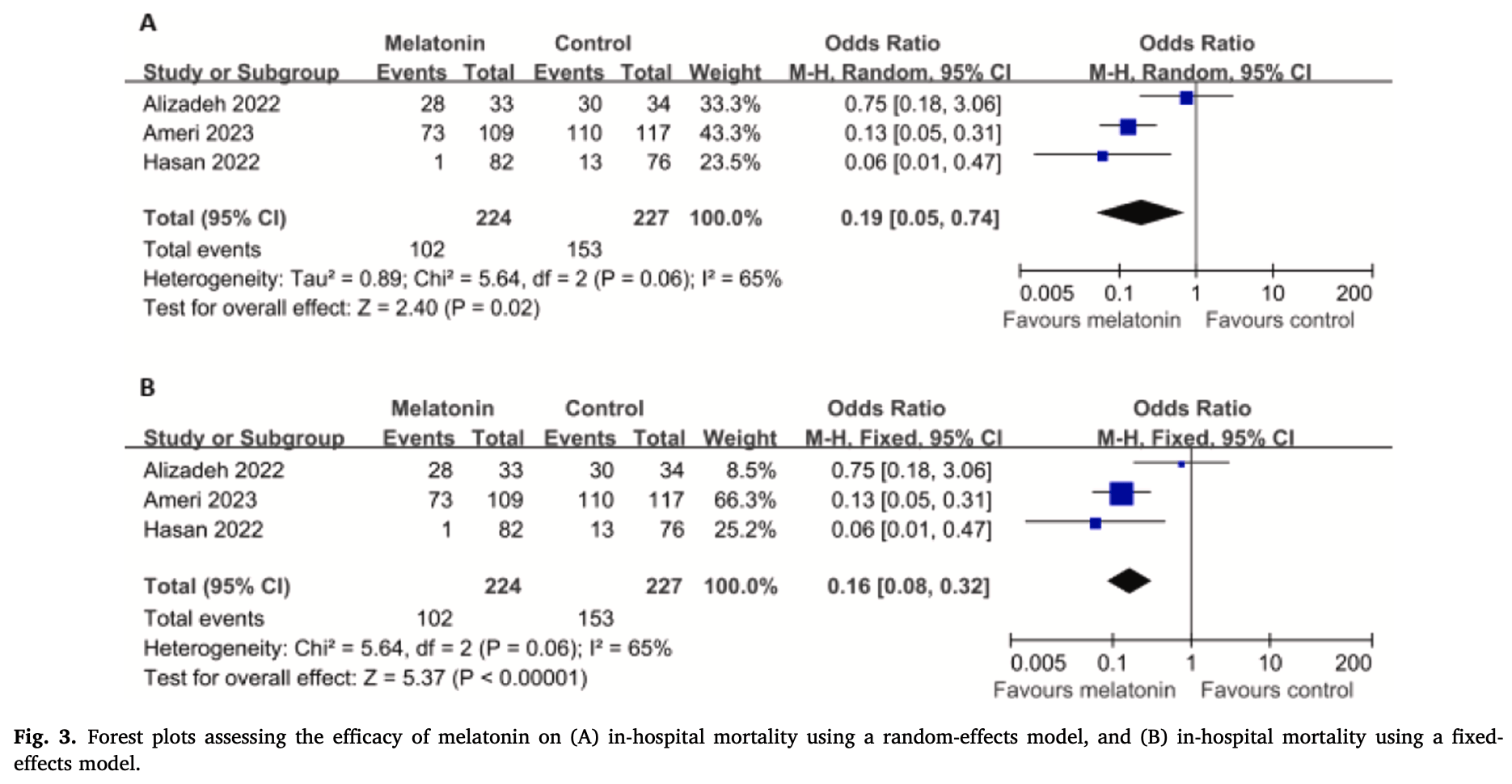
Meta-analysis of 3 RCTs (451 patients) showing significantly lower in-hospital mortality with melatonin treatment in severe-to-critical COVID-19 patients. Authors propose melatonin's effectiveness stems from its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties that may help combat cytokine storm syndrome and reduce oxidative stress in severely ill patients.
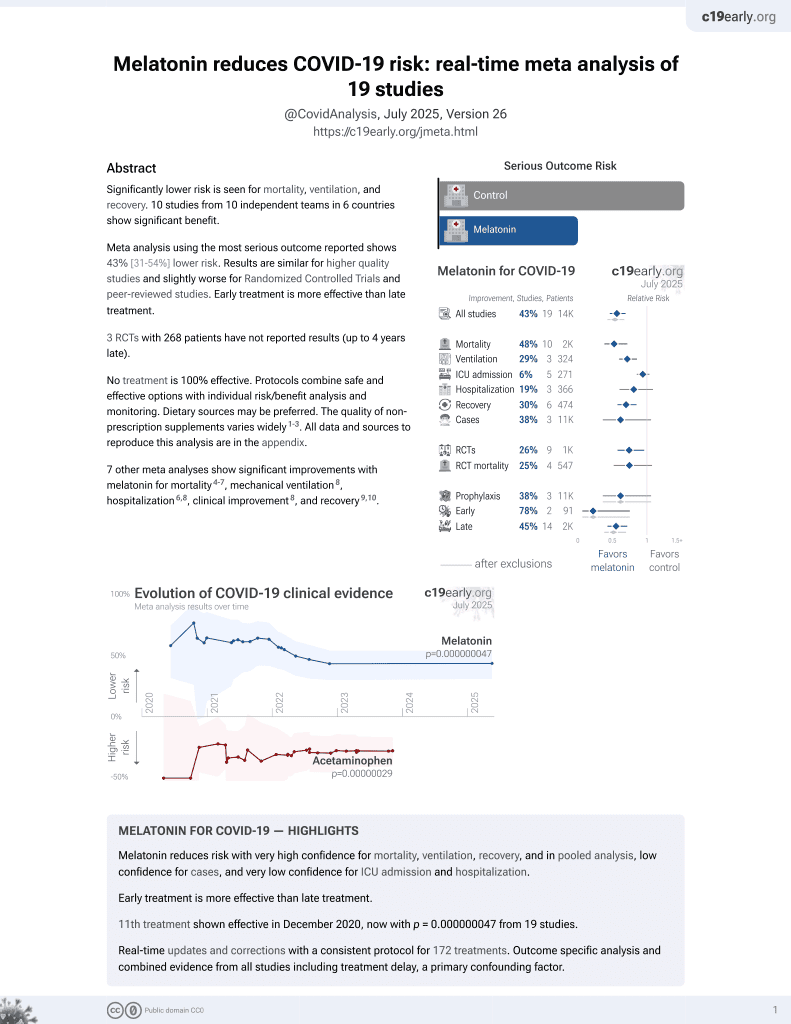
7 meta-analyses show significant improvements with melatonin for mortality1-4,
mechanical ventilation5,
hospitalization3,5,
improvement5, and
recovery6,7.
Currently there are 19 melatonin for COVID-19 studies, showing 33% lower mortality [19‑44%], 32% lower ventilation [19‑43%], 14% lower ICU admission [-1‑28%], 18% lower hospitalization [3‑30%], and 38% fewer cases [-6‑64%].
1.
Pilia et al., Does melatonin reduce mortality in COVID-19?, Annals of Medicine and Surgery, doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103817.
2.
Tóth et al., Melatonin as adjuvant treatment in COVID-19 patients. A meta-analysis of randomized and propensity matched studies, Signa Vitae, doi:10.22514/sv.2023.076.
3.
Amin et al., Role of Melatonin in Management of COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Microbes, Infection and Chemotherapy, doi:10.54034/mic.e1982.
4.
Qin et al., Benefits of melatonin on mortality in severe-to-critical COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinics, doi:10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638.
5.
Taha et al., Safety and efficacy of melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in COVID-19 patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Advances in Medical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.advms.2023.09.007.
Qin et al., 31 Jan 2025, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42023466646.
Contact: sesory@yeah.net.
Benefits of melatonin on mortality in severe-to-critical COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Clinics, doi:10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638
Objective: This meta-analysis aimed to determine the efficacy of melatonin on mortality in patients with severeto-critical illness COVID-19. Methods: A systematic search was made of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and clinicaltrials.gov, without language restrictions. Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) on the treatment of severe-to-critical COVID-19 with melatonin, compared with placebo or blank, were reviewed. Studies were pooled to Odds Ratios (ORs), with 95 % Confidence Intervals (95 % CIs). Results: Three RCTs (enrolling 451 participants) met the inclusion criteria. Melatonin showed a significant effect on in-hospital mortality (OR = 0.19, 95 % CI 0.05 to 0.74; p = 0.02). Conclusions: Melatonin significantly reduced in-hospital mortality in patients with severe-to-critical COVID-19. Melatonin should be considered for severe-to-critical COVID-19 patients.
Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Authors' contributions All authors, led by D.H., were involved in the concept and protocol design of the meta-analysis. J.Q. and G.W. screened the titles and abstracts and extracted data from the articles. J.Q. was primarily responsible for statistical analyses. G.W. was primarily involved in the interpretation of the quality data. All authors contributed to interpreting the results. J.Q. and D.H accessed and verified the data. All authors contributed to the writing of the article and approved its submission. D. H. was responsible for the decision to submit the article.
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638.
References
Alizadeh, Dianatkhah, Alimohamadi, Moradi, Akbarpour et al., High dose melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in intubated patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, J Taibah Univ Med Sci
Ameri, Frouz, Ziaei, Vatankhah, Safa et al., Efficacy and safety of oral melatonin in patients with severe COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial, Inflammopharmacology
Anderson, Maes, Markus, Rodriguez, Ebola virus: melatonin as a readily available treatment option, J Med Virol
Beraud, Hashami, Lozano, Bah, Keith, Role of therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of COVID-19-induced cytokine storm syndrome, Transfus Apher Sci
Boga, Coto-Montes, Rosales-Corral, Sa, Tan et al., Beneficial actions of melatonin in the management of viral infections: a new use for this "molecular handyman, Rev Med Virol
Cegolon, Javanbakht, Mastrangelo, Nasal disinfection for the prevention and control of COVID-19: a scoping review on potential chemo-preventive agents, Int J Hyg Environ Health
Cheng, Rao, Mehra, COVID-19 treatment: combining anti-inflammatory and antiviral therapeutics using a network-based approach, Cleve Clin J Med, doi:10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc037
Declercq, Van Damme, Leeuw, Maes, Bosteels et al., Effect of anti-interleukin drugs in patients with COVID-19 and signs of cytokine release syndrome (COV-AID): a factorial, randomised, controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
Detsky, Naylor, 'rourke, Mcgeer, Abbé, Incorporating variations in the quality of individual randomized trials into meta-analysis, J Clin Epidemiol
Hasan, Atrakji, Mehuaiden, The effect of melatonin on thrombosis, sepsis and mortality rate in COVID-19 patients, Int J Infect Dis
Henderson, Kim, Lee, Use of melatonin as adjunctive therapy in neonatal sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Complement Ther Med
Higgins, Altman, Gøtzsche, Jüni, Moher et al., The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, Lancet
Huang, Wu, Liu, Tsai, Chen et al., The clinical efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Front Med
Lan, Lee, Chao, Chang, Lu et al., Efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, J Med Virol
Leisman, Ronner, Pinotti, Taylor, Sinha et al., Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes, Lancet Respir Med
Liberati, Altman, Tetzlaff, Mulrow, Gøtzsche et al., The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration, Ann Int Med
Memish, Faqihi, Alharthy, Alqahtani, Karakitsos, Plasma exchange in the treatment of complex COVID-19-related critical illness: controversies and perspectives, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, Altman, Group, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement, Ann Intern Med
Mubashshir, Ahmad, Negi, Rawal, Singhvi et al., Therapeutic benefits of melatonin against COVID-19, Neuroimmunomodulation
Qin, Wang, Han, Benefits of plasma exchange on mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
Qin, Wang, Han, Selexipag in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Curr Probl Cardiol
Ren, Wang, Han, Statins in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, J Med Virol
Roa, Cipolla-Neto, Reiter, Linhares, Lepique et al., Effects of Melatonin alone or associated with Acyclovir on the suppressive treatment of recurrent genital Herpes: a prospective, randomized, and double-blind study, Biomedicines
Shang, Wang, Wang, Han, Benefits of ozone on mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Complement Ther Med
Shang, Zhang, Wang, Han, Anakinra was not associated with lower mortality in hospitalised COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Rev Med Virol
Shneider, Kudriavtsev, Vakhrusheva, Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic?, Int Rev Immunol
Veiga, Simões, Caviola, Abreu, Cavalli et al., Melatonin and the cardiovascular system in animals: systematic review and metaanalysis, Clinics
Wang, Qin, Han, Long-term safety of macitentan in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, Eur J Clin Invest
Ye, Wang, Mao, The pathogenesis and treatment of the `Cytokine Storm' in COVID-19, J Infect
Yuki, Fujiogi, Koutsogiannaki, COVID-19 pathophysiology: a review, Clin Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638",
"ISSN": [
"1807-5932"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638",
"alternative-id": [
"S180759322500064X"
],
"article-number": "100638",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Benefits of melatonin on mortality in severe-to-critical COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Clinics"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2025 HCFMUSP. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0006-4620-7033",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Qin",
"given": "Jinlv",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0000-9701-4019",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Guizuo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3775-4028",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Han",
"given": "Dong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinics",
"container-title-short": "Clinics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-07T18:19:21Z",
"timestamp": 1744049961000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-07T18:20:49Z",
"timestamp": 1744050049000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-07T18:40:09Z",
"timestamp": 1744051209929,
"version": "3.40.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735689600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735689600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 89,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1743379200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S180759322500064X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S180759322500064X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100638",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.014",
"article-title": "Benefits of plasma exchange on mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "332",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0001",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106273",
"article-title": "Plasma exchange in the treatment of complex COVID-19-related critical illness: controversies and perspectives",
"author": "Memish",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0002",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113605",
"article-title": "Nasal disinfection for the prevention and control of COVID-19: a scoping review on potential chemo-preventive agents",
"author": "Cegolon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Hyg Environ Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0003",
"volume": "230",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000531550",
"article-title": "Therapeutic benefits of melatonin against COVID-19",
"author": "Mubashshir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "196",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Neuroimmunomodulation",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0004",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135",
"article-title": "PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement",
"author": "Moher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0005",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0895-4356(92)90085-2",
"article-title": "Incorporating variations in the quality of individual randomized trials into meta-analysis",
"author": "Detsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "255",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0006",
"volume": "45",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28823",
"article-title": "Statins in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0007",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.d5928",
"article-title": "The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials",
"author": "Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "d5928",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0008",
"volume": "343",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101466",
"article-title": "Selexipag in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Curr Probl Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0009",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctim.2022.102907",
"article-title": "Benefits of ozone on mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Complement Ther Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0010",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2418",
"article-title": "Anakinra was not associated with lower mortality in hospitalised COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2418",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0011",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/eci.14059",
"article-title": "Long-term safety of macitentan in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0012",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "High dose melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in intubated patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Alizadeh",
"first-page": "454",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Taibah Univ Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0013",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-022-01096-7",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of oral melatonin in patients with severe COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Ameri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0014",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.10.012",
"article-title": "The effect of melatonin on thrombosis, sepsis and mortality rate in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Hasan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "79",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0015",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2022.103433",
"article-title": "Role of therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of COVID-19-induced cytokine storm syndrome",
"author": "Beraud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Transfus Apher Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0016",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00377-5",
"article-title": "Effect of anti-interleukin drugs in patients with COVID-19 and signs of cytokine release syndrome (COV-AID): a factorial, randomised, controlled trial",
"author": "Declercq",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1427",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0017",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30404-5",
"article-title": "Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes",
"author": "Leisman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1233",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0018",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0019",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108427",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pathophysiology: a review",
"author": "Yuki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0020",
"volume": "215",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037",
"article-title": "The pathogenesis and treatment of the `Cytokine Storm' in COVID-19",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "607",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0021",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctim.2018.06.002",
"article-title": "Use of melatonin as adjunctive therapy in neonatal sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Henderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "131",
"journal-title": "Complement Ther Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0022",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines11041088",
"article-title": "Effects of Melatonin alone or associated with Acyclovir on the suppressive treatment of recurrent genital Herpes: a prospective, randomized, and double-blind study",
"author": "Roa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1088",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0023",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.6061/clinics/2021/e2863",
"article-title": "Melatonin and the cardiovascular system in animals: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Veiga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2863",
"journal-title": "Clinics (Sao Paulo)",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0024",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08830185.2020.1756284",
"article-title": "Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic?",
"author": "Shneider",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0025",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.24130",
"article-title": "Ebola virus: melatonin as a readily available treatment option",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "537",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0026",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1714",
"article-title": "Reiter RJ. Beneficial actions of melatonin in the management of viral infections: a new use for this \"molecular handyman\"?",
"author": "Boga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "323",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0027",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc037",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0028",
"unstructured": "Cheng F, Rao S, Mehra R COVID-19 treatment: combining anti-inflammatory and antiviral therapeutics using a network-based approach. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020. doi:10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc037. Online ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27595",
"article-title": "Efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2102",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0029",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "The clinical efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Huang",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0030",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00136",
"article-title": "The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration",
"author": "Liberati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W65",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ann Int Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638_bib0031",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2009"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S180759322500064X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Benefits of melatonin on mortality in severe-to-critical COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "80"
}