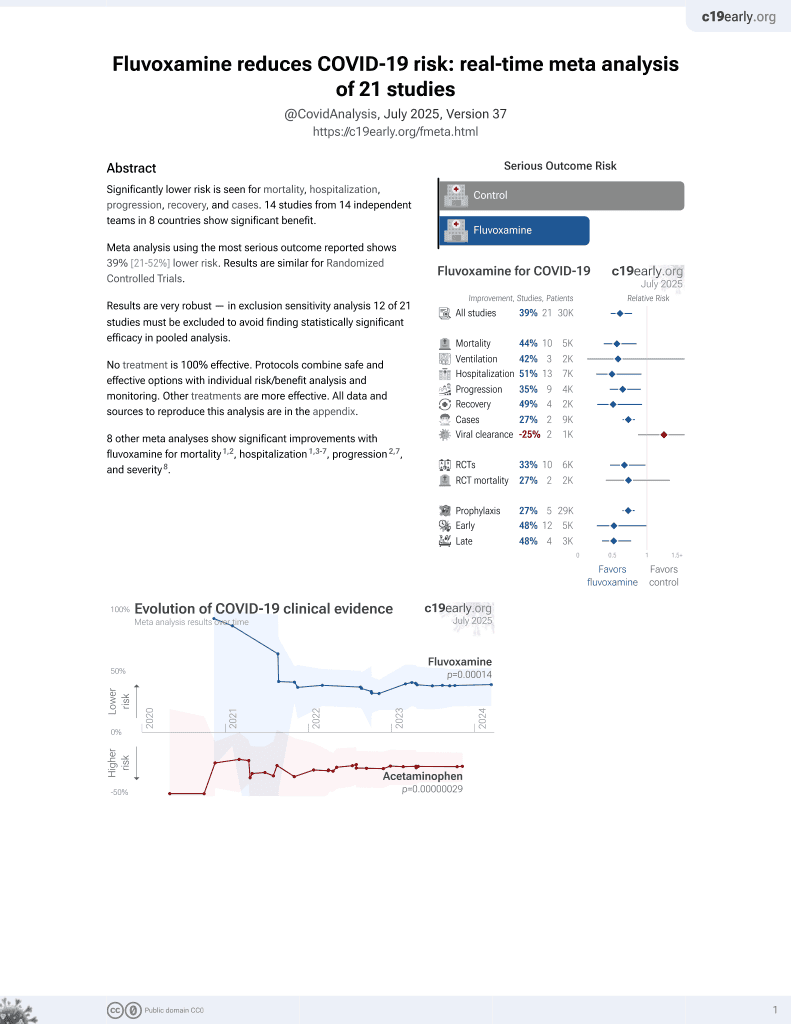
Protective effects of psychiatric medications against COVID-19 mortality before vaccines
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0310438, Feb 2025
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
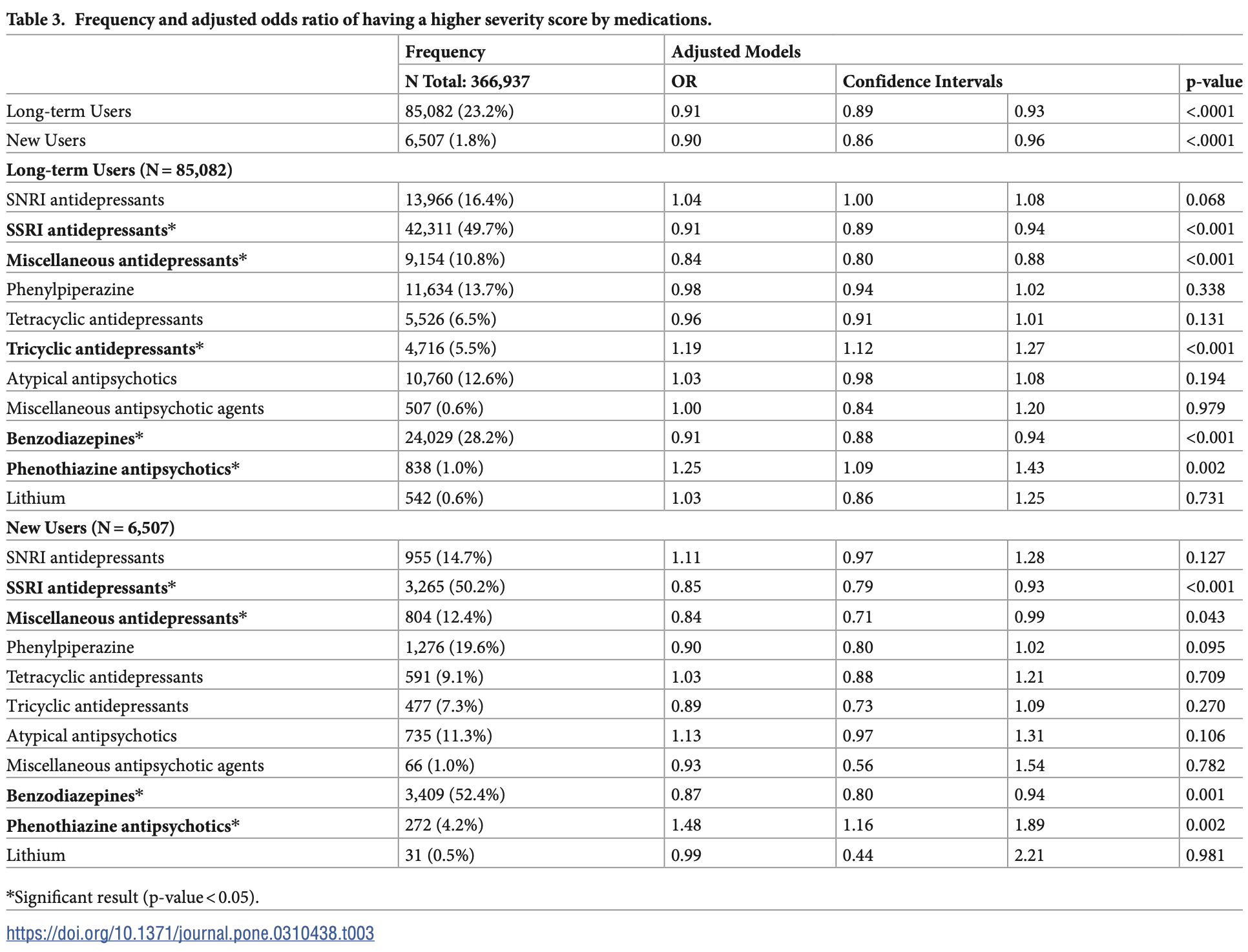
Retrospective 366,937 COVID-19 patients in the US showing protective effects of certain psychiatric medications including SSRIs against COVID-19 severity.
Machado-Vieira et al., 24 Feb 2025, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 31 December, 2020.
Contact: chau.n.truong@uth.tmc.edu.
Protective effects of psychiatric medications against COVID-19 mortality before vaccines
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0310438
The coronavirus disease pandemic caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which emerged in the United States in late 2019 to early 2020 and quickly escalated into a national public health crisis. Research has identified psychiatric conditions as possible risk factors associated with COVID-19 infection and symptom severity. This study aims to determine whether specific classes of psychiatric medications could reduce the likelihood of infection and alleviate the severity of the disease. The objective of this study is to investigate the relationship between neuropsychiatric medication usage and COVID-19 outcomes before the widespread utilization of COVID-19 vaccines. This cross-sectional study used Optum's de-identified Clinformatics Data Mart Database to identify patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in 2020 and their psychiatric medication prescriptions in the United States. Ordered logistic regression was used to predict the likelihood of a higher COVID-19 severity level for long-term and new users. Results were adjusted for demographic characteristics and medical and psychiatric comorbidities. Most users were classified into the long-term user analysis group. Long-term users were 9% less likely to have a higher severity score (CI: 0.89-0.93, p-value < 0.001) than non-users. SSRI antidepressant users, both long-term (OR: 1.09; CI: 1.06-1.12) and short-term (OR: 1.17; CI: 1.07-1.27) were significantly more likely to have a lower severity score. However, the results varied across long-term and short-term users for all medication classes. Results of the current study suggest that psychopharmacological agents are associated with reduced COVID-19 severity levels and that antidepressant medications may have a protective role against COVID-19.
Supporting information
S1 Table. Codes used to identify mental health disorder diagnosis and medical comorbidities. (DOCX)
Author contributions
References
Ahern, 5-HT and the immune system, Curr Opin Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.coph.2011.02.004
Barcella, Polcwiartek, Mohr, Hodges, Søndergaard et al., Severe mental illness is associated with increased mortality and severe course of COVID-19, Acta Psychiatr Scand
Baumeister, Ciufolini, Mondelli, Effects of psychotropic drugs on inflammation: consequence or mediator of therapeutic effects in psychiatric treatment?, Psychopharmacology (Berl), doi:10.1007/s00213-015-4044-5
Bulloch, Patten, Non-adherence with psychotropic medications in the general population, Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s00127-009-0041-5
Carpinteiro, Edwards, Hoffmann, Kochs, Gripp et al., Pharmacological inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase prevents uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by epithelial cells, Cell Rep Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142
Cramer, Rosenheck, Compliance With Medication Regimens for Mental and Physical Disorders, Psychiatric Ser, doi:10.1176/ps.49.2.196
De Sousa, Streck, Zanetti, Ferreira, Diniz et al., Lithium increases leukocyte mitochondrial complex I activity in bipolar disorder during depressive episodes, Psychopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s00213-014-3655-6
Dechaumes, Nekoua, Belouzard, Sane, Engelmann et al., Fluoxetine can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms9020339
Foley, Larkin, Lombard-Vance, Murphy, Hynes et al., Prevalence and predictors of medication non-adherence among people living with multimorbidity: a systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044987
Gradek-Kwinta, Slowik, Dziedzic, The use of anticholinergic medication is associated with an increased risk of stroke-associated pneumonia, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-022-02123-x
Hamed, Hagag, The possible immunoregulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in coronavirus disease patients, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110140
Hannestad, Dellagioia, Bloch, The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis, Neuropsychopharmacology, doi:10.1038/npp.2011.132
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Gulbins, Kornhuber, Carpinteiro et al., Association between FIASMA psychotropic medications and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals with psychiatric disorders hospitalized for severe COVID-19: an observational multicenter study, Transl Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41398-022-01804-5
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Gulbins, Kornhuber, Carpinteiro et al., Association between FIASMAs and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals hospitalized for severe COVID-19: An observational multicenter study, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.2317
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Gulbins, Kornhuber, Vernet et al., Association between benzodiazepine receptor agonist use and mortality in patients hospitalised for COVID-19: a multicentre observational study, Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci, doi:10.1017/S2045796021000743
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Kornhuber, Gulbins, Reiersen et al., on behalf of AP-HP/Université Paris Cité/INSERM COVID-19 Research Collaboration, AP-HP COVID CDR Initiative and "Entrepôt de Données de Santé, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm11195882
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Vernet, Beeker, Jannot et al., AP-HP / Universities / INSERM COVID-19 Research Collaboration and AP-HP COVID CDR Initiative. Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4
Krause, Greenberg, Ghosh, Wozny, Hansen et al., COVID-19 severity scale for claims data research, BMC Health Serv Res, doi:10.1186/s12913-023-09362-2
Kristiansen, Hansen, Inhibition of HIV replication by neuroleptic agents and their potential use in HIV infected patients with AIDS related dementia, doi:10.1016/s0924-8579(99)00157-0
Lee, Vigod, Bortolussi-Courval, Hanula, Boulware et al., Fluvoxamine for outpatient management of COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Marshall, Murthy, Diaz, Adhikari, Angus et al., A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research, Lancet Infect Dis
Marín-Corral, Rodríguez-Morató, Gomez-Gomez, Pascual-Guardia, Muñoz-Bermúdez et al., Metabolic signatures associated with severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22094794
May, Slitzky, Rostama, Barlow, Houseknecht, Antipsychotic-induced immune dysfunction: A consideration for COVID-19 risk, Brain Behav Immun Health, doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100097
Mccarthy, Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Stewart et al., Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators. Effect of fluvoxamine vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.24100
Oskotsky, Marić, Tang, Oskotsky, Wong et al., Mortality risk among patients with COVID-19 prescribed selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.33090
Park, Kwon, An, Park, A nationwide cohort study of the association of benzodiazepines with SARS-CoV-2 infection and clinical outcomes, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-20335-z
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Global Health, doi:10.1016/s2214-109x(21)00448-4
Rowan, Mcalpine, Blewett, Access and cost barriers to mental health care by insurance status, 1999 to 2010, Health Aff (Millwood)
Rössler, Salize, Van Os, Riecher-Rössler, Size of burden of schizophrenia and psychotic disorders, Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2005.04.009
Sacre, Medghalchi, Gregory, Brennan, Williams, Fluoxetine and citalopram exhibit potent antiinflammatory activity in human and murine models of rheumatoid arthritis and inhibit toll-like receptors, Arthritis Rheumatism
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab050
Teixeira, Krause, Ghosh, Shahani, Machado-Vieira et al., Analysis of COVID-19 infection and mortality among patients with psychiatric disorders, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34969
Zhang, Li, Sun, He, Xu et al., Physical activity and COVID-19: an observational and Mendelian randomisation study, J Glob Health
Zimniak, Kirschner, Hilpert, Geiger, Danov et al., The serotonin reuptake inhibitor Fluoxetine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung tissue, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85049-0
Zuo, Quinn, Kye, Cooper, Damoiseaux et al., Fluoxetine is a potent inhibitor of Coxsackievirus replication, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00983-12
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0310438",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0310438",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The coronavirus disease pandemic caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which emerged in the United States in late 2019 to early 2020 and quickly escalated into a national public health crisis. Research has identified psychiatric conditions as possible risk factors associated with COVID-19 infection and symptom severity. This study aims to determine whether specific classes of psychiatric medications could reduce the likelihood of infection and alleviate the severity of the disease. The objective of this study is to investigate the relationship between neuropsychiatric medication usage and COVID-19 outcomes before the widespread utilization of COVID-19 vaccines. This cross-sectional study used Optum’s de-identified Clinformatics Data Mart Database to identify patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in 2020 and their psychiatric medication prescriptions in the United States. Ordered logistic regression was used to predict the likelihood of a higher COVID-19 severity level for long-term and new users. Results were adjusted for demographic characteristics and medical and psychiatric comorbidities. Most users were classified into the long-term user analysis group. Long-term users were 9% less likely to have a higher severity score (CI: 0.89–0.93, p-value < 0.001) than non-users. SSRI antidepressant users, both long-term (OR: 1.09; CI: 1.06–1.12) and short-term (OR: 1.17; CI: 1.07–1.27) were significantly more likely to have a lower severity score. However, the results varied across long-term and short-term users for all medication classes. Results of the current study suggest that psychopharmacological agents are associated with reduced COVID-19 severity levels and that antidepressant medications may have a protective role against COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Machado-Vieira",
"given": "Rodrigo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6740-4734",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Krause",
"given": "Trudy M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Gregory",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9621-5422",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Teixeira",
"given": "Antonio L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahani",
"given": "Lokesh R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lane",
"given": "Scott D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soares",
"given": "Jair C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5982-6304",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Truong",
"given": "Chau N.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-24T18:34:36Z",
"timestamp": 1740422076000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-24T18:34:50Z",
"timestamp": 1740422090000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafi",
"given": "Hira",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-25T05:31:22Z",
"timestamp": 1740461482663,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1740355200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0310438",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0310438",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/acps.13309",
"article-title": "Severe mental illness is associated with increased mortality and severe course of COVID‐19",
"author": "CA Barcella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "82",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Psychiatr Scand",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref001",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34969",
"article-title": "Analysis of COVID-19 infection and mortality among patients with psychiatric disorders, 2020",
"author": "AL Teixeira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2134969",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref002",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms9020339",
"article-title": "Fluoxetine can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "A Dechaumes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "339",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Microorganisms",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref003",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85049-0",
"article-title": "The serotonin reuptake inhibitor Fluoxetine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung tissue",
"author": "M Zimniak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5890",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref004",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.33090",
"article-title": "Mortality risk among patients with COVID-19 prescribed selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants",
"author": "T Oskotsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2133090",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref005",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142",
"article-title": "Pharmacological inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase prevents uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by epithelial cells",
"author": "A Carpinteiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100142",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref006",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.27304",
"article-title": "Fluoxetine and citalopram exhibit potent antiinflammatory activity in human and murine models of rheumatoid arthritis and inhibit toll-like receptors",
"author": "S Sacre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "683",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheumatism",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref007",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/npp.2011.132",
"article-title": "The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis",
"author": "J Hannestad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2452",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Neuropsychopharmacology",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref008",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11195882",
"article-title": "Antidepressant use and its association with 28-day mortality in inpatients with SARS-CoV-2: Support for the FIASMA model against COVID-19",
"author": "on behalf of AP-HP/Université Paris Cité/INSERM COVID-19 Research Collaboration, AP-HP COVID CDR Initiative and “Entrepôt de Données de Santé” AP-HP Consortium",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5882",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref009",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial",
"author": "G Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e42",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Lancet Global Health",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref010",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab050",
"article-title": "Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19",
"author": "D Seftel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofab050",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref011",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.24100",
"article-title": "Effect of fluvoxamine vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "296",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref012",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine for outpatient management of COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization",
"author": "TC Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e226269",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref013",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100097",
"article-title": "Antipsychotic-induced immune dysfunction: A consideration for COVID-19 risk",
"author": "M May",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100097",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun Health",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref014",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12913-023-09362-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19 severity scale for claims data research",
"author": "TM Krause",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "402",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Health Serv Res",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref015",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"article-title": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research",
"author": "JC Marshall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e192",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref016",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00213-014-3655-6",
"article-title": "Lithium increases leukocyte mitochondrial complex I activity in bipolar disorder during depressive episodes",
"author": "RT de Sousa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Psychopharmacology (Berl)",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref017",
"volume": "232",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2011.02.004",
"article-title": "5-HT and the immune system",
"author": "GP Ahern",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Pharmacol",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref018",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110140",
"article-title": "The possible immunoregulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in coronavirus disease patients",
"author": "MGM Hamed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110140",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref019",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00213-015-4044-5",
"article-title": "Effects of psychotropic drugs on inflammation: consequence or mediator of therapeutic effects in psychiatric treatment?",
"author": "D Baumeister",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1575",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Psychopharmacology (Berl)",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref020",
"volume": "233",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0924-8579(99)00157-0",
"article-title": "Inhibition of HIV replication by neuroleptic agents and their potential use in HIV infected patients with AIDS related dementia",
"author": "JE Kristiansen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "209",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref021",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00983-12",
"article-title": "Fluoxetine is a potent inhibitor of Coxsackievirus replication",
"author": "J Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4838",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref022",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4",
"article-title": "Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study",
"author": "AP-HP / Universities / INSERM COVID-19 Research Collaboration and AP-HP COVID CDR Initiative",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5199",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Mol Psychiatry",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref023",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22094794",
"article-title": "Metabolic signatures associated with severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "J Marín-Corral",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4794",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref024",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2317",
"article-title": "Association between FIASMAs and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals hospitalized for severe COVID‐19: An observational multicenter study",
"author": "AP‐HP / Université de Paris / INSERM COVID‐19 research collaboration, AP‐HP COVID CDR Initiative, “Entrepôt de Données de Santé” AP‐HP Consortium",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1498",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref025",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "EJ Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2292",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref026",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41398-022-01804-5",
"article-title": "Association between FIASMA psychotropic medications and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals with psychiatric disorders hospitalized for severe COVID-19: an observational multicenter study",
"author": "AP-HP/Université de Paris/INSERM COVID-19 research collaboration/AP-HP COVID CDR Initiative/“Entrepôt de Données de Santé” AP-HP Consortium",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl Psychiatry",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref027",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-022-02123-x",
"article-title": "The use of anticholinergic medication is associated with an increased risk of stroke-associated pneumonia",
"author": "E Gradek-Kwinta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1935",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref028",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-20335-z",
"article-title": "A nationwide cohort study of the association of benzodiazepines with SARS-CoV-2 infection and clinical outcomes",
"author": "HY Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15947",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref029",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.euroneuro.2005.04.009",
"article-title": "Size of burden of schizophrenia and psychotic disorders",
"author": "W Rössler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Eur Neuropsychopharmacol",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref030",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S2045796021000743",
"article-title": "Association between benzodiazepine receptor agonist use and mortality in patients hospitalised for COVID-19: a multicentre observational study",
"author": "AP-HP/Université de Paris/INSERM COVID-19 Research Collaboration/AP-HP COVID CDR Initiative/‘Entrepôt de Données de Santé’ AP-HP Consortium",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e18",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref031",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1377/hlthaff.2013.0133",
"article-title": "Access and cost barriers to mental health care by insurance status, 1999 to 2010",
"author": "K Rowan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1723",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Health Aff (Millwood)",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref032",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7189/jogh.10.020514",
"article-title": "Physical activity and COVID-19: an observational and Mendelian randomisation study",
"author": "X Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "020514",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Glob Health",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref033",
"volume": "10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044987",
"article-title": "Prevalence and predictors of medication non-adherence among people living with multimorbidity: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "L Foley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e044987",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref034",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1176/ps.49.2.196",
"article-title": "Compliance With Medication Regimens for Mental and Physical Disorders",
"author": "JA Cramer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "196",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Psychiatric Ser",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref035",
"volume": "49",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00127-009-0041-5",
"article-title": "Non-adherence with psychotropic medications in the general population",
"author": "AGM Bulloch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol",
"key": "pone.0310438.ref036",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2010"
}
],
"reference-count": 36,
"references-count": 36,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0310438"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Protective effects of psychiatric medications against COVID-19 mortality before vaccines",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "20"
}