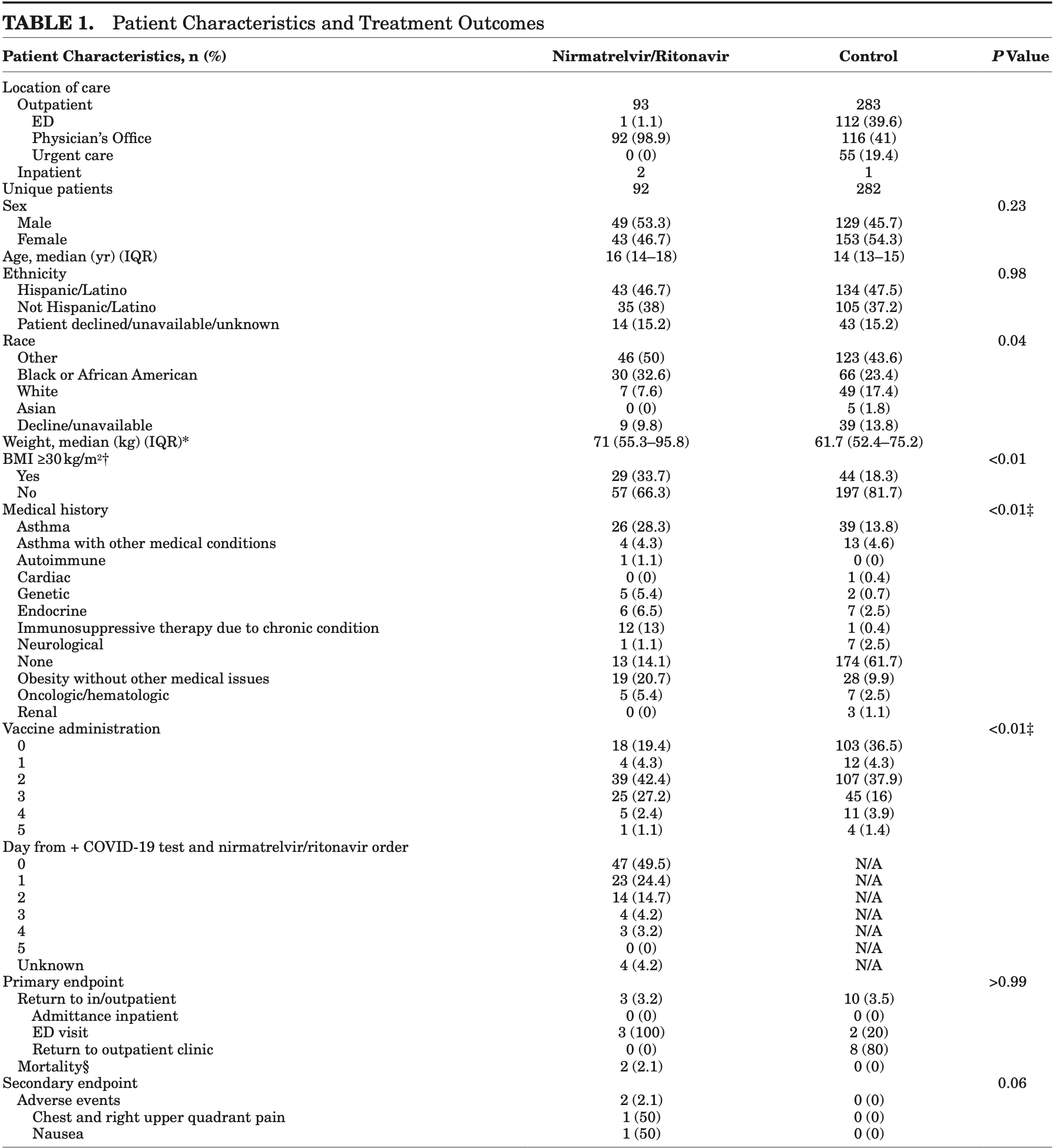
Evolving COVID-19 Landscape: Assessing the Effectiveness and Safety Profile of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in Adolescents
et al., Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000004594, Nov 2024
Retrospective 374 adolescent COVID-19 outpatients showing no significant differences with paxlovid treatment.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments18.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 813.0% higher, RR 9.13, p = 0.06, treatment 2 of 92 (2.2%), control 0 of 282 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of progression, 359.8% higher, RR 4.60, p = 0.10, treatment 3 of 92 (3.3%), control 2 of 282 (0.7%), emergency department visit.
|
|
risk of progression, 8.0% lower, RR 0.92, p = 1.00, treatment 3 of 92 (3.3%), control 10 of 282 (3.5%), NNT 351, COVID-19-related hospital admission, emergency department visit, or outpatient visit.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Lee et al., 14 Nov 2024, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, study period 1 January, 2022 - 31 July, 2023.
Contact: phle@montefiore.org.
Evolving COVID-19 Landscape: Assessing the Effectiveness and Safety Profile of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in Adolescents
Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, doi:10.1097/inf.0000000000004594
This study evaluates nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) in preventing severe coronavirus disease 2019 in adolescents (12-18). Conducted from January 2022 to July 2023, it compared hospital admissions and healthcare visits within 30 days post-treatment. Results showed similar follow-up rates between treated and untreated groups, with slightly more adverse effects in the nirmatrelvir/ritonavir group. Further research is needed to confirm its efficacy in this population.
References
Bahl, Mielke, Johnson, Severe COVID-19 outcomes in pediatrics: an observational cohort analysis comparing Alpha, Delta, and Omicron variants, Lancet Reg Health Am
Bose-Brill, Hirabayashi, Pajor, Pediatric nirmatrelvir/ritonavir prescribing patterns during the COVID-19 pandemic, medRxiv
Brown, Moore, Hooper, Interventions for preventing obesity in children, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Choi, Choi, Yun, Risk factors for severe COVID-19 in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Korean Med Sci
Costagliola, Spada, Consolini, Age-related differences in the immune response could contribute to determine the spectrum of severity of COVID-19, Immun Inflamm Dis
Esposito, Autore, Argentiero, Update on COVID-19 therapy in pediatric age, Pharmaceuticals
Fernandez, Perez, Hernandez, Factors and mechanisms for pharmacokinetic differences between pediatric population and adults, Pharmaceutics
Graff, Smith, Silveira, Risk factors for severe COVID-19 in children, Pediatr Infect Dis J
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for highrisk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hoering, Leblanc, Crowley, Seamless phase I-II trial design for assessing toxicity and efficacy for targeted agents, Clin Cancer Res
Iuliano, Brunkard, Boehmer, Trends in disease severity and health care utilization during the early Omicron variant period compared with previous SARS-CoV-2 high transmission periods-United States, December 2020-January 2022, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Jabakhanji, Boland, Ward, Body mass index changes in early childhood, J Pediatr
Levin, Whittaker, Balancing risk and benefit of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in children, Lancet Reg Health Eur
Lu, Rosenbaum, Developmental pharmacokinetics in pediatric populations, J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther
Rotulo, Palma, Understanding COVID-19 in children: immune determinants and post-infection conditions, Pediatr Res
Saravolatz, Depcinski, Sharma, Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs, Clin Infect Dis
Taylor, Whitaker, Anglin, COVID-19-associated hospitalizations among adults during SARS-CoV-2 delta and omicron variant predominance, by race/ethnicity and vaccination status-COVID-NET, 14 states, July 2021, Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Woodruff, Campbell, Taylor, Risk factors for severe COVID-19 in children, Pediatrics
Yaffe, Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in children versus adults
Yan, Zhou, Zhu, The feasibility, safety, and efficacy of Paxlovid treatment in SARS-CoV-2-infected children aged 6-14 years: a cohort study, Ann Transl Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/inf.0000000000004594",
"ISSN": [
"0891-3668",
"1532-0987"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000004594",
"abstract": "<jats:p>This study evaluates nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) in preventing severe coronavirus disease 2019 in adolescents (12–18). Conducted from January 2022 to July 2023, it compared hospital admissions and healthcare visits within 30 days post-treatment. Results showed similar follow-up rates between treated and untreated groups, with slightly more adverse effects in the nirmatrelvir/ritonavir group. Further research is needed to confirm its efficacy in this population.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5039-3522",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York"
},
{
"name": "Division of Pediatric Infectious Disease, Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, Bronx, New York"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, New York."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York"
},
{
"name": "Division of Pediatric Infectious Disease, Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, Bronx, New York"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Kiriam Escobar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York"
},
{
"name": "Division of Pediatric Infectious Disease, Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, Bronx, New York"
}
],
"family": "Anosike",
"given": "Brenda I.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"lww.com",
"ovid.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-14T15:02:14Z",
"timestamp": 1731596534000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-14T15:02:21Z",
"timestamp": 1731596541000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-14T15:40:10Z",
"timestamp": 1731598810848,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
14
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/INF.0000000000004594",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs.",
"author": "Saravolatz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "165",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "R3-20241114",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Interventions for preventing obesity in children.",
"author": "Brown",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "R5-20241114",
"volume": "2019",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.06.049",
"article-title": "Body mass index changes in early childhood.",
"author": "Jabakhanji",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr",
"key": "R6-20241114",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Pediatric nirmatrelvir/ritonavir prescribing patterns during the COVID-19 pandemic.",
"author": "Bose-Brill",
"first-page": "2022.12.23.222838682022",
"journal-title": "medRxiv [Preprint]",
"key": "R7-20241114",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19.",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R8-20241114",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Severe COVID-19 outcomes in pediatrics: an observational cohort analysis comparing Alpha, Delta, and Omicron variants.",
"author": "Bahl",
"first-page": "100405",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health Am",
"key": "R9-20241114",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7112e2",
"article-title": "COVID-19–associated hospitalizations among adults during SARS-CoV-2 delta and omicron variant predominance, by race/ethnicity and vaccination status—COVID-NET, 14 states, July 2021–January 2022.",
"author": "Taylor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "466",
"journal-title": "Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "R10-20241114",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e4",
"article-title": "Trends in disease severity and health care utilization during the early Omicron variant period compared with previous SARS-CoV-2 high transmission periods—United States, December 2020–January 2022.",
"author": "Iuliano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "R11-20241114",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1262",
"article-title": "Seamless phase I-II trial design for assessing toxicity and efficacy for targeted agents.",
"author": "Hoering",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "640",
"journal-title": "Clin Cancer Res",
"key": "R12-20241114",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics3010053",
"article-title": "Factors and mechanisms for pharmacokinetic differences between pediatric population and adults.",
"author": "Fernandez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutics",
"key": "R13-20241114",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Developmental pharmacokinetics in pediatric populations.",
"author": "Lu",
"first-page": "262",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "R14-20241114",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41390-023-02549-7",
"article-title": "Understanding COVID-19 in children: immune determinants and post-infection conditions.",
"author": "Rotulo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "434",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Res",
"key": "R16-20241114",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.404",
"article-title": "Age-related differences in the immune response could contribute to determine the spectrum of severity of COVID-19.",
"author": "Costagliola",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "331",
"journal-title": "Immun Inflamm Dis",
"key": "R17-20241114",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanepe.2022.100412",
"article-title": "Balancing risk and benefit of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in children.",
"author": "Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100412",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health Eur",
"key": "R18-20241114",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Risk factors for severe COVID-19 in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Choi",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Korean Med Sci",
"key": "R19-20241114",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/INF.0000000000003043",
"article-title": "Risk factors for severe COVID-19 in children.",
"author": "Graff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e137",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Infect Dis J",
"key": "R20-20241114",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2021-053418",
"article-title": "Risk factors for severe COVID-19 in children.",
"author": "Woodruff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2021053418",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "R21-20241114",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph15121512",
"article-title": "Update on COVID-19 therapy in pediatric age.",
"author": "Esposito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1512",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals",
"key": "R22-20241114",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/atm-22-2791",
"article-title": "The feasibility, safety, and efficacy of Paxlovid treatment in SARS-CoV-2-infected children aged 6–14 years: a cohort study.",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "Ann Transl Med",
"key": "R23-20241114",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/INF.0000000000004594"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evolving COVID-19 Landscape: Assessing the Effectiveness and Safety Profile of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in Adolescents",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/lww.0000000000001000"
}