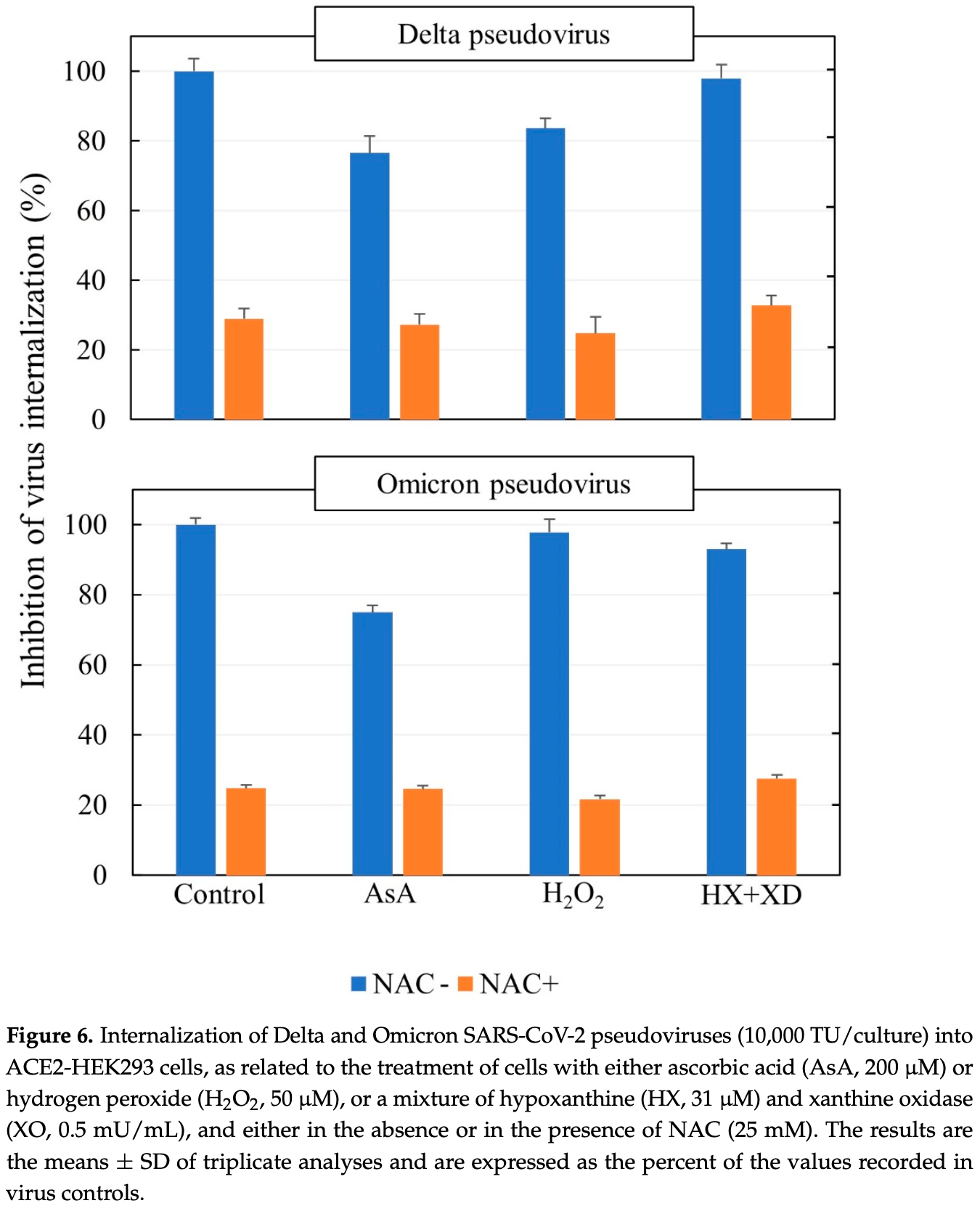
Inhibition of the Cell Uptake of Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Pseudoviruses by N-Acetylcysteine Irrespective of the Oxidoreductive Environment
et al., Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11203313, Oct 2022
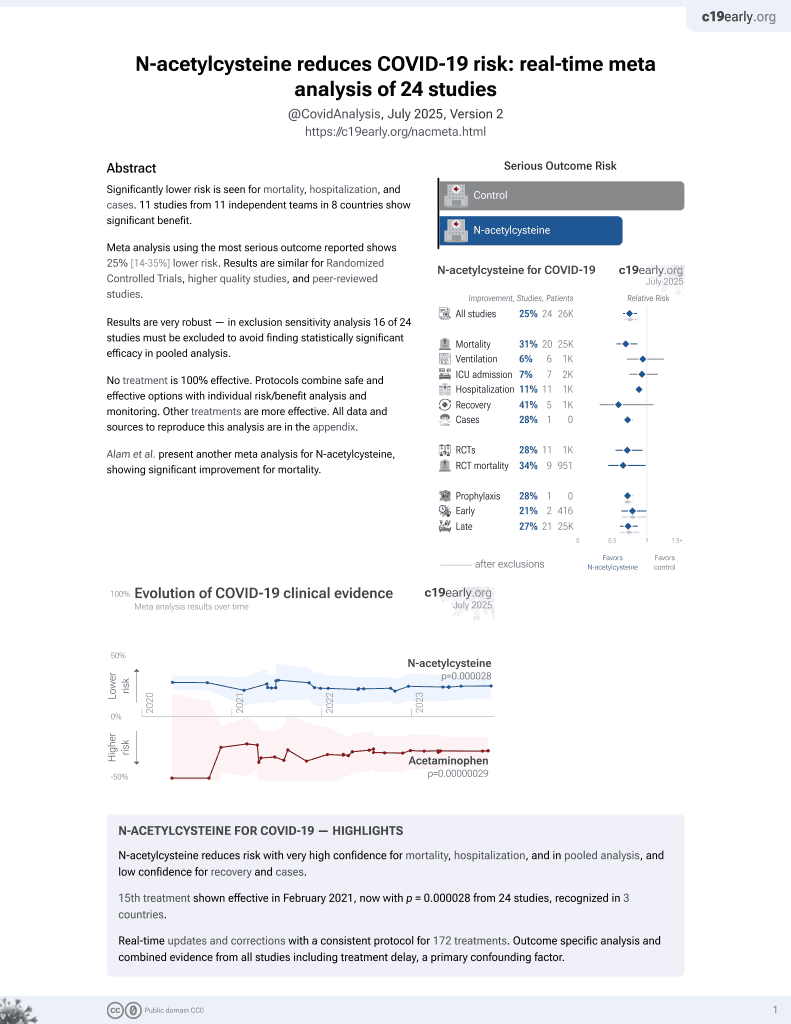
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
ACE2-HEK293 in vitro study showing dose-dependent inhibition of the uptake of delta and omicron SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses with N-acetylcysteine.
14 preclinical studies support the efficacy of N-acetylcysteine for COVID-19:
Severe COVID-19 is marked by endotheliopathy with elevated von Willebrand factor (VWF) levels and platelet/VWF-rich microthrombi; N-acetylcysteine can reduce VWF multimers and lyse VWF-dependent clots in vivo, potentially helping to alleviate thrombosis associated with COVID-1910-12.
N-acetylcysteine shows dose-dependent inhibition of SARS-CoV-24,7,9 , shows anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects against SARS-CoV-2-induced immune responses in combination with bromelain6, suppressed virus-induced reactive oxygen species and blocked viral replication in a humanized mouse model and in human lung cells5, may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by boosting cellular antioxidant defenses and potentially mitigating the oxidative stress caused by spike protein-induced ROS production in cardiac fibroblasts3, and reduces disulfide bonds in proteins and exhibits antioxidant properties that may inhibit viral replication and modulate inflammatory responses2.
NAC may be beneficial for COVID-19 by replenishing glutathione stores and reinforcing the glutathione peroxidase-4 pathway to inhibit ferroptosis, an oxidative stress-induced cell death pathway implicated in COVID-1913.
NAC reinforces glutathione levels, reduces ROS, and minimizes ferroptosis and cytokine storm14.
1.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
2.
Reis et al., Antiviral effect of Bromelain combined with acetylcysteine against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-92242-y.
3.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
4.
Chaopreecha et al., Andrographolide attenuates SARS-CoV-2 infection via an up-regulation of glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC), Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156279.
5.
Frasson et al., Identification of druggable host dependency factors shared by multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, Journal of Molecular Cell Biology. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjae004, academic.oup.com/jmcb/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jmcb/mjae004/7596546.
6.
Ferreira et al., Taming the SARS-CoV-2-mediated proinflammatory response with BromAc®, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477.
7.
La Maestra et al., Inhibition of the Cell Uptake of Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Pseudoviruses by N-Acetylcysteine Irrespective of the Oxidoreductive Environment, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11203313.
8.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
9.
Akhter et al., The Combination of Bromelain and Acetylcysteine (BromAc) Synergistically Inactivates SARS-CoV-2, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13030425.
10.
Martinez de Lizarrondo et al., Potent Thrombolytic Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on Arterial Thrombi, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027290.
11.
Chen et al., N-acetylcysteine reduces the size and activity of von Willebrand factor in human plasma and mice, Journal of Clinical Investigation, doi:10.1172/JCI41062.
12.
Goshua et al., Endotheliopathy in COVID-19-associated coagulopathy: evidence from a single-centre, cross-sectional study, The Lancet Haematology, doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30216-7.
La Maestra et al., 21 Oct 2022, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: sebastiano.lamaestra@unige.it (corresponding author), sdf@unige.it.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Inhibition of the Cell Uptake of Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Pseudoviruses by N-Acetylcysteine Irrespective of the Oxidoreductive Environment
Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11203313
The binding of SARS-CoV-2 spikes to the cell receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a crucial target both in the prevention and in the therapy of COVID-19. We explored the involvement of oxidoreductive mechanisms by investigating the effects of oxidants and antioxidants on virus uptake by ACE2-expressing cells of human origin (ACE2-HEK293). The cell uptake of pseudoviruses carrying the envelope of either Delta or Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2 was evaluated by means of a cytofluorimetric approach. The thiol N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) inhibited the uptake of both variants in a reproducible and dose-dependent fashion. Ascorbic acid showed modest effects. In contrast, neither hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) nor a system-generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), which play an important role in the intracellular alterations produced by SARS-CoV-2, were able to affect the ability of either Delta or Omicron SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses to be internalized into ACE2-expressing cells. In addition, neither H 2 O 2 nor the ROS generating system interfered with the ability of NAC to inhibit that mechanism. Moreover, based on previous studies, a preventive pharmacological approach with NAC would have the advantage of decreasing the risk of developing COVID-19, irrespective of its variants, and at the same time other respiratory viral infections and associated comorbidities.
Author Contributions: Planning, methodology, formal analysis, and editing, S.L.M.; methodology and formal analysis, S.G.; methodology, R.B., F.D. and R.T.M.; supervision, conceptualization, and writing, S.D.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. Funding: This research received no external funding excepting the supply of the materials specified under Acknowledgements.
Institutional Review Board Statement: Not applicable. Informed Consent Statement: Not applicable.
References
Akhter, Quéromès, Pillai, Kepenekian, Badar et al., The Combination of bromelain and acetylcysteine (BromAc) synergistically inactivates SARS-CoV-2, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13030425
Angeli, Reboldi, Trapasso, Zappa, Spanevello et al., COVID-19, vaccines and deficiency of ACE2 and other angiotensinases. Closing the loop on the "Spike effect, Eur. J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2022.06.015
Aruoma, Halliwell, Hoey, Butler, The antioxidant action of N-acetylcysteine: Its reaction with hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, superoxide, and hypochlorous acid, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/0891-5849(89)90066-X
Bartolini, Stabile, Bastianelli, Giustarini, Pierucci et al., SARS-CoV2 infection impairs the metabolism and redox function of cellular glutathione, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.102041
Basi, Turkoglu, In vitro effect of oxidized and reduced glutathione peptides on angiotensin converting enzyme purified from human plasma, J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.11.023
Beyerstedt, Casaro, Rangel, COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6
Capettini, Montecucco, Mach, Stergiopulos, Santos et al., Role of renin-angiotensin system in inflammation, immunity and aging, Curr. Pharm. Des, doi:10.2174/138161212799436593
De Flora, Balansky, La Maestra, Rationale for the use of N-acetylcysteine in both prevention and adjuvant therapy of COVID-19, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202001807
De Flora, Balansky, Lamaestra, Antioxidants and COVID-19, J. Prev. Med. Hyg, doi:10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.1S3.1895
De Flora, Grassi, Carati, Attenuation of influenza-like symptomatology and improvement of cell-mediated immunity with long-term N-acetylcysteine treatment, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/09031936.97.10071535
De Flora, Izzotti, D'agostini, Balansky, Mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine in the prevention of DNA damage and cancer, with special reference to smoking-related end-points, Carcinogenesis, doi:10.1093/carcin/22.7.999
Debnath, Mitra, Dewaker, Prabhakar, Tadala et al., N-acetyl cysteine: A tool to perturb SARS-CoV-2 spike protein conformation, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12687923.v2
Delgado-Roche, Mesta, Oxidative stress as key player in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection, Arch. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.04.019
Duarte Lana, Lana, Rodrigues, Santos, Navani et al., Nebulization of glutathione and N-Acetylcysteine as an adjuvant therapy for COVID-19 onset, Adv. Redox Res, doi:10.1016/j.arres.2021.100015
Foyer, Noctor, Ascorbate and glutathione: The heart of the redox hub, Plant Physiol, doi:10.1104/pp.110.167569
Galli, Marcantonini, Giustarini, Albertini, Migni et al., How aging and oxidative stress influence the cytopathic inflammatory effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection: The role of cellular glutathione and cysteine metabolism, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11071366
García-Sánchez, Miranda-Díaz, Cardona-Muñoz, The role of oxidative stress in physiopathology and pharmacological treatment with pro-and antioxidant properties in chronic diseases, Oxid. Med. Cell Longev
Grishin, Dolgova, Harms, Pickering, George et al., Disulfide Bonds Play a Critical Role in the Structure and Function of the Receptor-binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antigen, J. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167357
Halliwell, Clement, Long, Hydrogen peroxide in the human body, FEBS Lett, doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02197-9
Hati, Bhattacharyya, Impact of thiol-disulfide balance on the binding of COVID-19 spike protein with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor, ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c02125
Ivanov, Goc, Ivanova, Niedzwiecki, Rath, Inhibition of ACE2 Expression by ascorbic acid alone and its combinations with other natural compounds, Infect. Dis, doi:10.1177/1178633721994605
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Jorge-Aarón, Rosa-Ester, N-acetylcysteine as a potential treatment for COVID-19, Future Microbiol
Khanna, Raymond, Jin, Charbit, Gitlin et al., Thiol drugs decrease SARS-CoV-2 lung injury in vivo and disrupt SARS-CoV-2 spike complex binding to ACE2 in vitro, bioRxiv
Laforge, Elbim, Frère, Hémadi, Massaad et al., Tissue damage from neutrophilinduced oxidative stress in COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1
Laurent, Martinent, Lim, Pham, Kato et al., Thiol-mediated uptake, JACS Au, doi:10.1021/jacsau.1c00128
Li, Geng, Peng, Meng, Lu, Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19, J. Pharm. Anal, doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001
Lu, Regulation of glutathione synthesis, Mol. Aspects Med, doi:10.1016/j.mam.2008.05.005
Manček-Keber, Hafner-Bratkovič, Lainšček, Benčina, Govednik et al., Disruption of disulfides within RBD of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents fusion and represents a target for viral entry inhibition by registered drugs, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202100560R
Murae, Shimizu, Yamamoto, Kobayashi, Houri et al., The function of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is impaired by disulfide-bond disruption with mutation at cysteine-488 and by thiol-reactive N-acetyl-cysteine and glutathione, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.01.106
Oter, Jin, Cucullo, Dorman, Oxidants and antioxidants: Friends or foes? Oxid, Antioxid. Med. Sci, doi:10.5455/oams.080612.ed.001
Ruffmann, Wendel, GSH rescue by N-acetylcysteine, Klin. Wochenschr, doi:10.1007/BF01649460
Shi, Zeida, Edwards, Mallory, Sastre et al., Thiol-based chemical probes exhibit antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 via allosteric disulfide disruption in the spike glycoprotein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2120419119
Strålin, Karlsson, Johansson, Marklund, The interstitium of the human arterial wall contains very large amounts of extracellular superoxide dismutase, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol, doi:10.1161/01.ATV.15.11.2032
Van Den Brand, Haagmans, Van Riel, Osterhaus, Kuiken, The pathology and pathogenesis of experimental severe acute respiratory syndrome and influenza in animal models, J. Comp. Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.jcpa.2014.01.004
Vitiello, Ferrara, Auti, Di Domenico, Boccellino, Advances in the Omicron variant development, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13478
Walls, Park, Tortorici, Wall, Mcguire et al., Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058
Yi, Khosla, Thiol-disulfide exchange reactions in the mammalian extracellular environment, Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng, doi:10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-080615-033553
Zhao, Ding, Du, Fan, update on human coronaviruses: One health, one world, Med. Nov. Technol. Devices, doi:10.1016/j.medntd.2020.100043
Çakırca, Damar Çakırca, Üstünel, Torun, Koyuncu et al., Thiol level and total oxidant/antioxidant status in patients with COVID-19 infection, Ir. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1007/s11845-021-02743-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11203313",
"ISSN": [
"2073-4409"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/cells11203313",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The binding of SARS-CoV-2 spikes to the cell receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a crucial target both in the prevention and in the therapy of COVID-19. We explored the involvement of oxidoreductive mechanisms by investigating the effects of oxidants and antioxidants on virus uptake by ACE2-expressing cells of human origin (ACE2-HEK293). The cell uptake of pseudoviruses carrying the envelope of either Delta or Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2 was evaluated by means of a cytofluorimetric approach. The thiol N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) inhibited the uptake of both variants in a reproducible and dose-dependent fashion. Ascorbic acid showed modest effects. In contrast, neither hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) nor a system-generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), which play an important role in the intracellular alterations produced by SARS-CoV-2, were able to affect the ability of either Delta or Omicron SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses to be internalized into ACE2-expressing cells. In addition, neither H2O2 nor the ROS generating system interfered with the ability of NAC to inhibit that mechanism. Moreover, based on previous studies, a preventive pharmacological approach with NAC would have the advantage of decreasing the risk of developing COVID-19, irrespective of its variants, and at the same time other respiratory viral infections and associated comorbidities.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"cells11203313"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4939-2124",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "La Maestra",
"given": "Sebastiano",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garibaldi",
"given": "Silvano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balansky",
"given": "Roumen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6299-6873",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "D’Agostini",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Micale",
"given": "Rosanna T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8023-5541",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "De Flora",
"given": "Silvio",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cells",
"container-title-short": "Cells",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-24T00:43:50Z",
"timestamp": 1666572230000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-24T01:55:50Z",
"timestamp": 1666576550000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-24T06:25:52Z",
"timestamp": 1666592752557
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "20",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "20",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1666310400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/11/20/3313/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3313",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medntd.2020.100043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138161212799436593",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.11.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2022.06.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsomega.0c02125",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jacsau.1c00128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13030425",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167357",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202100560R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.12.08.415505",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26434/chemrxiv.12687923.v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.01.106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2120419119",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/carcin/22.7.999",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcpa.2014.01.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/2082145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5455/oams.080612.ed.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.1S3.1895",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mam.2008.05.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01649460",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11845-021-02743-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11071366",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2021.102041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02197-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1104/pp.110.167569",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13478",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fmb-2020-0074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202001807",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1178633721994605",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.04.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.ATV.15.11.2032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-080615-033553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0891-5849(89)90066-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arres.2021.100015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.97.10071535",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/11/20/3313"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Inhibition of the Cell Uptake of Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Pseudoviruses by N-Acetylcysteine Irrespective of the Oxidoreductive Environment",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}