Taming the SARS-CoV-2-mediated proinflammatory response with BromAc®
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477, Dec 2023
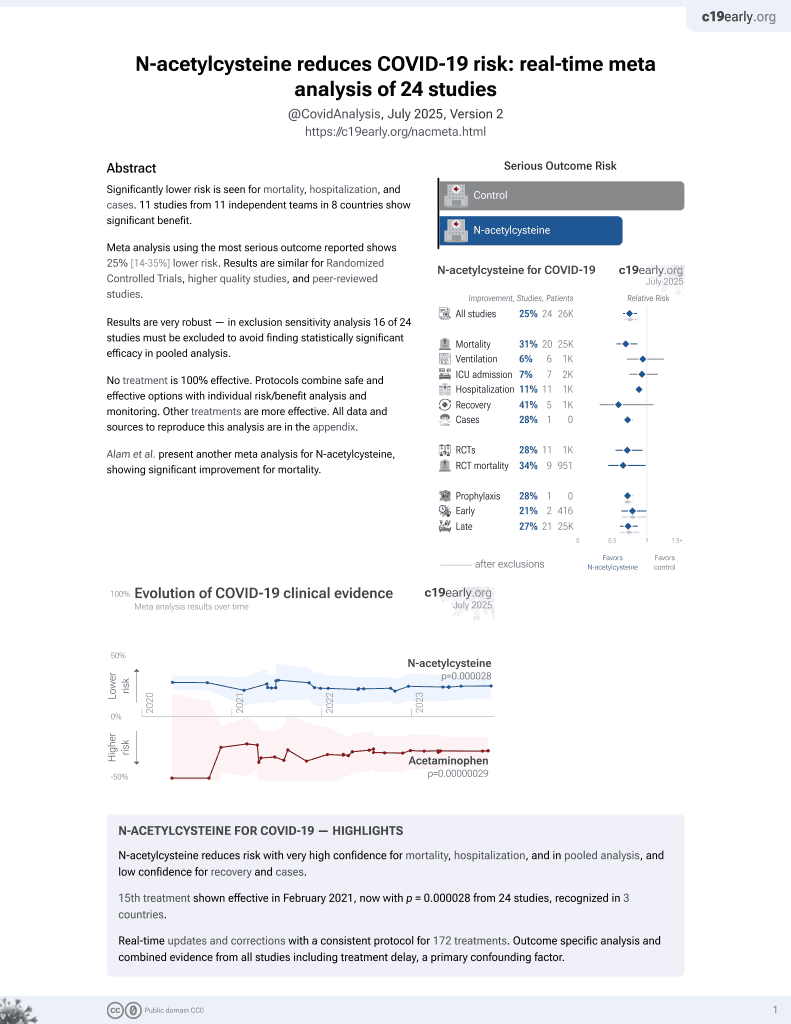
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
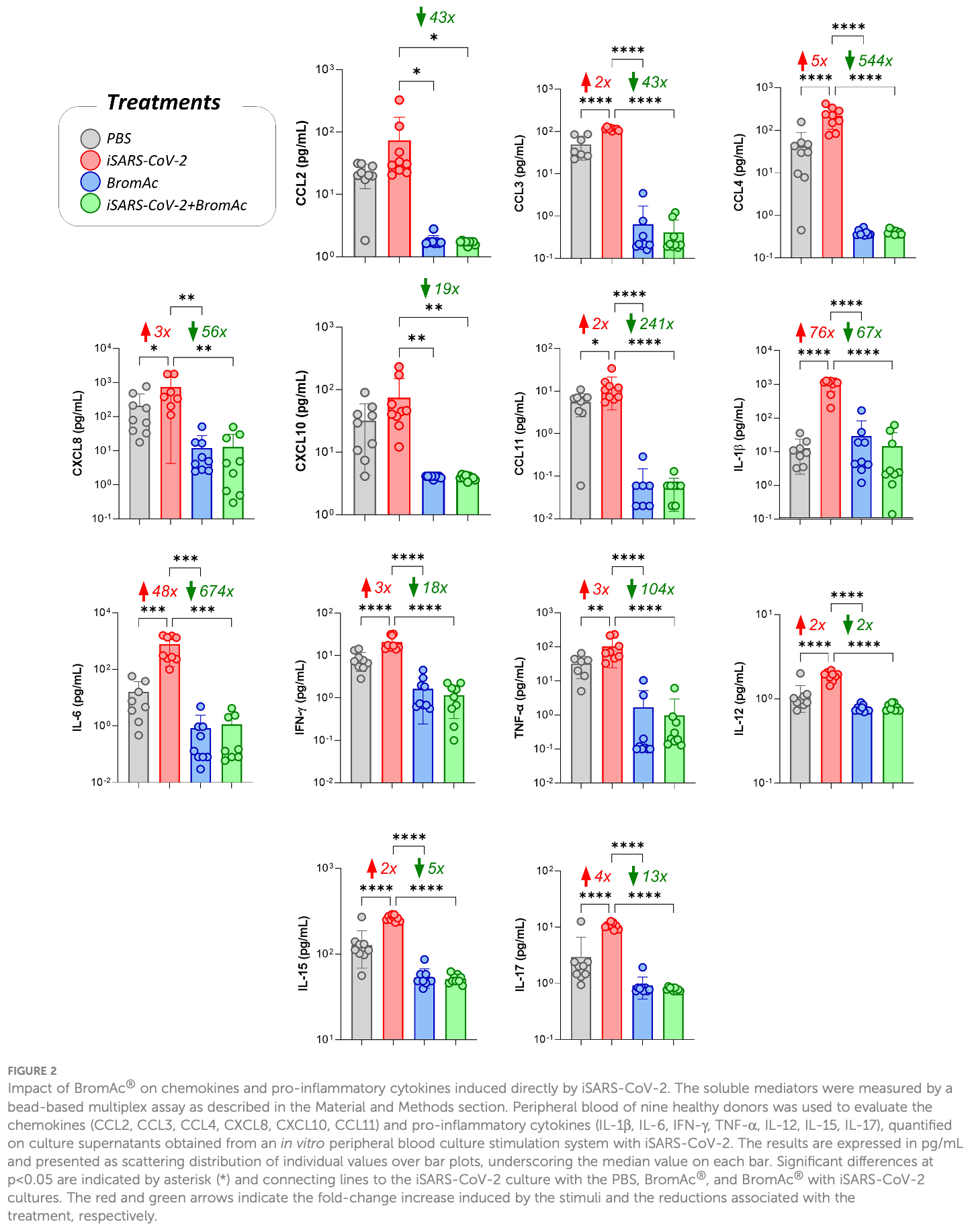
In vitro study of peripheral blood cells from 9 healthy donors showing reduced proinflammatory cytokines, growth factors, and regulatory cytokines; decreased neutrophils and monocytes; and increased HLA-DR expression on monocytes with BromAc (bromelain plus acetylcysteine) treatment in the presence of inactivated SARS-CoV-2. BromAc demonstrated anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects against SARS-CoV-2-induced immune responses.
14 preclinical studies support the efficacy of N-acetylcysteine for COVID-19:
Severe COVID-19 is marked by endotheliopathy with elevated von Willebrand factor (VWF) levels and platelet/VWF-rich microthrombi; N-acetylcysteine can reduce VWF multimers and lyse VWF-dependent clots in vivo, potentially helping to alleviate thrombosis associated with COVID-1910-12.
N-acetylcysteine shows dose-dependent inhibition of SARS-CoV-24,7,9 , shows anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects against SARS-CoV-2-induced immune responses in combination with bromelain6, suppressed virus-induced reactive oxygen species and blocked viral replication in a humanized mouse model and in human lung cells5, may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by boosting cellular antioxidant defenses and potentially mitigating the oxidative stress caused by spike protein-induced ROS production in cardiac fibroblasts3, and reduces disulfide bonds in proteins and exhibits antioxidant properties that may inhibit viral replication and modulate inflammatory responses2.
NAC may be beneficial for COVID-19 by replenishing glutathione stores and reinforcing the glutathione peroxidase-4 pathway to inhibit ferroptosis, an oxidative stress-induced cell death pathway implicated in COVID-1913.
NAC reinforces glutathione levels, reduces ROS, and minimizes ferroptosis and cytokine storm14.
1.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
2.
Reis et al., Antiviral effect of Bromelain combined with acetylcysteine against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-92242-y.
3.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
4.
Chaopreecha et al., Andrographolide attenuates SARS-CoV-2 infection via an up-regulation of glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC), Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156279.
5.
Frasson et al., Identification of druggable host dependency factors shared by multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, Journal of Molecular Cell Biology. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjae004, academic.oup.com/jmcb/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jmcb/mjae004/7596546.
6.
Ferreira et al., Taming the SARS-CoV-2-mediated proinflammatory response with BromAc®, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477.
7.
La Maestra et al., Inhibition of the Cell Uptake of Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Pseudoviruses by N-Acetylcysteine Irrespective of the Oxidoreductive Environment, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11203313.
8.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
9.
Akhter et al., The Combination of Bromelain and Acetylcysteine (BromAc) Synergistically Inactivates SARS-CoV-2, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13030425.
10.
Martinez de Lizarrondo et al., Potent Thrombolytic Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on Arterial Thrombi, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027290.
11.
Chen et al., N-acetylcysteine reduces the size and activity of von Willebrand factor in human plasma and mice, Journal of Clinical Investigation, doi:10.1172/JCI41062.
12.
Goshua et al., Endotheliopathy in COVID-19-associated coagulopathy: evidence from a single-centre, cross-sectional study, The Lancet Haematology, doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30216-7.
Ferreira et al., 13 Dec 2023, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 13 authors.
Contact: jreis@icb.ufmg.br, reisjordana@gmail.com, sarah@mucpharm.com, david@mucpharm.com.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Taming the SARS-CoV-2-mediated proinflammatory response with BromAc®
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477
Introduction: In the present study, the impact of BromAc®, a specific combination of bromelain and acetylcysteine, on the SARS-CoV-2-specific inflammatory response was evaluated. Methods: An in vitro stimulation system was standardized using blood samples from 9 healthy donors, luminex assays and flow cytometry were performed. Results and discussion: BromAc® demonstrated robust anti-inflammatory activity in human peripheral blood cells upon SARS-CoV-2 viral stimuli, reducing the cytokine storm, composed of chemokines, growth factors, and proinflammatory and regulatory cytokines produced after short-term in vitro culture with the inactivated virus (iSARS-CoV-2). A combined reduction in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induced by SARS-CoV-2, in addition to steady-state levels of platelet recruitment-associated growth factor-PDGFbb, was observed, indicating that BromAc® may be important to reduce thromboembolism in COVID-19. The immunophenotypic analysis of the impact of BromAc® on leukocytes upon viral stimuli showed that BromAc® was able to downmodulate the populations of CD16+ neutrophils and CD14+ monocytes observed after stimulation with iSARS-CoV-2. Conversely, BromAc® treatment increased steady-state HLA-DR expression in CD14 + monocytes and preserved this activation marker in this subset upon iSARS-CoV-2 stimuli, indicating improved monocyte activation upon BromAc® treatment. Additionally, BromAc® downmodulated the iSARS-CoV-2-induced production of TNF-a by the CD19+ B-cells. System biology approaches, utilizing comprehensive correlation matrices and networks, showed distinct patterns of connectivity in groups Frontiers in Immunology frontiersin.org 01
Ethics statement The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Universidade Estadual de Santa Cruz (UESC) and Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
Funding The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Fundacão de Amparo à Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG, APQ-01499-21), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientıfco e Tecnoloǵico (CNPq MCTI/CNPQ/Universal), EMBRAPII (Process # 30275) and Coordenacão de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nıvel Superior (CAPES). FF, OM, MT, and JC-d-R received PQ fellowships from CNPq. This work was also funded by extramural resources from Mucpharm Pty Ltd (AU). OF participated in the fellow program supported by the Universidade do Estado do Amazonas (PROVISIT N°005/2023-PROPESP/UEA).
Conflict of interest SV and DM are shareholders of Mucpharm Pty Ltd. and provided scientific input on the protocol and design of the study. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from Mucpharm Pty Ltd. The funder had the following..
References
Abdelrahman, Abd-Elrahman, Bakheet, Persistence of symptoms after improvement of acute COVID-19 infection, a longitudinal study, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27156
Akhter, Queŕomès, Pillai, Kepenekian, Badar et al., The combination of bromelain and acetylcysteine (BromAc) synergistically inactivates SARS-CoV-2, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13030425
Atanasova, Reznikov, Strategies for measuring airway mucus and mucins, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-019-1239-z
Barnes, Adrover, Baxter-Stoltzfus, Borczuk, Cools-Lartigue et al., Targeting potential drivers of COVID-19: Neutrophil extracellular traps, J Exp Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20200652
Barth, Guseo, Klein, In vitro study on the immunological effect of bromelain and trypsin on mononuclear cells from humans, Eur J Med Res
Bateman, Dear, Thanacoody, Thomas, Eddleston et al., Reduction of adverse effects from intravenous acetylcysteine treatment for paracetamol poisoning: a randomised controlled trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62062-0
Bösmüller, Traxler, Bitzer, Häberle, Raiser et al., The evolution of pulmonary pathology in fatal COVID-19 disease: an autopsy study with clinical correlation, Virchows Archiv, doi:10.1007/s00428-020-02881-x
Coelho Dos Reis, Ferreira, Lourenco, Ribeiro, ́l et al., Ex-vivo mucolytic and anti-inflammatory activity of BromAc in tracheal aspirates from COVID-19, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112753
Darif, Hammi, Kihel, Idrissi Saik, Guessous et al., The proinflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 pathogenesis: What goes wrong?, Microb Pathog, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104799
Declercq, Leeuw, Lambrecht, Inflammasomes and IL-1 family cytokines in SARS-CoV-2 infection: from prognostic marker to therapeutic agent, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155934
Ekstedt, Piersiala, Petro, Karlsson, Kågedal et al., A prolonged innate systemic immune response in COVID-19, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13986-5
Fitzhugh, Shan, Dewhirst, Hale, Bromelain treatment decreases neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation, Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2008.02.015
Goncalves, Da Mata, Lourenco, Ribeiro, ́l et al., Timeline kinetics of systemic and airway immune mediator storm for comprehensive analysis of disease outcome in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.903903
Gusev, Sarapultsev, Solomatina, Chereshnev, SARS-coV-2-specific immune response and the pathogenesis of COVID-19, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23031716
Hu, Huang, Yin, The cytokine storm and COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26232
Huang, Wu, Hou, Jeng, Bromelain inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production in human THP-1 monocytes via the removal of CD14, Immunol Invest, doi:10.1080/08820130802083622
Jukema, Smit, Hopman, Bongers, Pelgrim et al., Neutrophil and eosinophil responses remain abnormal for several months in primary care patients with COVID-19 disease, Front Allergy, doi:10.3389/falgy.2022.942699
Kang, Lee, Jeon, Jo, Roles of interleukin-17 and th17 responses in COVID-19, J Bacteriol Virol, doi:10.4167/jbv.2021.51.3.089
Khan, Khan, Charles, Pratap, Naeem et al., Cytokine storm and mucus hypersecretion in COVID-19: review of mechanisms, J Inflammation Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S271292
Kleef, Delohery, Bovbjerg, Selective modulation of cell adhesion molecules on lymphocytes by bromelain protease 5, Pathobiology, doi:10.1159/000164070
Knight, Caricchio, Casanova, Combes, Diamond et al., The intersection of COVID-19 and autoimmunity, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI154886
Knoll, Schultze, Schulte-Schrepping, Monocytes and macrophages in COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.720109
Li, Hilgenfeld, Whitley, Clercq, Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned, Nat Rev Drug Discovery, doi:10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y
Liu, Lv, Liu, Li, Xie et al., Mucus production stimulated by IFN-AhR signaling triggers hypoxia of COVID-19, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-00435-z
Lourda, Dzidic, Hertwig, Bergsten, Medina et al., High-dimensional profiling reveals phenotypic heterogeneity and disease-specific alterations of granulocytes in COVID-19, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2109123118
Meyerholz, Reznikov, Influence of SARS-CoV-2 on airway mucus production: A review and proposed model, Vet Pathol, doi:10.1177/03009858211058837
Mohanty, Padhy, Das, Meher, Therapeutic potential of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) in preventing cytokine storm in COVID-19: review of current evidence, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202103_25442
Mokhtari, Afsharian, Shahhoseini, Kalantar, Moini, A review on various uses of N-acetyl cysteine citation, Cell Journal, doi:10.22074/cellj.2016.4872
Montazersaheb, Khatibi, Hejazi, Tarhriz, Farjami et al., COVID-19 infection: an overview on cytokine storm and related interventions, Virol J, doi:10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1
Muralidharan, Wyatt, Reid, SARS-coV-2 dysregulates neutrophil degranulation and reduces lymphocyte counts, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020382
Nasrollahi, Talepoor, Saleh, Vakili, Heydarinezhad et al., Immune responses in mildly versus critically ill COVID-19 patients, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1077236
Onken, Greer, Calingaert, Hale, Bromelain treatment decreases secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines by colon biopsies in vitro, Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2007.11.002
Paho, Who, Pan American Health Organization, Update on variant of interest EG.5 and variant under surveillance BA
Potere, Buono, Caricchio, Cremer, Vecchiéa et al., Interleukin-1 and the NLRP3 inflammasome in COVID-19: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104299
Proal, Vanelzakker, Long COVID or post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC): an overview of biological factors that may contribute to persistent symptoms, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2021.698169
Rodrıǵuez, Novelli, Rojas, Santis, Acosta-Ampudia et al., Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102506
Salle, Coronavirus-induced autoimmunity, Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2021.108694
Saraiva, Vieira, Garra, Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10, J Exp Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20190418
Sharma, Vimal, Bromelain: an enzyme expanding its horizon from food to pharmaceutical industry, Curr Pharm Biotechnol, doi:10.2174/1389201024666230331115338
Tysnes, Maurert, Porwol, Probst, Bjerkvig et al., Bromelain reversibly inhibits invasive properties of glioma cells, Neoplasia, doi:10.1038/sj.neo.7900196
Valle, Akhter, Mekkawy, Lodh, Pillai et al., A novel treatment of bromelain and acetylcysteine (BromAc) in patients with peritoneal mucinous tumours: A phase I first in man study, Eur J Surg Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2019.10.033
Villadangos, Bryant, Deussing, Driessen, Lennon-Dumeńil et al., Proteases involved in MHC dass II antigen presentation, Immunol Rev, doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.1999.tb01360.x
Vj, Illescas-Montes, Puerta-Puerta, Ruiz, Melguizo-Rodrıǵuez, SARS-CoV-2 infection: The role of cytokines in COVID-19 disease, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.001
Wang, Wong, Ouyang, Rutz, Targeting IL-10 family cytokines for the treatment of human diseases, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a028548
Wilk, Rustagi, Zhao, Roque, Martıńez-Coloń et al., A single-cell atlas of the peripheral immune response in patients with severe COVID-19, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0944-y
Zhang, Qin, Li, Wang, Zhao et al., A novel scoring system for prediction of disease severity in COVID-19, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.00318
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>In the present study, the impact of BromAc®, a specific combination of bromelain and acetylcysteine, on the SARS-CoV-2-specific inflammatory response was evaluated.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>An in vitro stimulation system was standardized using blood samples from 9 healthy donors, luminex assays and flow cytometry were performed. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results and discussion</jats:title><jats:p>BromAc® demonstrated robust anti-inflammatory activity in human peripheral blood cells upon SARS-CoV-2 viral stimuli, reducing the cytokine storm, composed of chemokines, growth factors, and proinflammatory and regulatory cytokines produced after short-term in vitro culture with the inactivated virus (iSARS-CoV-2). A combined reduction in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induced by SARS-CoV-2, in addition to steady-state levels of platelet recruitment-associated growth factor-PDGFbb, was observed, indicating that BromAc® may be important to reduce thromboembolism in COVID-19. The immunophenotypic analysis of the impact of BromAc® on leukocytes upon viral stimuli showed that BromAc® was able to downmodulate the populations of CD16+ neutrophils and CD14+ monocytes observed after stimulation with iSARS-CoV-2. Conversely, BromAc® treatment increased steady-state HLA-DR expression in CD14+ monocytes and preserved this activation marker in this subset upon iSARS-CoV-2 stimuli, indicating improved monocyte activation upon BromAc® treatment. Additionally, BromAc® downmodulated the iSARS-CoV-2-induced production of TNF-a by the CD19+ B-cells. System biology approaches, utilizing comprehensive correlation matrices and networks, showed distinct patterns of connectivity in groups treated with BromAc®, suggesting loss of connections promoted by the compound and by iSARS-CoV-2 stimuli. Negative correlations amongst proinflammatory axis and other soluble and cellular factors were observed in the iSARS-CoV-2 group treated with BromAc® as compared to the untreated group, demonstrating that BromAc® disengages proinflammatory responses and their interactions with other soluble factors and the axis orchestrated by SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>These results give new insights into the mechanisms for the robust anti-inflammatory effect of BromAc® in the steady state and SARS-CoV-2-specific immune leukocyte responses, indicating its potential as a therapeutic strategy for COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferreira",
"given": "Geovane Marques",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clarindo",
"given": "Felipe Alves",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ribeiro",
"given": "Ágata Lopes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomes-de-Pontes",
"given": "Letícia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Carvalho",
"given": "Luciana Debortoli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martins-Filho",
"given": "Olindo Assis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "da Fonseca",
"given": "Flávio Guimarães",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teixeira",
"given": "Mauro Martins",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sabino",
"given": "Adriano de Paula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eapen",
"given": "Mathew Suji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "David L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valle",
"given": "Sarah J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coelho-dos-Reis",
"given": "Jordana Grazziela Alves",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Immunol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-13T04:27:59Z",
"timestamp": 1702441679000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-13T04:28:07Z",
"timestamp": 1702441687000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-14T00:58:55Z",
"timestamp": 1702515535915
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
13
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1702425600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"key": "B1",
"unstructured": "Pan American Health Organization, Update on variant of interest EG.5 and variant under surveillance BA.2.862023"
},
{
"key": "B2",
"unstructured": "l World Health Organization, EG.5 Initial Risk Evaluation2023"
},
{
"key": "B3",
"unstructured": "l government services United kingdom, SARS-CoV-2 genome sequence prevalence and growth rate update2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2021.698169",
"article-title": "Long COVID or post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC): an overview of biological factors that may contribute to persistent symptoms",
"author": "Proal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00428-020-02881-x",
"article-title": "The evolution of pulmonary pathology in fatal COVID-19 disease: an autopsy study with clinical correlation",
"author": "Bösmüller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Virchows Archiv",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "477",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-13986-5",
"article-title": "A prolonged innate systemic immune response in COVID-19",
"author": "Ekstedt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9915",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1077236",
"article-title": "Immune responses in mildly versus critically ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Nasrollahi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27156",
"article-title": "Persistence of symptoms after improvement of acute COVID-19 infection, a longitudinal study",
"author": "Abdelrahman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y",
"article-title": "Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Drug Discovery",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13030425",
"article-title": "The combination of bromelain and acetylcysteine (BromAc) synergistically inactivates SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Akhter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112753",
"article-title": "Ex-vivo mucolytic and anti-inflammatory activity of BromAc in tracheal aspirates from COVID-19",
"author": "Coelho dos Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112753",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "148",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389201024666230331115338",
"article-title": "Bromelain: an enzyme expanding its horizon from food to pharmaceutical industry",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Curr Pharm Biotechnol",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "A review on various uses of N-acetyl cysteine citation",
"author": "Mokhtari",
"key": "B13",
"volume-title": "Cell Journal",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62062-0",
"article-title": "Reduction of adverse effects from intravenous acetylcysteine treatment for paracetamol poisoning: a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Bateman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26355/eurrev_202103_25442",
"article-title": "Therapeutic potential of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) in preventing cytokine storm in COVID-19: review of current evidence",
"author": "Mohanty",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2802",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejso.2019.10.033",
"article-title": "A novel treatment of bromelain and acetylcysteine (BromAc) in patients with peritoneal mucinous tumours: A phase I first in man study",
"author": "Valle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Surg Oncol",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/falgy.2022.942699",
"article-title": "Neutrophil and eosinophil responses remain abnormal for several months in primary care patients with COVID-19 disease",
"author": "Jukema",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Allergy",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.903903",
"article-title": "Timeline kinetics of systemic and airway immune mediator storm for comprehensive analysis of disease outcome in critically ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Gonçalves",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20190418",
"article-title": "Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10",
"author": "Saraiva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "217",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a028548",
"article-title": "Targeting IL-10 family cytokines for the treatment of human diseases",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20200652",
"article-title": "Targeting potential drivers of COVID-19: Neutrophil extracellular traps",
"author": "Barnes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "217",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2008.02.015",
"article-title": "Bromelain treatment decreases neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation",
"author": "Fitzhugh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000164070",
"article-title": "Selective modulation of cell adhesion molecules on lymphocytes by bromelain protease 5",
"author": "Kleef",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pathobiology",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "64",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.neo.7900196",
"article-title": "Bromelain reversibly inhibits invasive properties of glioma cells",
"author": "Tysnes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Neoplasia",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.720109",
"article-title": "Monocytes and macrophages in COVID-19",
"author": "Knoll",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0944-y",
"article-title": "A single-cell atlas of the peripheral immune response in patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Wilk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-065X.1999.tb01360.x",
"article-title": "Proteases involved in MHC dass II antigen presentation",
"author": "Villadangos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunol Rev",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "172",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00318",
"article-title": "A novel scoring system for prediction of disease severity in COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1",
"article-title": "COVID-19 infection: an overview on cytokine storm and related interventions",
"author": "Montazersaheb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "92",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104799",
"article-title": "The pro-inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 pathogenesis: What goes wrong",
"author": "Darif",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Microb Pathog",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102506",
"article-title": "Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19",
"author": "Rodríguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Autoimmun",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI154886",
"article-title": "The intersection of COVID-19 and autoimmunity",
"author": "Knight",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2021.108694",
"article-title": "Coronavirus-induced autoimmunity",
"author": "Salle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "226",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23031716",
"article-title": "SARS-coV-2-specific immune response and the pathogenesis of COVID-19",
"author": "Gusev",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1716",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-019-1239-z",
"article-title": "Strategies for measuring airway mucus and mucins",
"author": "Atanasova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "261",
"journal-title": "Respir Res",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.001",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection: The role of cytokines in COVID-19 disease",
"author": "Costela-Ruiz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Cytokine Growth Factor Rev",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03009858211058837",
"article-title": "Influence of SARS-CoV-2 on airway mucus production: A review and proposed model",
"author": "Meyerholz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Vet Pathol",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S271292",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm and mucus hypersecretion in COVID-19: review of mechanisms",
"author": "Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Inflammation Res",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-00435-z",
"article-title": "Mucus production stimulated by IFN-AhR signaling triggers hypoxia of COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26232",
"article-title": "The cytokine storm and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "In vitro study on the immunological effect of bromelain and trypsin on mononuclear cells from humans",
"author": "Barth",
"journal-title": "Eur J Med Res",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08820130802083622",
"article-title": "Bromelain inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production in human THP-1 monocytes via the removal of CD14",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunol Invest",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2007.11.002",
"article-title": "Bromelain treatment decreases secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines by colon biopsies in vitro",
"author": "Onken",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104299",
"article-title": "Interleukin-1 and the NLRP3 inflammasome in COVID-19: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications",
"author": "Potere",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155934",
"article-title": "Inflammasomes and IL-1 family cytokines in SARS-CoV-2 infection: from prognostic marker to therapeutic agent",
"author": "Declercq",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4167/jbv.2021.51.3.089",
"article-title": "Roles of interleukin-17 and th17 responses in COVID-19",
"author": "Kang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "89",
"journal-title": "J Bacteriol Virol",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2109123118",
"article-title": "High-dimensional profiling reveals phenotypic heterogeneity and disease-specific alterations of granulocytes in COVID-19",
"author": "Lourda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10020382",
"article-title": "SARS-coV-2 dysregulates neutrophil degranulation and reduces lymphocyte counts",
"author": "Muralidharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308477/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Taming the SARS-CoV-2-mediated proinflammatory response with BromAc®",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "14"
}