Colchicine and/or Naltrexone for Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Not Requiring High Levels of Ventilatory Support (COLTREXONE): A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label Trial
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.60364, COLTREXONE, NCT04756128, May 2024
Colchicine for COVID-19
5th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.0000049 from 54 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
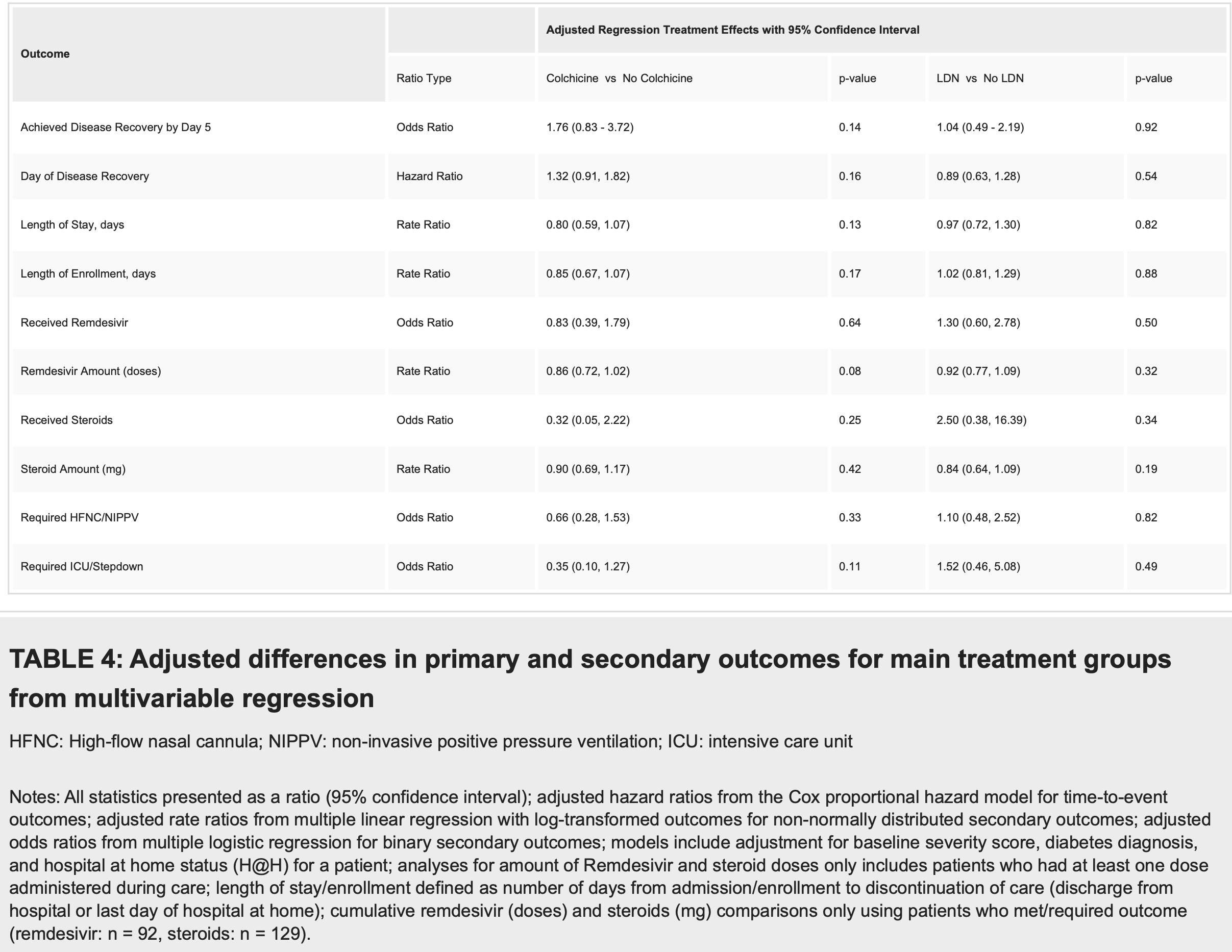
Open-label RCT 137 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, showing lower progression to ICU/step-down ICU and improved recovery with colchicine, both without statistical significance. The primary outcome was changed mid-trial due to the low number of patients progressing to severe disease.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
ICU/stepdown, 65.0% lower, OR 0.35, p = 0.11, treatment 67, control 70, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
recovery, 43.2% lower, OR 0.57, p = 0.14, treatment 67, control 70, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, multivariable, day 5, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
day of recovery, 24.2% lower, HR 0.76, p = 0.12, treatment 67, control 70, adjusted per study, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, primary outcome.
|
|
HFNC/NIPPV, 34.0% lower, OR 0.66, p = 0.34, treatment 67, control 70, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
hospitalization time, 20.0% lower, relative time 0.80, p = 0.13, treatment 67, control 70, adjusted per study, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Gertner et al., 15 May 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 58.0, 8 authors, study period 25 January, 2021 - 29 November, 2021, trial NCT04756128 (history) (COLTREXONE).
Contact: elie.x.gertner@healthpartners.com.
Colchicine and/or Naltrexone for Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Not Requiring High Levels of Ventilatory Support (COLTREXONE): A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label Trial
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.60364
We assessed the efficacy and safety of colchicine and low-dose naltrexone (LDN), alone and in combination, in preventing progression to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. In this prospective, randomized, open-label trial, colchicine and LDN were compared to standard of care (SOC) in patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 not requiring high levels of ventilatory support. Patients were randomly assigned to colchicine alone, LDN alone, colchicine/LDN in combination, or SOC. The primary outcome was time to disease recovery. Secondary outcomes included total time hospitalized, study enrollment, level of care, oxygen support, and adverse events. One-hundred and thirty-seven patients were randomized (N c = 34, N c+ldn = 33, N ldn = 35, N soc = 35). Eightyfour patients (61%) achieved disease recovery by day 5. There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients who experienced the primary efficacy outcome among those who received colchicine, LDN, or between the four study arms. Patients receiving colchicine had a shorter length of enrollment but not a significant reduction in the length of stay. Diarrhea was the most common adverse reaction. In adults hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 not requiring high-level ventilatory support, colchicine and LDN, alone and in combination, were not associated with significant reductions in progression to severe disease.
Additional Information Author Contributions All authors have reviewed the final version to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Concept and design: Elie
References
Assaly, Olson, Hammersley, Fan, Liu et al., Initial evidence of endothelial cell apoptosis as a mechanism of systemic capillary leak syndrome, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.120.4.1301
Bikdeli, Madhavan, Jimenez, COVID-19 and thrombotic or thromboembolic disease: implications for prevention, antithrombotic therapy, and follow-up: JACC state-of-the-art review, J Am Coll Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.031
Bonaventura, Vecchié, Dagna, Tangianu, Abbate et al., Colchicine for COVID-19: targeting NLRP3 inflammasome to blunt hyperinflammation, Inflamm Res, doi:10.1007/s00011-022-01540-y
Choubey, Dehury, Kumar, Medhi, Mondal, Naltrexone a potential therapeutic candidate for COVID-19, J Biomol Struct Dyn, doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1820379
Deftereos, Giannopoulos, Vrachatis, Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019; the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136
Della-Torre, Della-Torre, Kusanovic, Scotti, Ramirez et al., Treating COVID-19 with colchicine in community healthcare setting, Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108490
Diaz, Orlandini, Castellana, Effect of colchicine vs usual care alone on intubation and 28-day mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.41328
Imazio, Brucato, Lazaros, Anti-inflammatory therapies for pericardial diseases in the COVID-19 pandemic: safety and potentiality, J Cardiovasc Med, doi:10.2459/JCM.0000000000001059
Karatza, Ismailos, Karalis, Colchicine for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: efficacy, safety, and model informed dosage regimens, Xenobiotica, doi:10.1080/00498254.2021.1909782
Kow, Lee, Ramachandram, Hasan, Ming et al., The effect of colchicine on mortality outcome and duration of hospital stay in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis of randomized trials, Immun Inflamm Dis, doi:10.1002/iid3.562
Leung, Hui, Kraus, Colchicine--Update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses, Semin Arthritis Rheum, doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.06.013
Lin, Lu, Cao, Li, Hypothesis for potential pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection-a review of immune changes in patients with viral pneumonia, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1746199
Lopes, Bonjorno, Giannini, Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial, RMD Open, doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001455
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Mikolajewska, Fischer, Piechotta, Colchicine for the treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015045
Salehzadeh, Pourfarzi, Ataei, The impact of colchicine on COVID-19 patients: a clinical trial study, Mediterr J Rheumatol, doi:10.31138/mjr.33.2.232
Sandhu, Tieng, Chilimuri, Franchin, A case control study to evaluate the impact of colchicine on patients admitted to the hospital with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol, doi:10.1155/2020/8865954
Scarsi, Piantoni, Colombo, Association between treatment with colchicine and improved survival in a single-centre cohort of adult hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217712
Shah, Kumar, Patel, Myocarditis and pericarditis in patients with COVID-19, Heart Views, doi:10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_154_20
Tardif, Kouz, Waters, Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1912388
Toljan, Vrooman, Low-dose naltrexone (LDN)-review of therapeutic utilization, Med Sci, doi:10.3390/medsci6040082
Vitiello, Ferrara, Colchicine and SARS-CoV-2: management of the hyperinflammatory state, Respir Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106322
Vrachatis, Papathanasiou, Giotaki, Immunologic dysregulation and hypercoagulability as a pathophysiologic background in COVID-19 infection and the immunomodulating role of colchicine, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10215128
Welzel, Wildermuth, Deschner, Benseler, Kuemmerle-Deschner, Colchicine -an effective treatment for children with a clinical diagnosis of autoinflammatory diseases without pathogenic gene variants, Pediatr Rheumatol Online J, doi:10.1186/s12969-021-00588-0
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.60364",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.60364",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gertner",
"given": "Elie",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schullo-Feulner",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knutson",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chrenka",
"given": "Ella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Brien",
"given": "Meghan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Behrendt",
"given": "Christine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Delaney",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-15T19:31:40Z",
"timestamp": 1715801500000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-15T19:31:44Z",
"timestamp": 1715801504000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-16T00:36:43Z",
"timestamp": 1715819803289
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
15
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/240800-colchicine-andor-naltrexone-for-hospitalized-covid-19-patients-not-requiring-high-levels-of-ventilatory-support-coltrexone-a-prospective-randomized-open-label-trial",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta P",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020, 395:1033-4. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1746199",
"article-title": "Hypothesis for potential pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection-a review of immune changes in patients with viral pneumonia",
"author": "Lin L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Lin L, Lu L, Cao W, Li T. Hypothesis for potential pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection-a review of immune changes in patients with viral pneumonia. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020, 9:727-32. 10.1080/22221751.2020.1746199",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, et al.. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med. 2020, 180:934-43. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.031",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and thrombotic or thromboembolic disease: implications for prevention, antithrombotic therapy, and follow-up: JACC state-of-the-art review",
"author": "Bikdeli B",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Cardiol",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Bikdeli B, Madhavan MV, Jimenez D, et al.. COVID-19 and thrombotic or thromboembolic disease: implications for prevention, antithrombotic therapy, and follow-up: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020, 75:2950-73. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.031",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_154_20",
"article-title": "Myocarditis and pericarditis in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Shah JZ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Heart Views",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Shah JZ, Kumar SA, Patel AA. Myocarditis and pericarditis in patients with COVID-19. Heart Views. 2020, 21:209-14. 10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_154_20",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.06.013",
"article-title": "Colchicine--Update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses",
"author": "Leung YY",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Semin Arthritis Rheum",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Leung YY, Yao Hui LL, Kraus VB. Colchicine--Update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45:341-50. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.06.013",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1912388",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction",
"author": "Tardif JC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Tardif JC, Kouz S, Waters DD, et al.. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2019, 381:2497-505. 10.1056/NEJMoa1912388",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2459/JCM.0000000000001059",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory therapies for pericardial diseases in the COVID-19 pandemic: safety and potentiality",
"author": "Imazio M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown)",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Imazio M, Brucato A, Lazaros G, et al.. Anti-inflammatory therapies for pericardial diseases in the COVID-19 pandemic: safety and potentiality. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2020, 21:625-9. 10.2459/JCM.0000000000001059",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12969-021-00588-0",
"article-title": "Colchicine - an effective treatment for children with a clinical diagnosis of autoinflammatory diseases without pathogenic gene variants",
"author": "Welzel T",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Rheumatol Online J",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Welzel T, Wildermuth AL, Deschner N, Benseler SM, Kuemmerle-Deschner JB. Colchicine - an effective treatment for children with a clinical diagnosis of autoinflammatory diseases without pathogenic gene variants. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021, 19:142. 10.1186/s12969-021-00588-0",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106322",
"article-title": "Colchicine and SARS-CoV-2: management of the hyperinflammatory state",
"author": "Vitiello A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Respir Med",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Vitiello A, Ferrara F. Colchicine and SARS-CoV-2: management of the hyperinflammatory state. Respir Med. 2021, 178:106322. 10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106322",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00498254.2021.1909782",
"article-title": "Colchicine for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: efficacy, safety, and model informed dosage regimens",
"author": "Karatza E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Xenobiotica",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Karatza E, Ismailos G, Karalis V. Colchicine for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: efficacy, safety, and model informed dosage regimens. Xenobiotica. 2021, 51:643-56. 10.1080/00498254.2021.1909782",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-022-01540-y",
"article-title": "Colchicine for COVID-19: targeting NLRP3 inflammasome to blunt hyperinflammation",
"author": "Bonaventura A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Res",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Bonaventura A, Vecchié A, Dagna L, Tangianu F, Abbate A, Dentali F. Colchicine for COVID-19: targeting NLRP3 inflammasome to blunt hyperinflammation. Inflamm Res. 2022, 71:293-307. 10.1007/s00011-022-01540-y",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.120.4.1301",
"article-title": "Initial evidence of endothelial cell apoptosis as a mechanism of systemic capillary leak syndrome",
"author": "Assaly R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Assaly R, Olson D, Hammersley J, Fan PS, Liu J, Shapiro JI, Kahaleh MB. Initial evidence of endothelial cell apoptosis as a mechanism of systemic capillary leak syndrome. Chest. 2001, 120:1301-8. 10.1378/chest.120.4.1301",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10215128",
"article-title": "Immunologic dysregulation and hypercoagulability as a pathophysiologic background in COVID-19 infection and the immunomodulating role of colchicine",
"author": "Vrachatis DA",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Vrachatis DA, Papathanasiou KA, Giotaki SG, et al.. Immunologic dysregulation and hypercoagulability as a pathophysiologic background in COVID-19 infection and the immunomodulating role of colchicine. J Clin Med. 2021, 10:5128. 10.3390/jcm10215128",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108490",
"article-title": "Treating COVID-19 with colchicine in community healthcare setting",
"author": "Della-Torre E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Della-Torre E, Della-Torre F, Kusanovic M, Scotti R, Ramirez GA, Dagna L, Tresoldi M. Treating COVID-19 with colchicine in community healthcare setting. Clin Immunol. 2020, 217:108490. 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108490",
"volume": "217",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"article-title": "Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019; the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Deftereos SG",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Deftereos SG, Giannopoulos G, Vrachatis DA, et al.. Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019; the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2020, 3:e2013136. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001455",
"article-title": "Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Lopes MI",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "RMD Open",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Lopes MI, Bonjorno LP, Giannini MC, et al.. Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial. RMD Open. 2021, 7:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001455",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217712",
"article-title": "Association between treatment with colchicine and improved survival in a single-centre cohort of adult hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Scarsi M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ann Rheum Dis",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Scarsi M, Piantoni S, Colombo E, et al.. Association between treatment with colchicine and improved survival in a single-centre cohort of adult hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020, 79:1286-9. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217712",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/8865954",
"article-title": "A case control study to evaluate the impact of colchicine on patients admitted to the hospital with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Sandhu T",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Sandhu T, Tieng A, Chilimuri S, Franchin G. A case control study to evaluate the impact of colchicine on patients admitted to the hospital with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2020, 2020:8865954. 10.1155/2020/8865954",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31138/mjr.33.2.232",
"article-title": "The impact of colchicine on COVID-19 patients: a clinical trial study",
"author": "Salehzadeh F",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mediterr J Rheumatol",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Salehzadeh F, Pourfarzi F, Ataei S. The impact of colchicine on COVID-19 patients: a clinical trial study. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2022, 33:232-6. 10.31138/mjr.33.2.232",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medsci6040082",
"article-title": "Low-dose naltrexone (LDN)-review of therapeutic utilization",
"author": "Toljan K",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med Sci (Basel)",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Toljan K, Vrooman B. Low-dose naltrexone (LDN)-review of therapeutic utilization. Med Sci (Basel). 2018, 6:82. 10.3390/medsci6040082",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1820379",
"article-title": "Naltrexone a potential therapeutic candidate for COVID-19",
"author": "Choubey A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Choubey A, Dehury B, Kumar S, Medhi B, Mondal P. Naltrexone a potential therapeutic candidate for COVID-19. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022, 40:963-70. 10.1080/07391102.2020.1820379",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.41328",
"article-title": "Effect of colchicine vs usual care alone on intubation and 28-day mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Diaz R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Diaz R, Orlandini A, Castellana N, et al.. Effect of colchicine vs usual care alone on intubation and 28-day mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021, 4:e2141328. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.41328",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00435-5",
"article-title": "Colchicine in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Colchicine in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY). a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021, 9:1419-26. 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00435-5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD015045",
"article-title": "Colchicine for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Mikolajewska A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Mikolajewska A, Fischer AL, Piechotta V, et al.. Colchicine for the treatment of COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021, 10:CD015045. 10.1002/14651858.CD015045",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.562",
"article-title": "The effect of colchicine on mortality outcome and duration of hospital stay in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis of randomized trials",
"author": "Kow CS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immun Inflamm Dis",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Kow CS, Lee LH, Ramachandram DS, Hasan SS, Ming LC, Goh HP. The effect of colchicine on mortality outcome and duration of hospital stay in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022, 10:255-64. 10.1002/iid3.562",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 26,
"references-count": 26,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/240800-colchicine-andor-naltrexone-for-hospitalized-covid-19-patients-not-requiring-high-levels-of-ventilatory-support-coltrexone-a-prospective-randomized-open-label-trial"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Colchicine and/or Naltrexone for Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Not Requiring High Levels of Ventilatory Support (COLTREXONE): A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label Trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}
