Risk Factors for Infection and Health Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic in People with Autoimmune Diseases
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.02.03.21251069, Feb 2021
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
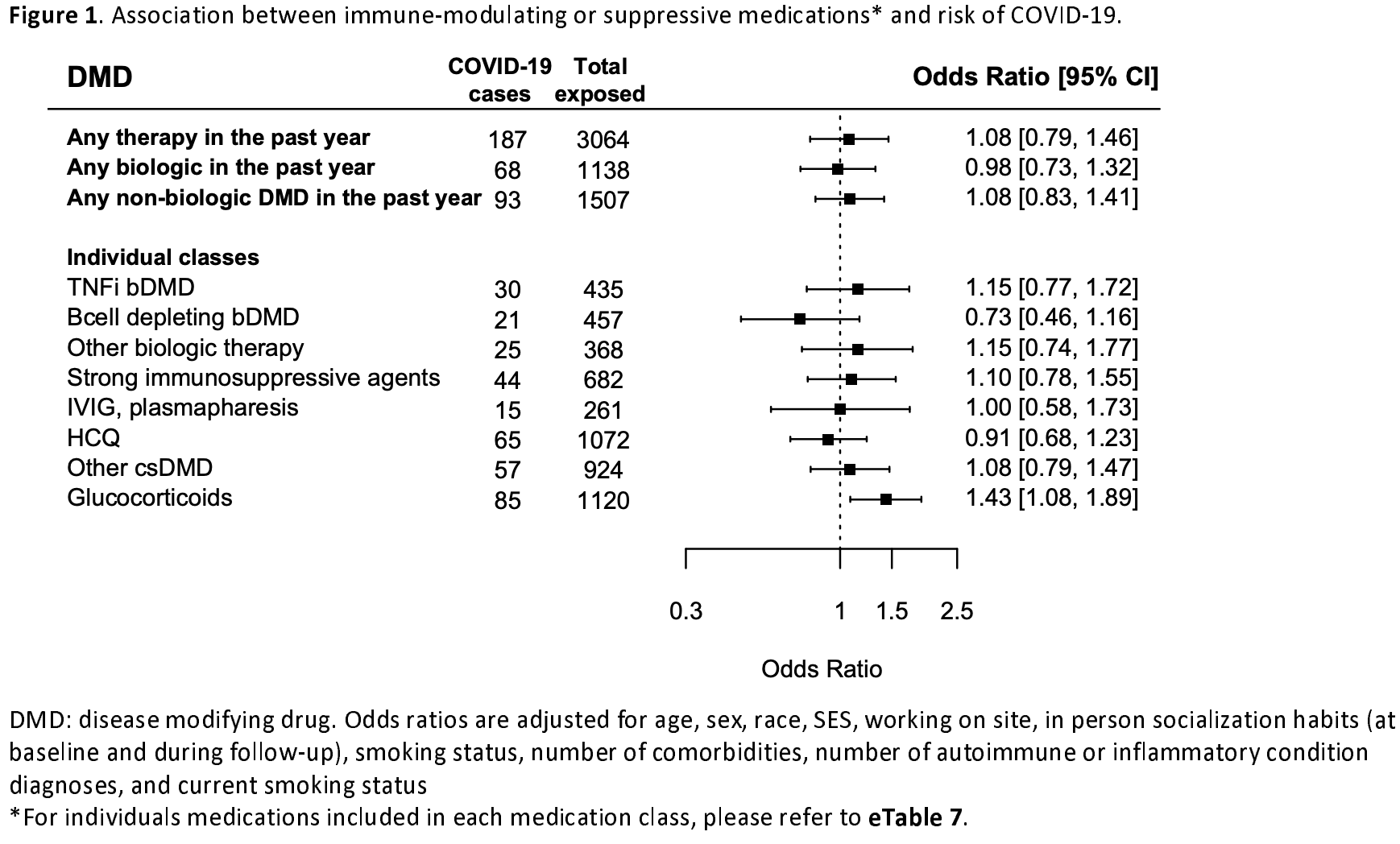
Retrospective 4666 people with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions, showing HCQ adjusted risk of COVID-19 OR 0.91 [0.68-1.23]. Results are not adjusted for the significantly different risk of COVID-19 depending on the type and severity of autoimmune or inflammatory condition.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
not fully adjusting for the baseline risk differences within systemic autoimmune patients.
|
risk of case, 8.5% lower, RR 0.91, p = 0.54, treatment 65 of 1,072 (6.1%), control 200 of 3,594 (5.6%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Fitzgerald et al., 5 Feb 2021, retrospective, USA, preprint, 34 authors.
RISK FACTORS FOR INFECTION AND HEALTH IMPACTS OF THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC IN PEOPLE WITH AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
doi:10.1101/2021.02.03.21251069
Background People with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions who take immunomodulatory/suppressive medications may have a higher risk of novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Chronic disease care has also changed for many patients, with uncertain downstream consequences.
Objective Assess whether COVID-19 risk is higher among those on immunomodulating or suppressive agents and characterize pandemic-associated changes to care.
Design Longitudinal registry study Participants 4666 individuals with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions followed by specialists in neurology, rheumatology, cardiology, pulmonology or gastroenterology at Johns Hopkins Measurements Periodic surveys querying comorbidities, disease-modifying medications, exposures, COVID-19 testing and outcomes, social behaviors, and disruptions to healthcare
Results A total of 265 (5.6%) developed COVID-19 over 9 months of follow-up (April-December 2020). Patient characteristics (age, race, comorbidity, medication exposure) were associated with differences in social distancing behaviors during the pandemic. Glucocorticoid exposure was associated with higher odds of COVID-19 in multivariable models incorporating behavior and other potential confounders (OR: 1.43;
Author disclosures Dr. Fitzgerald has nothing to disclose.
References
Akiyama, Hamdeh, Micic, Sakuraba, Prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218946
Bar-Or, Effect of ocrelizumab on vaccine responses in patients with multiple sclerosis: The VELOCE study, Neurology
Bartlett, Reliability and Validity of Selected PROMIS Measures in People with Rheumatoid Arthritis, PLOS ONE
Bernardinello, Prevalence of Depression in Sarcoidosis: a comparison with asthmatic and healthy controls, European Respiratory Journal
Bingham, Immunization responses in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with rituximab: Results from a controlled clinical trial, Arthritis & Rheumatism
Core, R: A language and environment for statistical computing
Dixon, Immediate and delayed impact of oral glucocorticoid therapy on risk of serious infection in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a nested case-control analysis, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
Doran, Crowson, Pond, O'fallon, Gabriel, Frequency of infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls: a population-based study, Arthritis Rheum
Emmi, SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with systemic autoimmune diseases, Autoimmun Rev
Ethgen, Esteves, De, Bruyere, Reginster, What do we know about the safety of corticosteroids in rheumatoid arthritis?, Current Medical Research and Opinion
Fardet, Petersen, Nazareth, Common Infections in Patients Prescribed Systemic Glucocorticoids in Primary Care: A Population-Based Cohort Study, PLoS Med
Feinstein, Magalhaes, Richard, Audet, Moore, The link between multiple sclerosis and depression, Nature Reviews Neurology
Kind, Neighborhood socioeconomic disadvantage and 30-day rehospitalization: a retrospective cohort study, Ann. Intern. Med
Koçer, Cognition, depression, fatigue, and quality of life in primary Sjögren's syndrome: correlations, Brain Behav
Louapre, Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Multiple Sclerosis, JAMA Neurol
Luna, Infection Risks Among Patients With Multiple Sclerosis Treated With Fingolimod, Natalizumab, Rituximab, and Injectable Therapies, JAMA Neurol
Miller, Validating Neuro-QoL Short Forms and Targeted Scales with Persons who have Multiple Sclerosis, Mult Scler
Monti, Clinical course of COVID-19 in a series of patients with chronic arthritis treated with immunosuppressive targeted therapies, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
Moss, Multiple sclerosis management during the COVID-19 pandemic, Mult Scler, doi:10.1177/1352458520948231
Peterson, The multifaceted impact of anxiety and depression on patients with rheumatoid arthritis, BMC Rheumatology
Pilkonis, Validation of the depression item bank from the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS®) in a three-month observational study, J Psychiatr Res
Schalet, Clinical validity of PROMIS Depression, Anxiety, and Anger across diverse clinical samples, J Clin Epidemiol
Singh, Area deprivation and widening inequalities in US mortality, 1969-1998, Am J Public Health
Slimano, Cancer, immune suppression and Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Need to manage drug safety (French Society for Oncology Pharmacy [SFPO] guidelines), Cancer Treatment Reviews
Sormani, An Italian programme for COVID-19 infection in multiple sclerosis, The Lancet Neurology
Sormani, Disease modifying therapies and Covid-19 severity in Multiple Sclerosis, Ann Neurol, doi:10.1002/ana.26028
Wijnands, Disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis and infection risk: a cohort study, J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry
Zabalza, COVID-19 in multiple sclerosis patients: susceptibility, severity risk factors and serological response, European Journal of Neurology n/a
Zen, SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases in northeast Italy: A cross-sectional study on 916 patients, Journal of Autoimmunity
Zhang, The Influence of Depression on Quality of Life in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Inflamm Bowel Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.02.03.21251069",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.03.21251069",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>People with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions who take immunomodulatory/suppressive medications may have a higher risk of novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Chronic disease care has also changed for many patients, with uncertain downstream consequences.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>Assess whether COVID-19 risk is higher among those on immunomodulating or suppressive agents and characterize pandemic-associated changes to care.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design</jats:title><jats:p>Longitudinal registry study</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Participants</jats:title><jats:p>4666 individuals with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions followed by specialists in neurology, rheumatology, cardiology, pulmonology or gastroenterology at Johns Hopkins</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Measurements</jats:title><jats:p>Periodic surveys querying comorbidities, disease-modifying medications, exposures, COVID-19 testing and outcomes, social behaviors, and disruptions to healthcare</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 265 (5.6%) developed COVID-19 over 9 months of follow-up (April-December 2020). Patient characteristics (age, race, comorbidity, medication exposure) were associated with differences in social distancing behaviors during the pandemic. Glucocorticoid exposure was associated with higher odds of COVID-19 in multivariable models incorporating behavior and other potential confounders (OR: 1.43; 95%CI: 1.08, 1.89). Other medication classes were not associated with COVID-19 risk. Diabetes (OR: 1.72; 95%CI: 1.08, 2.73), cardiovascular disease (OR: 1.68; 95%CI: 1.24, 2.28), and chronic kidney disease (OR: 1.76; 95%CI: 1.04, 2.97) were each associated with higher odds of COVID-19. Pandemic-related disruption to care was common. Of the 2156 reporting pre-pandemic utilization of infusion, mental health or rehabilitative services, 975 (45.2%) reported disruptions. Individuals experiencing changes to employment or income were at highest odds of care disruption.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Limitations</jats:title><jats:p>Results may not be generalizable to all patients with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions. Information was self-reported.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Exposure to glucocorticoids may increase risk of COVID-19 in people with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions. Disruption to healthcare and related services was common. Those with pandemic-related reduced income may be most vulnerable to care disruptions.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3137-0322",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fitzgerald",
"given": "Kathryn C.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mecoli",
"given": "Christopher A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Douglas",
"given": "Morgan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "Samantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aravidis",
"given": "Berna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Albayda",
"given": "Jemima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sotirchos",
"given": "Elias S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoke",
"given": "Ahmet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orbai",
"given": "Ana-Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petri",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christopher-Stine",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baer",
"given": "Alan N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paik",
"given": "Julie J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adler",
"given": "Brittany L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tiniakou",
"given": "Eleni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Timlin",
"given": "Homa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhargava",
"given": "Pavan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newsome",
"given": "Scott D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venkatesan",
"given": "Arun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhry",
"given": "Vinay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lloyd",
"given": "Thomas E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pardo",
"given": "Carlos A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stern",
"given": "Barney J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lazarev",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Truta",
"given": "Brindusa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saidha",
"given": "Shiv",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Edward S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharp",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilotra",
"given": "Nisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kasper",
"given": "Edward K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gelber",
"given": "Allan C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bingham",
"given": "Clifton O.",
"sequence": "additional",
"suffix": "III"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Ami A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mowry",
"given": "Ellen M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-07T10:44:09Z",
"timestamp": 1612694649000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-09T19:07:19Z",
"timestamp": 1612897639000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-05T00:28:12Z",
"timestamp": 1675556892557
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.02.03.21251069",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30147-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.1",
"unstructured": "Sormani, M. P. An Italian programme for COVID-19 infection in multiple sclerosis. The Lancet Neurology 0, (2020)."
},
{
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.2",
"unstructured": "Zabalza, A. et al. COVID-19 in multiple sclerosis patients: susceptibility, severity risk factors and serological response. European Journal of Neurology n/a,."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.10524",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jnnp-2017-317493",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217424",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102063",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.6",
"unstructured": "Slimano, F. et al. Cancer, immune suppression and Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Need to manage drug safety (French Society for Oncology Pharmacy [SFPO] guidelines). Cancer Treatment Reviews 88, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ana.26028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102502",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases in northeast Italy: A cross-sectional study on 916 patients",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102502",
"journal-title": "Journal of Autoimmunity",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.8",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1352458520948231",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2105/AJPH.93.7.1137",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M13-2946",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.05.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.08.036",
"article-title": "Clinical validity of PROMIS Depression, Anxiety, and Anger across diverse clinical samples",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.13",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0138543",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1352458515599450",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.15"
},
{
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.16",
"unstructured": "R Core Team (2019). R: A language and environment for statistical computing."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1002024",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.17",
"unstructured": "Fardet, L. , Petersen, I. & Nazareth, I. Common Infections in Patients Prescribed Systemic Glucocorticoids in Primary Care: A Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS Med 13, (2016)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3365",
"article-title": "Infection Risks Among Patients With Multiple Sclerosis Treated With Fingolimod, Natalizumab, Rituximab, and Injectable Therapies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.18",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200702",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1185/03007995.2013.818531",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.2581",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Multiple Sclerosis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1079",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.21",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218946",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/WNL.0000000000010380",
"article-title": "Effect of ocrelizumab on vaccine responses in patients with multiple sclerosis: The VELOCE study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1999",
"journal-title": "Neurology",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.24",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.25034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.congress-2019.PA1952",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.26",
"unstructured": "Bernardinello, N. et al. Prevalence of Depression in Sarcoidosis: a comparison with asthmatic and healthy controls. European Respiratory Journal 54, (2019)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MIB.0b013e318281f395",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/brb3.586",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.28",
"unstructured": "Koçer, B. et al. Cognition, depression, fatigue, and quality of life in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: correlations. Brain Behav 6, (2016)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrneurol.2014.139",
"article-title": "The link between multiple sclerosis and depression",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Neurology",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.29",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41927-019-0092-5",
"article-title": "The multifaceted impact of anxiety and depression on patients with rheumatoid arthritis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "BMC Rheumatology",
"key": "2021020805050885000_2021.02.03.21251069v1.30",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.02.03.21251069"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "RISK FACTORS FOR INFECTION AND HEALTH IMPACTS OF THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC IN PEOPLE WITH AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES",
"type": "posted-content"
}
