Association of vitamin D deficiency with COVID-19 severity and mortality in Iranian people: a prospective observational study
et al., Acute and Critical Care, doi:10.4266/acc.2021.00605, Nov 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 248 hospitalized COVID+ patients in Iran with vitamin D levels measured in the previous year and again at admission, showing vitamin D status associated with severity and mortality.
This is the 109th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
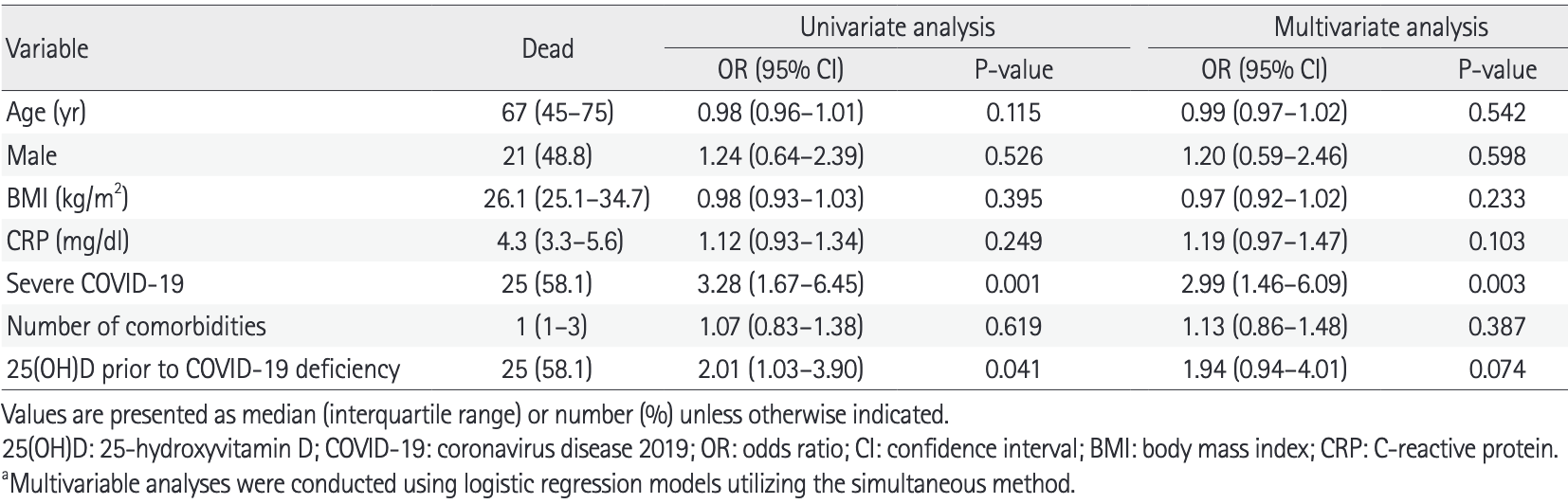
risk of death, 42.0% lower, RR 0.58, p = 0.07, high D levels 18 of 139 (12.9%), low D levels 25 of 109 (22.9%), NNT 10, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, vitamin D measured prior to COVID-19, multivariate.
|
|
risk of death, 51.1% lower, RR 0.49, p = 0.02, high D levels 13 of 115 (11.3%), low D levels 30 of 133 (22.6%), NNT 8.9, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, vitamin D measured on admission, multivariate.
|
|
risk of severe case, 37.9% lower, RR 0.62, p = 0.007, high D levels 38 of 139 (27.3%), low D levels 48 of 109 (44.0%), NNT 6.0, vitamin D measured prior to COVID-19.
|
|
risk of severe case, 34.8% lower, RR 0.65, p = 0.02, high D levels 31 of 115 (27.0%), low D levels 55 of 133 (41.4%), NNT 6.9, vitamin D measured on admission.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Fatemi et al., 30 Nov 2021, prospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period 1 October, 2020 - 31 May, 2021.
Association of vitamin D deficiency with COVID-19 severity and mortality in Iranian people: a prospective observational study
Acute and Critical Care, doi:10.4266/acc.2021.00605
Background: As the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to escalate, it is important to identify the prognostic factors related to increased mortality and disease severity. To assess the possible associations of vitamin D level with disease severity and survival, we studied 248 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in a single center in a prospective observational study from October 2020 to May 2021 in Tehran, Iran. Methods: Patients who had a record of their 25-hydroxyvitamin D level measured in the previous year before testing positive with COVID-19 were included. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level was measured upon admission in COVID-19 patients. The associations between clinical outcomes of patients and 25-hydroxyvitamin D level were assessed by adjusting for potential confounders and estimating a multivariate logistic regression model.
Results: The median (interquartile range) age of patients was 60 years (44-74 years), and 53% were male. The median serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level prior to admission decreased with increasing COVID-19 severity (P=0.009). Similar findings were obtained when comparing median serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D on admission between moderate and severe patients (P=0.014). A univariate logistic regression model showed that vitamin D deficiency prior to COVID-19 was associated with a significant increase in the odds of mortality (odds ratio, 2.01; P=0.041). The multivariate Cox model showed that vitamin D deficiency on admission was associated with a significant increase in risk for mortality (hazard ratio, 2.35; P=0.019). Conclusions: Based on our results, it is likely that deficient vitamin D status is associated with increased mortality in COVID-19 patients. Thus, evaluating vitamin D level in COVID-19 patients is warranted.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Conceptualization: AF, SHA, GE. Data curation: GE, SM. Formal analysis: SHA, GE, MN. Funding acquisition: AF, SHA, GE, MN. Methodology: AF, SHA, GE, SM. Project administration: GE. Visualization: AF, MN. Writing-original draft: AF, SHA, GE. Writing-review & editing: all authors.
References
Agier, Efenberger, Brzezińska-Błaszczyk, Cathelicidin impact on inflammatory cells, Cent Eur J Immunol
Aslan, Aslan, Özdemir, Letter to the editor: is vitamin d one of the key elements in COVID-19 days?, J Nutr Health Aging, doi:10.1007/s12603-020-1517-y
Bhatraju, Ghassemieh, Nichols, Kim, Jerome et al., COVID-19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle Region: case series, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2004500
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072097
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, Nicolò et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are low-Acute and, Critical Care
Fatemi, Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 er in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Herr, Shaykhiev, Bals, The role of cathelicidin and defensins in pulmonary inflammatory diseases, Expert Opin Biol Ther, doi:10.1517/14712598.7.9.1449
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Gordon, Hanley et al., Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
Holick, The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention, Rev Endocr Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-017-9424-1
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Infante, Buoso, Pieri, Lupisella, Nuccetelli et al., Low vitamin d status at admission as a risk factor for poor survival in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an Italian retrospective study, J Am Coll Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2021.1877580
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z
Liu, Sun, Wang, Zhang, Zhao et al., Low vitamin D status is associated with coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077
Luo, Liao, Shen, Li, Cheng, Vitamin D deficiency is associated with COVID-19 Incidence and disease severity in Chinese people, doi:10.1093/jn/nxaa332
Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Rev Med Virol
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da Mota, Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Pinheiro, Fabbri, Infante, Cytokine storm modulation in COVID-19: a proposed role for vitamin D and DPP-4 inhibitor combination therapy (VIDPP-4i), Immunotherapy, doi:10.2217/imt-2020-0349
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger, Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Tehrani, Khabiri, Moradi, Mosavat, Khabiri, Evaluation of vitamin D levels in COVID-19 patients referred to Labafinejad hospital in Tehran and its relationship with disease severity and mortality, Clin Nutr ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.01.014
Weiss, Murdoch, Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID-19, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30633-4
Worldometer, COVID-19 corona virus pandemic
Yisak, Ewunetei, Kefale, Mamuye, Teshome et al., Effects of vitamin D on COVID-19 infection and prognosis: a systematic review, Risk Manag Healthc Policy, doi:10.2147/rmhp.s291584
Zdrenghea, Makrinioti, Bagacean, Bush, Johnston et al., Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.1909
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4266/acc.2021.00605",
"ISSN": [
"2586-6052",
"2586-6060"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4266/acc.2021.00605",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: As the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to escalate, it is important to identify the prognostic factors related to increased mortality and disease severity. To assess the possible associations of vitamin D level with disease severity and survival, we studied 248 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in a single center in a prospective observational study from October 2020 to May 2021 in Tehran, Iran. Methods: Patients who had a record of their 25-hydroxyvitamin D level measured in the previous year before testing positive with COVID-19 were included. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level was measured upon admission in COVID-19 patients. The associations between clinical outcomes of patients and 25-hydroxyvitamin D level were assessed by adjusting for potential confounders and estimating a multivariate logistic regression model. Results: The median (interquartile range) age of patients was 60 years (44–74 years), and 53% were male. The median serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level prior to admission decreased with increasing COVID-19 severity (P=0.009). Similar findings were obtained when comparing median serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D on admission between moderate and severe patients (P=0.014). A univariate logistic regression model showed that vitamin D deficiency prior to COVID-19 was associated with a significant increase in the odds of mortality (odds ratio, 2.01; P=0.041). The Multivariate Cox model showed that vitamin D deficiency on admission was associated with a significant increase in risk for mortality (hazard ratio, 2.35; P=0.019).Conclusions: Based on our results, it is likely that deficient vitamin D status is associated with increased mortality in COVID-19 patients. Thus, evaluating vitamin D level in COVID-19 patients is warranted.</jats:p>",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-05-12"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-08-06"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published online",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-11-29"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Print publication",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2021-11-30"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0671-7611",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Fatemi",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6656-3875",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ardehali",
"given": "Seyed Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8960-5123",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Eslamian",
"given": "Ghazaleh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1971-8982",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Noormohammadi",
"given": "Morvarid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1705-3884",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Malek",
"given": "Shirin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Acute and Critical Care"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"accjournal.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-29T07:30:31Z",
"timestamp": 1638171031000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-30T18:14:23Z",
"timestamp": 1638296063000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T06:10:41Z",
"timestamp": 1638339041541
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2586-6052"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2586-6060"
}
],
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638144000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://accjournal.org/upload/pdf/acc-2021-00605.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://accjournal.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.4266/acc.2021.00605",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://accjournal.org/upload/pdf/acc-2021-00605.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2790",
"original-title": [],
"page": "300-307",
"prefix": "10.4266",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "The Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"volume-title": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30633-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-017-9424-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1909",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxaa332",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12603-020-1517-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1517/14712598.7.9.1449",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"author": "Agier",
"first-page": "225",
"key": "ref9",
"volume-title": "Cathelicidin impact on inflammatory cells",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/rmhp.s291584",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.077",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"key": "ref13",
"volume-title": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2004500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"author": "D'Avolio",
"first-page": "1359",
"key": "ref17",
"volume-title": "25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.01.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2021.1877580",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/imt-2020-0349",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"author": "Malek Mahdavi",
"first-page": "e2119",
"key": "ref25",
"volume-title": "A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Acute Crit Care"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Critical Care and Intensive Care Medicine",
"Critical Care"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Association of vitamin D deficiency with COVID-19 severity and mortality in Iranian people: a prospective observational study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4266/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "36"
}
