Vitamin D supplementation and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from the outbreak area of Lombardy, Italy
et al., Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055, Nov 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
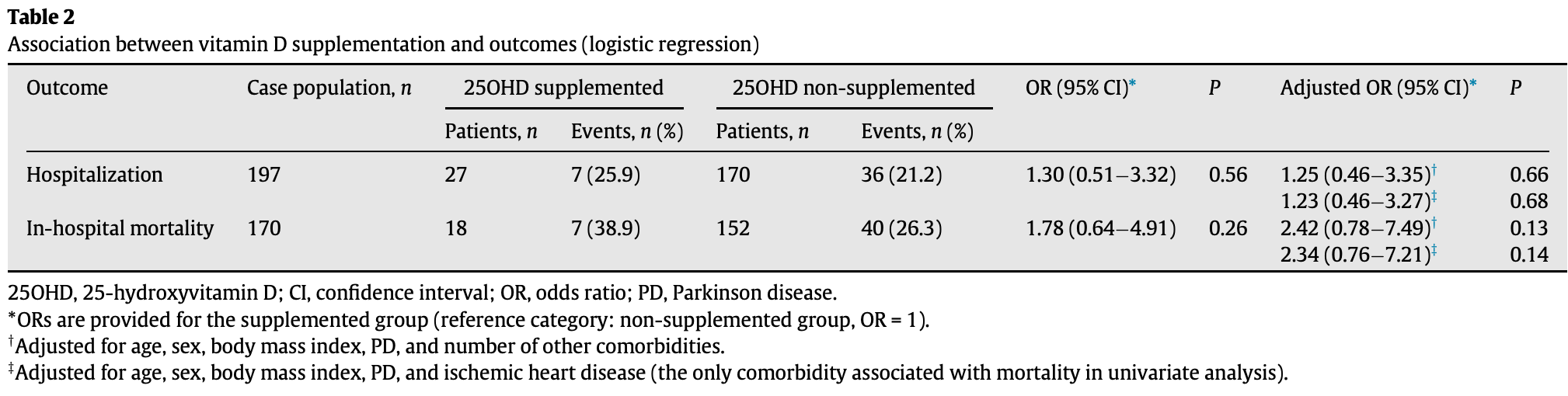
Retrospective 105 Parkinson's disease patients, 92 caregivers, and 127 hospital inpatients, showing higher, but not statistically significant mortality and hospitalization with treatment. Supplementation was defined as ≥25,000IU/month for at least 3 months.
This is the 10th of 136 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of death, 73.0% higher, RR 1.73, p = 0.14, treatment 7 of 18 (38.9%), control 40 of 152 (26.3%), odds ratio converted to relative risk, ≥25,000IU/month for at least 3 months.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 17.3% higher, RR 1.17, p = 0.68, treatment 7 of 27 (25.9%), control 36 of 170 (21.2%), odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Cereda et al., 11 Nov 2020, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, mean age 68.8, 7 authors, dosage varies.
Vitamin D supplementation and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from the outbreak area of Lombardy, Italy
Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
References
Abassi, Knaney, Karram, Heyman, The lung macrophage in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a friend or a foe?, Front Immunol
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J Infect Public Health
Cereda, Bogliolo, De Stefano, Caccialanza, A brief discussion of the benefit and mechanism of vitamin D supplementation on coronavirus disease
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, Nicol O et al., 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Fasano, Cereda, Barichella, Cassani, Ferri et al., COVID-19 in Parkinson's disease patients Living in Lombardy, Italy, Mov Disord
Ghavideldarestani, Honardoost, Khamseh, Role of Vitamin D in pathogenesis and severity of COVID-19 infection, doi:10.20944/pre-prints202004.0355
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Pazoki, Kafan et al., Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS One
Marik, Kory, Varon, Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Med Drug Discov
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw Open
Pizzini, Aichner, Sahanic, B€ Ohm, Egger et al., Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19-A prospective analysis from the CovILD registry, Nutrients
Reijven, Soeters, Vitamin D: a magic bullet or a myth?, Clin Nutr
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055",
"ISSN": [
"0899-9007"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055",
"alternative-id": [
"S0899900720303385"
],
"article-number": "111055",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Vitamin D supplementation and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from the outbreak area of Lombardy, Italy"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nutrition"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0747-1951",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cereda",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1661-0482",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bogliolo",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lobascio",
"given": "Federica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barichella",
"given": "Michela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zecchinelli",
"given": "Anna Lena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pezzoli",
"given": "Gianni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9379-3569",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Caccialanza",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-11T21:03:47Z",
"timestamp": 1605128627000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-29T10:16:06Z",
"timestamp": 1611915366000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100007365",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-13T07:28:08Z",
"timestamp": 1710314888198
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 51,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1612137600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900720303385?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900720303385?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "111055",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?",
"author": "Marik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Med Drug Discov",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0001",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0002",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0003",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mds.28176",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in Parkinson's disease patients Living in Lombardy, Italy",
"author": "Fasano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1089",
"journal-title": "Mov Disord",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0004",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"article-title": "25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "D'Avolio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1359",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0005",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0006",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2019.12.028",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: a magic bullet or a myth?",
"author": "Reijven",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2663",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0007",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCO.0000000000000701",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0008",
"unstructured": "Cereda E, Bogliolo L, de Stefano L, Caccialanza R. A brief discussion of the benefit and mechanism of vitamin D supplementation on coronavirus disease 2019 [e-pub ahead of print]. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000701, accessed Month DD, YYYY."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0009",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202004.0355.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0010",
"unstructured": "Ghavideldarestani M, Honardoost M, Khamseh ME. Role of Vitamin D in pathogenesis and severity of COVID-19 infection. Available at: doi:10.20944/preprints202004.0355.v1. Accessed Month DD, YYYY."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01312",
"article-title": "The lung macrophage in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a friend or a foe?",
"author": "Abassi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1312",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0011",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239799",
"article-title": "Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0012",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092775",
"article-title": "Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19—A prospective analysis from the CovILD registry",
"author": "Pizzini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E2775",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0013",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111055_bib0014",
"unstructured": "LARN IV revisione: livelli di assunzione di riferimento di nutrienti ed energia. Available at: https://sinu.it/larn/. Accessed Month 10, 2020."
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0899900720303385"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D supplementation and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from the outbreak area of Lombardy, Italy",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "82"
}
