Melatonin reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 20 studies
, Dec 2025
Melatonin for COVID-19
11th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000000011 from 20 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
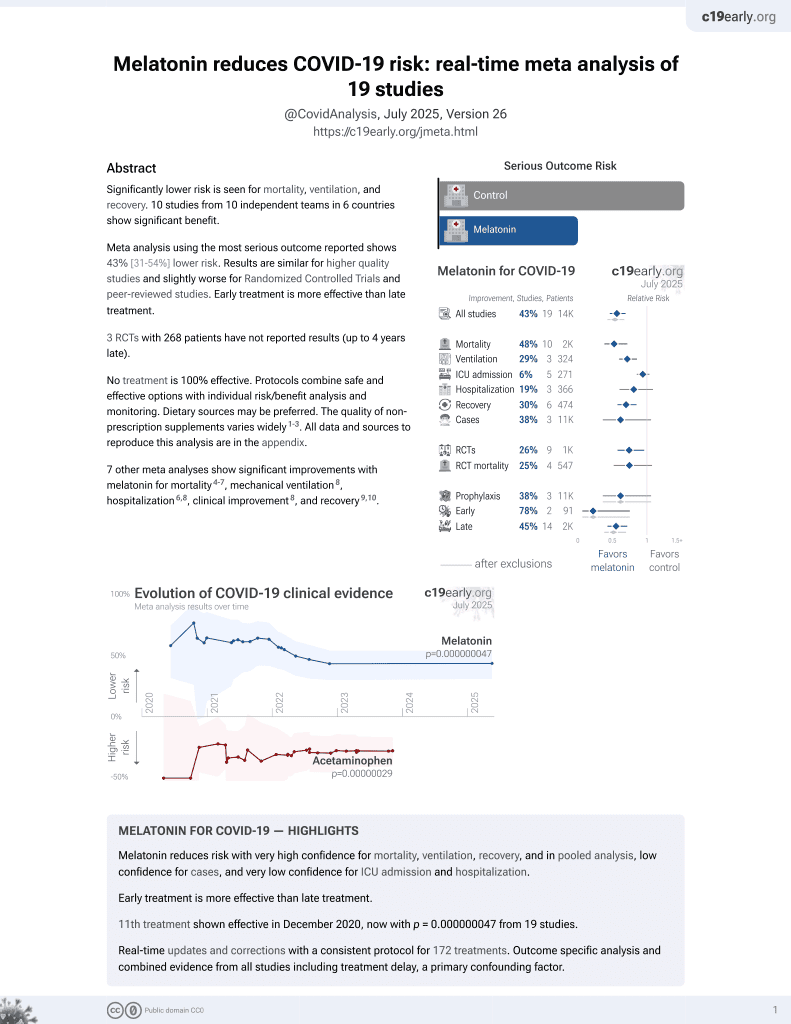
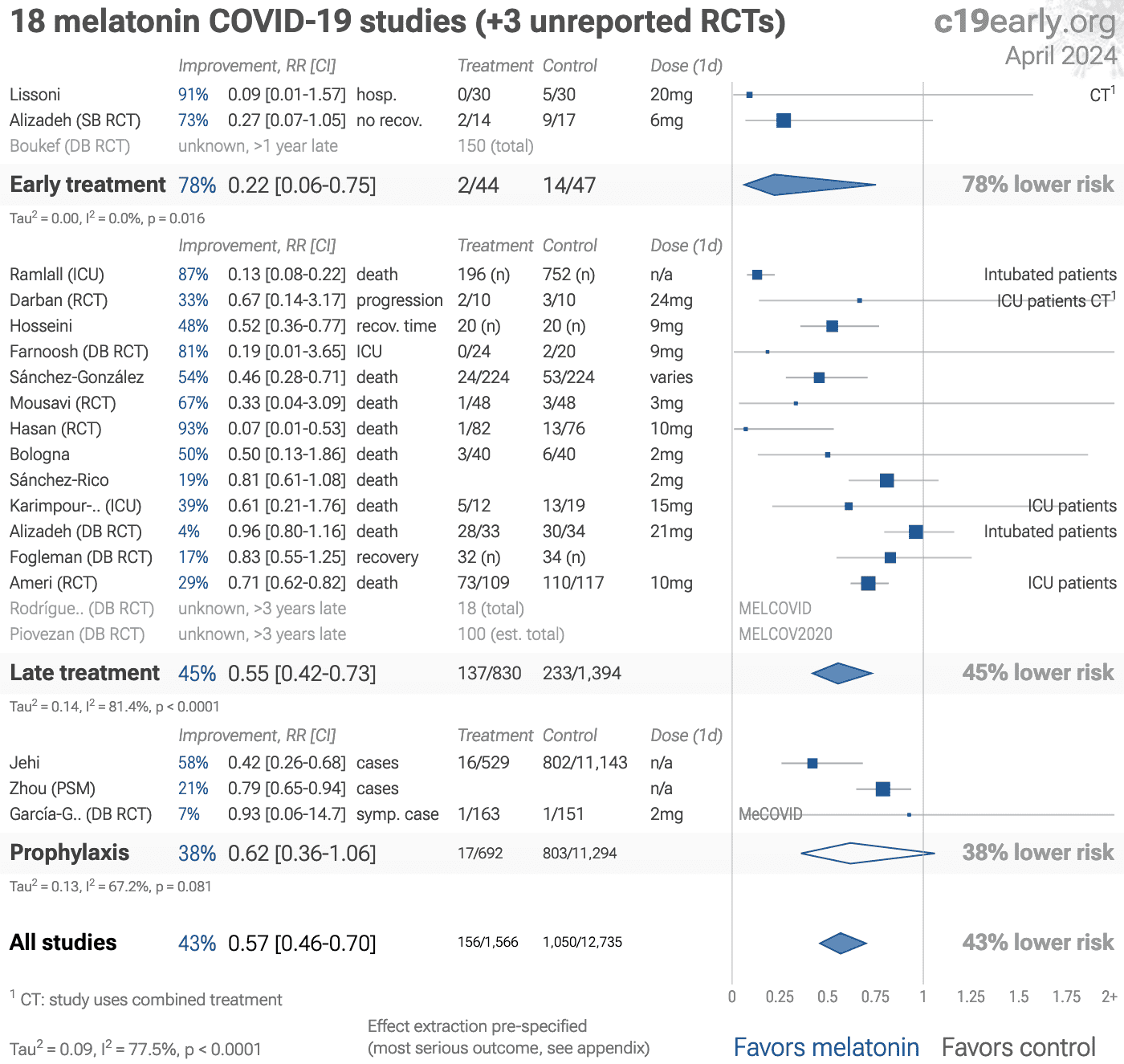
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ventilation, and recovery. 11 studies from 11 independent teams in 6 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 43% [31‑53%] lower risk. Results are similar for higher quality studies and slightly worse for Randomized Controlled Trials and peer-reviewed studies. Early treatment is more effective than late treatment.
Control Melatonin
3 RCTs with 268 patients have not reported results (up to 5 years late).
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Dietary sources may be preferred. The quality of non-prescription supplements varies widely1-3. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
7 other meta analyses show significant improvements with melatonin for mortality4-7, mechanical ventilation8, hospitalization6,8, clinical improvement8, and recovery9,10.
7 meta analyses show significant improvements with melatonin for mortality1-4,
mechanical ventilation5,
hospitalization3,5,
improvement5, and
recovery6,7.
1.
Pilia et al., Does melatonin reduce mortality in COVID-19?, Annals of Medicine and Surgery, doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103817.
2.
Tóth et al., Melatonin as adjuvant treatment in COVID-19 patients. A meta-analysis of randomized and propensity matched studies, Signa Vitae, doi:10.22514/sv.2023.076.
3.
Amin et al., Role of Melatonin in Management of COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Microbes, Infection and Chemotherapy, doi:10.54034/mic.e1982.
4.
Qin et al., Benefits of melatonin on mortality in severe-to-critical COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Clinics, doi:10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100638.
5.
Taha et al., Safety and efficacy of melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in COVID-19 patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Advances in Medical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.advms.2023.09.007.
Covid Analysis et al., Dec 2025, preprint, 1 author.