Interest of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Reducing the Occurrence of COVID-19: A Case-Control Study
et al., Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0016.v1, May 2020
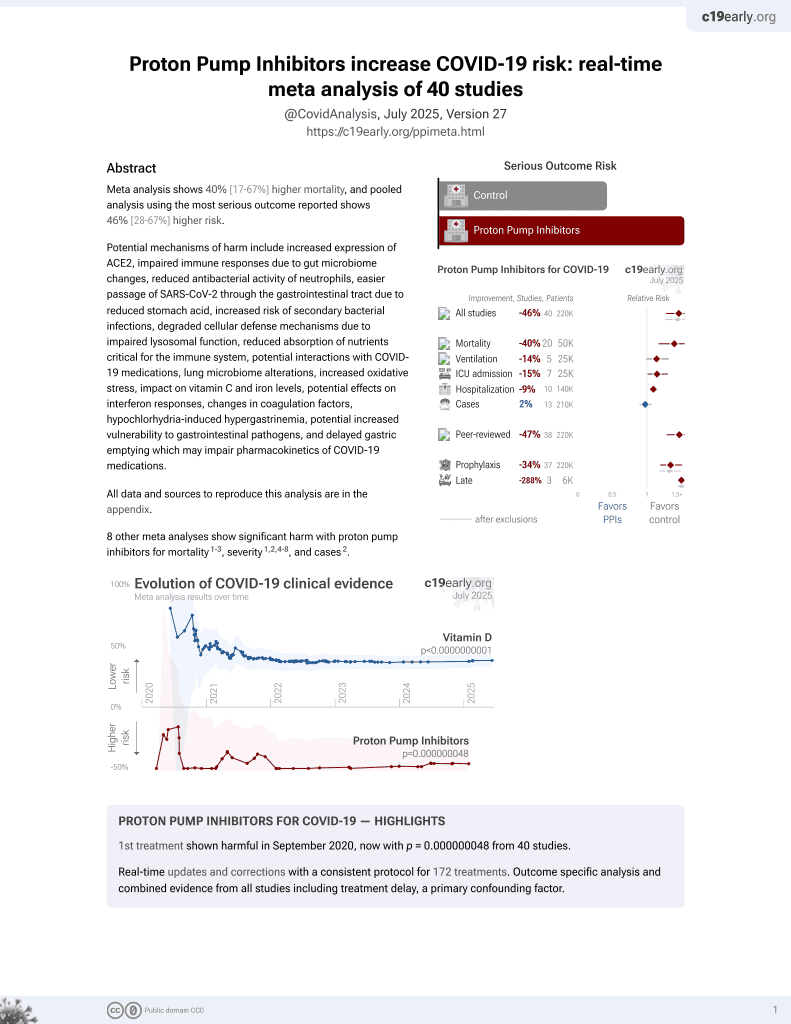
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 179 elderly patients in France, showing higher risk of COVID-19 cases with acetaminophen use, without statistical significance.
Study covers proton pump inhibitors and acetaminophen.
|
risk of case, 56.2% lower, OR 0.44, p = 0.005, treatment 63, control 116, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Blanc et al., 2 May 2020, retrospective, France, preprint, mean age 84.1, 22 authors, study period 2 March, 2020 - 8 April, 2020.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202005.0016.v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.20944/preprints202005.0016.v1",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: COVID-19 is a disease of the elderly as 95% of deaths related to COVID-19 occur in people over 60 years of age. Despite the urgent need for a preventive treatment there are currently no serious leads, other than the vaccination. Objective: To find a preventive treatment of COVID-19 in elderly patients. Design: Retrospective case-control study. Setting: Robertsau Geriatric Hospital of the University Hospitals of Strasbourg, France. Patients: 179 elderly patients who had been in contact with the SARS-CoV-2, of whom 89 had tested RT-PCR-positive (COVID-pos) for the virus and 90 had tested RT-PCR-negative (COVID-neg). Measurements: Treatments within 15 days prior to RT-PCR (including antihypertensive drugs, antipsychotics, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), paracetamol, anticoagulant, oral antidiabetics (OADs), corticosteroids, immunosuppressants), comorbidities, symptoms, laboratory values, and clinical outcome were all collected using the electronic patient record. Results: COVID-pos patients more frequently had a history of diabetes (P=.016) and alcoholism (P=.023), a lower leukocyte count (P=.014) and a higher mortality rate&ndash; 29.2% versus 14.4% &ndash; (P=.014) when compared to COVID-neg patients. Patients on PPIs were 2.3 times less likely (odds ratio [OR] = 0.4381, 95% confidence interval [CI] [0.2331, 0.8175], P=.0053) to develop COVID-19 infection, compared to those not on PPIs. No other treatment decreased or increased this risk. COVID-19 patients on antipsychotics (P=.0013) and OADs (P=.0166) were less likely to die. Limitations: retrospective study. Conclusion: PPIs treatment lowered the risk of development of COVID-19 infection, and antipsychotics and OADs decreased the risk of mortality in geriatric patients. If further studies confirm this finding, PPIs could be used preventatively in the elderly in this pandemic context. Moreover, OADS and antipsychotics should be tested in clinical trials.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
4,
28
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blanc",
"given": "Frederic",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waechter",
"given": "Cedric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vogel",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schorr",
"given": "Benoît",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Demuynck",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin-Hunyadi",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meyer",
"given": "Maxence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mutelica",
"given": "Denata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bougaa",
"given": "Nadjiba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fafi-Kremer",
"given": "Samira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calabrese",
"given": "Lidia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schmitt",
"given": "Elise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imperiale",
"given": "Delphine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jehl",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boussuge",
"given": "Alexandre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suna",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weill",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matzinger",
"given": "Alexia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muller",
"given": "Candice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karcher",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaltenbach",
"given": "Georges",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sauleau",
"given": "Erik",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-04T16:19:38Z",
"timestamp": 1588609178000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-04T16:20:08Z",
"timestamp": 1588609208000
},
"group-title": "MEDICINE & PHARMACOLOGY",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-14T07:32:23Z",
"timestamp": 1657783943788
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
2
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1588377600000
}
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
2
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.20944",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202005.0016/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Interest of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Reducing the Occurrence of COVID-19: A Case-Control Study",
"type": "posted-content"
}