The association between vitamin D3 deficiency and acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients
et al., Journal of Renal Injury Prevention, doi:10.34172/jrip.2022.32126, Jan 2023
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
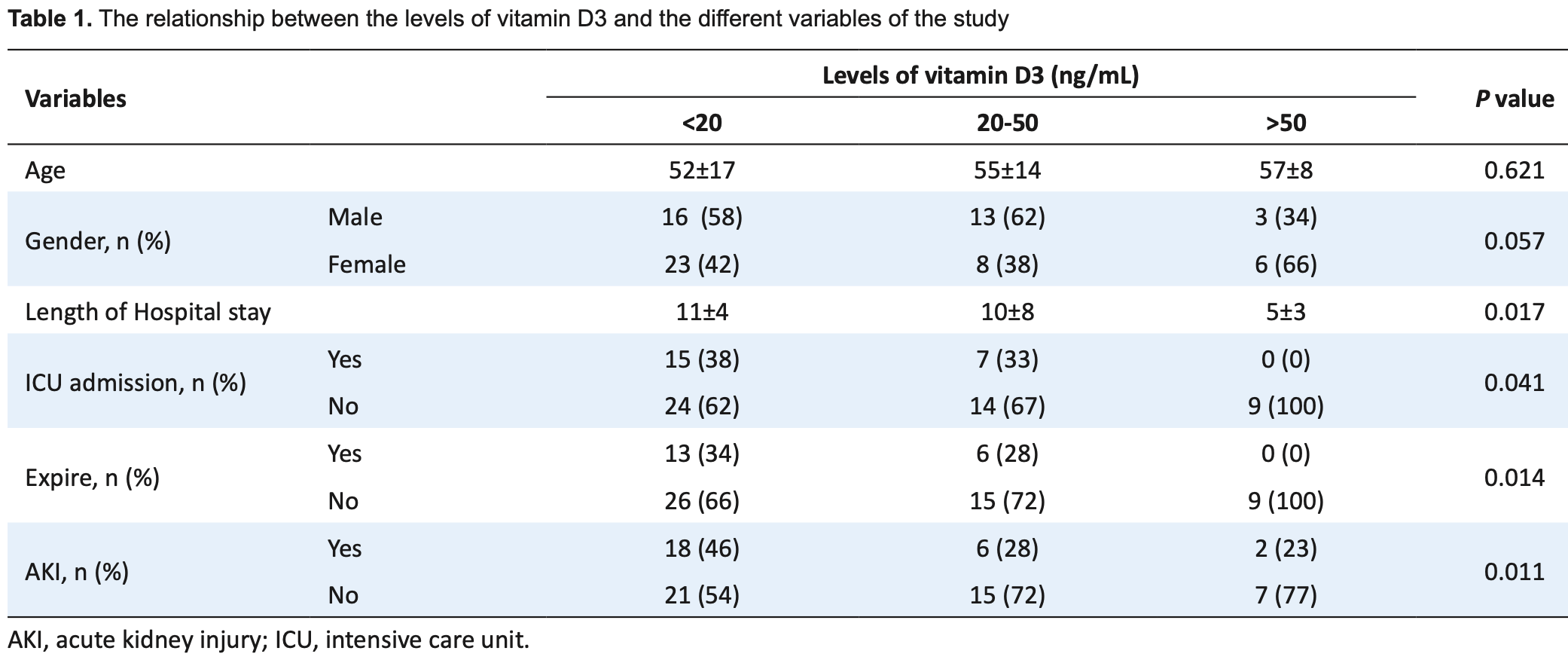
Retrospective 69 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Iran, showing lower vitamin D associated with higher mortality, ICU admission, and AKI in unadjusted results. The mean age of deficient patients was lower. Statistical significance is not reached for the binary comparison between the groups with levels <20 ng/mL and ≥20 ng/mL.
This is the 156th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 40.0% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.28, high D levels (≥20ng/mL) 6 of 30 (20.0%), low D levels (<20ng/mL) 13 of 39 (33.3%), NNT 7.5.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 39.3% lower, RR 0.61, p = 0.20, high D levels (≥20ng/mL) 7 of 30 (23.3%), low D levels (<20ng/mL) 15 of 39 (38.5%), NNT 6.6.
|
|
risk of AKI, 42.2% lower, RR 0.58, p = 0.13, high D levels (≥20ng/mL) 8 of 30 (26.7%), low D levels (<20ng/mL) 18 of 39 (46.2%), NNT 5.1.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Arabi et al., 22 Jan 2023, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
The association between vitamin D3 deficiency and acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients
Journal of Renal Injury Prevention, doi:10.34172/jrip.2022.32126
In a cross-sectional study on 69 hospitalized patients in the ward with COVID-19, we found significant association between vitamin D deficiency and acute kidney injury. Moreover, there was relationship between vitamin D deficiency and mortality, ICU (intensive care unit) admission and hospital length of stay. These results suggest the correction of vitamin D deficiency may be beneficial to reduce acute kidney injury in patient with COVID-19.
Authors' contribution
Conflicts of interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical issues At each research stage, we followed the principlesof the Declaration of Helsinki and the Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health. Each participant signed the informed written consent form. This project was also confirmed by the Ethics Committee of the Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences (ethical code #IR.HUMS. REC.1398.394). All participants signed the written informed consent. Besides, ethical issues (including plagiarism, data fabrication and double publication) have been completely observed by the authors.
References
Ala-Kokko, Mutt, Nisula, Koskenkari, Liisanantti et al., Vitamin D deficiency at admission is not associated with 90-day mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: Observational FINNAKI cohort study, Ann Med, doi:10.3109/07853890.2015.1134807
Ankova, Luini, Pedrazzoni, Riganti, Sironi et al., Impairment of cytokine production in mice fed a vitamin D3-deficient diet, Immunology
Arnson, Amital, Shoenfeld, Vitamin D and autoimmunity: new aetiological and therapeutic considerations, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:10.1136/ard.2007.069831
Braun, Litonjua, Moromizato, Gibbons, Giovannucci et al., Association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and acute kidney injury in the critically ill, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e318260c928
Cereda, Bogliolo, Klersy, Lobascio, Masi et al., Vitamin D 25OH deficiency in COVID-19 patients admitted to a tertiary referral hospital, Clin Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.055
Giovannucci, Liu, Hollis, Rimm, 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of myocardial infarction in men: a prospective study, Arch Intern Med, doi:10.1001/archinte.168.11.1174
Gregori, Casorati, Amuchastegui, Smiroldo, Davalli et al., Regulatory T cells induced by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and mycophenolate mofetil treatment mediate transplantation tolerance, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.167.4.1945
Guijarro, Egido, Transcription factor-kappa B (NFkappa B) and renal disease, Kidney Int, doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.059002415
Hernández, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, García-Unzueta, Hernández-Hernández et al., Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2
Holick, Vitamin D deficiency, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553
Hoste, Bagshaw, Bellomo, Cely, Colman et al., Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-015-3934-7
Hsieh, Hsiao, Liao, Hou, Chang et al., The Role of Vitamin D in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Acute Kidney Injury, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23137368
Khwaja, KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury, Nephron Clin Pract, doi:10.1159/000339789
Langlois, ' Aragon, Manzanares, Vitamin D in the ICU: More sun for critically ill adult patients?, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2018.11.001
Luo, Liao, Shen, Li, Cheng, Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated with COVID-19 Incidence and Disease Severity in Chinese People
Macaya, Paeres, Valls, Fernández-Ortiz, Del Castillo et al., Interaction between age and vitamin D deficiency in severe COVID-19 infection, Nutr Hosp, doi:10.20960/nh.03193
Moraes, Friedman, Wawrzeniak, Marques, Nagel et al., Vitamin D deficiency is independently associated with mortality among critically ill patients, Clinics, doi:10.6061/clinics/2015(05)04
Orchard, Baldry, Nasim-Mohi, Monck, Saeed et al., Vitamin-D levels and intensive care unit outcomes of a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients, Clin Chem Lab Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-1567
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Athar, Marchitelli et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH] D) levels in patients hospitalized with are associated with greater disease severity, Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), doi:10.1111/cen.14276
Pizzini, Aichner, Sahanic, Böhm, Egger et al., Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency on COVID-19-A Prospective Analysis from the CovILD Registry, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092775
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger, Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Shah, Sharma, Mavalankar, Does vitamin D supplementation reduce COVID-19 severity? -a systematic review, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcac040
Suzuki, Ichiyama, Ohsaki, Hasegawa, Shiraishi et al., Anti-inflammatory effect of 1alpha,25-Arabi M et al dihydroxyvitamin D(3) in human coronary arterial endothelial cells: Implication for the treatment of Kawasaki disease, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2008.12.004
Szeto, Zucker, Lasota, Rubin, Walker et al., Vitamin D Status and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients, Endocr Res, doi:10.1080/07435800.2020.1867162
Zapatero, Dot, Diaz, Gracia, Pérez-Terán et al., Severe vitamin D deficiency upon admission in critically ill patients is related to acute kidney injury and a poor prognosis, Med Intensiva (Engl Ed), doi:10.1016/j.medin.2017.07.004
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.34172/jrip.2022.32126",
"ISSN": [
"2345-2781"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/jrip.2022.32126",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Introduction: Vitamin D deficiency is a common clinical finding in the general population and hospitalized patients, including patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). Acute kidney injury (AKI) occurs in more than 50% in ICU admitted patients. Objectives: There are few studies regarding AKI in COVID-19 patients, therefore we investigated the relationship between vitamin D3 deficiency and the occurrence of AKI in COVID-19 patients. Patients and Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted on 69 COVID-19 patients who were hospitalized in the ward for 12 months. Their serum vitamin D3 levels were measured in the first 24 hours of hospitalization in the ward. Patients were divided into three groups based on the serum levels of vitamin D3: >50 ng/mL as normal, 20-50 ng/mL as insufficient and <20 ng/mL as deficiency status. The patients were studied until the occurrence of acute renal injury or the occurrence of death. Results: Out of 69 hospitalized patients in the ward with COVID-19, there were 39 patients in group vitamin D3<20 ng/mL, 21 patients in group vitamin D3 of 20-50ng/mL and 9 patients in group of vitamin D3>50 ng/mL. The frequencies of AKI in groups of vitamin D3<20 ng/mL, 20-50 ng/mL, and >50 ng/mL were 46%, 28%, and 23%, respectively. A significant relationship was observed between AKI and our study groups (P=0.011). Furthermore, there was a significant association between our study groups and mortality (P=0.014), ICU admission (P=0.041) and hospital length of stay (P=0.017). In another division in patients with different levels of vitamin D3 in the presence or absence of AKI, there were significant associations between patients with vitamin D3<20 ng/mL and the presence of AKI and also with mortality (P=0.042), ICU admission (P=0.024) and additionally with hospital length of stay (P=0.027). Conclusion: Our study showed significant association between vitamin D deficiency and AKI in ICU-admitted COVID-19 patients. Moreover, there were relationships between vitamin D deficiency and mortality, ICU admission and hospital length of stay. These results suggest the correction of vitamin D deficiency may be beneficial to reduce AKI in patient with COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Journal Owner",
"name": "journal_owner",
"value": "Nickan Research Institute"
},
{
"label": "Journal Publisher",
"name": "journal_publisher",
"value": "Nickan Research Institute"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-09-03"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-11-19"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2023-01-22"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3474-174X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Preventive Medicine and Public Health Research Center, Family Medicine Department, Iran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Arabi",
"given": "Mohsen",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6674-1731",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Research Development Center, Shahid Mohammadi Hospital, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Samimagham",
"given": "Hamid Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6872-3577",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Research Development Center, Shahid Mohammadi Hospital, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Moradkhani",
"given": "Azadeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9243-3660",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committe, Faculty of Medicie, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Khajavi Mayvan",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1849-040X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committe, Faculty of Medicie, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Binaei",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2345-8642",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committe, Faculty of Medicie, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Salimi Asl",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2491-5902",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Center, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Kazemi Jahromi",
"given": "Mitra",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Renal Injury Prevention",
"container-title-short": "J Renal Inj Prev",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"journalrip.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-15T21:15:40Z",
"timestamp": 1676495740000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-15T21:15:40Z",
"timestamp": 1676495740000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-16T05:44:14Z",
"timestamp": 1676526254403
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
22
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
24
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journalrip.com/PDF/jrip-12-e32126.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journalrip.com/PDF/jrip-12-e32126.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "20123",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e32126",
"prefix": "10.34172",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Maad Rayan Publishing Company",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journalrip.com/Article/jrip-32126"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Urology",
"Nephrology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The association between vitamin D3 deficiency and acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "12"
}
