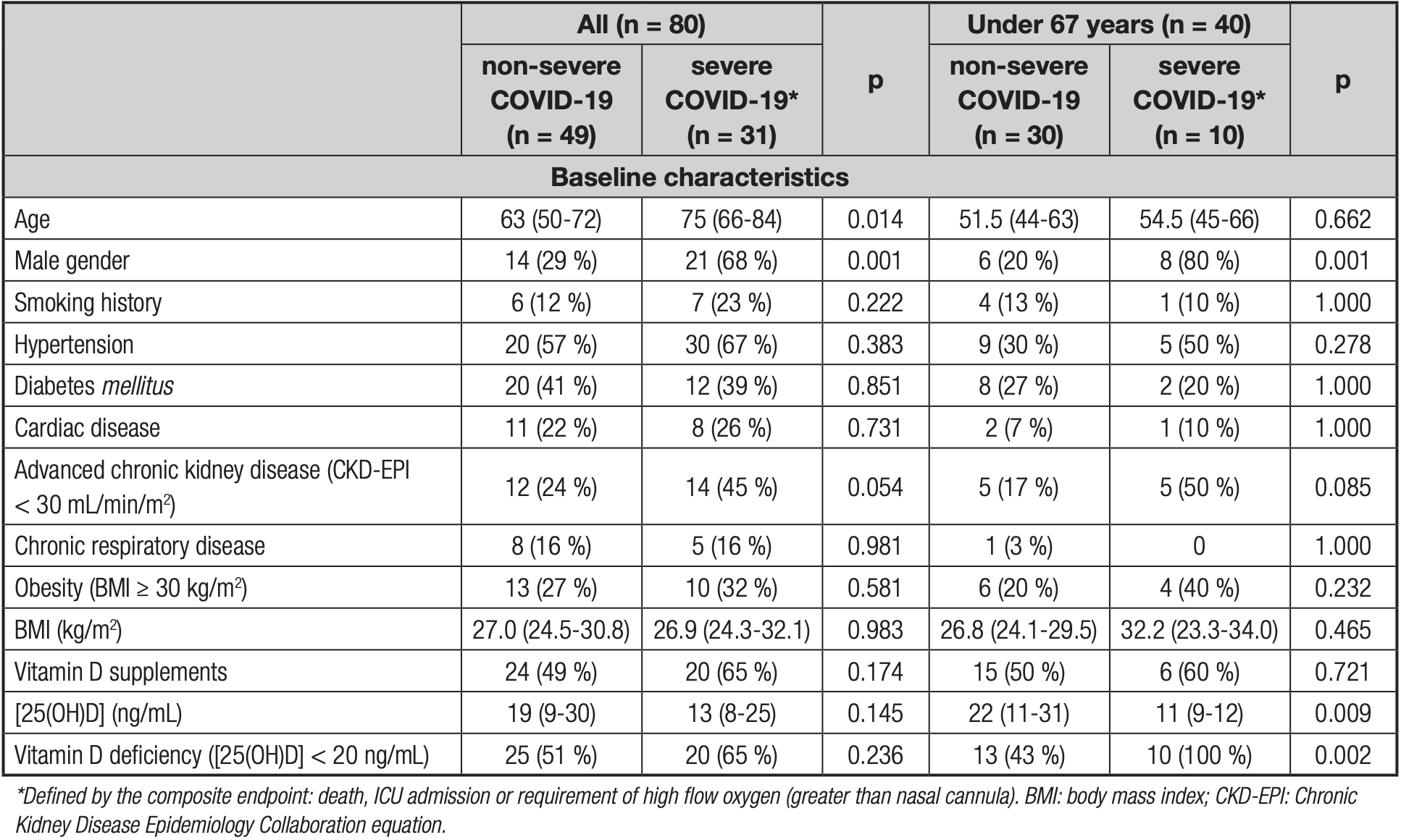
Interaction between age and vitamin D deficiency in severe COVID-19 infection
et al., Nutr. Hosp., doi:10.20960/nh.03193, Oct 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 80 hospitalized patients in Spain showing higher risk of severe COVID-19 with vitamin D deficiency.
This is the 21st of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of severe case, 55.0% lower, RR 0.45, p = 0.07, high D levels 11 of 35 (31.4%), low D levels 20 of 45 (44.4%), NNT 7.7, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, >20ng/mL.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Macaya et al., 21 Oct 2020, retrospective, Spain, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.20960/nh.03193",
"ISSN": [
"1699-5198",
"0212-1611"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.20960/nh.03193",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macaya",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Espejo Paeres",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valls",
"given": "Adrián",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernández-Ortiz",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "González del Castillo",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martín-Sánchez",
"given": "Javier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Runkle",
"given": "Isabelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rubio Herrera",
"given": "Miguel Ángel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrición Hospitalaria",
"container-title-short": "Nutr Hosp",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-17T14:59:10Z",
"timestamp": 1600354750000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-17T14:59:18Z",
"timestamp": 1600354758000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-10T17:35:33Z",
"timestamp": 1691688933681
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 28,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"member": "8588",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.20960",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"publisher": "ARAN Ediciones",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7546",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-017-1564-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ejcn.2010.265",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047659",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2019.10047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/me.2013-1146",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Kong J, Zhu X, Shi Y, Liu T, Chen Y, Bhan I, et al. VDR Attenuates Acute Lung Injury by Blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 Pathway and Renin-Angiotensin System. Molecular Endocrinology 2013;27:2116-25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsr2005760",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Vaduganathan M, Vardeny O, Michel T, McMurray JJV, Pfeffer MA, Solomon SD. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine 2020;382:1653-9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature03712",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Imai Y, Kuba K, Rao S, Huan Y, Guo F, Guan B, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 2005;436:112-6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "D’Avolio A, Avataneo V, Manca A, Cusato J, De Nicolò A, Lucchini R, et al. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2. Nutrients 2020;12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Ilie PC, Stefanescu S, Smith L. The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research [Internet] 2020 [cited 2020 May 17]. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Guo Y-R, Cao Q-D, Hong Z-S, Tan Y-Y, Chen S-D, Jin H-J, et al. The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak – an update on the status. Military Medical Research [Internet] 2020 [cited 2020 May 4]. Available from: https://mmrjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21082948",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "La Vignera S, Cannarella R, Condorelli RA, Torre F, Aversa A, Calogero AE. Sex-Specific SARS-CoV-2 Mortality: Among Hormone-Modulated ACE2 Expression, Risk of Venous Thromboembolism and Hypovitaminosis D. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020;21:2948."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.respe.2018.05.092",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Waldhoer T, Endler G, Yang L, Haidinger G, Wagner O, Marculescu R. Vitamin D deficiency, overall and cause-specific mortality: the impact of age. Revue d’Épidémiologie et de Santé Publique 2018;66:S271."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4110/in.2019.19.e37",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Oh S-J, Lee JK, Shin OS. Aging and the Immune System: the Impact of Immunosenescence on Viral Infection, Immunity and Vaccine Immunogenicity. Immune Network [Internet] 2019 [cited 2020 Apr 26]. Available from: https://synapse.koreamed.org/DOIx.php?id=10.4110/in.2019.19.e37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.endinu.2016.11.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Varsavsky M, Rozas Moreno P, Becerra Fernández A, Luque Fernández I, Quesada Gómez JM, Ávila Rubio V, et al. Recomendaciones de vitamina D para la población general. Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición 2017;64:7-14."
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nutricionhospitalaria.org/articles/03193/show"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Interaction between age and vitamin D deficiency in severe COVID-19 infection",
"type": "journal-article"
}
