Potent antiviral activity of simnotrelvir against key epidemic SARS-CoV-2 variants with a high resistance barrier
et al., Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1128/aac.01556-24, Apr 2025
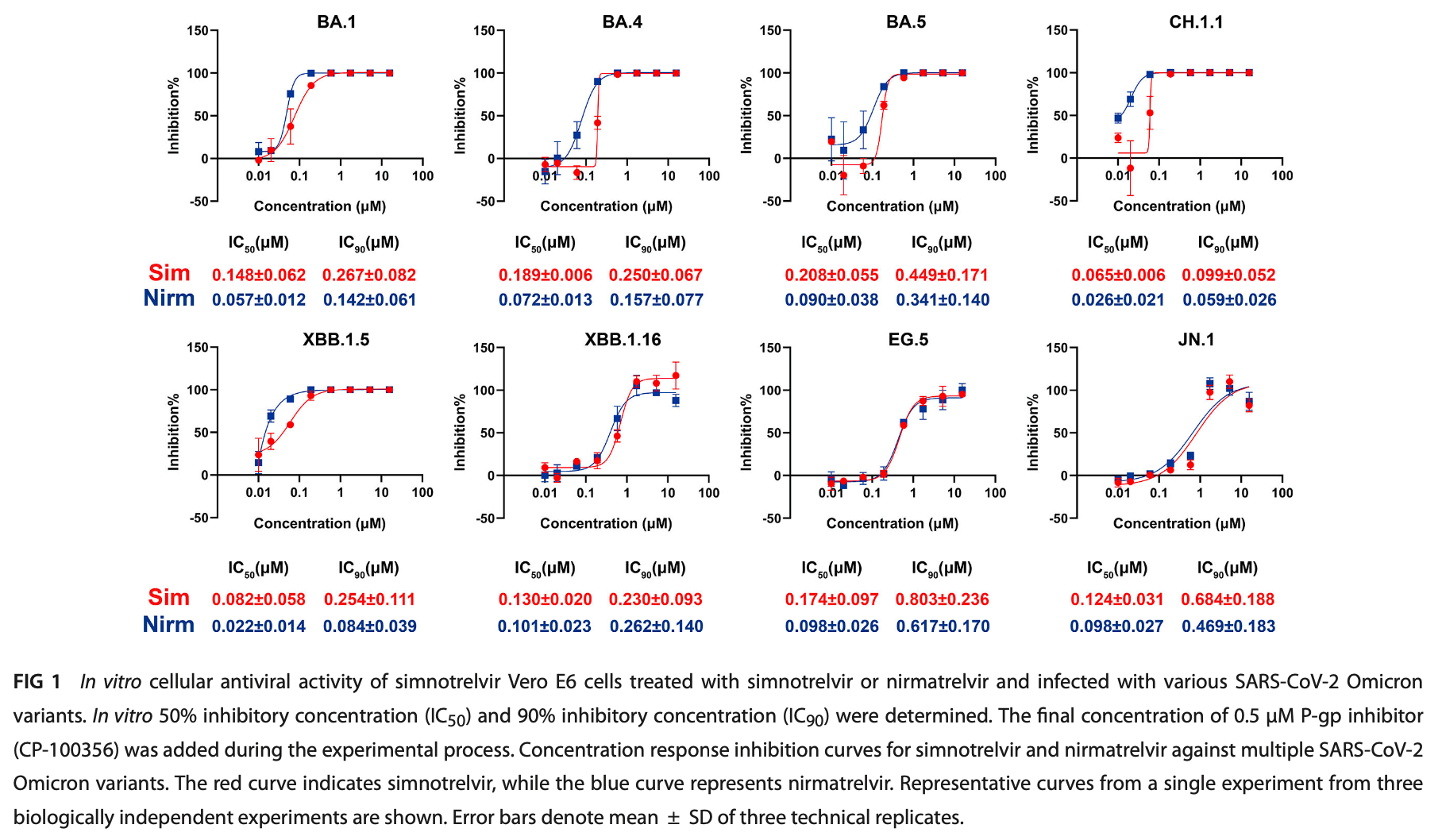
In vitro and clinical study showing potent antiviral activity of simnotrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 variants with a high resistance barrier. Authors demonstrated simnotrelvir's efficacy against multiple Omicron variants including BA.1, BA.4, BA.5, CH.1.1, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, EG.5, and JN.1 in Vero E6 cells with IC50 values ranging from 0.065 to 0.208 μM. Simnotrelvir also effectively inhibited nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease mutants. In resistance selection studies, SARS-CoV-2 BA.5 variant developed only modest decrease in sensitivity (4.5-fold) after 10 passages, and HCoV-OC43 showed an 8.3-fold decrease after 12 passages, indicating a high barrier to resistance development. Clinical trial analysis from 97 patients revealed no significant 3CL protease resistance mutations following simnotrelvir treatment.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of xiannuoxin for COVID-19:
Zhao et al., 2 Apr 2025, peer-reviewed, 17 authors.
Contact: yuxin.chen@nju.edu.cn, xiaofeng.zhao@cn.simcere.com.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Potent antiviral activity of simnotrelvir against key epidemic SARS-CoV-2 variants with a high resistance barrier
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1128/aac.01556-24
Simnotrelvir is an oral small-molecule antiviral agent targeting the 3C-like protease (3CL pro ) of SARS-CoV-2, proven effective against the Delta variant with favorable pharmacokinetics and safety in preclinical study. In this study, we further evaluated the antiviral efficacy of simnotrelvir against a range of emerging Omicron variants, including BA.1, BA.4, BA.5, CH.1.1, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, EG.5, and JN.1. In vitro assays with Vero E6 cells confirmed that simnotrelvir exhibited robust antiviral activity across these variants, comparable to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug nirmatrelvir. Additionally, simnotrelvir demonstrated effective inhibition against several nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 3CL pro mutants, including A260V, Y54A, (T21I + S144A), F140A, H172Y, and E166V. Importantly, simnotrelvir showed better potency against the E166V mutation compared to nirmatrelvir. Resistance selection studies revealed that BA.5 developed reduced sensitivity after 5 and 10 passages, increasing the IC 50 values by 3.2 and 4.5-fold, respectively, while HCoV-OC43 showed an 8.3-fold increase after 12 passages. Despite this, simnotrelvir's overall efficacy remains strong. Furthermore, clinical trials demonstrated that combining simnotrelvir with ritonavir significantly shortened symptom resolution in COVID-19 patients. Genomic analysis of treated patients found random nucleotide substitutions but no significant mutations linked to 3CL pro resistance. In conclusion, simnotrelvir shows strong antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants and maintains a high barrier to resistance, reinforcing its potential as an effective therapeutic option for current and future SARS-CoV-2 variants. KEYWORDS simnotrelvir, 3C-like protease, SARS-CoV-2, antiviral efficacy, antiviral resistance T he severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) emerged at the end of 2019, causing severe acute respiratory coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and triggering a global pandemic (1, 2). Large-scale vaccination is considered crucial for controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, such as KP.2 and KP.3, is rapidly increasing infection rates globally, becoming dominant strains in circulation (3). According to World Health Organization (WHO) surveillance data, as of 12 August 2024, the global infection rate has reached 21% (4). It is possibly due to the remarkable mutations of the Omicron variant and the waned immunity elicited by either infection or vaccination (3, 4). COVID-19 therapeu tics, especially monoclonal antibodies, had lost their efficacy against newly emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, highlighting the need for more effective antiviral drugs to treat COVID-19. The coronavirus 3C-like protease (3CL pro ), also known as main protease (M pro ), highly conserved across a range of pathogenic coronaviruses, is responsible for the cleavage of two polyproteins (pp1a and pp1b) during viral replication (5-7),..
AUTHOR AFFILIATIONS
ETHICS APPROVAL This research protocol was approved by the Clinical Trial Ethics Committee of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Drug (YW2022-035-09) and was carried out in accordance with The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
ADDITIONAL FILES The following material is available online.
Supplemental Material Supplemental tables (AAC01556-24-S0001.docx). Tables S1 and S2 .
References
Anand, Ziebuhr, Wadhwani, Mesters, Hilgenfeld, Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs, Science, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2301425
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Cao, Wang, Jian, Song, Yisimayi et al., Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3
Cao, Wang, Lu, Huang, Yang et al., Oral simnotrelvir for adult patients with mild-to-moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2301425
Chen, Chen, Yin, Tao, Zhu et al., The third dose of CoronVac vaccination induces broad and potent adaptive immune responses that recognize SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2022.2081614
Chen, Huang, Ma, Kuzmič, Zhou et al., Preclinical evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor Full-Length Text Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy April
Clayton, De Oliveira, Ibrahim, Sun, Mahinthichaichan et al., Integrative approach to dissect the drug resistance mechanism of the H172Y mutation of SARS-CoV-2 main protease, J Chem Inf Model, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Dejnirattisai, Huo, Zhou, Zahradník, Supasa et al., SARS-CoV-2 omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses, Cell, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04388-0
Duan, Zhou, Liu, Iketani, Lin et al., Molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06609-0
Fehr, Perlman, Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis, Methods Mol Biol, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2301425
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Wisemandle et al., None, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
Hansen, Baum, Pascal, Russo, Giordano et al., Studies in humanized mice and convales cent humans yield a SARS-CoV-2 antibody cocktail, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd0827
Havranek, Demissie, Lee, Lan, Zhang et al., Discovery of nirmatrelvir resistance mutations in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro: a computational-experimental approach, J Chem Inf Model, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Hirotsu, Kobayashi, Kakizaki, Saito, Tsutsui et al., Multidrug-resistant mutations to antiviral and antibody therapy in an immunocompromised patient infected with SARS-CoV-2, Med, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Hu, Lewandowski, Tan, Zhang, Morgan et al., Naturally occurring mutations of SARS-CoV-2 main protease confer drug resistance to nirmatrelvir, ACS Cent Sci, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Iketani, Hong, Sheng, Bahari, Culbertson et al., Functional map of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease reveals tolerant and immutable sites, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Iketani, Liu, Guo, Liu, Chan et al., Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 omicron sublineages, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4
Iketani, Mohri, Culbertson, Hong, Duan et al., Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrel vir, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Ip, Chu, Chan, Leung, Abdullah et al., Global prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease mutations associated with nirmatrelvir or ensitrelvir resistance, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Jiang, Su, Shang, Zhou, Zhang et al., Structure-based development and preclinical evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease inhibitor simnotrelvir, Nat Commun, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Jm, Investigators, Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Liu, Iketani, Guo, Chan, Wang et al., Striking antibody evasion manifested by the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04388-0
Liu, Wang, Nair, Yu, Rapp et al., Potent neutralizing antibodies against multiple epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 spike, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2571-7
Lu, Su, Yang, Jiang, Antivirals with common targets against highly pathogenic viruses, Cell, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2301425
Marra, Jones, Astell, Holt, Brooks-Wilson et al., The genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Nmpa, Simnotrelvir tablets/ritonavir tablets(Co-Packaged) and deuremidevir hydrobromide tablets for treating COVID-19 infection approved for marketing with conditions, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Ou, Lewandowski, Hu, Lipinski, Aljasser et al., A yeast-based system to study SARS-CoV-2 Mpro structure and to identify nirmatrelvir resistant mutations, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, Aschenbrenner, Avery et al., An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abl4784
Planas, Saunders, Maes, Guivel-Benhassine, Planchais et al., Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 omicron to antibody neutralization, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04389-z
St-Jean, Jacomy, Desforges, Vabret, Freymuth et al., Human respiratory coronavirus OC43: genetic stability and neuroinva sion, J Virol, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Stevens, Pruijssers, Lee, Gordon, Tchesnokov et al., Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase confer resistance to remdesivir by distinct mechanisms, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abo0718
Tombuloglu, Sabit, Al-Khallaf, Kabanja, Alsaeed et al., Multiplex real-time RT-PCR method for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 by targeting viral N, RdRP and human RP genes, Sci Rep
Tuekprakhon, Nutalai, Dijokaite-Guraliuc, Zhou, Ginn et al., Antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 from vaccine and BA.1 serum, Cell, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Unoh, Uehara, Nakahara, Nobori, Yamatsu et al., Discovery of S-217622, a noncovalent oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate for treating COVID-19, J Med Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00117
Wang, Iketani, Li, Liu, Guo et al., Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants, Cell, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Wang, Jia, Bao, Wang, Cao et al., Memory B cell repertoire from triple vaccinees against diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04466-x
Wang, Muecksch, Cho, Gaebler, Hoffmann et al., Analysis of memory B cells identifies conserved neutralizing epitopes on the N-terminal domain of variant SARS-Cov-2 spike proteins, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2022.04.003
Westendorf, Žentelis, Wang, Foster, Vaillancourt et al., LY-CoV1404 (bebtelovimab) potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants, Cell Rep, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04466-x
Xiong, Nie, Li, Hu, Su et al., Potency prediction of covalent inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 3CL-like protease and multiple mutants by multiscale simulations, J Chem Inf Model, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01594
Yang, Yang, Yao, Ye, Xu et al., A first-in-human phase 1 study of simnotrelvir, A 3CL-like protease inhibitor for treatment of COVID-19, in healthy adult subjects, Eur J Pharm Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106598
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhou, Gammeltoft, Ryberg, Pham, Tjørnelund et al., Nirmatrelvirresistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Sci Adv, doi:10.1126/science.1085953
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song et al., A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
Zost, Gilchuk, Case, Binshtein, Chen et al., Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, Nature New Biol, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2548-6
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.01556-24",
"ISSN": [
"0066-4804",
"1098-6596"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/aac.01556-24",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title/>\n <jats:p>\n Simnotrelvir is an oral small-molecule antiviral agent targeting the 3C-like protease (3CL\n <jats:sup>pro</jats:sup>\n ) of SARS-CoV-2, proven effective against the Delta variant with favorable pharmacokinetics and safety in preclinical study. In this study, we further evaluated the antiviral efficacy of simnotrelvir against a range of emerging Omicron variants, including BA.1, BA.4, BA.5, CH.1.1, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, EG.5, and JN.1.\n <jats:italic>In vitro</jats:italic>\n assays with Vero E6 cells confirmed that simnotrelvir exhibited robust antiviral activity across these variants, comparable to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug nirmatrelvir. Additionally, simnotrelvir demonstrated effective inhibition against several nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 3CL\n <jats:sup>pro</jats:sup>\n mutants, including A260V, Y54A, (T21I + S144A), F140A, H172Y, and E166V. Importantly, simnotrelvir showed better potency against the E166V mutation compared to nirmatrelvir. Resistance selection studies revealed that BA.5 developed reduced sensitivity after 5 and 10 passages, increasing the IC\n <jats:sub>50</jats:sub>\n values by 3.2 and 4.5-fold, respectively, while HCoV-OC43 showed an 8.3-fold increase after 12 passages. Despite this, simnotrelvir’s overall efficacy remains strong. Furthermore, clinical trials demonstrated that combining simnotrelvir with ritonavir significantly shortened symptom resolution in COVID-19 patients. Genomic analysis of treated patients found random nucleotide substitutions but no significant mutations linked to 3CL\n <jats:sup>pro</jats:sup>\n resistance. In conclusion, simnotrelvir shows strong antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants and maintains a high barrier to resistance, reinforcing its potential as an effective therapeutic option for current and future SARS-CoV-2 variants.\n </jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/aac.01556-24"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-10-24"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-02-04"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-03-10"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Clinical College of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Liwei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0003-3656-2187",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Clinical College of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Li",
"given": "Chuang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jiangsu Simcere Pharmaceutical Company Limited",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Neurology and Oncology Drug Development",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Mengyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jiangsu Simcere Pharmaceutical Company Limited",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Neurology and Oncology Drug Development",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Minyun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Simcere Zaiming Pharmaceutical Company Limited",
"place": [
"Shanghai, China"
]
},
{
"name": "Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University",
"place": [
"Beijing, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Clinical College of Nanjing Medical University",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Wanying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing University Medical School",
"place": [
"Nanjing, Jiangsu, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Jie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jiangsu Simcere Pharmaceutical Company Limited",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"place": [
"Wuhan, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Kangping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"place": [
"Wuhan, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Kai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, State Key Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases, Carol Yu Centre for Infection,The University of Hong Kong",
"place": [
"Hong Kong SAR, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Lam",
"given": "Hoi-Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, State Key Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases, Carol Yu Centre for Infection,The University of Hong Kong",
"place": [
"Hong Kong SAR, China"
]
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Queen Mary Hospital, The University of Hong Kong",
"place": [
"Hong Kong SAR, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Hung",
"given": "Ivan Fan-Ngai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, State Key Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases, Carol Yu Centre for Infection,The University of Hong Kong",
"place": [
"Hong Kong SAR, China"
]
},
{
"name": "Centre for Virology, Vaccinology and Therapeutics, Hong Kong Science and Technology Park",
"place": [
"Hong Kong SAR, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Kwok-Hung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jiangsu Simcere Pharmaceutical Company Limited",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Neurology and Oncology Drug Development",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Lian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jiangsu Simcere Pharmaceutical Company Limited",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Neurology and Oncology Drug Development",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Feng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0003-0357-7972",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Jiangsu Simcere Pharmaceutical Company Limited",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Neurology and Oncology Drug Development",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Xiaofeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5955-687X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Clinical College of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine",
"place": [
"Nanjing, China"
]
},
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing University Medical School",
"place": [
"Nanjing, Jiangsu, China"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yuxin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy",
"container-title-short": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-10T14:02:28Z",
"timestamp": 1741615348000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-04T05:38:39Z",
"timestamp": 1743745119000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martinez",
"given": "Miguel Angel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"2023YFC2309100"
],
"name": "National Key Research and Development Program of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"92269118, 92269205, 92369117"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100001809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"M2022013"
],
"name": "Scientific Rsearch Project of Jiangsu Health Comission"
},
{
"award": [
"NDYG2022003"
],
"name": "Project of Chinese Hospital Reform and Development Institute"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-05T04:03:44Z",
"timestamp": 1743825824937,
"version": "3.40.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1743552000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1743552000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/aac.01556-24",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/aac.01556-24",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_2_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_3_2",
"unstructured": "WHO COVID-19 dashboard. 2024. WHO. Available from: https://covid19.who.int"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_4_2",
"unstructured": "WHO coronavirus network (CoViNet). 2024. WHO. Available from: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/variants"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_5_2",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). 2023. WHO. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/coronavirus-disease-(covid-19)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1085658",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106598",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2301425",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-024-01618-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_13_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_14_2",
"unstructured": "NMPA. 2023. Simnotrelvir tablets/ritonavir tablets(Co-Packaged) and deuremidevir hydrobromide tablets for treating COVID-19 infection approved for marketing with conditions. Available from: https://english.nmpa.gov.cn/2023-01/29/c_882432.htm"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-42102-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medj.2023.08.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.12.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscentsci.3c00538",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104559",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1011592",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.add7197",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2022.08.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_23_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_24_2",
"unstructured": "FDA. 2021. Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Paxlovid"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.3c01269",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05514-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.3c00344",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.78.16.8824-8834.2004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1085953",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2081614",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04388-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd0827",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2548-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110812",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04466-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2022.04.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2571-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04389-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_44_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abo0718",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_45_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06609-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_46_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01594",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_47_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-06977-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_48_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 47,
"references-count": 47,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/aac.01556-24"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Potent antiviral activity of simnotrelvir against key epidemic SARS-CoV-2 variants with a high resistance barrier",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page",
"volume": "69"
}