The histamine receptor H1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2
et al., mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01088-24, Jul 2024
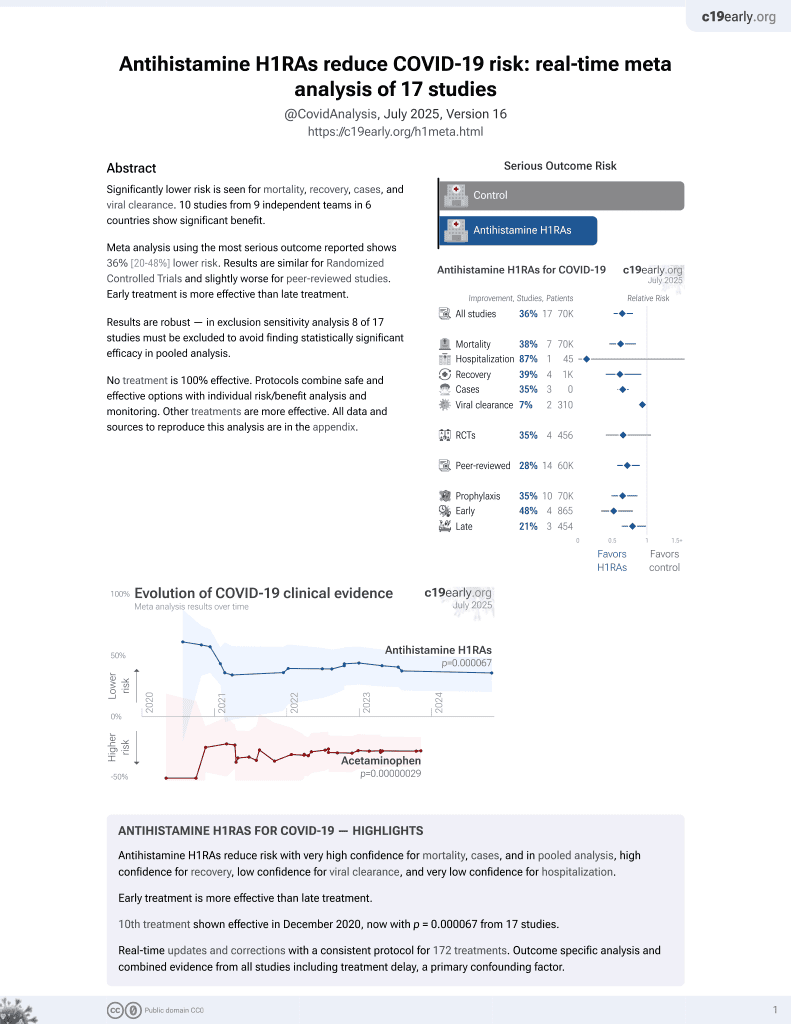
11th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000052 from 17 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
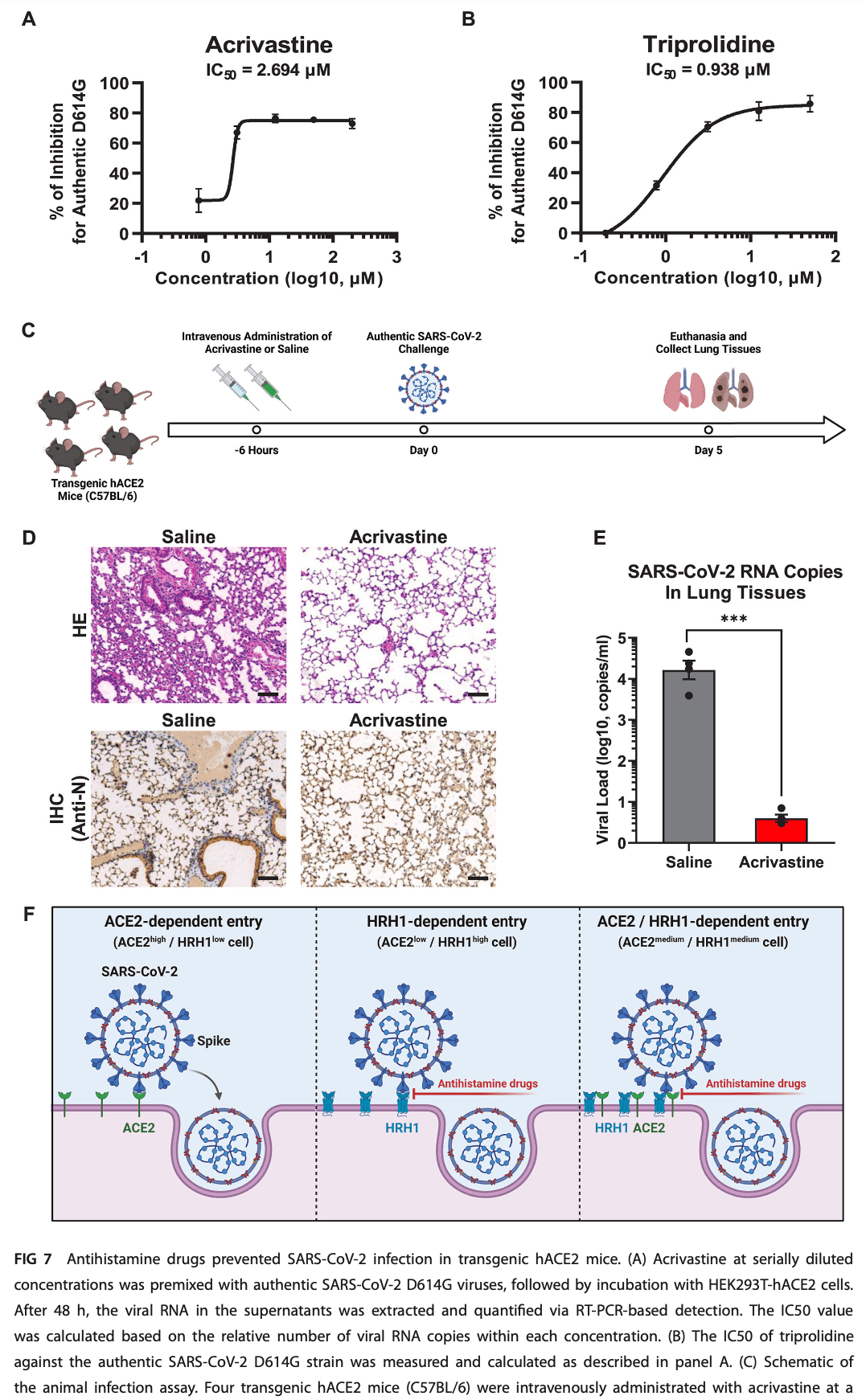
In vitro and mouse study showing that antihistamine drugs targeting the histamine receptor H1 (HRH1) inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection. Authors find that HRH1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2 by directly binding to the N-terminal domain of the viral spike protein. HRH1 also synergistically enhanced ACE2-dependent viral entry. Antihistamine drugs effectively prevented viral infection of various SARS-CoV-2 variants in HEK293T-hACE2, A549, Calu-3 and Huh7 cells with an average IC50 of 2.4 μM. In transgenic hACE2 mice challenged with SARS-CoV-2, acrivastine treatment prevented viral infection in the lungs.
13 preclinical studies support the efficacy of antihistamine H1RAs for COVID-19:
1.
Hamdan et al., In silico Evaluation of H1-Antihistamine as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase: Repurposing Study of COVID-19 Therapy, Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.4274/tjps.galenos.2024.49768.
2.
Elshaier et al., Chlorpheniramine Maleate Displaying Multiple Modes of Antiviral Action Against SARS-CoV-2: An Initial Mechanistic Study, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.92375.
3.
Black, S., Molecular Modeling and Preliminary Clinical Data Suggesting Antiviral Activity for Chlorpheniramine (Chlorphenamine) Against COVID-19, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.20980.
4.
Hou et al., Testing of the inhibitory effects of loratadine and desloratadine on SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudotyped virus viropexis, Chemico-Biological Interactions, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109420.
5.
Yu et al., The histamine receptor H1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01088-24.
6.
Sanchez-Gonzalez et al., Intranasal Chlorpheniramine Maleate for the treatment of COVID-19: Translational and Clinical Evidence, Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v10i3.2752.
7.
Morin-Dewaele et al., Desloratadine, an FDA-approved cationic amphiphilic drug, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in cell culture and primary human nasal epithelial cells by blocking viral entry, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25399-5.
8.
Reznikov et al., Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095.
Yu et al., 2 Jul 2024, peer-reviewed, 21 authors.
Contact: zhangh92@mail.sysu.edu.cn, pant8@mail.sysu.edu.cn, ma_xiancai@gzlab.ac.cn.
The histamine receptor H1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2
mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01088-24
Numerous host factors, in addition to human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2), have been identified as coreceptors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), demonstrating broad viral tropism and diversified druggable potential. We and others have found that antihistamine drugs, particularly histamine receptor H1 (HRH1) antagonists, potently inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection. In this study, we provided compelling evidence that HRH1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2 by directly binding to the viral spike protein. HRH1 also synergistically enhanced hACE2-dependent viral entry by interacting with hACE2. Antihistamine drugs effectively prevent viral infection by competitively binding to HRH1, thereby disrupting the interaction between the spike protein and its receptor. Multiple inhibition assays revealed that antihistamine drugs broadly inhibited the infection of various SARS-CoV-2 mutants with an average IC50 of 2.4 µM. The prophylactic function of these drugs was further confirmed by authentic SARS-CoV-2 infection assays and humanized mouse challenge experiments, demonstrating the therapeutic potential of antihistamine drugs for combating coronavirus disease 19.
IMPORTANCE In addition to human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can utilize alternative cofactors to facilitate viral entry. In this study, we discovered that histamine receptor H1 (HRH1) not only functions as an independent receptor for SARS-CoV-2 but also synergistically enhances ACE2-dependent viral entry by directly interacting with ACE2. Further studies have demonstrated that HRH1 facilitates the entry of SARS-CoV-2 by directly binding to the N-terminal domain of the spike protein. Conversely, antihistamine drugs, primarily HRH1 antagonists, can competitively bind to HRH1 and thereby prevent viral entry. These findings revealed that the administration of repurposable antihistamine drugs could be a therapeutic intervention to combat coronavirus disease 19. KEYWORDS SARS-CoV-2, receptor, HRH1, antihistamine, spike, viral entry T he coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has persistently threatened public health (1, 2). In addition to SARS-CoV-2, influenza virus (IFV) and respiratory syncytial virus have concurrently circulated within human society. The development of potent polyvalent vaccines or antibody cocktails to prevent this "tripledemic" is urgently needed. However, both SARS-CoV-2 and IFV undergo multiple rounds of immune evasion and enhanced transmissibility, which significantly decreases the effectiveness of vaccines or antibodies targeting ancestral strains. Recently, a newly emerged SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineage, designated JN.1, has started to prevail worldwide (3). Although the ACE2 binding affinity
Surface plasmon resonance The binding affinities of HRH1 for hACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 S (D614G) were determined by surface plasmon resonance with a Biacore 8K + instrument (Cytiva). Briefly, the aforemen tioned purified hACE2-ECD and S-8M-ECD proteins were immobilized on Flow Cell 2 (FC2) of the CM5 sensor chip utilizing an amine coupling kit. Flow Cell 1 (FC1), which was not loaded with ligand proteins, was treated as the reference surface. Serially diluted HRH1 proteins at concentrations ranging from 81.25 to 3,000 nM were injected over both FC1 and FC2 at a flow rate of 30 µL/min. For each cycle, the contact time was set to 120 s, while the dissociation time was set to 300 s. The binding affinity of hACE2 for S was also monitored as a positive control. The concentration range, flow rate, contact time, and dissociation time of hACE2-ECD were the same as those of the HRH1 proteins. Response units (RUs) were calculated by subtracting responses of the reference channel (FC1) from responses of the active channel (FC2). Adjusted RUs were fitted to a 1:1 binding model utilizing Biacore insight evaluation software version 4.0.8.19879 (Cytiva). Both the association rate ("on rate", Ka) and dissociation rate ("off rate", Kd) were measured and analyzed. The equilibrium dissociation constant ("binding constant", KD) was calculated by dividing Ka by Kd (Kd/Ka).
Authentic virus infection assay The inhibitory effects of the antihistamines were confirmed via an..
References
Afrin, Weinstock, Molderings, COVID-19 hyperinflammation and post-COVID-19 illness may be rooted in mast cell activation syndrome, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016
Amraei, Yin, Napoleon, Suder, Berrigan et al., CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN act as receptors for SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.22.165803
Araf, Akter, Tang, Fatemi, Parvez et al., Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: genomics, transmissibility, and responses to current COVID-19 vaccines, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27588
Arrindell, Atmeh, Jayet, Sereme, Mege et al., Vimentin is an important ACE2 co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in epithelial cells, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2022.105463
Baggen, Jacquemyn, Persoons, Vanstreels, Pye et al., TMEM106B is a receptor mediating ACE2-independent SARS-CoV-2 cell entry, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.005
Bakowski, Beutler, Wolff, Kirkpatrick, Chen et al., Drug repurposing screens identify chemical entities for the development of COVID-19 interventions, Nat Commun, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Blanco, Bonilla, Homma, Suzuki, Smith et al., Antihistamines and azithromycin as a treatment for COVID-19 on primary health care -A retrospective observational study in elderly patients, Pulmonary Pharm Therap, doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2021.101989
Blanco, Bonilla, Smith, Gómez De Las Heras, Antihistamines as an early treatment for COVID-19, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15772
Bryce, Mathias, Harrison, Watanabe, Geha et al., The H1 histamine receptor regulates allergic lung responses, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01878-5
Casale, Rodbard, Kaliner, Characterization of histamine H-1 receptors on human peripheral lung, Biochem Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01878-5
Chakraborty, Bhattacharya, Alshammari, Alharbi, Albekairi et al., Exploring the structural and molecular interaction landscape of nirmatrelvir and Mpro complex: the study might assist in designing more potent antivirals targeting SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses, J Infect Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2023.09.020
Chen, Shi, Pei, Vogt, Porritt et al., A systems-level study reveals host-targeted repurposable drugs against SARS-CoV-2 infection, Mol Syst Biol, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108959
Chu, Chan, Yuen, Shuai, Yuan et al., Comparative tropism, replication kinetics, and cell damage profiling of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV with implications for clinical manifestations, transmissibility, and laboratory studies of COVID-19: an observational study, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Conti, Caraffa, Tetè, Gallenga, Ross et al., Mast cells activated by SARS-CoV-2 release histamine which increases IL-1 levels causing cytokine storm and inflammatory reaction in COVID-19, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016
Daly, Simonetti, Klein, Chen, Williamson et al., Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd3072
Dittmar, Lee, Whig, Segrist, Li et al., Drug repurposing screens reveal cell-type-specific entry pathways and FDA-approved drugs active against SARS-CoV-2, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108959
Eldanasory, Eljaaly, Memish, Tawfiq, Histamine release theory and roles of antihistamine in the treatment of cytokines storm of COVID-19, Travel Med Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101874
Golightly, Greos, Second-generation antihistamines, Drugs, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1
Gu, Cao, Zhang, Gao, Wang et al., Receptome profiling identifies KREMEN1 and ASGR1 as alternative functional receptors of SARS-CoV-2, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-021-00595-6
Hashizume, Takashima, Ono, Okamoto, Iwasaki, Phenothiazines inhibit SARS-CoV-2 cell entry via a blockade of spike protein binding to neuropilin-1, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
He, Lin, Chu, Hu, Hu et al., Repurposing of the antihistamine chlorcycli zine and related compounds for treatment of hepatitis C virus infection, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016
Hikmet, Méar, Edvinsson, Micke, Uhlén et al., The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues, Mol Syst Biol, doi:10.15252/msb.20209610
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hogan, Rb, Hogan, Rb, Cannon et al., Dual-histamine receptor blockade with cetirizinefamotidine reduces pulmonary symptoms in COVID-19 patients, Pulmonary Pharm Therap, doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2020.101942
Hossain, Tang, Akter, Zheng, Roles of the polybasic furin cleavage site of spike protein in SARS-CoV-2 replication, pathogen esis, and host immune responses and vaccination, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27539
Jang, Jeon, Kim, Sy, Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Jia, Neptune, Cui, Targeting ACE2 for COVID-19 therapy: opportunities and challenges, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2023.09.020
Kaku, Okumura, Padilla-Blanco, Kosugi, Uriu et al., Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 variant, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1128/cmr.00014-22
Konrat, Papp, Kimpel, Rössler, Szijártó et al., The anti-histamine azelastine, identified by computa tional drug repurposing, inhibits infection by major variants of SARS-CoV-2 in cell cultures and reconstituted human nasal tissue, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01878-5
Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Lempp, Soriaga, Montiel-Ruiz, Benigni, Noack et al., Lectins enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection and influence neutralizing antibodies, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03925-1
Li, Hilgenfeld, Whitley, Clercq, Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned, Nat Rev Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Li, Zhang, Li, Zhai, Li et al., The role of SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a in autophagy flux disruption: implications for viral infection and pathogenesis, Autophagy, doi:10.1080/15548627.2024.2312787
Liang, Wang, Wang, Li, Meng et al., When 3D genome technology meets viral infection, including SARS-CoV-2, J Med Virol, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Liang, Xiao, Wu, Lv, Liu et al., Phenothia zines inhibit SARS-CoV-2 entry through targeting spike protein, Viruses, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Mashauri, COVID-19 Histamine theory: why antihistamines should be incorporated as the basic component in COVID-19 manage ment?, Health Sci Rep, doi:10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.12.016
Melano, Cheng, Kuo, Liu, Chou et al., A disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain 9 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells with low ACE2 expression, Microbiol Spectr, doi:10.1128/spectrum.03854-22
Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Goonawardane, Saito et al., Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x
Mirabelli, Wotring, Zhang, Mccarty, Fursmidt et al., Morphological cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies, Research Article mBio Month, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Okayama, Baraniuk, Hausfeld, Merida, Kaliner, Characterization and autoradiographic localization of histamine H1 receptors in human nasal turbinates, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01878-5
Parsons, Ganellin, Histamine and its receptors, Br J Pharmacol, doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706440
Pinto, Lambert, Downs, Abrahim, Hughes et al., Antihistamines for postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Nurse Pract, doi:10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.12.016
Reznikov, Norris, Vashisht, Bluhm, Li et al., Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01878-5
Riva, Yuan, Yin, Martin-Sancho, Matsunaga et al., Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1
Salvucci, Codella, Coppola, Zacchei, Grassi et al., Antihistamines improve cardiovascular manifestations and other symptoms of long-COVID attributed to mast cell activation, Front Cardiovasc Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2023.1202696
Schafer, Cheng, Xiong, Soloveva, Retterer et al., Repurposing potential of 1st generation H1specific antihistamines as anti-filovirus therapeutics, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016
Shang, Ye, Shi, Wan, Luo et al., Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Taylor, Adams, Hufford, De La Torre, Winthrop et al., Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Togias, H1-receptors: localization and role in airway physiology and in immune functions, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01878-5
Travi, Current status of antihistamine drugs repurposing for infectious diseases, Med Drug Dis, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Walsh, Annunziato, Frossard, Knol, Levander et al., New insights into the second generation antihistamines, Drugs, doi:10.2165/00003495-200161020-00006
Wang, Chen, Zhang, Deng, Lian et al., CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x
Wang, Qiu, Hou, Deng, Xu et al., AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-00460-y
Wei, Wan, Yan, Wang, Zhang et al., HDL-scavenger receptor B type 1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry, Nat Metab, doi:10.1038/s42255-020-00324-0
Wrapp, Wang, Corbett, Goldsmith, Hsieh et al., Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation, Science, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Wu, Zhao, Yu, Chen, Song et al., A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature, doi:10.1128/cmr.00014-22
Xu, Xia, Pu, Wang, Li et al., The antihistamine drugs carbinoxamine maleate and chlorpheniramine maleate exhibit potent antiviral activity against a broad spectrum of influenza viruses, Front Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016
Yang, Du, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: a key target for eliciting persistent neutralizing antibodies, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Yang, Pei, Li, Ma, Zhou et al., Identification of SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors among already approved drugs, Acta Pharmacol Sin, doi:10.1038/s41401-020-00556-6
Yang, Yu, Xu, Jian, Song et al., Fast evolution of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 to JN.1 under heavy immune pressure, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1128/cmr.00014-22
Yang, Zhang, Zeng, Chen, Chen et al., Kidney injury molecule-1 is a potential receptor for SARS-CoV-2, J Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjab003
Yu, Pan, Huang, Ying, Liu et al., Glycopeptide antibiotic teicoplanin inhibits cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 by suppressing the proteolytic activity of cathepsin L, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.884034
Yu, Wang, Liu, Zhai, Xue et al., Host antiviral factors hijack furin to block SARS-CoV-2, ebola virus, and HIV-1 glycoproteins cleavage, Emerging Micro Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2022.2164742
Zhao, Yang, Yang, Zhang, Huang et al., Cathepsin L plays a key role in SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and humanized mice and is a promising target for new drug development, Sig Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00558-8
Zhou, Møhlenberg, Thakor, Tuli, Wang et al., Sensitivity to vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and viral entry inhibitors and advances to counter the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Clin Microbiol Rev, doi:10.1128/cmr.00014-22
Zhou, Pan, Zhang, Li, Zhang et al., Glycopeptide antibiotics potently inhibit cathepsin L in the late endosome/lysosome and block the entry of Ebola virus, middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), J Biol Chem, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature, doi:10.1128/cmr.00014-22
Zhu, Liu, Zhou, Zhang, Xiao et al., Genome-wide CRISPR activation screen identifies candidate receptors for SARS-CoV-2 entry, Sci China Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s11427-021-1990-5
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song et al., A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.01088-24",
"ISSN": [
"2150-7511"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01088-24",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title/>\n <jats:p>Numerous host factors, in addition to human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2), have been identified as coreceptors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), demonstrating broad viral tropism and diversified druggable potential. We and others have found that antihistamine drugs, particularly histamine receptor H1 (HRH1) antagonists, potently inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection. In this study, we provided compelling evidence that HRH1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2 by directly binding to the viral spike protein. HRH1 also synergistically enhanced hACE2-dependent viral entry by interacting with hACE2. Antihistamine drugs effectively prevent viral infection by competitively binding to HRH1, thereby disrupting the interaction between the spike protein and its receptor. Multiple inhibition assays revealed that antihistamine drugs broadly inhibited the infection of various SARS-CoV-2 mutants with an average IC50 of 2.4 µM. The prophylactic function of these drugs was further confirmed by authentic SARS-CoV-2 infection assays and humanized mouse challenge experiments, demonstrating the therapeutic potential of antihistamine drugs for combating coronavirus disease 19.</jats:p>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>IMPORTANCE</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In addition to human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can utilize alternative cofactors to facilitate viral entry. In this study, we discovered that histamine receptor H1 (HRH1) not only functions as an independent receptor for SARS-CoV-2 but also synergistically enhances ACE2-dependent viral entry by directly interacting with ACE2. Further studies have demonstrated that HRH1 facilitates the entry of SARS-CoV-2 by directly binding to the N-terminal domain of the spike protein. Conversely, antihistamine drugs, primarily HRH1 antagonists, can competitively bind to HRH1 and thereby prevent viral entry. These findings revealed that the administration of repurposable antihistamine drugs could be a therapeutic intervention to combat coronavirus disease 19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/mbio.01088-24"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-04-09"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-05-29"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-07-02"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Institute, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Fei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Human Virology, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Xiaoqing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Institute, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Ou",
"given": "Hailan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Systems Medicine for Inflammatory Diseases, Shenzhen Campus of Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xinyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Systems Medicine for Inflammatory Diseases, Shenzhen Campus of Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Ruxin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Institute, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
},
{
"name": "School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Lv",
"given": "Xi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Xiao",
"given": "Shiqi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Breast Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Meilin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, National Clinical Research Center for Respiratory Disease, Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Liang",
"given": "Taizhen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, National Clinical Research Center for Respiratory Disease, Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Tao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Xuepeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Zhenglai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
},
{
"name": "School of Biology and Biological Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Sen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Han",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Yiqiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathogen Biology, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang, Liaoning, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Guangyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Tu",
"given": "Tianyong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Peiwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3620-610X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Human Virology, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7106-7312",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Systems Medicine for Inflammatory Diseases, Shenzhen Campus of Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Ting",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4934-4221",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Institute, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
},
{
"name": "Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou International Bio-Island, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, National Clinical Research Center for Respiratory Disease, Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Xiancai",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "mBio",
"container-title-short": "mBio",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-02T13:01:31Z",
"timestamp": 1719925291000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-02T13:02:25Z",
"timestamp": 1719925345000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Chunfu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"SRPG22-006, SRPG22-002"
],
"name": "R&D Programs of Guangzhou National Laboratory"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100021171",
"award": [
"2024B1515020068"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82102385"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"KJ012019376"
],
"name": "Talent Research Funding from Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital"
},
{
"award": [
"2022YFC0870700"
],
"name": "National Key R&D Program of Department of Science and Technology of China"
},
{
"award": [
"92169201"
],
"name": "Important Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82102367"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100021171",
"award": [
"2022A1515012422"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81971918"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100021171",
"award": [
"2022A1515011038"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation"
},
{
"award": [
"ZDSYS20220606100803007"
],
"name": "Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Systems Medicine for Inflammatory diseases"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82304574"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"2022-MS-409"
],
"name": "辽宁省科学技术厅 | Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province"
},
{
"award": [
"RC210215"
],
"name": "Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shenyang"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-03T00:21:08Z",
"timestamp": 1719966068958
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1719878400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1719878400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.01088-24",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.01088-24",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_2_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00813-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00744-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27588",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/cmr.00014-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2164742",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27539",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00558-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2022.884034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2024.2312787",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.20209610",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-020-00324-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd3072",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03925-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2022.105463",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/spectrum.03854-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.22.165803",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-00460-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jmcb/mjab003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-021-00595-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11427-021-1990-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/rcmb.2020-0322PS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2023.09.020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-020-00556-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.202110239",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108959",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.861295",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0006-2952(85)90347-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0091-6749(92)90298-g",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI26150",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01878-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0706440",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003495-200161020-00006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2105815118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_44_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30004-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_45_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_46_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_47_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2507",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_48_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00523-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_49_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003495-200565030-00004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_50_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_51_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_52_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00542-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_53_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23328-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_54_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2024302118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_55_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M116.716100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_56_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15081666",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_57_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105481",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_58_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100140",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_59_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.3010286",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_60_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2018.02643",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_61_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.07.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_62_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23812/20-2EDIT",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_63_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_64_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pupt.2020.101942",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_65_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pupt.2021.101989",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_66_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15772",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_67_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101874",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_68_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hsr2.1109",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_69_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.12.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_70_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2023.1202696",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_71_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 70,
"references-count": 70,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mbio.01088-24"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The histamine receptor H1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page"
}