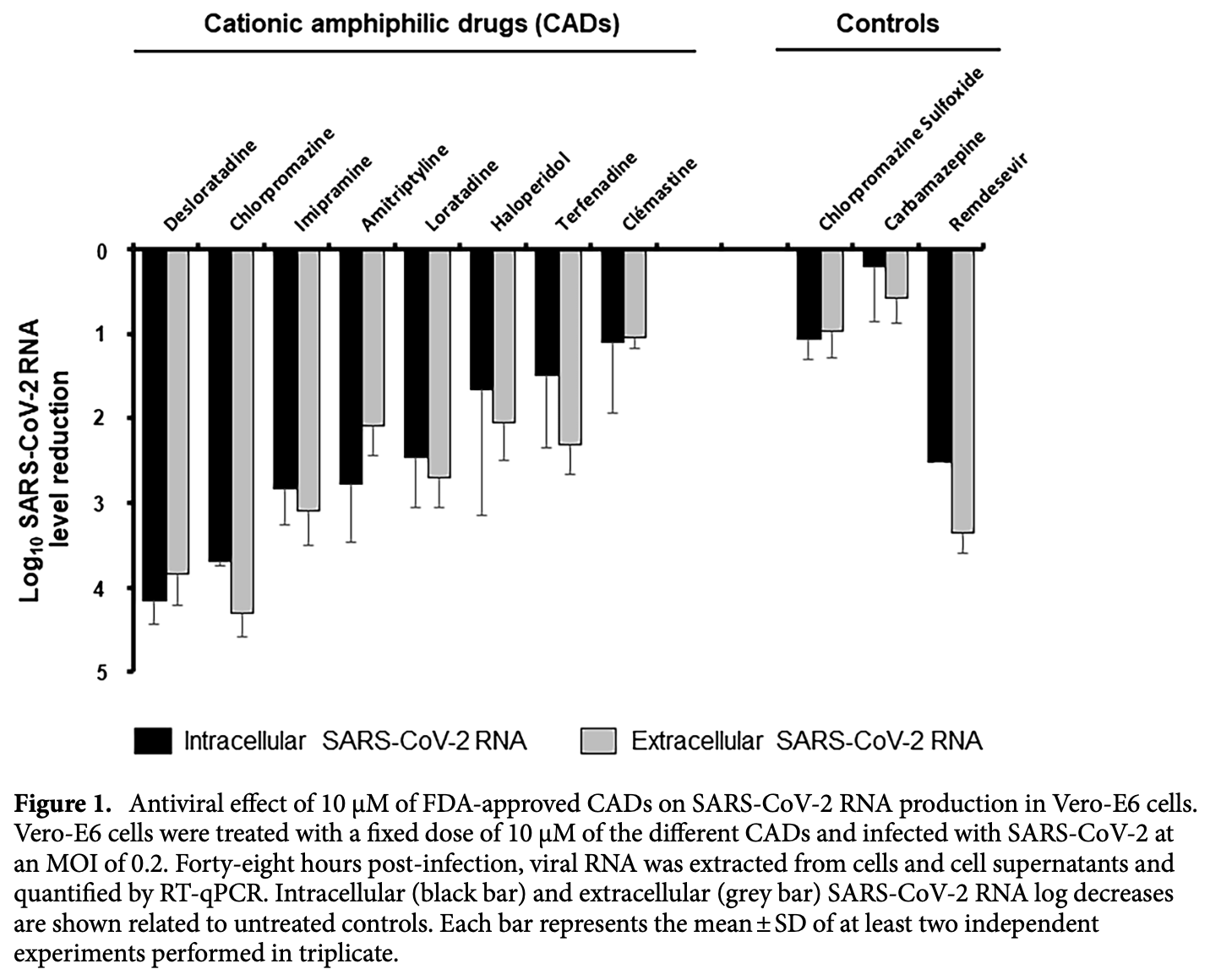
Desloratadine, an FDA-approved cationic amphiphilic drug, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in cell culture and primary human nasal epithelial cells by blocking viral entry
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25399-5, Dec 2022
11th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000052 from 17 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro study showing that desloratadine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero E6 cells, Calu-3 cells, and primary human nasal epithelial cells (HNECs) by blocking viral entry through the endosomal pathway. Authors screened 8 FDA-approved cationic amphiphilic drugs (CADs) and found that desloratadine was the most potent, with an EC50 of 0.7-0.9 μM. Desloratadine also inhibited the related coronaviruses HCoV-229E and HCoV-OC43, suggesting broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus activity. Time-of-addition experiments showed that desloratadine targets an early step of the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle. In primary HNECs, desloratadine treatment significantly delayed viral RNA production, with maximal reduction after 72 hours. The results suggest desloratadine could potentially contribute to COVID-19 prophylaxis and therapy.
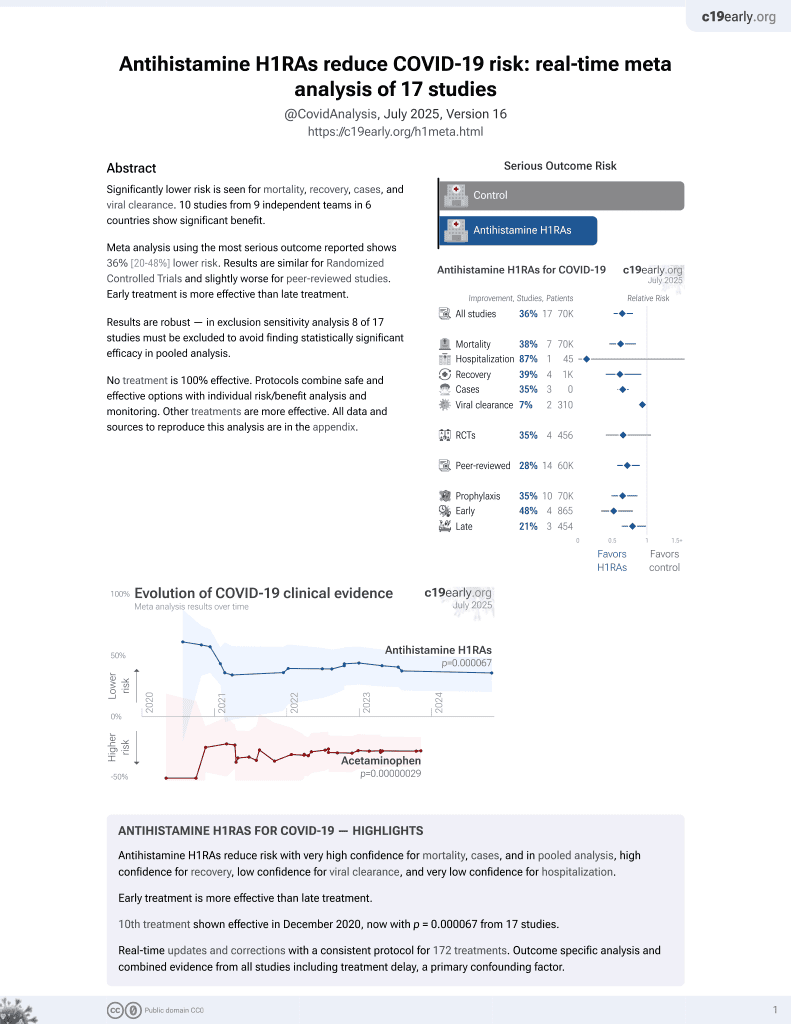
13 preclinical studies support the efficacy of antihistamine H1RAs for COVID-19:
1.
Hamdan et al., In silico Evaluation of H1-Antihistamine as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase: Repurposing Study of COVID-19 Therapy, Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.4274/tjps.galenos.2024.49768.
2.
Elshaier et al., Chlorpheniramine Maleate Displaying Multiple Modes of Antiviral Action Against SARS-CoV-2: An Initial Mechanistic Study, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.92375.
3.
Black, S., Molecular Modeling and Preliminary Clinical Data Suggesting Antiviral Activity for Chlorpheniramine (Chlorphenamine) Against COVID-19, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.20980.
4.
Hou et al., Testing of the inhibitory effects of loratadine and desloratadine on SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudotyped virus viropexis, Chemico-Biological Interactions, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109420.
5.
Yu et al., The histamine receptor H1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01088-24.
6.
Sanchez-Gonzalez et al., Intranasal Chlorpheniramine Maleate for the treatment of COVID-19: Translational and Clinical Evidence, Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v10i3.2752.
7.
Morin-Dewaele et al., Desloratadine, an FDA-approved cationic amphiphilic drug, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in cell culture and primary human nasal epithelial cells by blocking viral entry, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25399-5.
8.
Reznikov et al., Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095.
Morin-Dewaele et al., 6 Dec 2022, France, peer-reviewed, 18 authors.
Contact: hakim.ahmed-belkacem@inserm.fr.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Desloratadine, an FDA-approved cationic amphiphilic drug, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in cell culture and primary human nasal epithelial cells by blocking viral entry
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25399-5
The 2019 global coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has brought the world to a grinding halt, highlighting the urgent need for therapeutic and preventive solutions to slow the spread of emerging viruses. The objective of this study was to assess the anti-SARS-CoV-2 effectiveness of 8 FDAapproved cationic amphiphilic drugs (CADs). SARS-CoV-2-infected Vero cells, Calu-3 cells and primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells (HNEC) were used to investigate the effects of CADs and revealed their antiviral mode of action. Among the CADs tested, desloratadine, a commonly used antiallergic, welltolerated with no major side effects, potently reduced the production of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Vero-E6 cells. Interestingly, desloratadine was also effective against HCoV-229E and HCoV-OC43 showing that it possessed broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus activity. Investigation of its mode of action revealed that it targeted an early step of virus lifecycle and blocked SARS-CoV-2 entry through the endosomal pathway. Finally, the ex vivo kinetic of the antiviral effect of desloratadine was evaluated on primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells (HNEC), showing a significant delay of viral RNA production with a maximal reduction reached after 72 h of treatment. Thus, this treatment could provide a substantial contribution to prophylaxis and systemic therapy of COVID-19 or other coronaviruses infections and requires further studies. Coronaviruses are a group of enveloped positive-sense RNA viruses. Until recently, most human infections were caused by four human coronaviruses (HCoV) inducing benign respiratory tract diseases, including HCoV-OC43, HCoV-229E, HCoV-NL63 and HKU1. In the last two decades, three zoonotic coronaviruses capable to induce severe lung disease with moderate to high lethality rates have emerged in human populations. The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) emerged in 2003 in China and caused a self-limiting outbreak 1 . In 2012, the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) emerged in Saudi Arabia. This virus is rarely transmitted between humans, but has a very high lethality rate 2 . Lastly, the SARS-CoV-2, a hitherto unknown member of the Orthocoronavirinae subfamily, emerged in december 2019 in China and rapidly spread OPEN
Author contributions M.M-D.: acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data; participation in the drafting of the manuscript. S.B.: contribution to the experimental design of experiments on primary nasal epithelial cells and acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data, participation in the drafting of the manuscript. F.B.: acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data. R.B. and D.L-M.: acquisition and analysis of data. C.T.N., P.M., K.S.: acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of histologic data. Q.N., L.S., J-M.V., B.L., J-M.P., A.C.: critical revision of the manuscript. E.B.: contribution to the experimental design of primary nasal epithelial, critical revision of the manuscript. P.B.: data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the manuscript. S.J., A.A-B.: study supervision; analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content.
Competing interests J-M.P. has served as an advisor and/or speaker for Abbvie, Gilead, Merck, Regulus, Assembly Biosciences, Arbutus and Memo Therapeutics. A.C. has participated in advisory boards for ALK, GSK and Sanofi. The rest of the authors have no competing interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1038/ s41598-022-25399-5.
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Reprints and permissions..
References
Agrawal, Pharmacology and clinical efficacy of desloratadine as an anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory drug, Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs
Ahn, Nasal ciliated cells are primary targets for SARS-CoV-2 replication in the early stage of COVID-19, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI148517
Ashoor, The contribution of lysosomotropism to autophagy perturbation, PLoS ONE
Bertram, TMPRSS2 activates the human coronavirus 229E for cathepsin-independent host cell entry and is expressed in viral target cells in the respiratory epithelium, J. Virol
Blaess, COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 infection: Lysosomes and lysosomotropism implicate new treatment strategies and personal risks, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Carpinteiro, Pharmacological inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase prevents uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by epithelial cells, Cell Rep. Med
Coste, Inflammatory cells as well as epithelial cells in nasal polyps express vascular endothelial growth factor, Eur. Respir. J
De Duve, Lysosomotropic agents, Biochem. Pharmacol
Drosten, Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome, N. Engl. J. Med
Edwards, Swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus replication in primary human cells reveals potential susceptibility to infection, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci
Fritz, Association between antidepressant use and ED or hospital visits in outpatients with SARS-CoV-2, Transl. Psychiatry
Funk, Krise, Cationic amphiphilic drugs cause a marked expansion of apparent lysosomal volume: Implications for an intracellular distribution-based drug interaction, Mol. Pharm
Glebov, Understanding SARS-CoV-2 endocytosis for COVID-19 drug repurposing, FEBS J
Halliwell, Cationic amphiphilic drug-induced phospholipidosis, Toxicol. Pathol
Hoertel, Association between FIASMAs and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals hospitalized for severe COVID-19: An observational multicenter study, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther
Hoertel, Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: Results from an observational study, Mol. Psychiatry
Hoffmann, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Kleine-Weber, Functional analysis of potential cleavage sites in the MERS-coronavirus spike protein, Sci. Rep
Koch, TMPRSS2expression dictates the entry route used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect host cells, EMBO J
Kornhuber, Functional Inhibitors of Acid Sphingomyelinase (FIASMAs): A novel pharmacological group of drugs with broad clinical applications, Cell Physiol. Biochem
Lenze, Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Matsuyama, Efficient activation of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein by the transmembrane protease TMPRSS2, J. Virol
Menachery, A SARS-like cluster of circulating bat coronaviruses shows potential for human emergence, Nat. Med
Norinder, Existing highly accumulating lysosomotropic drugs with potential for repurposing to target COVID-19, Biomed. Pharmacother
Nujic, Impairment of lysosomal functions by azithromycin and chloroquine contributes to anti-inflammatory phenotype, Cell Immunol
Okuma, Kishimoto, A history of investigation on the mood stabilizing effect of carbamazepine in Japan, Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci
Ou, Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV, Nat. Commun
Padmanabhan, Desikan, Dixit, Targeting TMPRSS2 and Cathepsin B/L together may be synergistic against SARS-CoV-2 infection, PLoS Comput. Biol
Papon, HLA-DR and ICAM-1 expression and modulation in epithelial cells from nasal polyps, Laryngoscope
Plaze, Inhibition of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in human cells by the FDA-approved drug chlorpromazine, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents
Plaze, Repurposing chlorpromazine to treat COVID-19: The reCoVery study, Encephale
Pollack, Latest outbreak news from ProMED-mail: Novel coronavirus-Middle east, Int. J. Infect. Dis
Schloer, Targeting the endolysosomal host-SARS-CoV-2 interface by clinically licensed functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA) including the antidepressant fluoxetine, Emerg. Microbes Infect
Shang, Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A
Shirato, Kawase, Matsuyama, Wild-type human coronaviruses prefer cell-surface TMPRSS2 to endosomal cathepsins for cell entry, Virology
Softic, Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection by the cyclophilin inhibitor alisporivir (Debio 025), Antimicrob. Agents Chemother
Sungnak, SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes, Nat. Med
Trapp, Quantitative modeling of selective lysosomal targeting for drug design, Eur. Biophys. J
Tummino, Drug-induced phospholipidosis confounds drug repurposing for SARS-CoV-2, Science
Vaugeois, Psychotropics drugs with cationic amphiphilic properties may afford some protection against SARS-CoV-2: A mechanistic hypothesis, Psychiatry Res
Wang, Broad-spectrum coronavirus fusion inhibitors to combat COVID-19 and other emerging coronavirus diseases, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Wang, Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Yang, Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A singlecentered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir. Med
Yu, Glycopeptide Antibiotic Teicoplanin Inhibits Cell Entry of SARS-CoV-2 by Suppressing the Proteolytic Activity of Cathepsin L, Front Microbiol
Zhao, Cathepsin L plays a key role in SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and humanized mice and is a promising target for new drug development, Signal Transduct. Target Ther
Zhu, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-25399-5",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-25399-5",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>The 2019 global coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has brought the world to a grinding halt, highlighting the urgent need for therapeutic and preventive solutions to slow the spread of emerging viruses. The objective of this study was to assess the anti-SARS-CoV-2 effectiveness of 8 FDA-approved cationic amphiphilic drugs (CADs). SARS-CoV-2-infected Vero cells, Calu-3 cells and primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells (HNEC) were used to investigate the effects of CADs and revealed their antiviral mode of action. Among the CADs tested, desloratadine, a commonly used antiallergic, well-tolerated with no major side effects, potently reduced the production of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Vero-E6 cells. Interestingly, desloratadine was also effective against HCoV-229E and HCoV-OC43 showing that it possessed broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus activity. Investigation of its mode of action revealed that it targeted an early step of virus lifecycle and blocked SARS-CoV-2 entry through the endosomal pathway. Finally, the ex vivo kinetic of the antiviral effect of desloratadine was evaluated on primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells (HNEC), showing a significant delay of viral RNA production with a maximal reduction reached after 72 h of treatment. Thus, this treatment could provide a substantial contribution to prophylaxis and systemic therapy of COVID-19 or other coronaviruses infections and requires further studies.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"25399"
],
"article-number": "21053",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "12 January 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "28 November 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "6 December 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "J-M.P. has served as an advisor and/or speaker for Abbvie, Gilead, Merck, Regulus, Assembly Biosciences, Arbutus and Memo Therapeutics. A.C. has participated in advisory boards for ALK, GSK and Sanofi. The rest of the authors have no competing interest."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morin-Dewaele",
"given": "Margot",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartier",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berry",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brillet",
"given": "Rozenn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "López-Molina",
"given": "Dennis Salomón",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyễn",
"given": "Công Trung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maille",
"given": "Pascale",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sereno",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nevers",
"given": "Quentin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Softic",
"given": "Laurent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vaugeois",
"given": "Jean-Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Louis",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bequignon",
"given": "Emilie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0719-0826",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bruscella",
"given": "Patrice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coste",
"given": "André",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0745-7559",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pawlotsky",
"given": "Jean-Michel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamain",
"given": "Stéphane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6489-5091",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ahmed-Belkacem",
"given": "Abdelhakim",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-06T12:46:12Z",
"timestamp": 1670330772000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-09T19:30:55Z",
"timestamp": 1670614255000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003323",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Agence Nationale de Recherches sur le Sida et les Hépatites Virales"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002915",
"award": [
"ANR Flash COVID"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001665",
"award": [
"ANR Flash COVID"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "Agence Nationale de la Recherche"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-09T17:30:50Z",
"timestamp": 1683653450960
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1670284800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1670284800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-25399-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-25399-5",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-25399-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa030747",
"author": "C Drosten",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1967",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "25399_CR1",
"unstructured": "Drosten, C. et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348(20), 1967–1976 (2003).",
"volume": "348",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2012.12.001",
"author": "MP Pollack",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e143",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "25399_CR2",
"unstructured": "Pollack, M. P. et al. Latest outbreak news from ProMED-mail: Novel coronavirus—Middle east. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 17(2), e143–e144 (2013).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"author": "N Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "25399_CR3",
"unstructured": "Zhu, N. et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382(8), 727–733 (2020).",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.3985",
"author": "VD Menachery",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1508",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "25399_CR4",
"unstructured": "Menachery, V. D. et al. A SARS-like cluster of circulating bat coronaviruses shows potential for human emergence. Nat. Med. 21(12), 1508–1513 (2015).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2001046117",
"author": "CE Edwards",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "26915",
"issue": "43",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "25399_CR5",
"unstructured": "Edwards, C. E. et al. Swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus replication in primary human cells reveals potential susceptibility to infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 117(43), 26915–26925 (2020).",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000315101",
"author": "J Kornhuber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Physiol. Biochem.",
"key": "25399_CR6",
"unstructured": "Kornhuber, J. et al. Functional Inhibitors of Acid Sphingomyelinase (FIASMAs): A novel pharmacological group of drugs with broad clinical applications. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 26(1), 9–20 (2010).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113220",
"author": "JM Vaugeois",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "113220",
"journal-title": "Psychiatry Res.",
"key": "25399_CR7",
"unstructured": "Vaugeois, J. M. Psychotropics drugs with cationic amphiphilic properties may afford some protection against SARS-CoV-2: A mechanistic hypothesis. Psychiatry Res. 291, 113220 (2020).",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/mp200641e",
"author": "RS Funk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1384",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Mol. Pharm.",
"key": "25399_CR8",
"unstructured": "Funk, R. S. & Krise, J. P. Cationic amphiphilic drugs cause a marked expansion of apparent lysosomal volume: Implications for an intracellular distribution-based drug interaction. Mol. Pharm. 9(5), 1384–1395 (2012).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0082481",
"author": "R Ashoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e82481",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "25399_CR9",
"unstructured": "Ashoor, R. et al. The contribution of lysosomotropism to autophagy perturbation. PLoS ONE 8(11), e82481 (2013).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.09.007",
"author": "K Nujic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "78",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Immunol.",
"key": "25399_CR10",
"unstructured": "Nujic, K. et al. Impairment of lysosomal functions by azithromycin and chloroquine contributes to anti-inflammatory phenotype. Cell Immunol. 279(1), 78–86 (2012).",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21144953",
"author": "M Blaess",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4953",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "25399_CR11",
"unstructured": "Blaess, M. et al. COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 infection: Lysosomes and lysosomotropism implicate new treatment strategies and personal risks.\nInt. J. Mol. Sci. 21(14), 4953 (2020).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15369",
"author": "OO Glebov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3664",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "25399_CR12",
"unstructured": "Glebov, O. O. Understanding SARS-CoV-2 endocytosis for COVID-19 drug repurposing. FEBS J. 287(17), 3664–3671 (2020).",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1829082",
"author": "S Schloer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2245",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "25399_CR13",
"unstructured": "Schloer, S. et al. Targeting the endolysosomal host-SARS-CoV-2 interface by clinically licensed functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA) including the antidepressant fluoxetine. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 9(1), 2245–2255 (2020).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110582",
"author": "U Norinder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110582",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "25399_CR14",
"unstructured": "Norinder, U. et al. Existing highly accumulating lysosomotropic drugs with potential for repurposing to target COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 130, 110582 (2020).",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"author": "M Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "271",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "25399_CR15",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 181(2), 271-280e8 (2020).",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9",
"author": "X Ou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1620",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "25399_CR16",
"unstructured": "Ou, X. et al. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 1620 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00558-8",
"author": "MM Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "134",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target Ther.",
"key": "25399_CR17",
"unstructured": "Zhao, M. M. et al. Cathepsin L plays a key role in SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and humanized mice and is a promising target for new drug development. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6(1), 134 (2021).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1517/13543784.10.3.547",
"author": "DK Agrawal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "547",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs",
"key": "25399_CR18",
"unstructured": "Agrawal, D. K. Pharmacology and clinical efficacy of desloratadine as an anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory drug. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 10(3), 547–560 (2001).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.15b24.x",
"author": "A Coste",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "367",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "25399_CR19",
"unstructured": "Coste, A. et al. Inflammatory cells as well as epithelial cells in nasal polyps express vascular endothelial growth factor. Eur. Respir. J. 15(2), 367–372 (2000).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005537-200211000-00030",
"author": "JF Papon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2067",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Laryngoscope",
"key": "25399_CR20",
"unstructured": "Papon, J. F. et al. HLA-DR and ICAM-1 expression and modulation in epithelial cells from nasal polyps. Laryngoscope 112(11), 2067–2075 (2002).",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00876-20",
"author": "L Softic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e00876",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "25399_CR21",
"unstructured": "Softic, L. et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection by the cyclophilin inhibitor alisporivir (Debio 025). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 64(7), e00876-e920 (2020).",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1440-1819.1998.tb00966.x",
"author": "T Okuma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci.",
"key": "25399_CR22",
"unstructured": "Okuma, T. & Kishimoto, A. A history of investigation on the mood stabilizing effect of carbamazepine in Japan. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 52(1), 3–12 (1998).",
"volume": "52",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"author": "M Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "269",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "25399_CR23",
"unstructured": "Wang, M. et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 30(3), 269–271 (2020).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2021107821",
"author": "J Koch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e107821",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "25399_CR24",
"unstructured": "Koch, J. et al. TMPRSS2 \nexpression dictates the entry route used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect host cells. EMBO J. 40(16), e107821 (2021).",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"author": "X Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "475",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "25399_CR25",
"unstructured": "Yang, X. et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 8(5), 475–481 (2020).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01542-10",
"author": "S Matsuyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12658",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "25399_CR26",
"unstructured": "Matsuyama, S. et al. Efficient activation of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein by the transmembrane protease TMPRSS2. J. Virol. 84(24), 12658–12664 (2010).",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2003138117",
"author": "J Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11727",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.",
"key": "25399_CR27",
"unstructured": "Shang, J. et al. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117(21), 11727–11734 (2020).",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21113843",
"author": "X Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3843",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "25399_CR28",
"unstructured": "Wang, X. et al. Broad-spectrum coronavirus fusion inhibitors to combat COVID-19 and other emerging coronavirus diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21(11), 3843 (2020).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008461",
"author": "P Padmanabhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1008461",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "PLoS Comput. Biol.",
"key": "25399_CR29",
"unstructured": "Padmanabhan, P., Desikan, R. & Dixit, N. M. Targeting TMPRSS2 and Cathepsin B/L together may be synergistic against SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS Comput. Biol. 16(12), e1008461 (2020).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2022.884034",
"author": "F Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "884034",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol.",
"key": "25399_CR30",
"unstructured": "Yu, F., et al. Glycopeptide Antibiotic Teicoplanin Inhibits Cell Entry of SARS-CoV-2 by Suppressing the Proteolytic Activity of Cathepsin L. Front Microbiol. 13, 884034 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.03372-12",
"author": "S Bertram",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6150",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "25399_CR31",
"unstructured": "Bertram, S. et al. TMPRSS2 activates the human coronavirus 229E for cathepsin-independent host cell entry and is expressed in viral target cells in the respiratory epithelium. J. Virol. 87(11), 6150–6160 (2013).",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2017.11.012",
"author": "K Shirato",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "25399_CR32",
"unstructured": "Shirato, K., Kawase, M. & Matsuyama, S. Wild-type human coronaviruses prefer cell-surface TMPRSS2 to endosomal cathepsins for cell entry. Virology 517, 9–15 (2018).",
"volume": "517",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-34859-w",
"author": "H Kleine-Weber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16597",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "25399_CR33",
"unstructured": "Kleine-Weber, H. et al. Functional analysis of potential cleavage sites in the MERS-coronavirus spike protein. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 16597 (2018).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/019262339702500111",
"author": "WH Halliwell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "53",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Toxicol. Pathol.",
"key": "25399_CR34",
"unstructured": "Halliwell, W. H. Cationic amphiphilic drug-induced phospholipidosis. Toxicol. Pathol. 25(1), 53–60 (1997).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9",
"author": "C de Duve",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2495",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharmacol.",
"key": "25399_CR35",
"unstructured": "de Duve, C. et al. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23(18), 2495–2531 (1974).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "1974"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00249-008-0338-4",
"author": "S Trapp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1317",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Eur. Biophys. J.",
"key": "25399_CR36",
"unstructured": "Trapp, S. et al. Quantitative modeling of selective lysosomal targeting for drug design. Eur. Biophys. J. 37(8), 1317–1328 (2008).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abi4708",
"author": "TA Tummino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "541",
"issue": "6554",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "25399_CR37",
"unstructured": "Tummino, T. A. et al. Drug-induced phospholipidosis confounds drug repurposing for SARS-CoV-2. Science 373(6554), 541–547 (2021).",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142",
"author": "A Carpinteiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100142",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "25399_CR38",
"unstructured": "Carpinteiro, A. et al. Pharmacological inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase prevents uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by epithelial cells. Cell Rep. Med. 1(8), 100142 (2020).",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI148517",
"author": "JH Ahn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e148517",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest.",
"key": "25399_CR39",
"unstructured": "Ahn, J.H., et al. Nasal ciliated cells are primary targets for SARS-CoV-2 replication in the early stage of COVID-19. J Clin Invest. 131(13), e148517. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI148517 (2021).",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6",
"author": "W Sungnak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "681",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "25399_CR40",
"unstructured": "Sungnak, W. et al. SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes. Nat. Med. 26(5), 681–687 (2020).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.encep.2020.05.006",
"author": "M Plaze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "169",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Encephale",
"key": "25399_CR41",
"unstructured": "Plaze, M. et al. Repurposing chlorpromazine to treat COVID-19: The reCoVery study. Encephale 46(3), 169–172 (2020).",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4",
"author": "N Hoertel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5199",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Mol. Psychiatry",
"key": "25399_CR42",
"unstructured": "Hoertel, N. et al. Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: Results from an observational study. Mol. Psychiatry 26(9), 5199–5212 (2021).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106274",
"author": "M Plaze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106274",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents",
"key": "25399_CR43",
"unstructured": "Plaze, M. et al. Inhibition of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in human cells by the FDA-approved drug chlorpromazine. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 57(3), 106274 (2021).",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"author": "EJ Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2292",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "25399_CR44",
"unstructured": "Lenze, E. J. et al. Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 324(22), 2292–2300 (2020).",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2317",
"author": "N Hoertel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1498",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "25399_CR45",
"unstructured": "Hoertel, N. et al. Association between FIASMAs and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals hospitalized for severe COVID-19: An observational multicenter study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 110(6), 1498–1511 (2021).",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41398-022-02109-3",
"author": "BA Fritz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "341",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl. Psychiatry",
"key": "25399_CR46",
"unstructured": "Fritz, B. A. et al. Association between antidepressant use and ED or hospital visits in outpatients with SARS-CoV-2. Transl. Psychiatry 12(1), 341 (2022).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 46,
"references-count": 46,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-25399-5"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Desloratadine, an FDA-approved cationic amphiphilic drug, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in cell culture and primary human nasal epithelial cells by blocking viral entry",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "12"
}