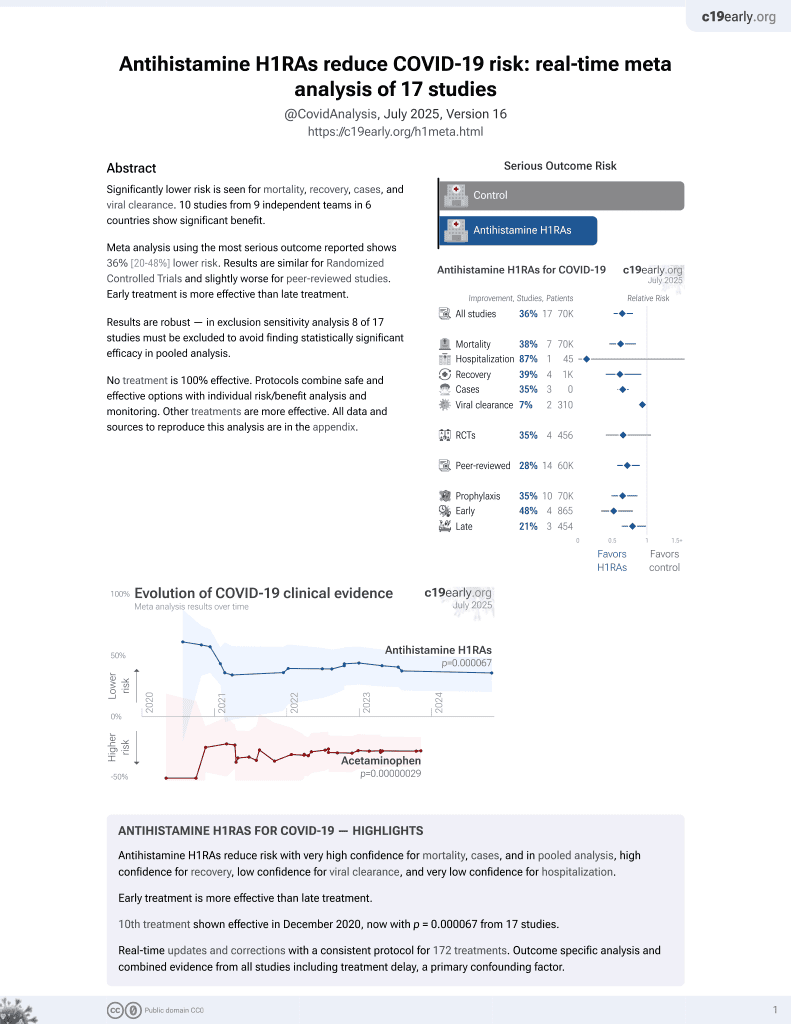
Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing
et al., Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095, Jan 2021
11th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000052 from 17 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
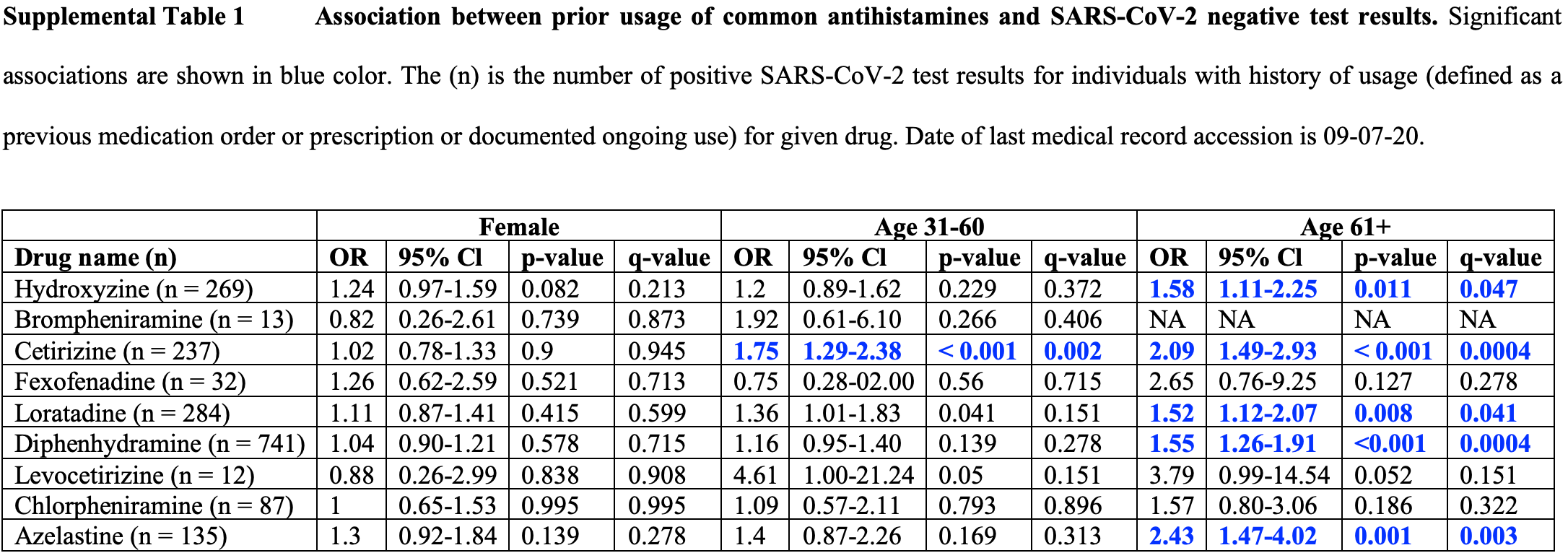
Retrospective 219,000 patients showing lower risk of COVID-19 with antihistamine H1RA use.
In vitro study showing these drugs exhibit direct antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2. Molecular docking suggests hydroxyzine and azelastine may exert antiviral effects by binding ACE2 and the sigma-1 receptor.
13 preclinical studies support the efficacy of antihistamine H1RAs for COVID-19:
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments11.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers azelastine and antihistamine H1RAs.
|
risk of case, 34.0% lower, RR 0.66, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, all medications and age groups combined.
|
|
risk of case, 36.7% lower, OR 0.63, p = 0.01, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, hydroxyzine, 61+, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 16.7% lower, OR 0.83, p = 0.24, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, hydroxyzine, 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 47.9% lower, OR 0.52, p = 0.27, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, brompheniramine , 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 52.2% lower, OR 0.48, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, cetirizine, 61+, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 42.9% lower, OR 0.57, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, cetirizine, 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 62.3% lower, OR 0.38, p = 0.13, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, fexofenadine, 61+, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 33.3% higher, OR 1.33, p = 0.58, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, fexofenadine, 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 34.2% lower, OR 0.66, p = 0.008, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, loratadine, 61+, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 26.5% lower, OR 0.74, p = 0.04, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, loratadine, 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 35.5% lower, OR 0.65, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, diphenhydramine, 61+, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 13.8% lower, OR 0.86, p = 0.13, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, diphenhydramine, 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 73.6% lower, OR 0.26, p = 0.05, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, levocetirizine, 61+, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 78.3% lower, OR 0.22, p = 0.0496, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, levocetirizine, 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 36.3% lower, OR 0.64, p = 0.19, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, chlorpheniramine, 61+, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 8.3% lower, OR 0.92, p = 0.81, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, chlorpheniramine, 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 58.8% lower, OR 0.41, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, azelastine, 61+, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 28.6% lower, OR 0.71, p = 0.17, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, azelastine, 31-60, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Hamdan et al., In silico Evaluation of H1-Antihistamine as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase: Repurposing Study of COVID-19 Therapy, Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.4274/tjps.galenos.2024.49768.
2.
Elshaier et al., Chlorpheniramine Maleate Displaying Multiple Modes of Antiviral Action Against SARS-CoV-2: An Initial Mechanistic Study, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.92375.
3.
Black, S., Molecular Modeling and Preliminary Clinical Data Suggesting Antiviral Activity for Chlorpheniramine (Chlorphenamine) Against COVID-19, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.20980.
4.
Hou et al., Testing of the inhibitory effects of loratadine and desloratadine on SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudotyped virus viropexis, Chemico-Biological Interactions, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109420.
5.
Yu et al., The histamine receptor H1 acts as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01088-24.
6.
Sanchez-Gonzalez et al., Intranasal Chlorpheniramine Maleate for the treatment of COVID-19: Translational and Clinical Evidence, Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v10i3.2752.
7.
Morin-Dewaele et al., Desloratadine, an FDA-approved cationic amphiphilic drug, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in cell culture and primary human nasal epithelial cells by blocking viral entry, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25399-5.
8.
Reznikov et al., Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095.
9.
Rivas et al., Hydroxyzine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein binding to ACE2 in a qualitative in vitro assay, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.01.04.424792.
Reznikov et al., 31 Jan 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095
a b s t r a c t There is an urgent need to identify therapies that prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and improve the outcome of COVID-19 patients. Although repurposed drugs with favorable safety profiles could have significant benefit, widely available prevention or treatment options for COVID-19 have yet to be identified. Efforts to identify approved drugs with in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2 resulted in identification of antiviral sigma-1 receptor ligands, including antihistamines in the histamine-1 receptor binding class. We identified antihistamine candidates for repurposing by mining electronic health records of usage in population of more than 219,000 subjects tested for SARS-CoV-2. Usage of diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine and azelastine was associated with reduced incidence of SARS-CoV-2 positivity in subjects greater than age 61. We found diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine and azelastine to exhibit direct antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Although mechanisms by which specific antihistamines exert antiviral effects is not clear, hydroxyzine, and possibly azelastine, bind Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) and the sigma-1 receptor as off-targets. Clinical studies are needed to measure the effectiveness of diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine and azelastine for disease prevention, for early intervention, or as adjuvant therapy for severe COVID-19.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data related to this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095.
References
Basile, Paul, Mirchevich, Kuijpers, Costa, Modulation of (þ)-[3H]pentazocine binding to Guinea pig cerebellum by divalent cations, Mol. Pharmacol
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009575
Blyden, Greenblatt, Scavone, Shader, Pharmacokinetics of diphenhydramine and a demethylated metabolite following intravenous and oral administration, J. Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1986.tb02946.x
Core, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Cottam, Whelband, Wileman, Coronavirus NSP6 restricts autophagosome expansion, Autophagy, doi:10.4161/auto.29309
D'alessandro, Scaccabarozzi, Signorini, The use of antimalarial drugs against viral infection, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8010085
Derendorf, Munzel, Petzold, Bioavailability and disposition of azelastine and fluticasone propionate when delivered by MP29-02, a novel aqueous nasal spray, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04222.x
Dyall, Gross, Kindrachuk, Middle east respiratory syndrome and severe acute respiratory syndrome: current therapeutic options and potential targets for novel therapies, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-017-0830-1
Fouda, Hobbs, Stambaugh, Sensitive assay for determination of hydroxyzine in plasma and its human pharmacokinetics, J. Pharmaceut. Sci
Freedberg, Conigliaro, Wang, Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study, Gastroenterology
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, A SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interaction Map reveals Drug Targets and Potential Drug-repurposing, bioRxiv
Hernandez Prada, Ferreira, Katovich, Structure-based identification of small-molecule angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activators as novel antihypertensive agents, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.108944
Huentelman, Zubcevic, Hernandez Prada, Structure-based discovery of a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibitor, Hypertension
Huentelman, Zubcevic, Hernandez Prada, Structure-based discovery of a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibitor, Hypertension
Joshi, Joshi, Degani, Tackling SARS-CoV-2: proposed targets and repurposed drugs, Future Med. Chem, doi:10.4155/fmc-2020-0147
Klionsky, Abdelmohsen, Abe, Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition), Autophagy, doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1100356
Kulemina, Ostrov, Prediction of off-target effects on angiotensinconverting enzyme 2, J. Biomol. Screen, doi:10.1177/1087057111413919
Liao, Kuan, Guevara, Acid exposure disrupts mucus secretion and impairs mucociliary transport in neonatal piglet airways, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00025.2020
Lieberman-Cribbin, Rapp, Alpert, Tuminello, Taioli, The impact of asthma on mortality in patients with COVID-19, Chest
Liu, Cao, Xu, Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Cell Discov, doi:10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0
Morris, Huey, Lindstrom, AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility, J. Comput. Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.21256
Mossel, Huang, Narayanan, Makino, Tesh et al., Exogenous ACE2 expression allows refractory cell lines to support severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication, J. Virol
Poduri, Joshi, Jagadeesh, Drugs targeting various stages of the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle: exploring promising drugs for the treatment of covid-19, Cell. Signal
Riva, Yuan, Yin, Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1
Rogosnitzky, Berkowitz, Jadad, Delivering benefits at speed through real-world repurposing of off-patent drugs: the COVID-19 pandemic as a case in point, JMIR Public Health Surveill, doi:10.2196/19199
Schmidt, Zheng, Gurpinar, Koehl, Manglik et al., Crystal structure of the human sigma1 receptor, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature17391
Towler, Staker, Prasad, ACE2 X-ray structures reveal a large hinge-bending motion important for inhibitor binding and catalysis, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M311191200
Vincent, Bergeron, Benjannet, Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread, Virol. J
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2762
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095",
"ISSN": [
"0006-291X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095",
"alternative-id": [
"S0006291X20321409"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4074-9070",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Reznikov",
"given": "Leah R.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5285-0432",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Norris",
"given": "Michael H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vashisht",
"given": "Rohit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bluhm",
"given": "Andrew P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Danmeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Yan-Shin J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Ashley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butte",
"given": "Atul J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4696-875X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ostrov",
"given": "David A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications",
"container-title-short": "Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-03T14:44:42Z",
"timestamp": 1607006682000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-23T15:44:28Z",
"timestamp": 1616514268000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-26T21:17:45Z",
"timestamp": 1703625465935
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 69,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0006291X20321409?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0006291X20321409?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "173-179",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.2196/19199",
"article-title": "Delivering benefits at speed through real-world repurposing of off-patent drugs: the COVID-19 pandemic as a case in point",
"author": "Rogosnitzky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "JMIR Public Health Surveill",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Gautret",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105949",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib2",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cell Discov",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib3",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib4",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1743-422X-2-69",
"article-title": "Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread",
"author": "Vincent",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib5",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"author": "Gordon",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib6",
"series-title": "A SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interaction Map reveals Drug Targets and Potential Drug-repurposing",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-017-0830-1",
"article-title": "Middle east respiratory syndrome and severe acute respiratory syndrome: current therapeutic options and potential targets for novel therapies",
"author": "Dyall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1935",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib7",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8010085",
"article-title": "The use of antimalarial drugs against viral infection",
"author": "D’Alessandro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Microorganisms",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib8",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"issue": "6485",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib9",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M311191200",
"article-title": "ACE2 X-ray structures reveal a large hinge-bending motion important for inhibitor binding and catalysis",
"author": "Towler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17996",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib10",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.HYP.0000146120.29648.36",
"article-title": "Structure-based discovery of a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibitor",
"author": "Huentelman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "903",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib11",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.108944",
"article-title": "Structure-based identification of small-molecule angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activators as novel antihypertensive agents",
"author": "Hernandez Prada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1312",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib12",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1087057111413919",
"article-title": "Prediction of off-target effects on angiotensin-converting enzyme 2",
"author": "Kulemina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "878",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Screen",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib13",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4155/fmc-2020-0147",
"article-title": "Tackling SARS-CoV-2: proposed targets and repurposed drugs",
"author": "Joshi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1579",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "Future Med. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib14",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109721",
"article-title": "Drugs targeting various stages of the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle: exploring promising drugs for the treatment of covid-19",
"author": "Poduri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109721",
"journal-title": "Cell. Signal.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib15",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "7816",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib16",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1",
"article-title": "Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing",
"author": "Riva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"article-title": "Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Freedberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.21256",
"article-title": "AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility",
"author": "Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2785",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib19",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature17391",
"article-title": "Crystal structure of the human sigma1 receptor",
"author": "Schmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "527",
"issue": "7600",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib20",
"volume": "532",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2015.1100356",
"article-title": "Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition)",
"author": "Klionsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Autophagy",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib21",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib22",
"series-title": "R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.6.3846-3850.2005",
"article-title": "Exogenous ACE2 expression allows refractory cell lines to support severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication",
"author": "Mossel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3846",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib23",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00025.2020",
"article-title": "Acid exposure disrupts mucus secretion and impairs mucociliary transport in neonatal piglet airways",
"author": "Liao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "L873",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib24",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Modulation of (+)-[3H]pentazocine binding to Guinea pig cerebellum by divalent cations",
"author": "Basile",
"first-page": "882",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Mol. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib25",
"volume": "42",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/auto.29309",
"article-title": "Coronavirus NSP6 restricts autophagosome expansion",
"author": "Cottam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1426",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Autophagy",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib26",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.HYP.0000146120.29648.36",
"article-title": "Structure-based discovery of a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibitor",
"author": "Huentelman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "903",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib27",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jps.2600681134",
"article-title": "Sensitive assay for determination of hydroxyzine in plasma and its human pharmacokinetics",
"author": "Fouda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1456",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Pharmaceut. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib28",
"volume": "68",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/j.1552-4604.1986.tb02946.x",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics of diphenhydramine and a demethylated metabolite following intravenous and oral administration",
"author": "Blyden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "529",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib29",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04222.x",
"article-title": "Bioavailability and disposition of azelastine and fluticasone propionate when delivered by MP29-02, a novel aqueous nasal spray",
"author": "Derendorf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib30",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"article-title": "Severe covid-19",
"author": "Berlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.575",
"article-title": "The impact of asthma on mortality in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Lieberman-Cribbin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095_bib32",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0006291X20321409"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cell Biology",
"Molecular Biology",
"Biochemistry",
"Biophysics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "538"
}