Correlation between metformin use and mortality in acute respiratory failure: a retrospective ICU cohort study
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1584230, Aug 2025
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 1,429 ICU patients with acute respiratory failure showing significantly lower mortality with metformin use.
Yang et al., 26 Aug 2025, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: hliang_1022@163.com, weiweieric0405@163.com.
Correlation between metformin use and mortality in acute respiratory failure: a retrospective ICU cohort study
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1584230
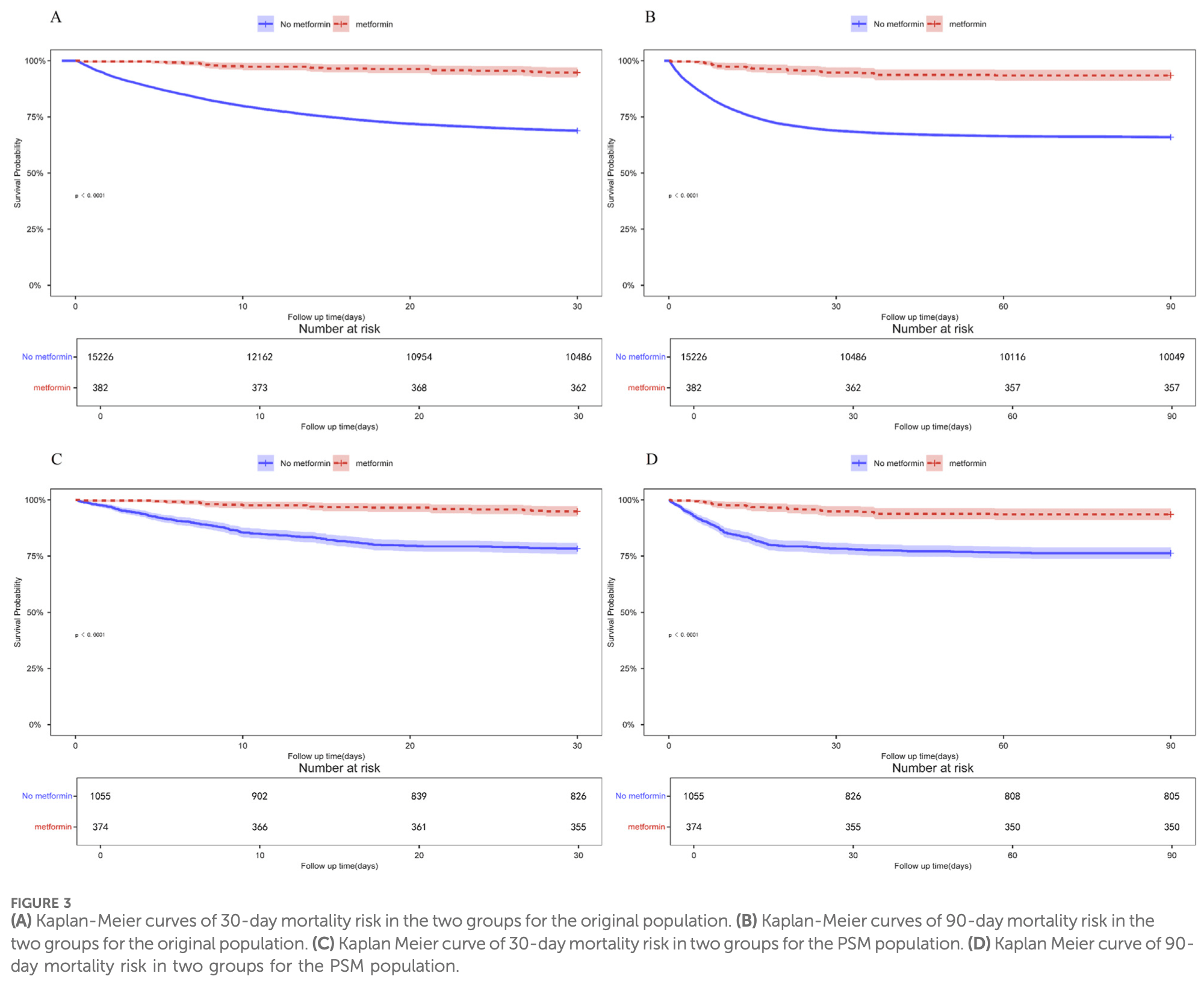
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the association of metformin use with the risk of in-hospital mortality and prognosis in acute respiratory failure (ARF) patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the MIMIC-IV database. Patients were categorized into metformin and non-metformin groups based on medication exposure. Primary outcomes were in-hospital and ICU mortality, while 30-day and 90-day all-cause mortality served as secondary endpoints. We applied Kaplan-Meier survival curves, Cox proportional hazards models, and logistic regression to assess associations. Propensity score matching (PSM) and machine learning algorithms were used for confounder adjustment and feature selection. Results: After PSM, 1,429 patients with ARF were included (374 metformin users; 1,055 non-users). Multivariate logistic regression revealed that metformin use was associated with significantly reduced in-hospital mortality (OR = 0.202, 95% CI: 0.123-0.317, p < 0.001) and ICU mortality (OR = 0.245, 95% CI: 0.142-0.399, p < 0.001). Cox models showed consistent reductions in 30-day (HR = 0.199, 95% CI: 0.124-0.320, p < 0.001) and 90-day (HR = 0.230, 95% CI: 0.150-0.352, p < 0.001) mortality. Kaplan-Meier curves confirmed better survival in the metformin group (p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses supported a consistent protective effect of metformin across most patient strata. Conclusion: Metformin use was significantly associated with decreased shortterm mortality among ICU patients with ARF. These findings suggest that metformin, beyond its glucose-lowering effects, may offer survival benefits in critically ill populations. Clinicians should consider the potential role of metformin when managing ICU patients with type 2 diabetes and ARF. Further prospective studies are warranted to confirm these findings and optimize clinical application strategies.
Author contributions YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writingoriginal draft, Writingreview and editing. JL: Investigation, Software, Writingreview and editing. YH: Supervision, Validation, Writingoriginal draft. YW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Writingreview and editing. LH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writingoriginal draft, Writingreview and editing. WW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writingoriginal draft, Writingreview and editing. expertise and insights greatly contributed to the design and execution of this research. We also thank the developers and maintainers of the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care-IV (MIMIC-IV) database for providing open access to high-quality clinical data, which was essential for the completion of this study.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors..
References
Ali, Prieto-Alhambra, Lopes, Ramos, Bispo et al., Propensity score methods in health technology assessment: principles, extended applications, and recent advances, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00973
Austin, An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies, Multivar. Behav. Res, doi:10.1080/00273171.2011.568786
Azoulay, Mokart, Kouatchet, Demoule, Lemiale, Acute respiratory failure in immunocompromised adults, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(18)30345-x
Bai, Chen, Metformin: a novel weapon against inflammation, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.622262
Bellani, Laffey, Pham, Fan, Brochard et al., Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2016.0291
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hovertsen et al., Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis, Lancet Healthy Longev, doi:10.1016/s2666-7568(20)30033-7
Cameron, Morrison, Levin, Mohan, Forteath et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/circresaha.116.308445
Chowdhury, Islam, Zhou, Hasan, Chowdhury et al., Metformin for covid-19: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, BMJ Med, doi:10.1136/bmjmed-2024-001126
Degenhardt, Seifert, Szymczak, Evaluation of variable selection methods for random forests and omics data sets, Brief. Bioinform, doi:10.1093/bib/bbx124
Diamanti-Kandarakis, Paterakis, Alexandraki, Piperi, Aessopos et al., Indices of low-grade chronic inflammation in polycystic ovary syndrome and the beneficial effect of metformin, Hum. Reprod, doi:10.1093/humrep/del003
Ferguson, Fan, Camporota, Antonelli, Anzueto et al., The Berlin definition of ARDS: an expanded rationale, justification, and supplementary material, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-012-2682-1
Fujishima, Gando, Saitoh, Kushimoto, Ogura et al., Demographics, treatments, and outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome: the focused outcomes research in emergency care in acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and trauma (FORECAST) study, Shock, doi:10.1097/shk.0000000000001416
Fujishima, Guideline-based management of acute respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome, J. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s40560-023-00658-3
Haffner, Temprosa, Crandall, Fowler, Goldberg et al., Intensive lifestyle intervention or metformin on inflammation and coagulation in participants with impaired glucose tolerance, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/diabetes.54.5.1566
Hashimoto, Sanui, Egi, Ohshimo, Shiotsuka et al., The clinical practice guideline for the management of ARDS in Japan, J. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s40560-017-0222-3
Hernán, Dahabreh, Dickerman, Swanson, The target trial framework for causal inference from observational data: why and when is it helpful?, Ann. Intern Med, doi:10.7326/annals-24-01871
Herridge, Cheung, Tansey, Matte-Martyn, Diaz-Granados et al., One-year outcomes in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022450
Isoda, Young, Zirlik, Macfarlane, Tsuboi et al., Metformin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB in human vascular wall cells, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol, doi:10.1161/01.Atv.0000201938.78044.75
Johnson, Bulgarelli, Shen, Gayles, Shammout et al., MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset, Sci. Data, doi:10.1038/s41597-022-01899-x
Khunti, Knighton, Zaccardi, Bakhai, Barron et al., Prescription of glucose-lowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide observational study in England, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00050-4
Kim, Choi, Metformin inhibits inflammatory response via AMPK-PTEN pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.165
Koh, Kim, Kim, Ko, Kim, Anti-inflammatory mechanism of metformin and its effects in intestinal inflammation and colitisassociated Colon cancer, J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1111/jgh.12435
Kristófi, Eriksson, Metformin as an anti-inflammatory agent: a short review, J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/joe-21-0194
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, Goronflot, Wiernsperger et al., Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216
Lamoia, Shulman, Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin action, Endocr. Rev, doi:10.1210/endrev/bnaa023
Li, Yang, Yan, Sun, Zeng et al., Metformin in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666
Liang, Ding, Li, Wang, Kan et al., Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4
Lin, Ao, Guo, Liu, The role and mechanism of metformin in inflammatory diseases, J. Inflamm. Res, doi:10.2147/jir.S436147
Ling, Ponnapa Reddy, Subramaniam, Moran, Ramanathan et al., Epidemiology of acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure in Australian and New Zealand intensive care units during 2005-2022. A binational, registry-based study, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-024-07609-y
Liu, Gao, Wang, Wu, Zhou, Protective effect of metformin on pulmonary fibrosis caused by paraquat through activating AMP-activated protein kinase pathway, Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue, doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230407-00250
Liu, Wu, Zhang, Dai, Huang et al., Metformin attenuated endotoxin-induced acute myocarditis via activating AMPK, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.04.002
Lu, Yu, Meng, Shi, Huang et al., MicroRNAs: important regulatory molecules in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23105545
Lukito, Pranata, Henrina, Lim, Lawrensia et al., The effect of metformin consumption on mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006
Lund, Tarnow, Stehouwer, Schalkwijk, Teerlink et al., Impact of metformin versus repaglinide on non-glycaemic cardiovascular risk markers related to inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes, Eur. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/eje-07-0815
Lundberg, Erion, Chen, Degrave, Prutkin et al., From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees, Nat. Mach. Intell, doi:10.1038/s42256-019-0138-9
Mendy, Gopal, Alcorn, Forno, Reduced mortality from lower respiratory tract disease in adult diabetic patients treated with metformin, Respirology, doi:10.1111/resp.13486
Nohara, Matsumoto, Soejima, Nakashima, Explanation of machine learning models using shapley additive explanation and application for real data in hospital, Comput. Methods Programs Biomed, doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106584
Parsons, Eisner, Thompson, Matthay, Ancukiewicz et al., Lower tidal volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of inflammation in patients with acute lung injury, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/01.ccm.0000149854.61192.dc
Phua, Badia, Adhikari, Friedrich, Fowler et al., Has mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome decreased over time? a systematic review, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.200805-722OC
Rena, Hardie, Pearson, The mechanisms of action of metformin, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z
Suissa, Immortal time bias in observational studies of drug effects, Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf, doi:10.1002/pds.1357
Thompson, Chambers, Liu, Acute respiratory distress syndrome, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra1608077
Tsilchorozidou, Mohamed-Ali, Conway, Determinants of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein vary in polycystic ovary syndrome, as do effects of short-and long-term metformin therapy, Horm. Res, doi:10.1159/000197871
Umakanthan, Sahu, Ranade, Bukelo, Rao et al., Origin, transmission, diagnosis and management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138234
Vanderweele, Ding, Sensitivity analysis in observational research: introducing the E-Value, Ann. Intern Med, doi:10.7326/m16-2607
Von Elm, Altman, Egger, Pocock, Gøtzsche et al., The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(07)61602-x
Wang, Wang, Liao, Gao, Hua et al., Locally organised and activated Fth1(hi) neutrophils aggravate inflammation of acute lung injury in an IL-10-dependent manner, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-35492-y
Wedzicha, Seemungal, COPD exacerbations: defining their cause and prevention, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(07)61382-8
Xian, Liu, Rundberg Nilsson, Gatchalian, Crother et al., Metformin inhibition of mitochondrial ATP and DNA synthesis abrogates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pulmonary inflammation, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.05.004
Yang, Wang, Chen, Zhou, Yang et al., A comprehensive stepby-step approach for the implementation of target trial emulation: evaluating fluid resuscitation strategies in post-laparoscopic septic shock as an example, Laparosc. Endosc. Robotic Surg, doi:10.1016/j.lers.2025.01.001
Yang, Zhang, Bo, Hu, Jiang et al., Identification of clinical subphenotypes of sepsis after laparoscopic surgery, Laparosc. Endosc. Robotic Surg, doi:10.1016/j.lers.2024.02.001
Yuan, Li, Zheng, Wan, Ge et al., Antidiabetic drug metformin alleviates endotoxin-induced fulminant liver injury in mice, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2012.01.015
Zhou, Myers, Li, Chen, Shen et al., Role of AMP-Activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action, J. Clin. Invest, doi:10.1172/jci13505
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2025.1584230",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1584230",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The aim of this study was to investigate the association of metformin use with the risk of in-hospital mortality and prognosis in acute respiratory failure (ARF) patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the MIMIC-IV database. Patients were categorized into metformin and non-metformin groups based on medication exposure. Primary outcomes were in-hospital and ICU mortality, while 30-day and 90-day all-cause mortality served as secondary endpoints. We applied Kaplan–Meier survival curves, Cox proportional hazards models, and logistic regression to assess associations. Propensity score matching (PSM) and machine learning algorithms were used for confounder adjustment and feature selection.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>After PSM, 1,429 patients with ARF were included (374 metformin users; 1,055 non-users). Multivariate logistic regression revealed that metformin use was associated with significantly reduced in-hospital mortality (OR = 0.202, 95% CI: 0.123–0.317, p &lt; 0.001) and ICU mortality (OR = 0.245, 95% CI: 0.142–0.399, p &lt; 0.001). Cox models showed consistent reductions in 30-day (HR = 0.199, 95% CI: 0.124–0.320, p &lt; 0.001) and 90-day (HR = 0.230, 95% CI: 0.150–0.352, p &lt; 0.001) mortality. Kaplan–Meier curves confirmed better survival in the metformin group (p &lt; 0.001). Subgroup analyses supported a consistent protective effect of metformin across most patient strata.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Metformin use was significantly associated with decreased short-term mortality among ICU patients with ARF. These findings suggest that metformin, beyond its glucose-lowering effects, may offer survival benefits in critically ill populations. Clinicians should consider the potential role of metformin when managing ICU patients with type 2 diabetes and ARF. Further prospective studies are warranted to confirm these findings and optimize clinical application strategies.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2025.1584230"
],
"article-number": "1584230",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yunlin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Jinfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hou",
"given": "Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Yuxun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-26T05:28:33Z",
"timestamp": 1756186113000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-26T05:28:36Z",
"timestamp": 1756186116000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-26T06:10:33Z",
"timestamp": 1756188633659,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
26
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1756166400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1584230/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2019.00973",
"article-title": "Propensity score methods in health technology assessment: principles, extended applications, and recent advances",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "973",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00273171.2011.568786",
"article-title": "An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "399",
"journal-title": "Multivar. Behav. Res.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-2600(18)30345-x",
"article-title": "Acute respiratory failure in immunocompromised adults",
"author": "Azoulay",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.622262",
"article-title": "Metformin: a novel weapon against inflammation",
"author": "Bai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "622262",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2016.0291",
"article-title": "Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries",
"author": "Bellani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "788",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "315",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"article-title": "Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e34",
"journal-title": "Lancet Healthy Longev.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/circresaha.116.308445",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status",
"author": "Cameron",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "652",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjmed-2024-001126",
"article-title": "Metformin for covid-19: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Chowdhury",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e001126",
"journal-title": "BMJ Med.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bib/bbx124",
"article-title": "Evaluation of variable selection methods for random forests and omics data sets",
"author": "Degenhardt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "492",
"journal-title": "Brief. Bioinform",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/humrep/del003",
"article-title": "Indices of low-grade chronic inflammation in polycystic ovary syndrome and the beneficial effect of metformin",
"author": "Diamanti-Kandarakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1426",
"journal-title": "Hum. Reprod.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-012-2682-1",
"article-title": "The Berlin definition of ARDS: an expanded rationale, justification, and supplementary material",
"author": "Ferguson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1573",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40560-023-00658-3",
"article-title": "Guideline-based management of acute respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Fujishima",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Intensive Care",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/shk.0000000000001416",
"article-title": "Demographics, treatments, and outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome: the focused outcomes research in emergency care in acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and trauma (FORECAST) study",
"author": "Fujishima",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "544",
"journal-title": "Shock",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diabetes.54.5.1566",
"article-title": "Intensive lifestyle intervention or metformin on inflammation and coagulation in participants with impaired glucose tolerance",
"author": "Haffner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1566",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40560-017-0222-3",
"article-title": "The clinical practice guideline for the management of ARDS in Japan",
"author": "Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "J. Intensive Care",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/annals-24-01871",
"article-title": "The target trial framework for causal inference from observational data: why and when is it helpful?",
"author": "Hernán",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "402",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern Med.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa022450",
"article-title": "One-year outcomes in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Herridge",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "683",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "348",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.Atv.0000201938.78044.75",
"article-title": "Metformin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB in human vascular wall cells",
"author": "Isoda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "611",
"journal-title": "Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41597-022-01899-x",
"article-title": "MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Data",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00050-4",
"article-title": "Prescription of glucose-lowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide observational study in England",
"author": "Khunti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.165",
"article-title": "Metformin inhibits inflammatory response via AMPK-PTEN pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "866",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "425",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgh.12435",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory mechanism of metformin and its effects in intestinal inflammation and colitis-associated Colon cancer",
"author": "Koh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "502",
"journal-title": "J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/joe-21-0194",
"article-title": "Metformin as an anti-inflammatory agent: a short review",
"author": "Kristófi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "R11",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "251",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19",
"author": "Lalau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101216",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endrev/bnaa023",
"article-title": "Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin action",
"author": "LaMoia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Rev.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.704666",
"article-title": "Metformin in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "704666",
"journal-title": "Front. Med. (Lausanne)",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4",
"article-title": "Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/jir.S436147",
"article-title": "The role and mechanism of metformin in inflammatory diseases",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5545",
"journal-title": "J. Inflamm. Res.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-024-07609-y",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure in Australian and New Zealand intensive care units during 2005-2022. A binational, registry-based study",
"author": "Ling",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1861",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2017.04.002",
"article-title": "Metformin attenuated endotoxin-induced acute myocarditis via activating AMPK",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "166",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230407-00250",
"article-title": "Protective effect of metformin on pulmonary fibrosis caused by paraquat through activating AMP-activated protein kinase pathway",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1309",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23105545",
"article-title": "MicroRNAs: important regulatory molecules in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5545",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006",
"article-title": "The effect of metformin consumption on mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lukito",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2177",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/eje-07-0815",
"article-title": "Impact of metformin versus repaglinide on non-glycaemic cardiovascular risk markers related to inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Lund",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "631",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Endocrinol.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42256-019-0138-9",
"article-title": "From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees",
"author": "Lundberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "56",
"journal-title": "Nat. Mach. Intell.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/resp.13486",
"article-title": "Reduced mortality from lower respiratory tract disease in adult diabetic patients treated with metformin",
"author": "Mendy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "646",
"journal-title": "Respirology",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106584",
"article-title": "Explanation of machine learning models using shapley additive explanation and application for real data in hospital",
"author": "Nohara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106584",
"journal-title": "Comput. Methods Programs Biomed.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.ccm.0000149854.61192.dc",
"article-title": "Lower tidal volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of inflammation in patients with acute lung injury",
"author": "Parsons",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.200805-722OC",
"article-title": "Has mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome decreased over time? a systematic review",
"author": "Phua",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "220",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "179",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z",
"article-title": "The mechanisms of action of metformin",
"author": "Rena",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1577",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.1357",
"article-title": "Immortal time bias in observational studies of drug effects",
"author": "Suissa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "241",
"journal-title": "Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra1608077",
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "562",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "377",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000197871",
"article-title": "Determinants of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein vary in polycystic ovary syndrome, as do effects of short- and long-term metformin therapy",
"author": "Tsilchorozidou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "148",
"journal-title": "Horm. Res.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138234",
"article-title": "Origin, transmission, diagnosis and management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Umakanthan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "753",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/m16-2607",
"article-title": "Sensitivity analysis in observational research: introducing the E-Value",
"author": "VanderWeele",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern Med.",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(07)61602-x",
"article-title": "The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies",
"author": "von Elm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1453",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-35492-y",
"article-title": "Locally organised and activated Fth1(hi) neutrophils aggravate inflammation of acute lung injury in an IL-10-dependent manner",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7703",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(07)61382-8",
"article-title": "COPD exacerbations: defining their cause and prevention",
"author": "Wedzicha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "786",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2021.05.004",
"article-title": "Metformin inhibition of mitochondrial ATP and DNA synthesis abrogates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pulmonary inflammation",
"author": "Xian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1463",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lers.2024.02.001",
"article-title": "Identification of clinical subphenotypes of sepsis after laparoscopic surgery",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Laparosc. Endosc. Robotic Surg.",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lers.2025.01.001",
"article-title": "A comprehensive step-by-step approach for the implementation of target trial emulation: evaluating fluid resuscitation strategies in post-laparoscopic septic shock as an example",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Laparosc. Endosc. Robotic Surg.",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2012.01.015",
"article-title": "Antidiabetic drug metformin alleviates endotoxin-induced fulminant liver injury in mice",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "682",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci13505",
"article-title": "Role of AMP-Activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1167",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2001"
}
],
"reference-count": 53,
"references-count": 53,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1584230/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Correlation between metformin use and mortality in acute respiratory failure: a retrospective ICU cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "16"
}
