The GPR4 antagonist NE-52-QQ57 increases survival, mitigates the hyperinflammatory response and reduces viral load in SARS-CoV-2-infected K18-hACE2 transgenic mice
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1549296, Jul 2025
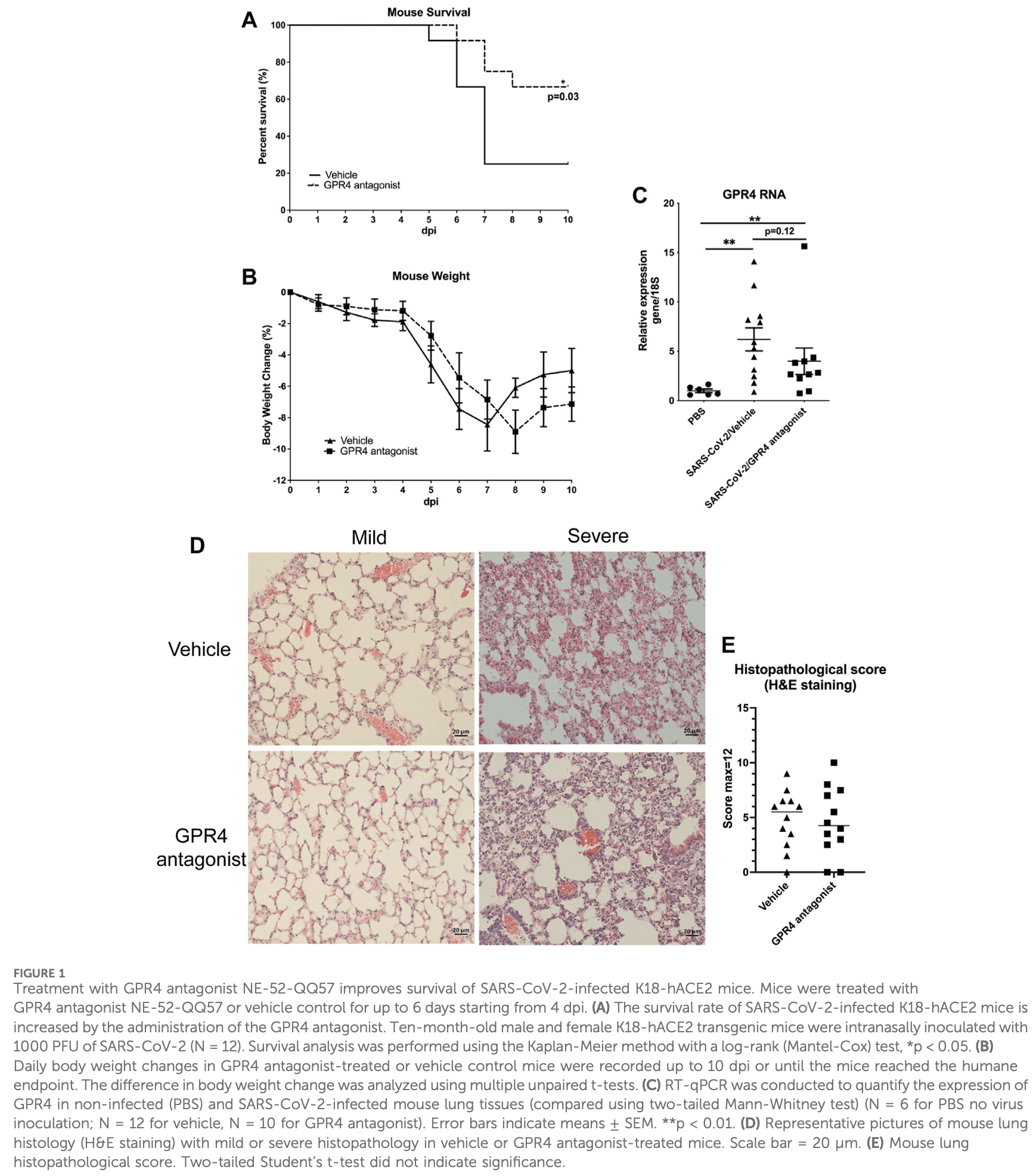
Mouse study showing that GPR4 antagonist NE-52-QQ57 increases survival, reduces inflammation, and decreases viral load in SARS-CoV-2-infected K18-hACE2 transgenic mice. GPR4 expression was upregulated approximately 7-fold in infected mouse lungs compared to controls.
Wu et al., 9 Jul 2025, placebo-controlled, China, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Contact: yangl@ecu.edu.
The GPR4 antagonist NE-52-QQ57 increases survival, mitigates the hyperinflammatory response and reduces viral load in SARS-CoV-2-infected K18-hACE2 transgenic mice
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1549296
COVID-19 (Coronavirus disease 19 ) is caused by infection with SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) in the respiratory system and other organ systems. Tissue injuries resulting from viral infection and host hyperinflammatory responses may lead to moderate to severe pneumonia, systemic complications, and even death. While anti-inflammatory agents have been used to treat patients with severe COVID-19, their therapeutic effects are limited. GPR4 (G protein-coupled receptor 4) is a proinflammatory receptor expressed on vascular endothelial cells, regulating leukocyte infiltration and inflammatory responses. In this study, we evaluated the effects of a GPR4 antagonist, NE-52-QQ57, in the SARS-CoV-2-infected K18-hACE2 transgenic mouse model. Our results demonstrated that GPR4 antagonist treatment increased the survival rate in this severe COVID-19 mouse model. The inflammatory response, characterized by proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, was reduced in the GPR4 antagonist group compared with the vehicle group. Additionally, both SARS-CoV-2 RNA copy numbers and infectious viral titers in the mouse lung were decreased in the GPR4 antagonist group. The percentage of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-positive mouse brains was also decreased in the GPR4 antagonist group compared to the vehicle group. Furthermore, the GPR4 antagonist inhibited SARS-CoV-2 propagation in Vero E6 and Caco-2 cells. Together, these results suggest that GPR4 antagonism may be explored as a novel approach for the treatment of COVID-19 and other similar viral diseases.
Ethics statement Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used. The animal study was approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of East Carolina University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1549296/ full#supplementary-material
..
References
Abani, Abbas, Abbas, Abbas, Abbas et al., Baricitinib in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial and updated meta-analysis, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(22)01109-6
Aganovic, pH-dependent endocytosis mechanisms for influenza A and SARS-Coronavirus, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1190463
An, Tsai, Goetzl, Cloning, sequencing and tissue distribution of two related G protein-coupled receptor candidates expressed prominently in human lung tissue, FEBS Lett, doi:10.1016/0014-5793(95)01196-l
Antar, Cox, Translating insights into therapies for long covid, Sci. Transl. Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.ado2106
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-preliminary report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Català, Mercadé-Besora, Kolde, Trinh, Roel et al., The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines to prevent long COVID symptoms: staggered cohort study of data from the UK, Spain, and Estonia, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00414-9
Chan, Yuan, Chu, Sridhar, Yuen, COVID-19 drug discovery and treatment options, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-024-01036-y
Chen, Dong, Leffler, Asch, Witte et al., Activation of GPR4 by acidosis increases endothelial cell adhesion through the cAMP/ Epac pathway, PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027586
Coperchini, Chiovato, Croce, Magri, Rotondi, The cytokine storm in COVID-19: an overview of the involvement of the chemokine/ chemokine-receptor system, Cytokine and Growth Factor Rev, doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.05.003
Dong, Krewson, Yang, Acidosis activates endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways through GPR4 in human vascular endothelial cells, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms18020278
Dong, Li, Leffler, Asch, Chi et al., Acidosis activation of the proton-sensing GPR4 receptor stimulates vascular endothelial cell inflammatory responses revealed by transcriptome analysis, PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061991
Dubey, Das, Ghosh, Dubey, Chakraborty et al., The effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the cognitive functioning of patients with preexisting dementia, J. Alzheimer's Dis. Rep, doi:10.3233/ADR-220090
Ely, Ramanan, Kartman, De Bono, Liao et al., Efficacy and safety of baricitinib plus standard of care for the treatment of critically ill hospitalised adults with COVID-19 on invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: an exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00006-6
Fares, Duhaini, Tripathy, Srour, Kondapalli, Acidic pH of early endosomes governs SARS-CoV-2 transport in host cells, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2024.108144
Group, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2021436
Guan, -J, Ni, Hu, Liang et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Gupta, Madhavan, Sehgal, Nair, Mahajan et al., Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3
Hammond, Fountaine, Yunis, Fleishaker, Almas et al., Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2309003
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Bao et al., Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Hassan, Case, Winkler, Thackray, Kafai et al., A SARS-CoV-2 infection model in mice demonstrates protection by neutralizing antibodies, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.011
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Justus, Dong, Yang, Acidic tumor microenvironment and pH-sensing G protein-coupled receptors, Front. Physiology, doi:10.3389/fphys.2013.00354
Justus, Marie, Sanderlin, Yang, The roles of protonsensing G-Protein-Coupled receptors in inflammation and cancer, Genes, doi:10.3390/genes15091151
Khanna, Raymond, Jin, Charbit, Gitlin et al., Exploring antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects of thiol drugs in COVID-19, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00136.2022
Krewson, Sanderlin, Marie, Akhtar, Velcicky et al., The proton-sensing GPR4 receptor regulates paracellular gap formation and permeability of vascular endothelial cells, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2020.100848
Kumari, Rothan, Natekar, Stone, Pathak et al., Neuroinvasion and encephalitis following intranasal inoculation of SARS-CoV-2 in K18-hACE2 mice, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13010132
Lardner, The effects of extracellular pH on immune function, J. Leukoc. Biol, doi:10.1189/jlb.69.4.522
Li, Hilgenfeld, Whitley, De Clercq, Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y
Link-Gelles, Weber, Reese, Payne, Gaglani et al., Estimates of bivalent mRNA vaccine durability in preventing COVID-19-associated hospitalization and critical illness among adults with and without immunocompromising conditions-Vision network, September 2022-April 2023, MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7221a3
Louis, Qasem, Abdelli, Naser, Li et al., Phillyrin (KD-1) exerts anti-viral and anti-inflammatory activities against novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E) by suppressing the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, Microorganisms, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153296
Mahadevan, Baird, Bailly, Shutler, Sabourin et al., Isolation of a novel G protein-coupled receptor (GPR4) localized to chromosome 19q13. 3, Genomics, doi:10.1006/geno.1995.0013
Marconi, Ramanan, De Bono, Kartman, Krishnan et al., Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Merad, Martin, Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4
Miltz, Velcicky, Dawson, Littlewood-Evans, Ludwig et al., Design and synthesis of potent and orally active GPR4 antagonists with modulatory effects on nociception, inflammation, and angiogenesis, Bioorg. and Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2017.06.050
Murakami, Hayden, Hills, Al-Samkari, Casey et al., Therapeutic advances in COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Nephrol, doi:10.1038/s41581-022-00642-4
Okajima, Regulation of inflammation by extracellular acidification and proton-sensing GPCRs, Cell. Signal, doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.07.022
Pang, Tang, He, Fan, Yang et al., Neurological complications caused by SARS-CoV-2, Clin. Microbiol. Rev, doi:10.1128/cmr.00131-24
Richardson, Griffin, Tucker, Smith, Oechsle et al., Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30304-4
Sanderlin, Leffler, Lertpiriyapong, Cai, Hong et al., GPR4 deficiency alleviates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of acute experimental colitis, Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis Dis, doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.12.005
Sanderlin, Marie, Velcicky, Loetscher, Yang, Pharmacological inhibition of GPR4 remediates intestinal inflammation in a mouse colitis model, Eur. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.038
Sarkesh, Sorkhabi, Sheykhsaran, Alinezhad, Mohammadzadeh et al., Extrapulmonary clinical manifestations in COVID-19 patients, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0986
Sasaki, Sugi, Iida, Hirata, Kusakabe et al., Combination therapy with oral antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs improves the efficacy of delayed treatment in a COVID-19 hamster model, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104950
Schwabenland, Salié, Tanevski, Killmer, Lago et al., Deep spatial profiling of human COVID-19 brains reveals neuroinflammation with distinct microanatomical microglia-T-cell interactions, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.002
Scobie, Johnson, Suthar, Severson, Alden et al., Monitoring incidence of COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths, by vaccination status-13 US jurisdictions, MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7037e1
Short, Gupta, Brenner, Hayek, Srivastava et al., d-dimer and death in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000004917
Stein, Ramelli, Grazioli, Chung, Singh et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection and persistence in the human body and brain at autopsy, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05542-y
Sun, Zhuang, Zheng, Li, Wong et al., Generation of a broadly useful model for COVID-19 pathogenesis, vaccination, and treatment, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.010
Tobo, Tobo, Nakakura, Ebara, Tomura et al., Characterization of imidazopyridine compounds as negative allosteric modulators of proton-sensing GPR4 in extracellular acidification-induced responses, PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0129334
Toniati, Piva, Cattalini, Garrafa, Regola et al., Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory Frontiers in Pharmacology frontiersin
Valle, Kim-Schulze, Huang, Beckmann, Nirenberg et al., An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9
Velcicky, Miltz, Oberhauser, Orain, Vaupel et al., Development of selective, orally active GPR4 antagonists with modulatory effects on nociception, inflammation, and angiogenesis, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01703
Villadiego, García-Arriaza, Ramírez-Lorca, García-Swinburn, Cabello-Rivera et al., Full protection from SARS-CoV-2 brain infection and damage in susceptible transgenic mice conferred by MVA-CoV2-S vaccine candidate, Nat. Neurosci, doi:10.1038/s41593-022-01242-y
Wang, De Vallière, Imenez Silva, Leonardi, Gruber et al., The proton-activated receptor GPR4 modulates intestinal inflammation, J. Crohn's Colitis, doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx147
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
Winkler, Bailey, Kafai, Nair, Mccune et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-020-0778-2
Wu, 3389/fphar.2025.1549296 syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in brescia, Italy, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Wu, None
Xu, Han, Li, Sun, Wang et al., Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2005615117
Yang, Oppelt, Thomassen, Marie, Nik Akhtar et al., Can GPR4 be a potential therapeutic target for COVID-19?, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.626796
Yung-Fang, Chien, Yarmishyn, Yi-Ying, Yung-Hung et al., A review of SARS-CoV-2 and the ongoing clinical trials, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21072657
Zaim, Chong, Sankaranarayanan, Harky, COVID-19 and multiorgan response, Curr. Problems Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100618
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2025.1549296",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1549296",
"abstract": "<jats:p>COVID-19 (Coronavirus disease 19) is caused by infection with SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) in the respiratory system and other organ systems. Tissue injuries resulting from viral infection and host hyperinflammatory responses may lead to moderate to severe pneumonia, systemic complications, and even death. While anti-inflammatory agents have been used to treat patients with severe COVID-19, their therapeutic effects are limited. GPR4 (G protein-coupled receptor 4) is a pro-inflammatory receptor expressed on vascular endothelial cells, regulating leukocyte infiltration and inflammatory responses. In this study, we evaluated the effects of a GPR4 antagonist, NE-52-QQ57, in the SARS-CoV-2-infected K18-hACE2 transgenic mouse model. Our results demonstrated that GPR4 antagonist treatment increased the survival rate in this severe COVID-19 mouse model. The inflammatory response, characterized by proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, was reduced in the GPR4 antagonist group compared with the vehicle group. Additionally, both SARS-CoV-2 RNA copy numbers and infectious viral titers in the mouse lung were decreased in the GPR4 antagonist group. The percentage of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-positive mouse brains was also decreased in the GPR4 antagonist group compared to the vehicle group. Furthermore, the GPR4 antagonist inhibited SARS-CoV-2 propagation in Vero E6 and Caco-2 cells. Together, these results suggest that GPR4 antagonism may be explored as a novel approach for the treatment of COVID-19 and other similar viral diseases.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2025.1549296"
],
"article-number": "1549296",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Xin-Jun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oppelt",
"given": "Karen A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fan",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marie",
"given": "Mona A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swyers",
"given": "Madison M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Ashley J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lemasson",
"given": "Isabelle M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roper",
"given": "Rachel L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bolin",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Li V.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-10T05:46:08Z",
"timestamp": 1752126368000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-10T13:39:03Z",
"timestamp": 1752154743000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-10T14:10:08Z",
"timestamp": 1752156608199,
"version": "3.41.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
9
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1752019200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1549296/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(22)01109-6",
"article-title": "Baricitinib in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial and updated meta-analysis",
"author": "Abani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2023.1190463",
"article-title": "pH-dependent endocytosis mechanisms for influenza A and SARS-Coronavirus",
"author": "Aganovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1190463",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0014-5793(95)01196-l",
"article-title": "Cloning, sequencing and tissue distribution of two related G protein‐coupled receptor candidates expressed prominently in human lung tissue",
"author": "An",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "FEBS Lett.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "375",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.ado2106",
"article-title": "Translating insights into therapies for long covid",
"author": "Antar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eado2106",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—preliminary report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00414-9",
"article-title": "The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines to prevent long COVID symptoms: staggered cohort study of data from the UK, Spain, and Estonia",
"author": "Català",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "225",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-024-01036-y",
"article-title": "COVID-19 drug discovery and treatment options",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0027586",
"article-title": "Activation of GPR4 by acidosis increases endothelial cell adhesion through the cAMP/Epac pathway",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e27586",
"journal-title": "PLOS One",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.05.003",
"article-title": "The cytokine storm in COVID-19: an overview of the involvement of the chemokine/chemokine-receptor system",
"author": "Coperchini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "Cytokine and Growth Factor Rev.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9",
"article-title": "An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival",
"author": "Del Valle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1636",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18020278",
"article-title": "Acidosis activates endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways through GPR4 in human vascular endothelial cells",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "278",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0061991",
"article-title": "Acidosis activation of the proton-sensing GPR4 receptor stimulates vascular endothelial cell inflammatory responses revealed by transcriptome analysis",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e61991",
"journal-title": "PLOS One",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/ADR-220090",
"article-title": "The effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the cognitive functioning of patients with pre-existing dementia",
"author": "Dubey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "J. Alzheimer's Dis. Rep.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00006-6",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of baricitinib plus standard of care for the treatment of critically ill hospitalised adults with COVID-19 on invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: an exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Ely",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2024.108144",
"article-title": "Acidic pH of early endosomes governs SARS-CoV-2 transport in host cells",
"author": "Fares",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108144",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "301",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1017",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2309003",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1186",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.011",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 infection model in mice demonstrates protection by neutralizing antibodies",
"author": "Hassan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "744",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2013.00354",
"article-title": "Acidic tumor microenvironment and pH-sensing G protein-coupled receptors",
"author": "Justus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "354",
"journal-title": "Front. Physiology",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/genes15091151",
"article-title": "The roles of proton-sensing G-Protein-Coupled receptors in inflammation and cancer",
"author": "Justus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1151",
"journal-title": "Genes",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00136.2022",
"article-title": "Exploring antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects of thiol drugs in COVID-19",
"author": "Khanna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "L372",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2020.100848",
"article-title": "The proton-sensing GPR4 receptor regulates paracellular gap formation and permeability of vascular endothelial cells",
"author": "Krewson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100848",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13010132",
"article-title": "Neuroinvasion and encephalitis following intranasal inoculation of SARS-CoV-2 in K18-hACE2 mice",
"author": "Kumari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "132",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1189/jlb.69.4.522",
"article-title": "The effects of extracellular pH on immune function",
"author": "Lardner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "522",
"journal-title": "J. Leukoc. Biol.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y",
"article-title": "Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7221a3",
"article-title": "Estimates of bivalent mRNA vaccine durability in preventing COVID-19–associated hospitalization and critical illness among adults with and without immunocompromising conditions—Vision network, September 2022–April 2023",
"author": "Link-Gelles",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "579",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms10010153",
"article-title": "Extra-pulmonary complications in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a comprehensive multi organ-system review",
"author": "Louis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Microorganisms",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153296",
"article-title": "Phillyrin (KD-1) exerts anti-viral and anti-inflammatory activities against novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E) by suppressing the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "153296",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/geno.1995.0013",
"article-title": "Isolation of a novel G protein-coupled receptor (GPR4) localized to chromosome 19q13. 3",
"author": "Mahadevan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "Genomics",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "30",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial",
"author": "Marconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1407",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4",
"article-title": "Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages",
"author": "Merad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmc.2017.06.050",
"article-title": "Design and synthesis of potent and orally active GPR4 antagonists with modulatory effects on nociception, inflammation, and angiogenesis",
"author": "Miltz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4512",
"journal-title": "Bioorg. and Med. Chem.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41581-022-00642-4",
"article-title": "Therapeutic advances in COVID-19",
"author": "Murakami",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Nephrol.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.07.022",
"article-title": "Regulation of inflammation by extracellular acidification and proton-sensing GPCRs",
"author": "Okajima",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2263",
"journal-title": "Cell. Signal.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/cmr.00131-24",
"article-title": "Neurological complications caused by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Pang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0013124",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Rev.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30304-4",
"article-title": "Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease",
"author": "Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e30",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.12.005",
"article-title": "GPR4 deficiency alleviates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of acute experimental colitis",
"author": "Sanderlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "569",
"journal-title": "Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis Dis.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "1863",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.038",
"article-title": "Pharmacological inhibition of GPR4 remediates intestinal inflammation in a mouse colitis model",
"author": "Sanderlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "218",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "852",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0986",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary clinical manifestations in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Sarkesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1783",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104950",
"article-title": "Combination therapy with oral antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs improves the efficacy of delayed treatment in a COVID-19 hamster model",
"author": "Sasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104950",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.002",
"article-title": "Deep spatial profiling of human COVID-19 brains reveals neuroinflammation with distinct microanatomical microglia-T-cell interactions",
"author": "Schwabenland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1594",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7037e1",
"article-title": "Monitoring incidence of COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths, by vaccination status—13 US jurisdictions, April 4–July 17, 2021",
"author": "Scobie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1284",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep.",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000004917",
"article-title": "d-dimer and death in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Short",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e500",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05542-y",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection and persistence in the human body and brain at autopsy",
"author": "Stein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "758",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "612",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.010",
"article-title": "Generation of a broadly useful model for COVID-19 pathogenesis, vaccination, and treatment",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "734",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0129334",
"article-title": "Characterization of imidazopyridine compounds as negative allosteric modulators of proton-sensing GPR4 in extracellular acidification-induced responses",
"author": "Tobo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0129334",
"journal-title": "PLOS One",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in brescia, Italy",
"author": "Toniati",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102568",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01703",
"article-title": "Development of selective, orally active GPR4 antagonists with modulatory effects on nociception, inflammation, and angiogenesis",
"author": "Velcicky",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3672",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41593-022-01242-y",
"article-title": "Full protection from SARS-CoV-2 brain infection and damage in susceptible transgenic mice conferred by MVA-CoV2-S vaccine candidate",
"author": "Villadiego",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "226",
"journal-title": "Nat. Neurosci.",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx147",
"article-title": "The proton-activated receptor GPR4 modulates intestinal inflammation",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "J. Crohn's Colitis",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-0778-2",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function",
"author": "Winkler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1327",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1239",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"article-title": "Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10970",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.626796",
"article-title": "Can GPR4 be a potential therapeutic target for COVID-19?",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "626796",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21072657",
"article-title": "A review of SARS-CoV-2 and the ongoing clinical trials",
"author": "Yung-Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2657",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100618",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and multiorgan response",
"author": "Zaim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100618",
"journal-title": "Curr. Problems Cardiol.",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 63,
"references-count": 63,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1549296/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The GPR4 antagonist NE-52-QQ57 increases survival, mitigates the hyperinflammatory response and reduces viral load in SARS-CoV-2-infected K18-hACE2 transgenic mice",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "16"
}